Culver PQ-14 Cadet (original) (raw)
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| PQ-14 | |
|---|---|
 Culver PQ-14B at Langley, 1945 Culver PQ-14B at Langley, 1945 |
|
| General information | |
| Type | Target drone |
| Manufacturer | Culver Aircraft Company |
| Designer | Albert Mooney |
| Primary users | U.S. Army Air Corps United States Navy U.S. Army Air ForceUnited States Air Force |
| Number built | 2,043 |
| History | |
| Introduction date | 1942 |
| Retired | 1950 |
| Developed from | Culver PQ-8 |
The Culver PQ-14 Cadet is a modified version of the Culver LFA Cadet used as a target drone.
In 1940, the U.S. Army Air Corps drew up a requirement for a radio-controlled target drone for training anti-aircraft artillery gunners. The first aircraft in a series of target drones was a modification of the Culver LFA Cadet which eventually led to the PQ-14 series used throughout World War II and beyond.
Design and development
[edit]
Culver proposed a modification of its civilian Model LFA Cadet which the Army purchased as the PQ-8. The success of the PQ-8 led to the development of the "NRD"; a single PQ-8 was converted to the new configuration and tested by the USAAF as the XPQ-14. Larger and faster than the PQ-8, the PQ-14 also had retractable landing gear and fuselage, wings and tail components made of wood with stressed plywood skin.
This prototype was followed by YPQ-14A service test aircraft and 1,348 PQ-14A production models. Of the latter, 1,198 were transferred to the US Navy, which designated them as TD2C-1 with the decidedly unattractive name Turkey.
The YPQ-14B was a slightly heavier variant; a total of 25 were produced before production shifted to the PQ-14B. A total of 594 PQ-14Bs served as target drones for the USAAF. A single PQ-14B was converted to use an O-300-9 engine and designated XPQ-14C. After World War II, the Culver company developed the XPQ-15 from their Model V light aircraft. After only four were delivered the company went bankrupt in 1946.
Operational history
[edit]
A U.S. Navy TD2C-1 in flight, circa 1945.
The XPQ-14 was first flown in 1942 and began to be received in training units shortly after. The aircraft was flown unmanned, controlled by radio, but was flown by a pilot for ferry flights, using a rudimentary control panel installed for that purpose and using their parachutes as a seat. Docile and easy to fly, the aircraft was finished in a bright red target color scheme although operationally, a silver or red finish was applied. Without a pilot they were flown from a "mother ship" aircraft. The typical mother ship was a Beech C-45. Despite their short lifespan, the aircraft performed well and the Franklin engine was considered "trouble-free".[1] Most of the Culver target aircraft were "blasted out of the sky" by Army anti-aircraft gunners but a dozen or more survived and were surplused after 1950. Flown as a recreational aircraft, their new owners found that the aircraft had a sprightly performance.
A PQ-14 under restoration at the Aviation Unmanned Vehicle Museum
- 44-21895 – PQ-14B airworthy at the Planes of Fame Air Museum in Chino, California.[2]
- 44-68334 – PQ-14B on display at the EAA Aviation Museum in Oshkosh, Wisconsin.[3][4]
- 44-68462 – PQ-14B in storage at the National Museum of the United States Air Force in Dayton, Ohio.[5]
- 45-59043 – TD2C-1 airworthy with Russ Cronk of Big Bear, California.[6]
- 120035 – TD2C-1 in storage at the Paul E. Garber Preservation, Restoration, and Storage Facility of the National Air and Space Museum in Suitland, Maryland.[7]
- N917 – PQ-14B airworthy at the Airpower Museum in Blakesburg, Iowa.[8]
- PQ-14 under restoration at the Aviation Unmanned Vehicle Museum in Caddo Mills, Texas.[9]
- PQ-14B airworthy with Robert F. Holwey of Colorado Springs, Colorado.[10]
Specifications (Culver PQ-14A)
[edit]
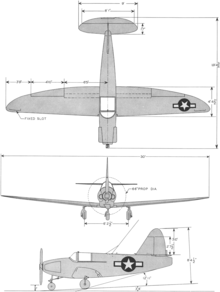
3-view line drawing of the Culver PQ-14
Data from Mormillo.[11]
General characteristics
- Crew: One
- Length: 19 ft 6 in (5.94 m)
- Wingspan: 30 ft 0 in (9.14 m)
- Height: 8 ft 4.5 in (2.55 m)
- Gross weight: 1,830 lb (830 kg)
- Powerplant: 1 × Franklin 6ACT-298-35 6-cyl. air-cooled horizontally-opposed piston engine , 150 hp (97 kW)
Performance
- Maximum speed: 185 mph (300 km/h, 161 kn)
- Cruise speed: 150 mph (241 km/h, 130 kn)
- Range: 512 mi (823 km, 445 nmi)
- Service ceiling: 17,000 ft (5,184 m)
Related development
- ^ Mormillo 2001, p. 7.
- ^ "Airframe Dossier - Culver PQ-14B, s/n 44-21895 USAAF, c/n N-839, c/r N15HM". Aerial Visuals. Retrieved 13 October 2020.
- ^ "1944 Culver PQ-14B - N999ML". EAA. Retrieved 13 October 2020.
- ^ "Airframe Dossier - Culver Q-14B, s/n 44-68334 USAF, c/r N999ML". Aerial Visuals. Retrieved 13 October 2020.
- ^ "Culver PQ-14B". National Museum of the United States Air Force. 20 April 2015. Retrieved 13 October 2020.
- ^ "FAA REGISTRY [N2775]". Federal Aviation Administration. U.S. Department of Transportation. Archived from the original on 17 October 2020. Retrieved 13 October 2020.
- ^ "Culver TD2C-1". National Air and Space Museum. Smithsonian Institution. Archived from the original on 4 September 2019. Retrieved 4 September 2019.
- ^ "Culver PQ-14B". Antique Airfield. Archived from the original on 19 April 2022. Retrieved 18 October 2020.
- ^ "BGM-34B ATTACK & MULTI-MISSION RPV". AUVM. Archived from the original on 27 October 2020. Retrieved 12 October 2020.
- ^ "Airframe Dossier - Culver PQ-14B, c/r N5526A". Aerial Visuals. Retrieved 13 October 2020.
- ^ Mormillo 2001, p. 6.
- Anderson, C. E. "Bud" (December 1981 – March 1982). "Caught by the Wing-tip". Air Enthusiast. No. 17. pp. 74–80. ISSN 0143-5450.
- Mondey, David. American Aircraft of World War II (Hamlyn Concise Guide). London: Bounty Books, 2006. ISBN 978-0-7537-1461-4.
- Mormillo, Frank B. "Defenceless Warrior: Culver's PQ-14 Drone." Air Enthusiast Issue 93, May/June 2001. ISSN 0143-5450
- Culver PQ-14/Q-14/TD2C
- Culver PQ-14B – National Museum of the United States Air Force