M (original) (raw)
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
13th letter of the Latin alphabet
Not to be confused with ញ, ᛖ, ₥, ℳ, ෆ, or ʍ.
| M | |
|---|---|
| M m | |
 |
|
| Usage | |
| Writing system | Latin script |
| Type | Alphabetic and Logographic |
| Language of origin | Latin language |
| Sound values | [m][ɱ][n][n̼] |
| In Unicode | U+004D, U+006D |
| Alphabetical position | 13Numerical value: 1000 |
| History | |
| Development |   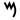   Μ μ Μ μ 𐌌M m 𐌌M m |
| Time period | ~−700 to present |
| Descendants | ₥™℠ᴟꬺꟽ ɯ ɰꟿᛗ |
| Sisters | МӍמםمܡמּﬦ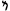 Ⰿࠌ𐌼 Ⰿࠌ𐌼 |
| Other | |
| Associated graphs | m(x) |
| Associated numbers | 1000 |
| Writing direction | Left-to-right |
| This article contains phonetic transcriptions in the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA). For an introductory guide on IPA symbols, see Help:IPA. For the distinction between [ ], / / and ⟨ ⟩, see IPA § Brackets and transcription delimiters. |
M, or m, is the thirteenth letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of several western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is em (pronounced ), plural ems.[1]
History
| Egyptian hieroglyph"n" | PhoenicianMem | Western GreekMu | EtruscanM | LatinM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
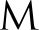 |
The letter M is derived from the Phoenician Mem via the Greek Mu (Μ, μ). Semitic Mem is most likely derived from a "Proto-Sinaitic" (Bronze Age) adoption of the "water" ideogram in Egyptian writing. The Egyptian sign had the acrophonic value /n/, from the Egyptian word for "water", nt; the adoption as the Semitic letter for /m/ was presumably also on acrophonic grounds, from the Semitic word for "water", *mā(y)-.[2]
Use in writing systems
Pronunciation of ⟨m⟩ by language
| Orthography | Phonemes |
|---|---|
| Standard Chinese (Pinyin) | /m/ |
| English | /m/, silent |
| French | /m/ |
| German | /m/ |
| Portuguese | /m/, silent |
| Spanish | /m/ |
| Turkish | /m/ |
English
In English, ⟨m⟩ represents the voiced bilabial nasal /m/.
The Oxford English Dictionary (first edition) says that ⟨m⟩ is sometimes a vowel, such as in words like spasm and in the suffix -ism. In modern terminology, this is described as a syllabic consonant (IPA: /m̩/).
M is the fourteenth most frequently used letter in the English language.
Other languages
The letter ⟨m⟩ represents the voiced bilabial nasal /m/ in the orthography of Latin as well as in those of many modern languages.
In Washo, lower-case ⟨m⟩ represents a voiced bilabial nasal /m/, while upper-case ⟨M⟩ represents a voiceless bilabial nasal /m̥/.
Other systems
In the International Phonetic Alphabet, ⟨m⟩ represents the voiced bilabial nasal /m/.
Other uses
Styled letter M in the coat of arms of Miehikkälä
- The Roman numeral M represents the number 1000, though it was not used in Roman times. There is, however, scant evidence that the letter was later introduced in the early centuries A.D. by the Romans.[3]
- Unit prefix M (mega), meaning one million times, and m (milli) meaning one-thousandth.[4][5]
- m is the standard abbreviation for metre (or meter) in the International System of Units (SI).[4] However, m is also used as an abbreviation for mile.[5]
- M is used as the unit abbreviation for molarity.[4]
- With money amounts, m or M is ambiguous. In the finance industry,[6] m or M means 1,000. In this context, five million dollars is written 5mmor5mm or 5mmor5MM. Outside of finance, some people use M like the metric system "mega-" to mean one million and write $5M.[4][5]
- M often represents male or masculine, especially in conjunction with F for female or feminine.[4][5]
- In typography, an em dash is a punctuation symbol whose width is similar to that of a capital letter M.
