Genomic Regions Enrichment of Annotations Tool, Bejerano Lab, Stanford University (original) (raw)
Associating genomic regions with genes
GREAT calculates statistics by associating genomic regions with nearby genes and applying the gene annotations to the regions. Association is a two step process. First, every gene is assigned a regulatory domain. Then, each genomic region is associated with all genes whose regulatory domain it overlaps.
Basal plus extension
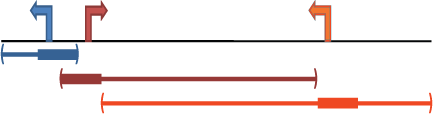
Proximal: kb upstream, kb downstream, plus Distal: up to kb
Gene regulatory domain definition: Each gene is assigned a basal regulatory domain of a minimum distance upstream and downstream of the TSS (regardless of other nearby genes). The gene regulatory domain is extended in both directions to the nearest gene's basal domain but no more than the maximum extension in one direction.
Two nearest genes
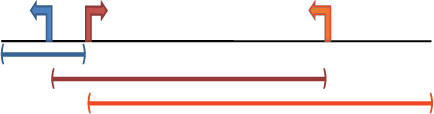
within kb
Gene regulatory domain definition: Each gene is assigned a regulatory domain that extends in both directions to the nearest gene's TSS but no more than the maximum extension in one direction.
Single nearest gene

within kb
Gene regulatory domain definition: Each gene is assigned a regulatory domain that extends in both directions to the midpoint between the gene's TSS and the nearest gene's TSS but no more than the maximum extension in one direction.
 Gene Transcription Start Site (TSS)
Gene Transcription Start Site (TSS)
Include curated regulatory domains