Sodium tellurite (original) (raw)
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Sodium tellurite
 |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Names | |
| Other namesSodium Tellurite IV, Tellurous acid disodium salt | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | 10102-20-2  N N |
| 3D model (JSmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 23309  Y Y |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.030.231 |
| EC Number | 233-268-4 |
| PubChem CID | 24935 |
| RTECS number | WY2450000 |
| UNII | 0BB57LA23Y  Y Y |
| UN number | 3288 |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | DTXSID2064943 |
InChI InChI=1S/2Na.H2O3Te/c;;1-4(2)3/h;;(H2,1,2,3)/q2*+1;/p-2  YKey: VOADVZVYWFSHSM-UHFFFAOYSA-L YKey: VOADVZVYWFSHSM-UHFFFAOYSA-L  YInChI=1/2Na.H2O3Te/c;;1-4(2)3/h;;(H2,1,2,3)/q2*+1;/p-2Key: VOADVZVYWFSHSM-NUQVWONBAS YInChI=1/2Na.H2O3Te/c;;1-4(2)3/h;;(H2,1,2,3)/q2*+1;/p-2Key: VOADVZVYWFSHSM-NUQVWONBAS |
|
| SMILES [Na+].[Na+].[O-][Te]([O-])=O | |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | Na2TeO3 |
| Molar mass | 221.57774 g/mol |
| Appearance | white crystals, powder |
| Density | 6.245 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 710 °C (1,310 °F; 983 K) |
| Solubility in water | soluble greater than or equal to 100 mg/mL at 68°F |
| Structure | |
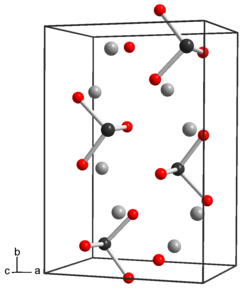
| Crystal structure | rhombic |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
| Pictograms |  |
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statements | H300, H301, H311, H330, H331 |
| Precautionary statements | P260, P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P284, P301+P310, P302+P352, P304+P340, P310, P311, P312, P320, P321, P322, P330, P361, P363, P403+P233, P405, P501 |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
| LD50 (median dose) | 83 mg/kg (rat, oral) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).  N verify (what is N verify (what is  Y Y N ?) Infobox references N ?) Infobox references |
Chemical compound
Sodium tellurite is an inorganic tellurium compound with formula Na2TeO3. It is a water-soluble white solid and a weak reducing agent. Sodium tellurite is an intermediate in the extraction of the element, tellurium; it is a product obtained from anode slimes and is a precursor to tellurium.
The main source of tellurium is from copper anode slimes, which contain precious metals as well as various tellurides. These slimes are roasted with sodium carbonate and oxygen to produce sodium tellurite.[1]
Ag2Te + Na2CO3 + O2 → 2Ag + Na2TeO3 + CO2 (400–500 °C)
This is a reaction with silver telluride. The telluride is oxidized to tellurite and the silver(I) is reduced to silver.
The electrolysis of a tellurite solution yields purified tellurium.[1]
Anode: 4OH− → 2H2O + O2 + 4e−
Cathode: TeO32− + 3H2O + 4e− → Te + 6OH−
Structure and properties
[edit]
Tellurium has properties similar to sulfur and selenium. In the anhydrous form Na2TeO3 the tellurium atoms are 6 coordinate, three Te-O at 1.87 Å and three at 2.9 Å, with distorted octahedra sharing edges.[2] In the pentahydrate, Na2TeO3.5H2O there are discrete tellurite anions, TeO32− which are pyramidal. The Te-O distance is 1.85 - 1.86 Å and the O-Te-O angle is close to 99.5°.[3] The tellurite anion is a weak base. Sodium tellurite would be similar to sodium selenite and sodium sulfite. Sodium tellurite is both a weak oxidizing agent and a weak reducing agent.
H2TeO3 → H+ + HTeO3− pK 2.48
Telluric acid loses a proton at this pKa.
HTeO3− → H+ + TeO32− pK 7.7
Hydrogen tellurite loses a proton at this pKa to become the tellurite ion. This would happen in the reaction of tellurous acid with sodium hydroxide to make sodium tellurite.
TeO2 + 2OH− → TeO32− + H2O
This is the reaction of tellurium dioxide with a base to make a tellurite salt.
Sodium tellurite improves the corrosion resistance of electroplated nickel layers. Solutions of sodium tellurite are used for black or blue-black coatings on iron, steel, aluminum, and copper. In microbiology, sodium tellurite can be added to the growth medium to isolate bacteria with an inherent physiological resistance to its toxicity.[4]
- ^ a b Wiberg, Egon; Holleman, Arnold Frederick (2001). Nils Wiberg (ed.). Inorganic chemistry. translated by Mary Eagleson. Academic Press. p. 588. ISBN 0-12-352651-5.
- ^ Masse, R.; Guitel, J.C.; Tordjman, I. (1980). "Preparation chimique et structure cristalline des tellurites de sodium et d'argent: Na2TeO3, Ag2TeO3". Materials Research Bulletin. 15 (4): 431–436. doi:10.1016/0025-5408(80)90048-3. ISSN 0025-5408.
- ^ "Etude cristallographique du tellurite de sodium à cinq molécules d'eau, Na2TeIVO3·5H2O". Acta Crystallogr. B. 35: 1337–1340. 1979. doi:10.1107/S0567740879006403.
- ^ Borsetti, Francesca; Toninello, Antonio; Zannoni, Davide (2003). "Tellurite uptake by cells of the facultative phototroph Rhodobacter capsulatus is a pH-dependent process." Federation of European Biochemical Societies. Volume 554, Issue 3, 20 November 2003, pp. 315–318. Elsevier B.V. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(03)01180-3
- Cameo Chemicals. Sodium Tellurite. Retrieved March 8, 2009. Website: http://cameochemical.noaa.gov/chemical/5185[_permanent dead link_].
- Knockaert, Guy (2002). "Tellurium and Tellurium Compounds". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a26_177.pub2. ISBN 978-3527306732.