What is difference between HashMap and Hashtable in Java? (original) (raw)
HashMap vs Hashtable in Java
Though both Hashtable and HashMap are data-structure based upon hashing and implementation of Map interface, the main difference between them is that HashMap is not thread-safe but Hashtable is thread-safe. This means you cannot use HashMap in a multi-threaded Java application without external synchronization. Another difference is HashMap allows one null key and null values but Hashtable doesn't allow null key or values. Also, the thread-safety of the hash table is achieved using internal synchronization, which makes it slower than HashMap.
By the way, the difference between HashMap and Hashtable in Java is one of the frequently asked in core Java interviews to check whether the candidate understands the correct usage of collection classes and aware of alternative solutions available.
Along with How HashMap internally works in Java and ArrayList vs Vector, this is one of the oldest questions from the Collection framework in Java. Hashtable is a legacy Collection class and it's there in Java API for a long time but it got refactored to implement Map interface in Java 4 and from there Hashtable became part of the Java Collection framework.
Hashtable vs HashMap in Java is so popular a question that it can top any list of Java Collection Interview Questions. You just can't afford to prepare HashMap vs Hashtable before going to any Java programming interview.
In this Java article, we will not only see some important differences between HashMap and Hashtable but also some similarities between these two collection classes. Though for complete preparation,
Let's first see How different they are:
Difference between HashMap and Hashtable in Java
Both HashMap and Hashtable implements Map interface but there is some significant difference between them which is important to remember before deciding whether to use HashMap or Hashtable in Java. Some of them are thread-safety, synchronization, and speed. here are those differences :
1.The HashMap class is roughly equivalent to Hashtable, except that it is non-synchronized and permits nulls. (HashMap allows null values as key and value whereas Hashtable doesn't allow nulls).
2. One of the major differences between HashMap and Hashtable is that HashMap is non-synchronized whereas Hashtable is synchronized, which means Hashtable is thread-safe and can be shared between multiple threads but HashMap can not be shared between multiple threads without proper synchronization. Java 5 introduces ConcurrentHashMap which is an alternative of Hashtable and provides better scalability than Hashtable in Java.
3. Another significant difference between HashMap vs Hashtable is that Iterator in the HashMap is a fail-fast iterator while the enumerator for the Hashtable is not and throw ConcurrentModificationException if any other Thread modifies the map structurally by adding or removing any element except Iterator's own remove() method. But this is not a guaranteed behavior and will be done by JVM on best effort. This is also an important difference between Enumeration and Iterator in Java.
4. One more notable difference between Hashtable and HashMap is that because of thread-safety and synchronization Hashtable is much slower than HashMap if used in Single threaded environment. So if you don't need synchronization and HashMap are only used by one thread, it outperforms Hashtable in Java.
5. HashMap does not guarantee that the order of the map will remain constant over time.
If you are preparing this question as part of your Java interview preparation, I suggest preparing every important topic as given in Programming Interviews Exposed. It covers basics, core java, threads, a framework like Spring and Hibernate and many others key topics.
HashMap and Hashtable : note on Some Important Terms
1)Synchronized means only one Thread can modify a hash table at one point of time. Basically, it means that any thread before performing an update on a Hashtable will have to acquire a lock on the object while others will wait for the lock to be released.
- Fail-safe is relevant from the context of iterators. If an Iterator or ListIterator has been created on a collection object and some other thread tries to modify the collection object "structurally", a concurrent modification exception will be thrown. It is possible for other threads though to invoke "set" method since it doesn't modify the collection "structurally". However, if prior to calling "set", the collection has been modified structurally, "IllegalArgumentException" will be thrown.
- Structurally modification means deleting or inserting element which could effectively change the structure of the map.
HashMap can be synchronized by
Map m = Collections.synchronizeMap(hashMap);
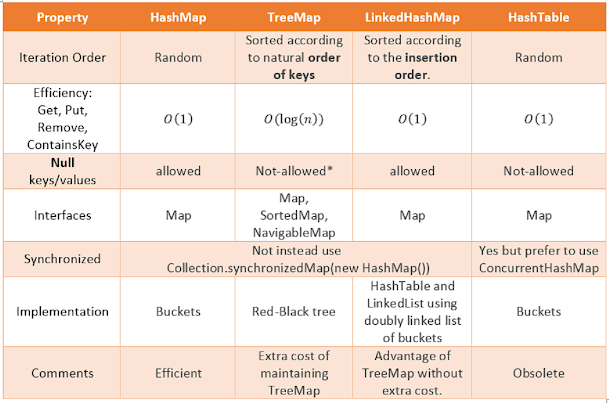
Also, here is one more table which shows more differences between HashMap and Hashtable in Java:
In Summary, there are significant _differences between Hashtable and HashMap in Jav_a e.g. thread-safety and speed and based upon that only use Hashtable if you absolutely need thread-safety if you are running Java 5 consider using ConcurrentHashMap in Java.
Other Java Collection tutorials you may like
How to sort a Map by keys and values in Java? (tutorial)
How to sort an ArrayList in ascending and descending order in Java? (tutorial)
Difference between ArrayList and HashSet in Java? (answer)
The difference between TreeMap and TreeSet in Java? (answer)
The difference between HashMap and ConcurrentHashMap in Java? (answer)
The difference between HashMap and LinkedHashMap in Java? (answer)
The difference between Hashtable and HashMap in Java? (answer)
The difference between HashSet and TreeSet in Java? (answer)
The difference between ArrayList and LinkedList in Java? (answer)
The difference between Vector and ArrayList in Java? (answer)
Difference between EnumMap and HashMap in Java
Thanks for reading this article so far. If you like this article then please share with your friends and colleagues. If you have any question or feedback then please drop a comment.