A Lineage all but Forgotten: The Yushinkan (Nakayama Hakudo) (original) (raw)
(Note this is a guest post from Jeff Karinya)
Introduction
There are few martial artists in history who have been able to influence an entire generation of politicians, military personnel, police, educators, and civilians alike. Who’s student’s (if only for a day) talked about their experiences with him in detail nearly seventy years after his death. The first San-Dou-no-Hanshi (三道の範士) in history. The “_God of Kendo_” (剣道の神様) Nakayama Hakudo.
Nakayama Hakudo was arguably the most influential martial artist in modern history. Many instructors and students around the world claim to have some “connection” to him, having practiced some form or another of his Iaido. Yet, these same people (in Japan and abroad) know little more than his name. Only by looking at his humble origins, ambitions, accomplishments, and outlooks can we come closer to understanding the man and his styles.
Nakayama Hakudo
- Second Generation Headmaster of the Yushinkan Dojo (有信館道場の第二代館長)
- Second Generation Headmaster of Kanto Ha Shindo Munen Ryu Kenjutsu (関東派神道無念流剣術の第二代目宗家)
- Creator of Muso Shinden Ryu Iaido (夢想神傳流居合道) and Nakayama no Jo (中山の杖)
- Kendo_・_Iaido_・_Jodo_・_San-Dou-no-Hanshi (剣道・居合道・杖道・三道の範士)
Nakayama Otsuyoshi (中山乙吉) was born in in Imae, Komatsu City, Ishikawa Prefecture in 1873, the eighth son of former Maeda clansman Nakayama Gennosho. At the age of five his family moved to Nakacho in Toyama where they opened a small yakitori restaurant located in East Sogawa Merchant Lane. The restaurant was located on the first avenue off of Main Street, and was a modest shop by most accounts. At age eight the young Otsuyoshi came to work in local inn (ryokan: a Japanese traditional inn) called “Toyama Hall” located just two streets over from his family’s yakitori shop.
There in Toyama Hall he worked in the kitchen. As his luck would have it the manager of the inn, one Takazawa Toyoshi (a kind and loving man by all accounts) encouraged the young Otsuyoshi to pursue swordsmanship after seeing the eight year old playing with a bokken (wooden sword) fashioned from a tree branch. At age eleven he gained entrance to Saito Michinori’s dojo of the Yamaguchi Ha Itto Ryu school of swordsmanship in Hoshiicho off Sogawa Lane. The young Otsuyoshi had a busy schedule. In the morning he would travel to Nishi-jubucho where he learned how to read and write at the Ada Kanji Academy (a supplementary school). In the afternoon after school he would go to Michinori’s dojo where he to trained in Yamaguchi Ha Itto Ryu. He then went straight from the dojo to work at the “Toyama Hall.”
 Hakudo demonstrates proper kiriotoshi
Hakudo demonstrates proper kiriotoshi
Otsuyoshi progressed under his various teachers until a visitor from Tokyo changed his life forever. A swordsman of sizable skill by the name of Hosoda Kenzo took up residence in the “Toyama Hall”. Kenzo, an educator by trade was just transferred to Toyama by The Ministry of Education. He was a member of the _Yushinkan Dojo (_有信館道場), a Shindo Munen Ryu school run by Negishi Shingoro. Highly impressed the young Otsuyoshi talked to Kenzo for hours. Kenzo’s stories and insights into swordsmanship left a great impression on the Otsuyoshi, ultimately shaping his entire life.
In 1890 Kenzo handed in his letter of resignation to the Toyama school district and returned to Toyko. His departure left the young Otsuyoshi with many questions. Otsuyoshi felt it was time. He received permission from his family and employer to travel to Tokyo to pursue kenjutsu.
Takazawa was kind enough to escort the young Otsuyoshi to Iwasehama, a small port in Toyama Prefecture. There Otsuyoshi boarded a ship to Naoetsu, Niigata Prefecture. At Naoetsu he boarded a steam ship that sailed to Ueno, Tokyo. It was there on the open Japanese Sea that Otsuyoshi, with the cold sea air on his face remembered the words of Takazawa: “Otsuyoshi, you’ll be a man who other men fall in love with“. These words stuck with Otsuyoshi well into his adulthood.
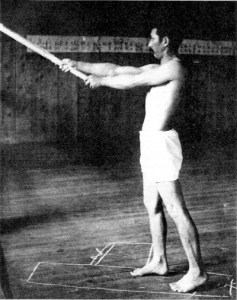 Hakudo demonstrating proper striking
Hakudo demonstrating proper striking
Otsuyoshi arrived in Tokyo in 1891. There, armed with a letter of introduction from Kenzo, Otsuyoshi was successfully admitted into Shingoro’s Yushinkan at the age of eighteen. Otsuyoshi trained hard, changing his name to Hakudo (博道) at age nineteen. Shingoro encouraged him to study other styles and literature. He tried his hand at various ryu, or schools, sleeping only four hours a day so that he could attend around five-six practices a day.
Hakudo was not perfect, however and had several bad habits to overcome. In shiai geiko Hakudo’s hip rose every time before a strike, telegraphing his intentions to his opponent. In order to correct this Hakudo was forced to wear stones around his waist to improve his center of gravity. To learn to execute suri-ashi in a more effective way, Hakudo was made to wear geta (Japanese wooden sandals) with a loose thread. This allowed him to develop a type of scraping suri-ashi, making his movement harder to see.
