Phanephos (original) (raw)
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Phanephos
 |
|
|---|---|
| Names | |
| IUPAC name (S)-(+)-4,12-Bis(diphenylphosphino)-[2.2]-paracyclophane; (R)-(−)-4,12-Bis(diphenylphosphino)-[2.2]-paracyclophane | |
| Other names(S)-Phanephos; (R)-Phanephos | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | (S): 364732-88-7  Y(R): 192463-40-4 Y(R): 192463-40-4  Y Y |
| 3D model (JSmol) | (S): Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | (S): 9040059 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.217.129 |
| EC Number | (R): 690-034-8 |
| PubChem CID | (S): 10864772 |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | (S): DTXSID301045593 |
| InChI InChI=1S/C40H34P2/c1-5-13-35(14-6-1)41(36-15-7-2-8-16-36)39-29-31-21-25-33(39)27-23-32-22-26-34(28-24-31)40(30-32)42(37-17-9-3-10-18-37)38-19-11-4-12-20-38/h1-22,25-26,29-30H,23-24,27-28H2Key: GYZZZILPVUYAFJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N(S): InChI=1/C40H34P2/c1-5-13-35(14-6-1)41(36-15-7-2-8-16-36)39-29-31-21-25-33(39)27-23-32-22-26-34(28-24-31)40(30-32)42(37-17-9-3-10-18-37)38-19-11-4-12-20-38/h1-22,25-26,29-30H,23-24,27-28H2Key: GYZZZILPVUYAFJ-UHFFFAOYAH | |
| SMILES (S): C1CC2=C(C=C(CCC3=C(C=C1C=C3)P(C4=CC=CC=C4)C5=CC=CC=C5)C=C2)P(C6=CC=CC=C6)C7=CC=CC=C7 | |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C40H34P2 |
| Molar mass | 576.660 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White to off-white powder or crystals |
| Melting point | 222 to 225 °C (432 to 437 °F; 495 to 498 K) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). Infobox references |
Chemical compound
Phanephos is an organophosphorus compound with the chemical formula (C2H4)2(C6H3PPh2)2 (Ph = C6H5). It is a white solid that is soluble in organic solvents. It is an example of a chiral C2-symmetric diphosphine ligand used in asymmetric hydrogenation. Many substituents have been introduced in place of the phenyl groups, e.g., _i_-Pr, C6H11, etc. and a variety of chiral diphosphine ligands have been reported in asymmetric catalysis since the 1960s.
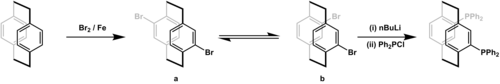
Phanephos can be prepared in two steps from [2.2]paracyclophane. In the first step, [2.2]paracyclophane is dibrominated to give a pseudo-para dibromide. Thermal isomerisation then gives pseudo-ortho atropisomer of the dibromide. This isomer is subjected to lithium-halogen exchange by nBuLi and the resulting dilithium compound is treated with PPh2Cl to give a racemic mixture of phanephos.[1]
Phanephos preparation
Phanephos has been used in rhodium- and ruthenium- mediated stereoselective hydrogenation of dehydro amino acid methyl esters and asymmetric reduction of various β-ketoesters with about 90% ee.[2]
- ^ G. J. Rowlands, Planar Chiral Phosphines Derived from [2.2]Paracyclophane , Israel Journal of Chemistry, 2012, 52. 60-75, doi:10.1002/ijch.201100098
- ^ R. Gleiter, H. Hopf, Modern Cyclophane Chemistry, Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 2005, p.449-451 doi:10.1002/3527603964