How to Set Classpath for Java on Windows and Linux? Steps and Example (original) (raw)
What is CLASSPATH in Java?
Classpath in Java is the path to the directory or list of the directory which is used by ClassLoaders to find and load classes in the Java program. Classpath can be specified using CLASSPATH environment variable which is case insensitive, -cp or -classpath command-line option or Class-Path attribute in manifest.mf file inside the JAR file in Java. In this Java tutorial, we will learn What is Classpath in Java, how Java resolves classpath and how Classpath works in Java alongside How to set the classpath for Java in Windows and UNIX environment.
I have experience in the finance and insurance domain and Java is heavily used in this domain for writing sophisticated Equity, Fixed income trading applications. Most of these investment banks have written tests as part of their core Java interview questions and I always find at least one question related to CLASSPATH in Java on those interviews.
Java CLASSPATH is one of the most important concepts in Java, but, I must say mostly overlooked. This should be the first thing you should learn while writing Java programs because without the correct understanding of Classpath in Java you can't understand how Java locates your class files.
Also don't confuse Classpath with PATH in Java, which is another environment variable used to find java binaries located in the JDK installation directory, also known as JAVA_HOME.
Unfortunately, Java Programming books like Head First Java don't teach you much about the subtleties of PATH and CLASSPATH. If you really want to test your Java skill, the one book I would suggest reading is Java Puzzlers, whose puzzles and explanations will help more to understand this kind of not so easy concept.
Difference between PATH and Classpath in Java
The main difference between PATH and CLASSPATH is that the former is used to locate Java commands while the latter is used to locate Java class files. So let’s start with basics and then we will see some examples and improvisation of Classpath in Java.
In fact, CLASSPATH is an environment variable that is used by Java Virtual Machine to locate user-defined classes.
As I said In this tutorial we will see How to set up the classpath for java in windows and Linux, java -classpath example in different scenarios, and the use of java -classpath or java -cp.
By the way, If you have just started learning Java, then I also suggest you follow a structured online course to learn Java like these Java Programming courses for beginners. That will help you to grasp most of the fundamental concepts in Java in a systematic manner.
How to Set ClassPath for Java in Windows? Example
In order to set Classpath for Java in Windows (any version either Windows XP, Windows 2000, or Windows 10) you need to specify the value of the environmentvariable CLASSPATH, the name of this variable is not case sensitive and it doesn’t matter if the name of your environment variable is Classpath, CLASSPATH or classpath in Java.
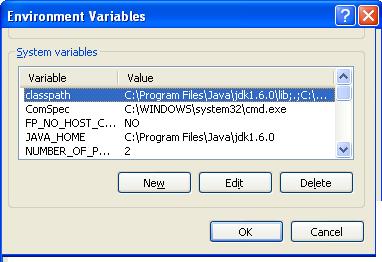
Here is Step by Step guide for setting Java Classpath in Windows:
- Go to Environment variable window in Windows by pressing "Windows + Pause “--> Advanced --> Environment variable " or you can go from right click on my computer than choosing properties and then Advanced and then Environment variable this will open the Environment variable window in windows.
- Now specify your environment variable CLASSPATH and put the value of your JAVA_HOME\lib and also include current directory by including (dot or period sign).
- Now to check the value of Java classpath in windows type "echo %CLASSPATH" in your DOS command prompt and it will show you the value of the directory which is included in CLASSPATH.
- You can also set classpath in windows by using DOS commands like:
$ set CLASSPATH=%CLASSPATH%;JAVA_HOME\lib;
This way you can set the classpath in Windows XP, Windows 2000, or Windows 7 and 8, 10 as they all come with a command prompt.
Setting Java Classpath in UNIX or Linux
To set Classpath for Java In Linux, you can simply export CLASSPATH="your classpath" from either your **_._**bash_profile or .bashrc script which will run whenever your login into your Linux or Unix Machine.
