Vastus intermedius muscle (original) (raw)
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Body of the femur muscle
| Vastus intermedius muscle | |
|---|---|
 Muscles of lower extremity (Rectus Femoris has been removed) Muscles of lower extremity (Rectus Femoris has been removed) |
|
| Details | |
| Origin | Anterolateral femur |
| Insertion | Quadriceps tendon |
| Artery | Femoral artery |
| Nerve | Femoral nerve |
| Actions | Extension of knee joint |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculus vastus intermedius |
| TA98 | A04.7.02.022 |
| TA2 | 2619 |
| FMA | 22433 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle[edit on Wikidata] |
The vastus intermedius () (Cruraeus) arises from the front and lateral surfaces of the body of the femur in its upper two-thirds, sitting under the rectus femoris muscle and from the lower part of the lateral intermuscular septum. Its fibers end in a superficial aponeurosis, which forms the deep part of the quadriceps femoris tendon.
The vastus medialis and vastus intermedius appear to be inseparably united, but when the rectus femoris has been reflected during dissection a narrow interval will be observed extending upward from the medial border of the patella between the two muscles, and the separation may be continued as far as the lower part of the intertrochanteric line, where, however, the two muscles are frequently continuous.
Due to being the deeper middle-most of the quadriceps muscle group, the intermedius is the most difficult to stretch once maximum knee flexion is attained. It cannot be further stretched by hip extension as the rectus femoris can, nor is it accessible to manipulate with massage therapy to stretch the fibres sideways as the vastus lateralis and vastus medialis are.

Right femur. Anterior surface.
Right femur. Posterior surface.
Muscles of the iliac and anterior femoral regions.
Cross-section through the middle of the thigh.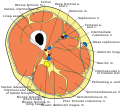
Cross section through thigh.
Vastus intermedius muscle
Vastus intermedius muscle
Muscles of thigh. Cross section.
Muscles of Thigh. Anterior views.
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 471 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 471 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)



