White Elster (original) (raw)
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
River in Germany
| White Elster_Weiße Elster_, Bílý Halštrov | |
|---|---|
 White Elster valley near Wünschendorf/Elster White Elster valley near Wünschendorf/Elster |
|
 |
|
| Location | |
| Countries | GermanyCzech Republic |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | |
| • location | Hazlov, Karlovy Vary Region, Czech Republic |
| • elevation | 724 m (2,375 ft) |
| Mouth | |
| • location | Saale |
| • coordinates | 51°25′57″N 11°57′10″E / 51.43250°N 11.95278°E / 51.43250; 11.95278 |
| Length | 257 km (160 mi) |
| Basin features | |
| Progression | Saale→ Elbe→ North Sea |
| Tributaries | |
| • left | Weida |
| • right | Schwarzbach, Trieb, Göltzsch, Schnauder, Pleiße, Parthe, Reide |
 |
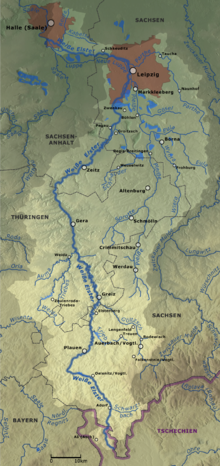
The White Elster[1][2][3] (German: Weiße Elster, Czech: Bílý Halštrov) is a 257-kilometre-long (160 mi) river in central Europe. It is a right tributary of the Saale. The source of the White Elster is in the westernmost part of the Czech Republic, in the territory of Hazlov. After a few kilometres, it flows into eastern Germany where it cuts through the Vogtland in (according to the Encyclopædia Britannica) a "deep and picturesque valley".[4] In Germany it flows through the states of Saxony, Thuringia and Saxony-Anhalt. The White Elster flows through the cities of Plauen, Greiz, Gera, Zeitz, Pegau and Leipzig, and into the river Saale in Halle.
Although "Elster" is German for "magpie", the origin of the name has nothing to do with the bird. The name comes from the Indo-European root el-/ol- meaning "flow" and the Germanic ending "-str". Alster has the same etymology.[5] The White Elster never meets the Black Elster, which flows from Lusatia into the River Elbe. The rivers have the names "white" and "black" to distinguish between them.
The White Elster proved disastrous to the French troops when they retreated from Leipzig in October 1813, as a part of the Napoleonic Wars.[2] Józef Poniatowski, Marshal of France, drowned in the river on 19 October 1813.

Source of the White Elster- Black Elster
- Elster glaciation
- Bodies of water in Leipzig
- ^ The "White Elster" river Archived 2011-09-27 at the Wayback Machine at www.germany-tourism.co.uk
- ^ a b Brookes, Richard and Marshall, John (1832). A new universal gazetteer: containing a description of the principal nations, W.W. Reed & Co,, New York, p. 270
- ^ White Elster from National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency, Bethesda, MD, USA. Accessed on 16 Jan 2011.
- ^ Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Elster" . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 9 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 300.
- ^ Jürgen Udolph: Namenkundliche Studien zum Germanenproblem, S. 245, Sieboldshausen 1993, oder Archived at eurasischesmagazin.de , im Eurasischen Magazin, 26. März 2004