Linagliptin (original) (raw)
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Chemical compound
Pharmaceutical compound
Linagliptin
 |
|
|---|---|
| Clinical data | |
| Pronunciation | LIN-ə-GLIP-tin |
| Trade names | Tradjenta, Trajenta, Trazenta |
| Other names | BI-1356 |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a611036 |
| License data | US DailyMed: Linagliptin |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | A10BH05 (WHO) |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | AU: S4 (Prescription only)[1][2] CA: ℞-only[3] UK: POM (Prescription only)[4] US: ℞-only[5] EU: Rx-only[6] In general: ℞ (Prescription only) |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | ~30% (Tmax = 1.5 hours) |
| Protein binding | 75–99% (concentration-dependent) |
| Metabolism | Minimal (~10% metabolized) |
| Metabolites | Pharmacologically inactive |
| Elimination half-life | ~24 hours |
| Excretion | Feces (80%), urine (5%)[5] |
| Identifiers | |
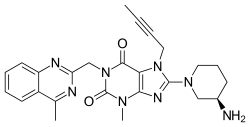
| IUPAC name 8-[(3_R_)-3-Aminopiperidin-1-yl]-7-(but-2-yn-1-yl)-3-methyl-1-[(4-methylquinazolin-2-yl)methyl]-3,7-dihydro-1_H_-purine-2,6-dione | |
| CAS Number | 668270-12-0  Y Y |
| PubChem CID | 10096344 |
| IUPHAR/BPS | 6318 |
| DrugBank | DB08882  Y Y |
| ChemSpider | 8271879  N N |
| UNII | 3X29ZEJ4R2 |
| KEGG | D09566  Y Y |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:68610  N N |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL237500  N N |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | DTXSID201021653 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C25H28N8O2 |
| Molar mass | 472.553 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | Interactive image |
| Melting point | 202 °C (396 °F) |
| SMILES CC#CCN1C2=C(N=C1N3CCC[C@H](C3)N)N(C(=O)N(C2=O)CC4=NC5=CC=CC=C5C(=N4)C)C | |
InChI InChI=1S/C25H28N8O2/c1-4-5-13-32-21-22(29-24(32)31-12-8-9-17(26)14-31)30(3)25(35)33(23(21)34)15-20-27-16(2)18-10-6-7-11-19(18)28-20/h6-7,10-11,17H,8-9,12-15,26H2,1-3H3/t17-/m1/s1  NKey:LTXREWYXXSTFRX-QGZVFWFLSA-N NKey:LTXREWYXXSTFRX-QGZVFWFLSA-N  N N |
|
 N N Y (what is this?) (verify) Y (what is this?) (verify) |
Linagliptin, sold under the brand name Tradjenta among others, is a medication used to treat type 2 diabetes (but not type 1) in conjunction with exercise and diet.[7][8] Linagliptin is a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor[7] that works by increasing the production of insulin and decreasing the production of glucagon by the pancreas.[7] It is generally less preferred than metformin and sulfonylureas as an initial treatment.[7][9] It is taken by mouth.[7]
Common side effects include inflammation of the nose and throat.[7] Serious side effects may include angioedema, pancreatitis, joint pain.[9][7] Use in pregnancy and breastfeeding is not recommended.[9]
Linagliptin was approved for medical use in the United States,[10] Japan, the European Union, Canada, and Australia in 2011.[7][11] In 2023, it was the 254th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 1 million prescriptions.[12][13] From August 2021, linagliptin became available as a generic medicine in the US.[14]
Linagliptin is indicated as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes.[5]
Linagliptin may cause severe joint pain.[5][15]
Mechanism of action
[edit]
Linagliptin belongs to a class of drugs called DPP-4 inhibitors.[5]
Linagliptin is the international nonproprietary name (INN).[16] Brand names: Trajenta,[17] Tradjenta.
- ^ "Linagliptin, tablet, 5 mg, Trajenta". Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme (PBS). July 2012. Archived from the original on 31 March 2015. Retrieved 26 September 2014.
- ^ "AusPAR: Linagliptin". Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA). 21 June 2022. Retrieved 9 April 2023.
- ^ "Trajenta Product information". Health Canada. 25 April 2012. Archived from the original on 27 September 2021. Retrieved 3 October 2022.
- ^ "Trajenta 5 mg film-coated tablets - Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC)". (emc). 27 September 2021. Archived from the original on 19 January 2022. Retrieved 3 October 2022.
- ^ a b c d e "Tradjenta- linagliptin tablet, film coated". DailyMed. 21 April 2022. Archived from the original on 15 August 2022. Retrieved 3 October 2022.
- ^ "Trajenta EPAR". European Medicines Agency (EMA). 17 September 2018. Archived from the original on 29 December 2019. Retrieved 11 February 2020.
- ^ a b c d e f g h "Linagliptin Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Archived from the original on 6 April 2019. Retrieved 6 April 2019.
- ^ Neumiller JJ (March 2012). "Pharmacology, efficacy, and safety of linagliptin for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus". The Annals of Pharmacotherapy. 46 (3): 358–67. doi:10.1345/aph.1Q522. PMID 22318932. S2CID 207264493.
- ^ a b c British national formulary : BNF 76 (76 ed.). Pharmaceutical Press. 2018. p. 680. ISBN 9780857113382.
- ^ "Drug Approval Package: Tradjenta (linagliptin) Tablets NDA #201280". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 7 June 2011. Archived from the original on 3 April 2022. Retrieved 3 October 2022.
- ^ "10 years". Boehringer Ingelheim Limited. Archived from the original on 3 October 2022. Retrieved 3 October 2022.
- ^ "The Top 300 of 2023". ClinCalc. Archived from the original on 17 August 2025. Retrieved 17 August 2025.
- ^ "Linagliptin Drug Usage Statistics, United States, 2014 - 2023". ClinCalc. Retrieved 17 August 2025.
- ^ "Linagliptin: FDA-Approved Drugs". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Archived from the original on 25 September 2021. Retrieved 24 September 2021.
- ^ "DPP-4 Inhibitors for Type 2 Diabetes: Drug Safety Communication - May Cause Severe Joint Pain". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 28 August 2015. Archived from the original on 13 December 2019. Retrieved 1 September 2015.
- ^ "International Nonproprietary Names for Pharmaceutical Substances (INN). Recommended International Nonproprietary names: List 61" (PDF). World Health Organization. p. 66. Archived (PDF) from the original on 3 October 2020. Retrieved 10 November 2016.
- ^ "Linagliptin: medicine to treat type 2 diabetes". NHS UK. 25 March 2022. Retrieved 21 November 2022.