Descendants and related characters in the Latin alphabet
- M with diacritics: Ḿ ḿ Ṁ ṁ Ṃ ṃ M̃ m̃ ᵯ[7]
- IPA-specific symbols related to M: ɱ ɰ
- Ɱ : Capital M with hook
- Uralic Phonetic Alphabet-specific symbols related to M:[8]
- U+1D0D ᴍ LATIN LETTER SMALL CAPITAL M
- U+1D1F ᴟ LATIN SMALL LETTER SIDEWAYS TURNED M
- U+1D39 ᴹ MODIFIER LETTER CAPITAL M
- U+1D50 ᵐ MODIFIER LETTER SMALL M
- U+1D5A ᵚ MODIFIER LETTER SMALL TURNED M
- Some symbols related to M were used by the Uralic Phonetic Alphabet prior to its formal standardization in 1902:[9]
- U+2098 ₘ LATIN SUBSCRIPT SMALL LETTER M
- U+A7FA ꟺ LATIN LETTER SMALL CAPITAL TURNED M
- The Teuthonista phonetic transcription system uses U+AB3A ꬺ LATIN SMALL LETTER M WITH CROSSED-TAIL[10]
- Other variations used for phonetic transcription:[11] ᶆ ᶬ ᶭ
- Ɯ ɯ : Turned M
- ꟽ : Inverted M was used in ancient Roman texts to stand for mulier (woman)[12]
- ꟿ : Archaic M was used in ancient Roman texts to abbreviate the personal name 'Manius' (A regular capital M was used for the more common personal name 'Marcus')[12]
- ℳ : currency symbol for Mark
Ancestors and siblings in other alphabets
- 𐤌 : Semitic letter Mem, from which the following symbols originally derive:
- Μ μ : Greek letter Mu, from which M derives
* Ⲙ ⲙ : Coptic letter Me, which derives from Greek Mu
* М м : Cyrillic letter Em, also derived from Mu
* 𐌌 : Old Italic M, which derives from Greek Mu, and is the ancestor of modern Latin M
* ᛗ : Runic letter Mannaz, which derives from old Italic M
* 𐌼 : Gothic letter manna, which derives from Greek Mu
- Μ μ : Greek letter Mu, from which M derives
Ligatures and abbreviations
- ₥ : Mill (currency)
- ™ : Trademark symbol
- ℠ : Service mark symbol
Other representations
Computing
Character information
| Preview | M | m | M | m | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unicode name | LATIN CAPITAL LETTER M | LATIN SMALL LETTER M | FULLWIDTH LATIN CAPITAL LETTER M | FULLWIDTH LATIN SMALL LETTER M | ||||
| Encodings | decimal | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex |
| Unicode | 77 | U+004D | 109 | U+006D | 65325 | U+FF2D | 65357 | U+FF4D |
| UTF-8 | 77 | 4D | 109 | 6D | 239 188 173 | EF BC AD | 239 189 141 | EF BD 8D |
| Numeric character reference | M | M | m | m | M | M | m | m |
| EBCDIC family | 212 | D4 | 148 | 94 | ||||
| ASCII[a] | 77 | 4D | 109 | 6D |
Other
Notes
- ^ Also for encodings based on ASCII, including the DOS, Windows, ISO-8859 and Macintosh families of encodings.
References
- ^ "M" Oxford English Dictionary, 2nd edition (1989); Merriam-Webster's Third New International Dictionary of the English Language, Unabridged (1993); "em," op. cit.
- ^ See F. Simons, "Proto-Sinaitic — Progenitor of the Alphabet" Rosetta 9 (2011): Figure Two: "Representative selection of proto-Sinaitic characters with comparison to Egyptian hieroglyphs", (p. 38) Figure Three: "Chart of all early proto-Canaanite letters with comparison to proto-Sinaitic signs" (p. 39), Figure Four: "Representative selection of later proto-Canaanite letters with comparison to early proto-Canaanite and proto-Sinaitic signs" (p. 40). See also: Goldwasser (2010), following Albright (1966), "Schematic Table of Proto-Sinaitic Characters" (fig. 1 Archived 2016-07-03 at the Wayback Machine).
- ^ Gordon, Arthur E. (1983). Illustrated Introduction to Latin Epigraphy. University of California Press. pp. 45. ISBN 9780520038981. Retrieved October 3, 2015. roman numerals.
- ^ a b c d e "What does M stand for?". The Free Dictionary. Archived from the original on November 25, 2020. Retrieved February 9, 2021.
- ^ a b c d "M definition and meaning". Collins English Dictionary. Archived from the original on February 27, 2021. Retrieved February 9, 2021.
- ^ "MM (Millions)". corporatefinanceinstitute.com. corporate finance institute. Archived from the original on August 5, 2024. Retrieved August 5, 2024.
- ^ Constable, Peter (September 30, 2003). "L2/03-174R2: Proposal to Encode Phonetic Symbols with Middle Tilde in the UCS" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on October 11, 2017. Retrieved March 24, 2018.
- ^ Everson, Michael; et al. (March 20, 2002). "L2/02-141: Uralic Phonetic Alphabet characters for the UCS" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on February 19, 2018. Retrieved March 24, 2018.
- ^ Ruppel, Klaas; Aalto, Tero; Everson, Michael (January 27, 2009). "L2/09-028: Proposal to encode additional characters for the Uralic Phonetic Alphabet" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on October 11, 2017. Retrieved March 24, 2018.
- ^ Everson, Michael; Dicklberger, Alois; Pentzlin, Karl; Wandl-Vogt, Eveline (June 2, 2011). "L2/11-202: Revised proposal to encode "Teuthonista" phonetic characters in the UCS" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on October 11, 2017. Retrieved March 24, 2018.
- ^ Constable, Peter (April 19, 2004). "L2/04-132 Proposal to add additional phonetic characters to the UCS" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on October 11, 2017. Retrieved March 24, 2018.
- ^ a b Perry, David J. (August 1, 2006). "L2/06-269: Proposal to Add Additional Ancient Roman Characters to UCS" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on June 14, 2019. Retrieved March 24, 2018.

