Glückstadt (original) (raw)
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Town in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany
| Glückstadt | |
|---|---|
| Town | |
 Northside of Glückstadt harbour Northside of Glückstadt harbour |
|
 Flag Flag Coat of arms Coat of arms |
|
Location of Glückstadt within Steinburg district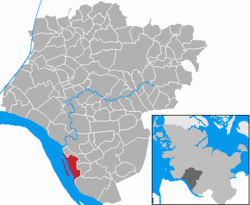 |
|
  Glückstadt Show map of Germany Glückstadt Show map of Germany  Glückstadt Show map of Schleswig-Holstein Glückstadt Show map of Schleswig-Holstein |
|
| Coordinates: 53°47′30″N 9°25′19″E / 53.79167°N 9.42194°E / 53.79167; 9.42194 | |
| Country | Germany |
| State | Schleswig-Holstein |
| District | Steinburg |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Manja Biel |
| Area | |
| • Total | 22.76 km2 (8.79 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 2 m (7 ft) |
| Population (2022-12-31)[1] | |
| • Total | 10,885 |
| • Density | 480/km2 (1,200/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+01:00 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+02:00 (CEST) |
| Postal codes | 25348 |
| Dialling codes | 04124 |
| Vehicle registration | IZ |
| Website | www.glueckstadt.de |
Glückstadt (German pronunciation: [ˈɡlʏkˌʃtat] ⓘ; Danish: Lykstad) is a town in the Steinburg district of Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. It is located on the right bank of the Lower Elbe at the confluence of the small Rhin river, about 45 km (28 mi) northwest of Altona. Glückstadt is part of the Hamburg Metropolitan Region (Metropolregion Hamburg).
Glückstadt was founded in 1617 on the marsh lands along the Elbe by the Duke of Holstein, King Christian IV of Denmark, who had levees and fortifications built as well as a ducal residence. Its name translates to English literally as "Luck City" or "Fortune City". As Christian IV promised the settlers tax exemption and freedom of religion, Glückstadt soon became an important trading centre, intended to compete with the Imperial city of Hamburg, located upstream on the Elbe. Calvinists, Remonstrants and Mennonites (Anabaptists) from the Netherlands settled here, as well as Sephardic Jews and Catholics.
After the king had interfered in the Thirty Years' War, the town in 1627/28 was besieged for fifteen weeks by the united Imperial and Catholic troops under the command of Albrecht von Wallenstein and Count Tilly, though without success.[2]
In 1649 Christian’s son and successor King Frederik III of Denmark had the seat of the Holstein administration moved to Glückstadt, whereafter the duchy became known as Holstein-Glückstadt. In 1773 the town became the capital of all Holstein lands, when the lands of the Holstein-Gottorp line were finally incorporated. During the War of the Sixth Coalition in 1814 Glückstadt was blockaded by the allies and capitulated, whereupon its fortifications were demolished. In 1830 it was made a free port.[2]
Holstein-Glückstadt remained a possession of the Danish Crown until its defeat in the Second Schleswig War of 1864. It was occupied by Austria, but finally incorporated into the Prussian Province of Schleswig-Holstein in the aftermath of the 1866 Austro-Prussian War.
In 1845, Glückstadt station opened on the Marsh Railway line from Elmshorn, which in 1857 was continued to Itzehoe. Today trains run from Hamburg-Altona station to Westerland on Sylt island. Glückstadt also has a ferry service across the Elbe to Wischhafen in Lower Saxony. It is a stop on the Deutsche Fährstraße theme road and the Elbe Cycle Route.

Glückstadt market square
Aerial view of Glückstadt across the Lower Elbe
Former Glückstadt salt storage
Former church of the Calvinists, Remonstrants and Mennonits (Dutch Church or Reformed Church)
Former jewish cemetery
Chronological list
- Christoffer Gabel (1617-1673), Danish statesman and merchant, governor of the Faroe Islands and Copenhagen, most powerful adviser of Frederick III of Denmark.[3]
- Frederic Louis Norden (1708–1742), a Danish naval captain, cartographer and archaeological explorer.[4]
- Ludvig Manthey (1769-1842), a Danish pharmacist.
- Adolph Carl Peter Callisen(1786–1866), a German-Danish physician and lexicographer.
- August Detlev Christian Twesten (1789-1876), Lutheran theologian.[5]
- Theodor Olshausen (1802-1869), lawyer, politician, 1848 revolutionary.[6]
- August Friedrich Schenck (1828-1901), a painter, well known for his landscapes and paintings of animals
- John C. Petersen (1842-1887), butcher, farmer, and Wisconsin legislator
- Rudolf von Willemoes-Suhm (1847-1875), zoologist, and research traveller
- Theodor Heinrich Engelbrecht (1853–1934), an agronomist, geographer, farmer and politician.
- Fritz Lau (1872–1966), Low German playwright and author.[7]
- Kurt Benirschke (1924-2018), pathologist, geneticist, inventor of the Frozen zoo
- Willi Holdorf (1940 in Blomesche Wildnis - 2020), 1964 Summer Olympics gold medallist in the decathlon
- ^ "Bevölkerung der Gemeinden in Schleswig-Holstein 4. Quartal 2022" (XLS) (in German). Statistisches Amt für Hamburg und Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ a b Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Glückstadt" . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 12 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 141.
- ^ "Gabel, Kristoffer" . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 11 (11th ed.). 1911. p. 378.
- ^ Wroth, Warwick William (1895). "Norden, Frederick Lewis" . Dictionary of National Biography. Vol. 41. pp. 104–105.
- ^ "Twesten, August Detlev Christian" . The American Cyclopædia. Vol. XVI. 1879.
- ^ "Olshausen, Theodor" . New International Encyclopedia. Vol. 14. 1905.
- ^ Ehrenbürger. In: glueckstadt.de. Retrieved 15 December 2020.
Wikimedia Commons has media related to Glückstadt.


