STS-51-G (original) (raw)
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
1985 American crewed spaceflight to deploy communications satellites
STS-51-G
 Discovery deploys Morelos-1. Discovery deploys Morelos-1. |
|
|---|---|
| Names | Space Transportation System-18 |
| Mission type | Satellites deployment |
| Operator | NASA |
| COSPAR ID | 1985-048A |
| SATCAT no. | 15823 |
| Mission duration | 7 days, 1 hour, 38 minutes, 52 seconds |
| Distance travelled | 4,693,051 km (2,916,127 mi) |
| Orbits completed | 112 |
| Spacecraft properties | |
| Spacecraft | Space Shuttle Discovery |
| Launch mass | 116,357 kg (256,523 lb) |
| Landing mass | 92,610 kg (204,170 lb) |
| Payload mass | 17,280 kg (38,100 lb) |
| Crew | |
| Crew size | 7 |
| Members | Daniel C. BrandensteinJohn O. CreightonShannon W. LucidSteven R. NagelJohn M. FabianPatrick BaudrySultan bin Salman Al Saud |
| Start of mission | |
| Launch date | June 17, 1985, 11:33:00 (June 17, 1985, 11:33:00) UTC (7:33 am EDT) |
| Launch site | Kennedy, LC-39A |
| Contractor | Rockwell International |
| End of mission | |
| Landing date | June 24, 1985, 13:11:52 (June 24, 1985, 13:11:52) UTC (6:11:52 am PDT) |
| Landing site | Edwards, Runway 23 |
| Orbital parameters | |
| Reference system | Geocentric orbit[1] |
| Regime | Low Earth orbit |
| Perigee altitude | 353 km (219 mi) |
| Apogee altitude | 359 km (223 mi) |
| Inclination | 28.45° |
| Period | 91.70 minutes |
| Instruments | |
| Automated Directional Solidification Furnace (ADSF)French Echocardiograph Experiment (FEE)French Postural Experiment (FPE)High Precision Tracking Experiment (HPTE)Shuttle Pointed Autonomous Research Tool for AstroNomy (SPARTAN-1) | |
 STS-51-G mission patch STS-51-G mission patch  Back: Lucid, Nagel, Fabian, Al Saud and BaudryFront: Brandenstein and CreightonSpace Shuttle program← STS-51-B (17)STS-51-F (19) → Back: Lucid, Nagel, Fabian, Al Saud and BaudryFront: Brandenstein and CreightonSpace Shuttle program← STS-51-B (17)STS-51-F (19) → |
STS-51-G was the 18th flight of NASA's Space Shuttle program, and the fifth flight of Space Shuttle Discovery. The seven-day mission launched from Kennedy Space Center, Florida, on June 17, 1985, and landed at Edwards Air Force Base, California, on June 24, 1985. Sultan bin Salman Al Saud from Saudi Arabia was on board as a payload specialist; Al Saud became the first Arab, the first Muslim, and the first member of a royal family to fly into space.[2] It was also the first Space Shuttle mission which flew without at least one astronaut from the pre-Shuttle era among its crew.
Crew seat assignments
[edit]
| Seat[3] | Launch | Landing | 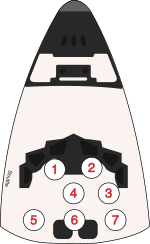 Seats 1–4 are on the flight deck.Seats 5–7 are on the mid-deck. Seats 1–4 are on the flight deck.Seats 5–7 are on the mid-deck. |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Brandenstein | ||
| 2 | Creighton | ||
| 3 | Lucid | Fabian | |
| 4 | Nagel | ||
| 5 | Fabian | Lucid | |
| 6 | Baudry | ||
| 7 | Al Saud |
Discovery lifted off from Launch Complex 39A, Kennedy Space Center (KSC), at 7:33 a.m. EDT on June 17, 1985. The mission's crew members included Daniel C. Brandenstein, commander; John O. Creighton, pilot; Shannon W. Lucid, Steven R. Nagel, and John M. Fabian, mission specialists; and Patrick Baudry, from France, and Prince Sultan Sultan bin Salman Al Saud, from Saudi Arabia, both payload specialists.
