Tricyclic (original) (raw)
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Organic compound having 3 fused rings
Tricyclics are cyclic chemical compounds that contain three fused rings of atoms.
Many compounds have a tricyclic structure, but in pharmacology, the term has traditionally been reserved to describe heterocyclic drugs. They include antidepressants, antipsychotics, anticonvulsants, and antihistamines (as antiallergens, anti-motion sickness drugs, antipruritics, and hypnotics/sedatives) of the dibenzazepine, dibenzocycloheptene, dibenzothiazepine, dibenzothiepin, phenothiazine, and thioxanthene chemical classes, and others.
- Promethazine and other first generation antihistamines with a tricyclic structure were discovered in the 1940s.
- Chlorpromazine, derived from promethazine originally as a sedative, was found to have neuroleptic properties in the early 1950s, and was the first typical antipsychotic.
- Imipramine, originally investigated as an antipsychotic, was discovered in the early 1950s, and was the first tricyclic antidepressant.
- Carbamazepine was discovered in 1953, and was subsequently introduced as an anticonvulsant in 1965.
- Clozapine, a derivative of imipramine, was synthesized in 1958 and entered the European market in 1972 under the name Leponex.
- Antidepressants with a tetracyclic structure such as mianserin and maprotiline were first developed in the 1970s as tetracyclic antidepressants.
- Loratadine was introduced as a non-sedating second generation antihistamine in the 1990s.[1]
| Antidepressants | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
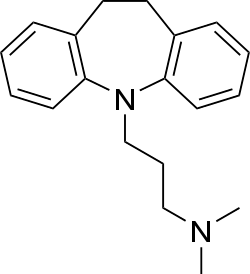 Imipramine Imipramine |
 Amitriptyline Amitriptyline |
 Iprindole Iprindole |
 Tianeptine Tianeptine |
 Doxepin Doxepin |
| Antipsychotics | ||||
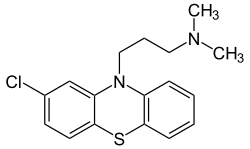 Chlorpromazine Chlorpromazine |
 Thioridazine Thioridazine |
 Chlorprothixene Chlorprothixene |
 Loxapine Loxapine |
 Clozapine Clozapine |
| Antihistamines | ||||
 Promethazine Promethazine |
 Cyproheptadine Cyproheptadine |
 Latrepirdine Latrepirdine |
 Loratadine Loratadine |
 Rupatadine Rupatadine |
| Others | ||||
 Carbamazepine Carbamazepine |
 Carvedilol Carvedilol |
 Cyclobenzaprine Cyclobenzaprine |
 Pizotifen Pizotifen |
- ^ Kay, G. G.; Harris, A. G. (1999). "Loratadine: a non-sedating antihistamine. Review of its effects on cognition, psychomotor performance, mood and sedation". Clinical and Experimental Allergy. 29 Suppl 3: 147–150. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2222.1999.0290s3147.x. PMID 10444229.

