Nylon 12 (original) (raw)
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
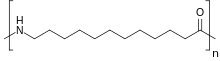
Nylon 12
 |
|
|---|---|
| Names | |
| IUPAC name Poly(dodecano-12-lactam) | |
| Other namesPolyamide 12, PA 12, polylaurolactam, Polylaurinlactam, poly(12-aminododecanoic acid lactam); Daiamid (Daicel Chemical Industries), Grilamid (EMS Chemie); Rilsan A (Elf Atochem); UBE Nylon 12 (UBE Industries); Vestamid (Creanova) | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | 24937-16-4  Y Y |
| ChemSpider | none |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.126.906 |
| UNII | 446U8J075B  Y Y |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | DTXSID3040803 |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | (C12H23NO)n |
| Density | 1.01 g/mL |
| Melting point | 178 to 180 °C (352 to 356 °F; 451 to 453 K) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). Infobox references |
Chemical compound
Nylon 12 is a nylon polymer with the formula [(CH2)11C(O)NH]n. It is made from ω-aminolauric acid or laurolactam monomers that each have 12 carbons, hence the name ‘Nylon 12’. It is one of several nylon polymers.[1]
Nylon 12 can be produced through two routes. The first being polycondensation of ω-aminolauric acid, a bifunctional monomer with one amine and one carboxylic acid group.
n H2N(CH2)11CO2H → [(CH2)11CONH]n + n H2O
The second route is ring-opening polymerization of laurolactam at 260-300˚C. Ring opening can be carried out by cationic or anionic initiators, although cationic initiators have not been used commercially due to the product being less stable and oxidized relatively quickly in comparison to those produced by activated anionic polymerization (monomer casting).[2] Ring-opening polymerization is the preferred route for commercial production.
n [(CH2)11CONH] → [(CH2)11CONH]n
Nylon 12 exhibits properties between short chain aliphatic nylons (e.g., nylon 6 and nylon 66) and polyolefins.[3]At 178-180 °C, the melting point of nylon 12 is the lowest among the important polyamides. Its mechanical properties, such as hardness, tensile strength, and resistance to abrasion, are similar to those of nylon 6 and nylon 66. Low water absorption and density, 1.01 g/mL, result from its relatively long hydrocarbon chain length, which also confers it dimensional stability and an almost paraffin-like structure. Nylon 12 is also chemical resistant and insensitive to stress cracking.
Nylon 12 has a broad range of applications as polyamide additives. Nylon 12 is mainly used for films for packing material in the food industry and sterilized films and bags for use in the pharmaceutical and medical fields. When added to polyethylene films, it improves water vapor permeability and aroma impermeability.
It is also prepared as sheets and sintered powder for coating metals. In the electronics field, it is used for covering cables and insulating material, while in the automobile industry it is used to prepare oil and gasoline resistant tubes. In the cosmetic and personal care industries, it is used as bulking and opacifying agents in the face and body powders, and skin creams.[4] Nylon 12 has also found uses in the textile industry and for producing sporting and leisure goods among other applications.
Significant suppliers of nylon 12 include EMS-Chemie, the Marl Chemical Park operated by Evonik, Arkema and South Korea's SH Energy & Chemical Co.
- ^ Wolfgang. Griehl , Djavid. Ruestem "Nylon 12-Preparation, Properties, and Applications" Ind. Eng. Chem., 1970, vol. 62, pp 16–22. doi:10.1021/ie50723a005
- ^ Kubisa, P.; Matyjaszewski, K.; Penczek, S. (1985). Cationic Ring-Opening Polymerization. Advances in Polymer Science. Vol. 68/69. Springer Berlin Heidelberg. pp. 201–208. doi:10.1007/3-540-13781-5_11. ISBN 978-3-540-13781-8. S2CID 242332714.
- ^ Mark, James E. (1999). Polymer Data Handbook. Oxford University Press, Inc. ISBN 978-0195181012.
- ^ "Regenerist Micro-Sculpting Cream Moisturizer". Olay. Procter & Gamble. Retrieved 10 December 2015.