Now to check the value of Java CLASSPATH in Linux type "echo ${CLASSPATH}" this will print the value of Classpath in the command prompt.
By using the export command, you can set the classpath for Java in Unix, Linux, Solaris, IBM AIX, or any other UNIX operating system. I hope this example for setting classpath in Java will enable to set classpath by yourself let me know if you face any problem while setting up classpath in Java
Overriding Classpath in Java
You can override classpath in Java, defined by environment variable CLASSPATH by providing option "-cp" or "-classpath" while running Java program and this is the best way to have different classpath for different Java applications running on the same Unix or Windows machine, the standard way to define classpath for Java application is creating start-up script for Java program and set classpath there as shown below :
CLASSPATH=/home/tester/classes $ java -cp $CLASSPATH Test
By default, Java CLASSPATH points to the current directory denoted by "." and it will look for any class only in the current directory.
Different examples of using Classpath in Java
In case you have multiple directories defined in the CLASSPATH variable, Java will look for a class starting from the first directory and only look at the second directory in case it did not find the specified class in the first directory.
This is an extremely useful feature of Classpath in java to understand and it’s very useful while debugging Java application or patch release kind of stuff. Let’s see the java -classpath example
I have set my classpath environment variable as CLASSPATH=/home/tester/first:/home/tester/second**.** Now I have a Test class of different versions in both the first and second directories. When I give the command "java Test" What will happen? Which Test class would be picked?
Since the JVM search directory in the order they have listed in CLASSPATH variable it will first go to the "first" directory and if it finds Test.class over there it will not go to /home/tester/second directory. Now if you delete Test.class from /home/tester/first directory it will go to /home/tester/second directory and will pick Test.class from there.
I have used this feature of Java Classpath to test my patch releases, we used to have a folder called "patch" listed as first element in Java CLASSPATH, and any point of time we want to put any debug statement or want to test any bug we just modify Java source file, compile it and generate class file and put that inside patch folder instead of creating JAR file and releasing whole new Java application.
This is very handy if you are working on a large project where you don't have a development environment setup in Windows and your project only runs on a Unix server. This approach is much faster than remote debugging Java applications in Eclipse
It's also worth noting that when you use the java -jar command-line option to run your Java program as an executable JAR, then the CLASSPATH environment variable will be ignored, and also the -cp and -classpath switches will be ignored.
In this case, you can set your Java classpath in the META-INF/MANIFEST.MF file by using the Class-Path attribute. In short Class-path attribute in manifest file overrides classpath specified by -cp, -classpath or CLASSPATH environment variable.
Now a common question if I have my CLASSPATH variable pointing to current directory "." and I have a class called "Test" inside package "testing" and with below directory structure C:\project\testing\Test.class in my computer.
What will happen if I run the command "java Test" from directory "C:\project\testing\"? will it run?
No, it will not run it will give you:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: Test
Since the name of the class is not Test, instead it’s testing.Test even though your classpath is set to the current directory.
Now, what will happen if I give command java testing.Test from C:\project\testing\ it will again not run and give an error?
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: testing/Test
Why because now it looking for a class called Test which is in package testing, starting from the current directory "." but don't find it since there is no directory called "testing after this path "C:\project\testing\".
To run it successfully you need to go back to directory C:\project and now run
C:\project>java testing.Test and It will run successfully because of Classpath issues I prefer to use Eclipse rather than running a Java program from the command prompt.
How to Fix errors related to Classpath in Java
If you are working in Java, you must have faced some errors and exception related to the classpath in java, two most common issues related to java classpath is ClassNotFoundException and NoClassDefFoundError.
I have seen that many Java developer tries to solve this error by trial and error; they just don’t look beyond the hood and try to understand what the reason for this java classpath related errors is. They often misunderstood that these two errors are the same also.
