Top 10 Frequently asked SQL Query Interview Questions Answers (original) (raw)
In this article, I am giving some examples of SQL queries which is frequently asked when you go for a programming interview, having one or two year experience in this field. Whether you go for a Java developer position, QA, BA, support professional, project manager, or any other technical position, may interviewer expects you to answer basic questions from Database and SQL. It's also obvious that if you are working for one or two years on any project there is a good chance that you come across to handle databases, writing SQL queries to insert, update, delete and select records.
One simple but effective way to check the candidate's SQL skill is by asking these types of simple queries. They are neither very complex nor very big, but yet they cover all key concepts a programmer should know about SQL.
These queries test your SQL skill on Joins, both INNER and OUTER join, filtering records by using WHERE and HAVING clause, grouping records using GROUP BY clause, calculating the sum, average, and counting records using an aggregate function like AVG(), SUM(), and COUNT(), searching records using wildcards in LIKE operator, searching records in a bound using BETWEEN and IN clause, DATE and TIME queries, etc.
If you have faced any interesting SQL query or you have any problem and searching for a solution, you can post it here for everyone's benefit.
20 Most Popular SQL Query Interview Questions and Answers
Without any further ado, here is a list of the most common SQL query Interview questions and answers from Programming Job interviews:
Question 1: SQL Query to find the second highest salary of Employee
Answer: There are many ways to find the second highest salary of an Employee in SQL, you can either use SQL Join or Subquery to solve this problem. Here is an SQL query using Subquery:
SELECT MAX(Salary) FROM Employee WHERE Salary NOT IN (select MAX(Salary) from Employee );
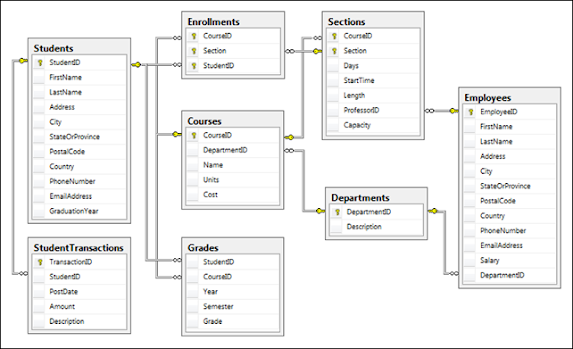
Question 2: SQL Query to find Max Salary from each department.
Answer: You can find the maximum salary for each department by grouping all records by DeptId and then using MAX() function to calculate the maximum salary in each group or each department.
SELECT DeptID, MAX(Salary) FROM Employee GROUP BY DeptID.
These questions become more interesting if the Interviewer will ask you to print the department name instead of the department id, in that case, you need to join the Employee table with Department using the foreign key DeptID, make sure you do LEFT or RIGHT OUTER JOIN to include departments without any employee as well.
Here is the query
SELECT DeptName, MAX(Salary) FROM Employee e RIGHT JOIN Department d ON e.DeptId = d.DeptID GROUP BY DeptName;
In this query, we have used RIGHT OUTER JOIN because we need the name of the department from the Department table which is on the right side of the JOIN clause, even if there is no reference of dept_id on the Employee table.
Question 3: Write SQL Query to display the current date?
Answer: SQL has built-in function called GetDate() which returns the current timestamp. This will work in Microsoft SQL Server, other vendors like Oracle and MySQL also have equivalent functions.
SELECT GetDate();
Question 4: Write an SQL Query to check whether the date passed to Query is the date of the given format or not?
Answer: SQL has IsDate() function which is used to check passed value is a date or not of specified format, it returns 1(true) or 0(false) accordingly. Remember the ISDATE() is an MSSQL function and it may not work on Oracle, MySQL, or any other database but there would be something similar.
SELECT ISDATE('1/08/13') AS "MM/DD/YY";
It will return 0 because the passed date is not in the correct format.
