Diadinoxanthin (original) (raw)
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Diadinoxanthin
 |
|
|---|---|
| Names | |
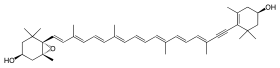
| IUPAC name (3_S_,5_R_,6_S_,3′R)-5,6-Epoxy-7′,8′-didehydro-5,6-dihydro-β,β-carotene-3,3′-diol | |
| Systematic IUPAC name (1_R_,3_S_,6_S_)-6-{(1_E_,3_E_,5_E_,7_E_,9_E_,11_E_,13_E_,15_E_)-18-[(4_R_)-4-Hydroxy-2,6,6-trimethylcyclohex-1-en-1-yl]-3,7,12,16-tetramethyloctadeca-1,3,5,7,9,11,13,15-octaen-17-yn-1-yl}-1,5,5-trimethyl-7-oxabicyclo[4.1.0]heptan-3-ol | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | 18457-54-0 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 16736328  Y Y |
| PubChem CID | 6449888 |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | DTXSID301015588 |
InChI InChI=1S/C40H54O3/c1-30(18-13-20-32(3)23-24-35-34(5)22-15-26-36(35,6)7)16-11-12-17-31(2)19-14-21-33(4)25-27-40-37(8,9)28-39(41,42)29-38(40,10)43-40/h11-14,16-21,25,27,41-42H,15,22,26,28-29H2,1-10H3/b12-11+,18-13+,19-14+,27-25+,30-16+,31-17+,32-20+,33-21+  YKey: CQEFYCLCHZUMAF-ACABJTFYSA-N YKey: CQEFYCLCHZUMAF-ACABJTFYSA-N  Y Y |
|
| SMILES CC23CC(O)(O)CC(C)(C)C3(/C=CC(\C)=C\C=C\C(\C)=C\C=C\C=C(/C)\C=C\C=C(/C)C#C\C1=C(/C)CCCC1(C)C)O2 | |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C40H54O3 |
| Molar mass | 582.869 g·mol−1 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). Infobox references |
Chemical compound
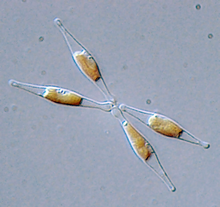
Diatoms, such as the diatom pictured here Phaeodactylum tricornutum, often contain diadinoxanthin pigments.
Diadinoxanthin is a pigment found in phytoplankton. It has the formula C40H54O3. It gives rise to the xanthophylls diatoxanthin and dinoxanthin.
Diadinoxanthin is a plastid pigment. Plastid pigments include chlorophylls a and c, fucoxanthin, heteroxanthin, diatoxanthin, and diadinoxanthin.[1]
Diadinoxanthin is a carotenoid. It is found in diatoms, along with other carotenoids like fucoxanthin and beta-carotene. Diatoms are referred to as golden-brown microalgae because of the color of their plastids and because the carotenoids mask chlorophyll-a and chlorophyll-c.[2]
Diadinoxanthin is a xanthophyll. Xanthophyll pigments are photoprotective pigments that help protect cells from harmful effects of too much light energy (light saturation).[3] It is present in cells along with diatoxanthin (another xanthophyll). Diadinoxanthin is stockpiled in the cell to become available when needed. Thus it is the inactive precursor of diatoxanthin, which is the active energy dissipator.[4]
- Accessory pigment
- Algae
- Carotenoid
- Diatom
- Diatoxanthin
- Dinoxanthin
- Photoprotection
- Phytoplankton
- Xanthophyll
- ^ Adl, Sina M.; et al. (2012). "The Revised Classification of Eukaryotes". Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology. 59 (5): 429–514. doi:10.1111/j.1550-7408.2012.00644.x. PMC 3483872.
- ^ Gastineau, Romain; et al. (2014). "Chapter Fifteen - Haslea ostrearia-like Diatoms: Biodiversity out of the Blue". Advances in Botanical Research. 61: 441–465. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-408062-1.00015-9.
- ^ Falkowski, P. G.; Raven, J. A. (2007). Aquatic Photosynthesis (2nd ed.). New Jersey: Princeton University Press.
- ^ Kooistra, Weibe H. C. F.; Gersonde, Rainer; Medlin, Linda K.; Mann, David G. (2007). "Chapter 11 - The Origin and Evolution of the Diatoms: Their Adaptation to a Planktonic Existence". Evolution of Primary Producers in the Sea: 207–249. doi:10.1016/B978-012370518-1/50012-6.