Here is the reason for these Java classpath errors:
ClassNotFoundException is an Exception and will be thrown when the Java program dynamically tries to load a Java class at runtime and doesn’t find the corresponding class file on the classpath. Two keywords here are “dynamically” and “runtime”.
A classic example of these errors is when you try to load the JDBC driver by using Class.forname(“driver name”) and are greeted with java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver. So this error essentially comes when Java tries to load a class using the forName() or by loadClass() method of ClassLoader.
The key thing to note is that presence of that class on the Java classpath is not checked on compile time. So even if those classes are not present on the Java classpath your program will compile successfully and only fail when you try to run.
On the other hand, NoClassDefFoundError is an Error and more critical than ClassNotFoundException which is an exception and recoverable. NoClassDefFoundError comes when a particular class was present in Java Classpath during compile time but not available during run-time.
A classic example of this error is using log4j.jar for logging purposes and forgot to include log4j.jar on the classpath in java during run-time. to read more about logging in to Java see.
The keyword here is, the class was present at compile time but not available at run-time. This is normally occurring due to any method invocation on a particular class that is part of the library and not available on the classpath in Java. This is also asked as common interview questions as
“What is the difference between NoClassDefFoundError and ClassNotFoundException Exception in Java” or “When do you see NoClassDefFoundError and ClassNotFoundException Exception in Java”.
By the way, NoClassDefFoundError can also come due to various other reasons like static initializer failure or class not visible to Classloaders in the J2EE environment. Read 3 ways to resolve NoClassDefFoundError in Java for complete details.
Summary of CLASSPATH in Java
Classpath in Java is an environment variable used by Java Virtual machine to locate or find class files in Java during class loading.
You can override the value of Classpath in Java defined by the environment variable CLASSPATH by providing the JVM command-line option –cp or –classpath while running your application.
If two classes with the same name exist in Java Classpath then the class which comes earlier in Classpath will be picked by Java Virtual Machine.
By default CLASSPATH in Java points to the current directory denoted by "." and it will look for any class only in the current directory.
When you use the -jar command-line option to run your program as an executable JAR, then the Java CLASSPATH environment variable will be ignored, and also the -cp and -classpath switches will be ignored and, In this case, you can set your java classpath in the META-INF/MANIFEST.MF file by using the Class-Path attribute.
In Unix or Linux operating system, Java Classpath contains names of the directory with a colon “:” separated, On Windows Java Classpath will be semicolon “;” separated while if you defined java classpath in Manifest file those will be space separated.
You can check value of classpath in java inside your application by looking at following system property “java.class.path” System.getProperty("java.class.path")
Class-Path attribute is used to contain classpath inside the manifest file. Also, make sure that your manifest file must end with a blank line (carriage return or new line), here is an example of java classpath in the manifest file.
Main-Class: com.classpathexample.Demo_Classpath Class-Path: lib/tibco.jar lib/log4j.jar
It’s also important to note that the path specified in the manifest file is not absolute instead they are relative from the application jar’s path. For example, in above if your application jar file is in C:\test directory you must need a lib directory inside test and tibco.jar and log4j.jar inside that.
ClassNotFoundException is an Exception and will be thrown when the Java program dynamically tries to load a particular Class at Runtime and doesn’t find that on Java classpath due to the result of Class.forName() or loadClass() method invocation.
10. NoClassDefFoundError comes when a particular class was present in Java Classpath during compile time but not available during runtime on Classpath in Java.
I hope you find this Java Classpath tutorial useful, please let me know if you have any doubts or any questions related to "How to set the classpath for java" and I would be happy to answer :) keep learning. Your suggestions and comments are always welcome.
If you like to read UNIX command tips you may find 10 tips for using the find command in Linux, 10 tips to increase speed on Unix command and 10 basic networking Commands in Unix useful. That's all on What is Classpath in Java, How Classpath works in Java, How to set Classpath in Java on Windows and Linux, and how to deal with Classpath issues in Java.
Other Java tutorials you may like: