What is Abstraction in Java? Abstract Class and Interface Example (original) (raw)
What is abstraction?
Abstraction in Java or Object-oriented programming is a way to segregate implementation from an interface and one of the five fundamentals along with Encapsulation, Inheritance, Polymorphism, Class, and Object. Abstraction in Java is achieved by using the interface and abstract class in Java. An interface or abstract class is something that is not concrete, something which is incomplete. In order to use interface or abstract class, we need to extend and implement an abstract method with concrete behavior.
One example of Abstraction is creating an interface to denote common behavior without specifying any details about how that behavior works like you create an interface called Server which has the start() and stop() method.
This is called abstraction of Server because every server should have a way to start and stop and details may differ.
As I said earlier Abstraction in Java is implemented using abstract class and interface as discussed in the next section. In fact, what is an abstraction in Java, the difference between Abstraction and Encapsulation is also a very popular core Java interview because strong OOPS skill is one of the primary requirements for Java developers?
Abstraction is also one of the hard to master the concept. The programmer often mixes different levels of abstraction which results in in-flexible code, so be careful with that.
What is an abstract class in Java? Example
An abstract class is something which is incomplete and you can not create an instance of the abstract class. If you want to use it you need to make it complete or concrete by extending it. A class is called concrete if it does not contain any abstract method and implements all abstract method inherited from the abstract class or interface it has implemented or extended.
By the way, Java has a concept of abstract classes, abstract method but a variable can not be abstract in Java.
A popular example of abstract class in Java is ActionListener which has an abstract method called actionPerformed(ActionEvent ae). This method is called when an ActionEvent is fired like when you click on JButton. It's common in java to attach ActionListener with JButton by implementing abstract method actionPerformed(ActionEvent ae) using Anonymous class, as shown in below Example :
JButton ok = new JButton("OK"); ok.addActionListener(new ActionListener(){ public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent ae){ //code to handle event } });
An abstract method in Java doesn't have the body , it's just a declaration. In order to use an abstract method, you need to override that method in sub class_**.**_
so when do you use abstraction? ( most important in my view )
when you know something needs to be there but not sure how exactly it should look like. e.g. when I am creating a class called Vehicle, I know there should be methods like start() and stop() but don't know how that start and stop method should work, because every vehicle can have a different start and stop mechanism e..g some can be started by kicking or some can be by pressing buttons . The Same concept applies to interface in Java as well, which we will discuss in some other post.
So the implementation of those start() and stop() methods should be left to their concrete implementation e.g. Scooter, MotorBike, Car, etc. See Head First Object-Oriented Analysis and Design book for more details on when to use Abstraction in object-oriented programming.
Abstraction Using Interface in Java
 InJava Interface is an another way of providing abstraction, Interfaces are by default abstract and only contains public, static, final constant or abstract methods. It's very common interview question is that where should we use abstract class and where should we use Java Interfaces in my view this is important to understand to design better Java application, you can go for java interface if you only know the name of methods your class should have e.g. for Server it should have start() and stop() method but we don't know how exactly these start and stop method will work.
InJava Interface is an another way of providing abstraction, Interfaces are by default abstract and only contains public, static, final constant or abstract methods. It's very common interview question is that where should we use abstract class and where should we use Java Interfaces in my view this is important to understand to design better Java application, you can go for java interface if you only know the name of methods your class should have e.g. for Server it should have start() and stop() method but we don't know how exactly these start and stop method will work.
If you know some of the behavior while designing class and that would remain common across all subclasses add that into an abstract class. An interface like Runnable interface is a good example of abstraction in Java which is used to abstract task executed by multiple threads. Callable is another good abstract of a task which can return value.
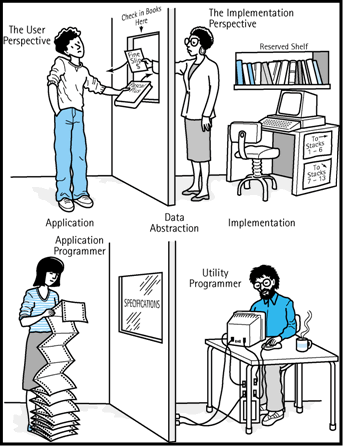
A picture is worth more than 100 words and this picture proves that. It nicely explanis the concept of data abstraction in object-oriented programming world:
Abstraction: Things to Remember
Use abstraction if you know something needs to be in class but the implementation of that varies. Abstraction is actually resulting of thought process and it really need good experience of both domain and Object oriented analysis and design to come up with good abstraction for your project.
In Java, you can not create an instance of the abstract class using the new operator, its a compiler error. Though abstract class can have a constructor.
abstract is a keyword in Java, which can be used with both class and method. Abstract class can contain both abstract and concrete method. An abstract method doesn't have the body, just declaration.
A class automatically becomes abstract class when any of its methods declared as abstract.
abstract method doesn't have a method body.
In Java, a variable can not be made abstract , its only class or methods which would be abstract.
If a class extends an abstract class or interface it has to provide implementation to all its abstract methods to be a concrete class. alternatively, this class can also be abstract.
Other Object oriented concept tutorials from the Javarevisited blog