Difference between Stack and Heap memory in Java? Example (original) (raw)
The difference between stack and heap memory is a common programming question asked by beginners learning Java or any other programming language. Stack and heap memory are two terms programmers start hearing once they started programming but without any clear and definite explanation. Lack of knowledge of what is a heap in Java and what is stack memory in Java results in misconceptions related to stack and heap. To add to this confusion, a stack is also a data structure that is used to store elements in LIFO(Last In First Out) order and is available in Java API as java.util.Stack.
In general, both stack and heap are part of memory, a program is allocated and used for different purposes. Java program runs on JVM which is launched as a process by the "java" command. Java also uses both stack and heap memory for different needs.
In our last article 10 points on Java heap space, I have touched base on Java heap space, and in this article, we will see the difference between stack and heap memory in Java.
Difference between Stack vs Heap in Java
Here are a few differences between stack and heap memory in Java:
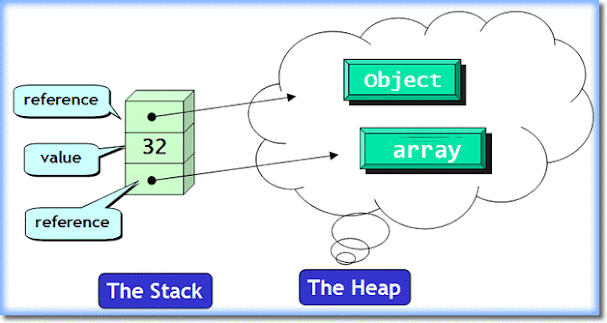
The main difference between heap and stack is that stack memory is used to store local variables and function calls while heap memory is used to store objects in Java. No matter, where the object is created in code e.g. as a member variable, local variable, or class variable, they are always created inside heap space in Java.
Each Thread in Java has its own stack which can be specified using the -Xss JVM parameter, similarly, you can also specify the heap size of the Java program using JVM option -Xms and -Xmx where -Xms is starting size of the heap and -Xmx is a maximum size of java heap. to learn more about JVM options see my post 10 JVM option Java programmers should know.
3. If there is no memory left in the stack for storing function call or local variable, JVM will throw java.lang.StackOverFlowError, while if there is no more heap space for creating an object, JVM will throw java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: Java Heap Space.
If you are using Recursion, on which method calls itself, You can quickly fill up stack memory. Another difference between stack and heap is that size of stack memory is a lot lesser than the size of heap memory in Java.
Variables stored in stacks are only visible to the owner Thread while objects created in the heap are visible to all threads. In other words, stack memory is a kind of private memory of Java Threads while heap memory is shared among all threads.
That's all on the difference between Stack and Heap memory in Java. As I said, It’s important to understand what is a heap and what is stack in Java and which kind of variables goes where, how you can run out of stack and heap memory in Java, etc. Let us know if you are familiar with any other difference between stack and heap memory in java.