Boron trifluoride etherate (original) (raw)
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
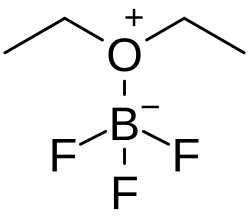
Boron trifluoride etherate
 |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Names | |
| Other namesBoron Trifluoride Ethyl Ether Boron Trifluoride Diethyl Etherate | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | 109-63-7 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL1710835 |
| ChemSpider | 17983029 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.355 |
| PubChem CID | 517922 |
| UNII | 422VHH19IT |
| UN number | 2604 |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | DTXSID90985377, DTXSID601015537 DTXSID40861733, DTXSID90985377, DTXSID601015537 |
| InChI InChI=1S/C4H10O.BF3/c1-3-5-4-2;2-1(3)4/h3-4H2,1-2H3;Key: KZMGYPLQYOPHEL-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| SMILES B(F)(F)F.CCOCC | |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C4H10BF3O |
| Molar mass | 141.93 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | colorless liquid |
| Density | 1.15 g cm3 |
| Melting point | −58 °C (−72 °F; 215 K) |
| Boiling point | 126 °C (259 °F; 399 K) |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
| Main hazards | Flammable, Reacts with water, Corrosive |
| GHS labelling: | |
| Pictograms |      |
| Signal word | Danger |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) |  3 2 2W 3 2 2W |
| Flash point | 58.5 °C (137.3 °F; 331.6 K) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). Infobox references |
Chemical compound
Boron trifluoride etherate, strictly boron trifluoride diethyl etherate, or boron trifluoride–ether complex, is the chemical compound with the formula BF3O(C2H5)2, often abbreviated BF3OEt2. It is a colorless liquid, although older samples can appear brown. The compound is used as a source of boron trifluoride in many chemical reactions that require a Lewis acid.[1] The compound features tetrahedral boron coordinated to a diethylether ligand.[2] Many analogues are known, including the methanol complex.
Boron trifluoride etherate serves as a source of boron trifluoride according to the equilibrium:
BF3OEt2 ↽ − ⇀ {\displaystyle {\ce {<=>>}}} 
The BF3 binds to even weak Lewis bases, inducing reactions of the resulting adducts with nucleophiles.[1]
- ^ a b Veronica Cornel; Carl J. Lovely (2007). "Boron Trifluoride Etherate". Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. John Wiley & Sons. pp. rb249.pub2. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rb249.pub2. ISBN 978-0-471-93623-7.
- ^ V. V. Saraev; P. B. Kraikivskii; I. Svoboda; A. S. Kuzakov; R. F. Jordan (2008). "Synthesis, Molecular Structure, and EPR Analysis of the Three-Coordinate Ni(I) Complex [Ni(PPh3)3][BF4]". J. Phys. Chem. A. 112 (48): 12449–12455. Bibcode:2008JPCA..11212449S. doi:10.1021/jp802462x. PMID 18991433.