Python Call function from another function (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 01 Jul, 2024
**Prerequisite: Functions in Python
In Python, any written function can be called by another function. Note that this could be the most elegant way of breaking a problem into chunks of small problems. In this article, we will learn how can we call a defined function from another function with the help of multiple examples.
What is Calling a Function and a Called Function?
The Function which calls another Function is called **Calling Function and the function which is called by another Function is called a **Called Function.
**How does Function Execution Work in Python?
A stack data structure is used during the execution of the function calls. Whenever a function is invoked then the calling function is pushed into the stack and called function is executed. When the called function completes its execution and returns then the calling function is popped from the stack and executed. Calling Function execution will be completed only when Called Function’s execution is completed.
In the below figure. The function call is made from the **Main function to **Function1_. Now the state of the Main function is stored in Stack, and execution of the Main function is continued when Function 1 returns. When Function1 _c_alls Function2, the state of the Function1is stored in the stack, and execution of Function 1 will be continued when Function 2 returns.
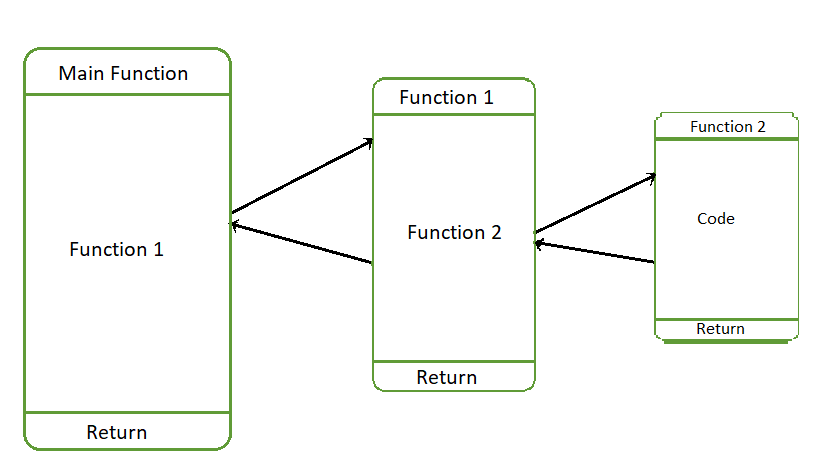
Working of Functions when one Function calls another Function
Examples of a Function Call from Another Function
Let us see a few different examples, that explain a function call from another function in Python.
**Example 1:
In this example, the **SumOfSquares() function calls the **Square() which returns the square of the number.
Python `
Python code to demonstrate calling the
function from another function
def Square(X): # computes the Square of the given number # and return to the caller function return (X * X)
def SumofSquares(Array, n):
# Initialize variable Sum to 0. It stores the
# Total sum of squares of the array of elements
Sum = 0
for i in range(n):
# Square of Array[i] element is stored in SquaredValue
SquaredValue = Square(Array[i])
# Cumulative sum is stored in Sum variable
Sum += SquaredValue
return SumDriver Function
Array = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10] n = len(Array)
Return value from the function
Sum of Squares is stored in Total
Total = SumofSquares(Array, n) print("Sum of the Square of List of Numbers:", Total)
`
**Output :
Sum of the Square of List of Numbers: 385
**Example 2:
In this example, we will call a function from another function within the same class. The class method **Function1() calls the method **Function2() from the **Main class.
Python `
''' Call a function from within another function in the same class in Python '''
class Main:
# constructor of Main class
def __init__(self):
# Initialization of the Strings
self.String1 = "Hello"
self.String2 = "World"
def Function1(self):
# calling Function2 Method
self.Function2()
print("Function1:", self.String2)
return
def Function2(self):
print("Function2:", self.String1)
returnInstance of Class Main
Object = Main()
Calling Function1
Object.Function1()
`
**Output :
Function2: Hello
Function1: World
**Example 3:
In this example, we will call the parent class function fromthe child class function. The child class inherits the attributes from the parent class.
Python `
Python code to demonstrate calling parent class
method from the child class method
class Parent:
# constructor of Parent class
def __init__(self):
# Initialization of the Strings
self.String1 = "Hello"
self.String2 = "World"
def Function2(self):
print("Function2:", self.String1)
returnChild class is inheriting from Parent class
class Child(Parent):
def Function1(self):
# calling Function2 Method in parent class
self.Function2()
print("Function1:", self.String2)
return Instance of Parent class
Object1 = Parent()
Instance of Child class
Object2 = Child()
Calling Function1 using Child class instance
Object2.Function1()
`
**Output :
Function2: Hello
Function1: World