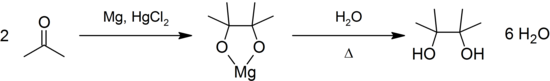Pinacol (original) (raw)
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Pinacol
 Pinacol Pinacol |
|
|---|---|
 Ball-and-stick model of pinacol Ball-and-stick model of pinacol |
|
| Names | |
| Preferred IUPAC name 2,3-Dimethylbutane-2,3-diol | |
| Other names2,3-Dimethyl-2,3-butanediolTetramethylethylene glycol1,1,2,2-Tetramethylethylene glycolPinacone | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | 76-09-5  Y Y |
| 3D model (JSmol) | Interactive imageInteractive image |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:131185  Y Y |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL3289669 |
| ChemSpider | 21109330  Y Y |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.849 |
| EC Number | 200-933-5 |
| PubChem CID | 6425 |
| UNII | 527QE7I5CO  Y Y |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | DTXSID3058793 |
InChI InChI=1S/C6H14O2/c1-5(2,7)6(3,4)8/h7-8H,1-4H3  YKey: IVDFJHOHABJVEH-UHFFFAOYSA-N YKey: IVDFJHOHABJVEH-UHFFFAOYSA-N  Y Y |
|
| SMILES CC(C)(O)C(C)(C)OCC(C)(O)C(C)(C)O | |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C6H14O2 |
| Molar mass | 118.174 g/mol |
| Appearance | White solid |
| Density | 0.967 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 40 to 43 °C (104 to 109 °F; 313 to 316 K) |
| Boiling point | 171 to 173 °C (340 to 343 °F; 444 to 446 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
| Pictograms |   |
| Signal word | Warning |
| Hazard statements | H228, H315, H319, H335 |
| Precautionary statements | P210, P240, P241, P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P321, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P370+P378, P403+P233, P405, P501 |
| Flash point | 77 °C (171 °F; 350 K) |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | External MSDS |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds | Pinacolone |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).  N verify (what is N verify (what is  Y Y N ?) Infobox references N ?) Infobox references |
Chemical compound
Pinacol is a branched alcohol which finds use in organic syntheses. It is a diol that has hydroxyl groups on vicinal carbon atoms. A white solid that melts just above room temperature, pinacol is notable for undergoing the pinacol rearrangement in the presence of acid and for being the namesake of the pinacol coupling reaction.
It may be produced by the pinacol coupling reaction from acetone:[1]
As a vicinal diol, it can rearrange to pinacolone by the pinacol rearrangement, e.g., by heating with sulfuric acid:[2]
Pinacol can be used with borane and boron trichloride to produce useful synthetic intermediates such as pinacolborane, bis(pinacolato)diboron,[3] and pinacolchloroborane.
- ^ Roger Adams and E. W. Adams. "Pinacol Hydrate". Organic Syntheses; Collected Volumes, vol. 1, p. 459.
- ^ G. A. Hill and E. W. Flosdorf (1941). "Pinacolone". Organic Syntheses; Collected Volumes, vol. 1, p. 462.
- ^ Tatsuo Ishiyama; Miki Murata; Taka-aki Ahiko; Norio Miyaura (2004). "Bis(pinacolato)diboron". Organic Syntheses; Collected Volumes, vol. 10, p. 115.