M-Cymene (original) (raw)
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Organic compound
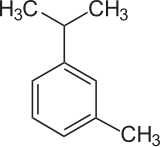
_m_-Cymene
 |
|
|---|---|
| Names | |
| Preferred IUPAC name 1-Methyl-3-(propan-2-yl)benzene | |
| Other names_m_-Cymene3-isopropyltoluene3-methylcumene1-isopropyl-3-methylbenzene | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | 535-77-3  Y Y |
| 3D model (JSmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:28768 |
| ChemSpider | 10355 |
| EC Number | 208-617-9 |
| PubChem CID | 10812 |
| UNII | 10ZH8R921S  Y Y |
| InChI InChI=1S/C10H14/c1-8(2)10-6-4-5-9(3)7-10/h4-8H,1-3H3Key: XCYJPXQACVEIOS-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| SMILES CC1=CC(=CC=C1)C(C)C | |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C10H14 |
| Molar mass | 134.22 |
| Appearance | colorless liquid |
| Density | 0.86 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | −63.8 °C (−82.8 °F; 209.3 K) |
| Boiling point | 175 °C (347 °F; 448 K) |
| Solubility in water | 42.5 mg/L |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
| Main hazards | Flammable |
| GHS labelling: | |
| Pictograms |  |
| Signal word | Warning |
| Hazard statements | H226 |
| Precautionary statements | P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P280, P303+P361+P353, P370+P378, P403+P235, P501 |
| Flash point | 47.8 °C (118.0 °F; 320.9 K) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). Infobox references |
Chemical compound
_m_-Cymene is an organic compound classified as an aromatic hydrocarbon. Its structure consists of a benzene ring _meta_-substituted with a methyl group and an isopropyl group. It is a flammable colorless liquid which is nearly insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents.
Isomers and production
[edit]
In addition to _m_-cymene, there are two other geometric isomers called _o_-cymene, in which the alkyl groups are _ortho_-substituted, and _p_-cymene, in which they are _para_-substituted. _p_-Cymene is the most common and only natural isomer. The three isomers form the group of cymenes.
Cymenes can be produced by alkylation of toluene with propylene.[1][2]
- ^ Vora, Bipin V.; Kocal, Joseph A.; Barger, Paul T.; Schmidt, Robert J.; Johnson, James A. (2003). "Alkylation". Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology. Kirk‐Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology. doi:10.1002/0471238961.0112112508011313.a01.pub2. ISBN 0471238961.
- ^ Griesbaum, Karl; Behr, Arno; Biedenkapp, Dieter; Voges, Heinz-Werner; Garbe, Dorothea; Paetz, Christian; Collin, Gerd; Mayer, Dieter; Höke, Hartmut (2002). "Hydrocarbons". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a13_227. ISBN 978-3527306732.