P-Cymene (original) (raw)
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
_p_-Cymene
 Skeletal formula Skeletal formula  Ball-and-stick model Ball-and-stick model |
|
|---|---|
| Names | |
| Preferred IUPAC name 1-Methyl-4-(propan-2-yl)benzene[1] | |
| Other names_para_-Cymene4-Isopropyltoluene4-MethylcumeneParacymene | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | 99-87-6  Y Y |
| 3D model (JSmol) | Interactive image |
| 3DMet | B00975 |
| Beilstein Reference | 1903377 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:28768 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL442915  Y Y |
| ChemSpider | 7183  Y Y |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.542 |
| EC Number | 202-796-7 |
| Gmelin Reference | 305912 |
| KEGG | C06575  Y Y |
| PubChem CID | 7463 |
| RTECS number | GZ5950000 |
| UNII | 1G1C8T1N7Q  Y Y |
| UN number | 2046 |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | DTXSID3026645 |
InChI InChI=1S/C10H14/c1-8(2)10-6-4-9(3)5-7-10/h4-8H,1-3H3  YKey: HFPZCAJZSCWRBC-UHFFFAOYSA-N YKey: HFPZCAJZSCWRBC-UHFFFAOYSA-N  YInChI=1/C10H14/c1-8(2)10-6-4-9(3)5-7-10/h4-8H,1-3H3Key: HFPZCAJZSCWRBC-UHFFFAOYAD YInChI=1/C10H14/c1-8(2)10-6-4-9(3)5-7-10/h4-8H,1-3H3Key: HFPZCAJZSCWRBC-UHFFFAOYAD |
|
| SMILES c1cc(ccc1C(C)C)C | |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C10H14 |
| Molar mass | 134.222 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colourless liquid |
| Density | 0.857 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | −68 °C (−90 °F; 205 K) |
| Boiling point | 177 °C (351 °F; 450 K) |
| Solubility in water | 23.4 mg/L |
| Magnetic susceptibility (χ) | −1.028×10−4 cm3/mol |
| Refractive index (_n_D) | 1.4908 (at 20 °C) [2] |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
| Pictograms |    |
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statements | H226, H304, H411 |
| Precautionary statements | P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P273, P280, P301+P310, P303+P361+P353, P331, P370+P378, P391, P403+P235, P405, P501 |
| Flash point | 47 °C (117 °F; 320 K) |
| Autoignition temperature | 435 °C (815 °F; 708 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).  Y verify (what is Y verify (what is  Y Y N ?) Infobox references N ?) Infobox references |
Chemical compound
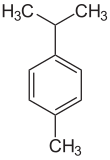
_p_-Cymene is a naturally occurring aromatic organic compound. It is classified as an alkylbenzene related to monocyclic monoterpenes.[3] Its structure consists of a benzene ring _para_-substituted with a methyl group and an isopropyl group. _p_-Cymene is insoluble in water, but miscible with organic solvents.
Isomers and production
[edit]
In addition to _p_-cymene, two less common geometric isomers are _o_-cymene, in which the alkyl groups are _ortho_-substituted, and _m_-cymene, in which they are _meta_-substituted. _p_-Cymene is the only natural isomer, as expected from the terpene rule. All three isomers form the group of cymenes.
Cymene is also produced by alkylation of toluene with propene.[4]
It is a constituent of a number of essential oils, most commonly the oil of cumin and thyme. Significant amounts are formed in sulfite pulping process from the wood terpenes.
_p_-Cymene is a common ligand for ruthenium. The parent compound is [(_η_6-cymene)RuCl2]2. This half-sandwich compound is prepared by the reaction of ruthenium trichloride with the terpene α-phellandrene. The osmium complex is also known.[5]
Hydrogenation gives the saturated derivative _p_-menthane.
- ^ Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry: IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013 (Blue Book). Cambridge: The Royal Society of Chemistry. 2014. pp. 139, 597. doi:10.1039/9781849733069-FP001. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- ^ Pabst, Florian; Blochowicz, Thomas (December 2022). "On the intensity of light scattered by molecular liquids - Comparison of experiment and quantum chemical calculations". The Journal of Chemical Physics. 157 (24): 244501. Bibcode:2022JChPh.157x4501P. doi:10.1063/5.0133511. PMID 36586992.
- ^ Balahbib, Abdelaali; El Omari, Nasreddine; Hachlafi, Naoufal EL.; Lakhdar, Fatima; El Menyiy, Naoual; Salhi, Najoua; Mrabti, Hanae Naceiri; Bakrim, Saad; Zengin, Gokhan; Bouyahya, Abdelhakim (2021-07-01). "Health beneficial and pharmacological properties of p-cymene". Food and Chemical Toxicology. 153: 112259. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2021.112259. ISSN 0278-6915.
- ^ Vora, Bipin V.; Kocal, Joseph A.; Barger, Paul T.; Schmidt, Robert J.; Johnson, James A. (2003). "Alkylation". Kirk‐Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology. doi:10.1002/0471238961.0112112508011313.a01.pub2. ISBN 0471238961.
- ^ Bennett, M. A.; Huang, T.-N.; Matheson, T. W.; Smith, A. K. (1982). "(_η_6-Hexamethylbenzene)Ruthenium Complexes". Inorganic Syntheses. 21: 74–78. doi:10.1002/9780470132524.ch16. ISBN 9780470132524.