Palatine process of maxilla (original) (raw)
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Thick, horizontal process of the maxilla
| Palatine process of maxilla | |
|---|---|
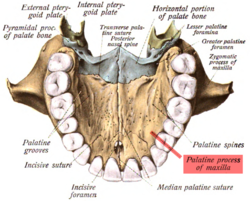 Inferior surface of maxilla. The bony palate and alveolar arch. (Palatine process labeled at bottom right.) Inferior surface of maxilla. The bony palate and alveolar arch. (Palatine process labeled at bottom right.) |
|
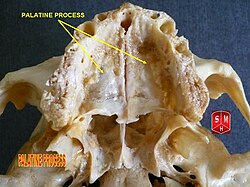 Inferior surface of maxilla. Inferior surface of maxilla. |
|
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | processus palatinus ossis maxillae, processus palatinus maxillae |
| TA98 | A02.1.12.029 |
| TA2 | 786 |
| FMA | 52896 |
| Anatomical terms of bone[edit on Wikidata] |
In human anatomy of the mouth, the palatine process of maxilla (palatal process), is a thick, horizontal process of the maxilla. It forms the anterior three quarters of the hard palate, the horizontal plate of the palatine bone making up the rest. It is the most important bone in the midface. It provides structural support for the viscerocranium.[1]
It is perforated by numerous foramina for the passage of the nutrient vessels; is channelled at the back part of its lateral border by a groove, sometimes a canal, for the transmission of the descending palatine vessels and the anterior palatine nerve from the spheno-palatine ganglion; and presents little depressions for the lodgement of the palatine glands.
When the two maxillae are articulated, a funnel-shaped opening, the incisive foramen, is seen in the middle line, immediately behind the incisor teeth.
In this opening the orifices of two lateral canals are visible; they are named the incisive canals or foramina of Stenson; through each of them passes the terminal branch of the descending palatine artery and the nasopalatine nerve.
On the under surface of the palatine process, a delicate linear suture, well seen in young skulls, may sometimes be noticed extending laterally and forward on either side from the incisive foramen to the interval between the lateral incisor and the canine tooth.
The small part in front of this suture constitutes the premaxilla (os incisivum), which in most vertebrates forms an independent bone; it includes the whole thickness of the alveolus, the corresponding part of the floor of the nose and the anterior nasal spine, and contains the sockets of the incisor teeth.
The upper surface of the palatine process is concave from side to side, smooth, and forms the greater part of the floor of the nasal cavity. It presents, close to its medial margin, the upper orifice of the incisive canal.
The lateral border of the process is incorporated with the rest of the bone.
The medial border is thicker in front than behind, and is raised above into a ridge, the nasal crest, which, with the corresponding ridge of the opposite bone, forms a groove for the reception of the vomer. The front part of this ridge rises to a considerable height, and is named the incisor crest; it is prolonged forward into a sharp process, which forms, together with a similar process of the opposite bone, the anterior nasal spine.
The posterior border is serrated for articulation with the horizontal part of the palatine bone.
Occasionally two additional canals are present in the middle line; they are termed the foramina of Scarpa, and when present transmit the nasopalatine nerves, the left passing through the anterior, and the right through the posterior canal.
Clinical significance
[edit]
[![[icon]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/1/1c/Wiki_letter_w_cropped.svg/20px-Wiki_letter_w_cropped.svg.png) ](/wiki/File:Wiki%5Fletter%5Fw%5Fcropped.svg) ](/wiki/File:Wiki%5Fletter%5Fw%5Fcropped.svg) |
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (April 2014) |
|---|

Position of palatine process (shown in red).
Maxilla. Palatine process shown in red.
Inferior surface of maxilla. Palatine process shown in red.
Inferior surface of maxilla. The bony palate and alveolar arch.
Left maxilla. Nasal surface.
Base of skull. Inferior surface.
Roof, floor, and lateral wall of left nasal cavity.
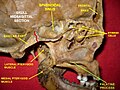
Sagittal section of skull. (Palatine process labeled at bottom right.)
Medial surface of right maxilla. (Palatine process labeled at center.)
- ^ Dalgorf D, Higgins K. Reconstruction of the midface and maxilla. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2008 Aug;16(4):303-11
- Anatomy photo:22:os-1909 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center – "Osteology of the Skull: The Maxilla"
- Atlas image: rsa1p7 at the University of Michigan Health System – "Nasal septum, lateral view"
- "Anatomy diagram: 34257.000-1". Roche Lexicon – illustrated navigator. Elsevier. Archived from the original on 2012-07-22.