STS-51-G carried three communications satellites as its primary cargo. These were Arabsat-1B (Arab Satellite Communications Organization); Morelos-1 (Mexico); and Telstar-303 (AT&T Corporation); all three were Hughes-built satellites. All three successfully utilized Payload Assist Module (PAM-D) booster stages to achieve geostationary transfer orbits (GTO) after being deployed from Discovery.
Also carried was the SPARTAN-1 (Shuttle Pointed Autonomous Research Tool for AstroNomy) a deployable/retrievable carrier module, designed to be deployed from the orbiter and fly free in space before being retrieved. SPARTAN-1 included 140 kg (310 lb) of astronomy experiments. It was deployed and operated successfully, independent of the orbiter, before being retrieved. Discovery furthermore carried an experimental materials-processing furnace, two French biomedical experiments (French Echocardiograph Experiment (FEE) and French Postural Experiment (FPE)),[3] and six Getaway Special (GAS) experiments, which were all successfully performed, although the GO34 Getaway Special shut down prematurely. This mission was also the first flight test of the OEX advanced autopilot which gave the orbiter capabilities above and beyond those of the baseline system.
The mission's final payload element was a High Precision Tracking Experiment (HPTE) for the Strategic Defense Initiative (SDI) (nicknamed "Star Wars"); the HPTE failed to deploy properly during its first try on the mission's 37th orbit, because the orbiter was not at the correct attitude. It was successfully deployed on orbit 64.
Discovery landed at Edwards Air Force Base at 9:11:52 a.m. EDT on June 24, 1985, after a mission duration of 7 days, 1 hour, 38 minutes, and 52 seconds.
The STS-51-G insignia illustrates the advances in aviation technology in the United States within a relatively short span of the twentieth century with Discovery flying over the Wright Flyer. A gold-and-orange-flame eagle forms the base of the insigna. The surnames of the crewmembers for the Discovery's mission appear near the center edge of the circular design, with the French and Saudi crewmembers added below, with a respective flag icon along their name. Although Baudry was the first French citizen to fly with a Space Shuttle mission into space, he was only the second Frenchman to go to space, following Jean-Loup Chrétien's earlier missions with Soyuz capsule, Soyuz T-6.
NASA began a tradition of playing music to astronauts during Project Gemini, and first used music to wake up a flight crew during Apollo 15. Each track is specially chosen, often by the astronauts' families, and usually has a special meaning to an individual member of the crew, or is applicable to their daily activities.[4]
| Flight Day | Song | Artist/Composer |
|---|---|---|
| Day 2 | "Eye in the Sky (song)" | The Alan Parsons Project |
| Day 3 | "Proud Mary" | Creedence Clearwater Revival |
| Day 4 | "Sailing" | Christopher Cross |
| Day 5 | "Jonathan Livingston Seagull" | Neil Diamond |
| Day 6 | "Wedding March" | Felix Mendelssohn |

Arabsat-1B deployment
Morelos-1 deployment
Telstar-303 deployment
SPARTAN-1 after deployment- List of human spaceflights
- List of Space Shuttle missions
- ^ "Trajectory: STS-51G (1985-048A)". NASA. January 7, 2022. Retrieved January 23, 2022.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. - ^ "A prince in space" (January/February 1986 ed.). pp. 20–29. Retrieved January 23, 2022.
- ^ a b "STS-51G". Spacefacts. Retrieved January 23, 2021.
- ^ Fries, Colin (June 25, 2007). "Chronology of Wakeup Calls" (PDF). NASA. Archived from the original (PDF) on December 20, 2023. Retrieved August 13, 2007.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- NASA mission summary Archived October 16, 2008, at the Wayback Machine
- STS-51G Video Highlights Archived September 21, 2013, at the Wayback Machine