Question 5: Write an SQL Query to print the name of the distinct employee whose DOB is between 01/01/1960 to 31/12/1975.
Answer: This SQL query is tricky, but you can use BETWEEN clause to get all records whose dates fall between two dates.
SELECT DISTINCT EmpName FROM Employees WHERE DOB BETWEEN ‘01/01/1960’ AND ‘31/12/1975’;
Question 6: Write an SQL Query to find the number of employees according to gender whose DOB is between 01/01/1960 to 31/12/1975.
Answer : Here is teh sql query to find the number of employees according to gender and whose date of birth is between two given dates
SELECT COUNT(*), sex
FROM Employees
WHERE DOB BETWEEN '01/01/1960' AND '31/12/1975'
GROUP BY sex;
Question 7: Write an SQL Query to find an employee whose salary is equal to or greater than 10000.
Answer : You can use WHERE clause with less than and equal to operator to solve this problem. Here is the sql query to find employees whose salary is equal to or greater than a given number
SELECT EmpName FROM Employees WHERE Salary>=10000;
Question 8: Write an SQL Query to find the name of an employee whose name Start with ‘M’
Answer : You can use the Llike operator to find the name of all employees whose name start with letter "M", here is an exmaple:
SELECT * FROM Employees WHERE EmpName like 'M%';
Question 9: find all Employee records containing the word "Joe", regardless of whether it was stored as JOE, Joe, or joe.
Answer :You can use SQL function like UPPER() and like operator to find all employees whose name contains a given word like "Joe" as shown in following example:
SELECT * from Employees WHERE UPPER(EmpName) like '%JOE%';
Question 10: Write an SQL Query to find the year from date.
Answer: You can use the GETDATE() function to get the current date and then you can use the YEAR() function to extract the year from the date in SQL server.
Here is how you can find Year from a Date in Microsoft SQL Server database
SELECT YEAR(GETDATE()) as "Year";
Question 11: Write SQL Query to find duplicate rows in a database? and then write SQL query to delete them?
Answer: You can use the following query to select distinct records:
SELECT * FROM emp a WHERE rowid = (SELECT MAX(rowid) FROM EMP b WHERE a.empno=b.empno)
to Delete:
DELETE FROM emp a WHERE rowid != (SELECT MAX(rowid) FROM emp b WHERE a.empno=b.empno);
Question 12: There is a table which contains two columns Student and Marks, you need to find all the students, whose marks are greater than average marks i.e. list of above-average students.
Answer: This query can be written using subquery as shown below:
SELECT student, marks FROM table WHERE marks > SELECT AVG(marks) from table)
Question 13: How do you find all employees who are also managers?
You have given a standard employee table with an additional column mgr_id, which contains the employee id of the manager.
Answer: You need to know about self-join to solve this problem. In Self Join, you can join two instances of the same table to find out additional details as shown below
SELECT e.name, m.name FROM Employee e, Employee m WHERE e.mgr_id = m.emp_id;
this will show employee name and manager name in two columns like
name manager_name
John David
One follow-up is to modify this query to include employees which don't have a manager. To solve that, instead of using the inner join, just use the left outer join, this will also include employees without managers.
Another interesting problem which is based upon Self join is to find all employees who earn more than their managers, which is also asked as follow up question after this one.
Question 14: You have a composite index of three columns, and you only provide the value of two columns in the WHERE clause of a select query? Will Index be used for this operation?
For example, if Index is on EmpId, EmpFirstName, and EmpSecondName and you write a query like
SELECT * FROM Employee WHERE EmpId=2 and EmpFirstName='Radhe'
If the given two columns are secondary index columns then the index will not invoke, but if the given 2 columns contain the primary index(first column while creating index) then the index will invoke. In this case, the Index will be used because EmpId and EmpFirstName are primary columns.
Hope this article will help you to take a quick practice whenever you are going to attend an interview and not have much time to go into the deep of each query.
Other Interview Questions posts from Java67 Blog