Hakudo’s intense dedication paid off and he rapidly advanced through the ranks. In 1906 he fought the bouts that came to define his early career as a swordsmen. At the Dai Nippon Butokusai Enbu Taikai he defeated Ozawa Jiro and Takano Shigeyoshi of the Hokushin Itto Ryu school, Koseki Kiyomasa of the Muhen Ryu school, and Sasaki Masanobu of the Suifu Ryu. At twenty three he received Jun-Menkyo and at twenty-seven was licensed Menkyo, Inkyo. At twenty-eight he was named Daihan or “Acting Headmaster” and was married to Shigoro’s daughter. Thus, Hakudo was adopted into the Negishi family (becoming Negishi Hakudo).
In 1912 Shingoro elected Hakudo to take his place on the committee responsible for creating the Dai Nippon Teikoku Kendo Kata. There were several problems, however and both Hakudo and his wife separated from the Negishi Family for personal reasons, rejoining the Hakudo Family. Hakudo then built his own dojo in Masagocho, Hongo ward (present day Bunkyo ward) and was given permission to use the Yushinkan name.
 Takano Sasaburo (left) and Nakayama Hakudo (right) during andemonstration of the Dai Nippon Teikoku Kendo Kata at Noma Dojo
Takano Sasaburo (left) and Nakayama Hakudo (right) during andemonstration of the Dai Nippon Teikoku Kendo Kata at Noma Dojo
Hakudo was now renowned around Japan for his skill, however this was not enough for him. He traveled across Japan to study various arts like: Itto Shoden Muto Ryu, Ono ha Itto Ryu, Hokushin Itto Ryu, (Toda) Buko Ryu, Nen Ryu, Shinkage Ryu, Musashi Enmei Ryu, Jigen Ryu, Ichiden Ryu, and Ooki-Isshin Ryu. In his search he found two ryu or schools that would effectively change his life forever, Shinto Muso Ryu (神道夢想流) and Muso Shinden Eishin Ryu (無双神傳英信流).
In 1912 Hakudo began training in Shinto Muso Ryu Jojutsu and calligraphy under Uchida Ryogoro at Shiba Park, Tokyo and with Takeda Kohachi at his residence in Kyobashi, Tokyo. He trained very hard, finding his study of the jo to be among the most valuable of his pursuits. Hakudo wrote:
“As a youth I was taught Shinto Muso Ryu by Shihan, Uchida Ryogoro. It was because of this training that I came to understand the Ura or inner methodologies of Kendo. I learned the ins and outs of handling the jo, manipulation of the feet, body mechanics, and other (fundamentals). Even in my Kendo practice I was able (utilize and) cultivate these (Jo) techniques. Thanks to this (integrated) practice I learned a lot. (In the world of martial arts) there are no kata as thoroughly developed as Shinto Muso Ryu Jojutsu’s. I believe Shinto Muso Ryu jojutsu is a national treasure.”
In 1916 Hakudo was introduced to Tosa Eishin Ryu by Itagaki Taisuke (a famous Meiji statesmen and a student of Oe Masamichi). Hakudo had learned Iai before in Shindo Munen Ryu, but felt something was missing. He initially approached Oe Masamichi about training, but was rejected. Taisuke saw Hakudo’s resolve to learn the style, however and introduced Hakudo to Hosokawa Yoshimasa of the Muso Shinden Eishin Ryu school (aka. Shinmomura Ha Hasegawa Eishin Ryu) and Morimoto Tokumi of the Goto Ha Muso Jikiden Eishin Ryu school (aka. Tanimura Ha Hasegawa Eishin Ryu). Hakudo was accepted as a student of both teachers, making him the first outsider to learn Tosa Eishin Ryu in history.
Hakudo trained earnestly and in 1920 the Nippon Butokukai awarded Hakudo the title of Hanshi in both Kendo and Iaido. Around this time Hakudo was said to have received Menkyo Kaiden in jojutsu from Uchida Ryogoro prior to his death in 1921 (though this is greatly debated). After receiving his certification Hakudo did something unexpected: he took what he learned and created his own version of Shinto Muso Ryu, commonly referred to as Nakayama-no-Jo, along with a set of five kihon (basic drills). Shimizu Takaji was said to have later incorporated Hakudo’s five kihon into his set of twelve some years later.
In 1922 Hakudo was awarded Menkyo Kaiden in Goto Ha Muso Jikiden Eishin Ryu from Tokumi and Menkyo in Muso Shinden Eishin Ryu from Yoshimasa. Contrary to popular belief, however Hakudo did not recieve Menkyo Kaiden from Yoshimasa. Hakudo continued to visit both Yoshimasa and Tokumi in Kochi. During his time there Hakudo trained with Yoshimasa at his house. He maintained a very good relationship with Yoshimasa until his death in 1923.
In 1925 Hakudo was asked by the head fencing instructor of the Rikugun Toyama Academy (a military academy) to assist him in creating a system of Gunto Soho ( 軍刀操法) or methods of manipulating military swords. Hakudo, through his research developed five standing iai kata that made the foundation of the Toyama Ryu Guntojutsu system. In the same year Hakudo supported Noma Seiji in the construction and development of the famed Noma dojo. Noma Dojo became a vessel for men and women of various ryu-ha or schools to test their skills and exchange their ideas with other kenshi. In 1927 at the age of fifty-five he received the rank of Hanshi in Jodo from the Nippon Butokukai.
In 1930 Hakudo was called on by the Butokukai to demonstrate Muso Shinden Eishin Ryu publicly (outside of Kochi) for the first time in history. Hakudo had a problem though: he never recieved Menkyo Kaiden in the system. As such, during the demonstration he presented the art as ”Muso Shinden Ryu Battojutsu” (無双神伝流抜刀術). This was done to avoid any altercations that might come from him using the school’s name.
In 1933 Hakudo restructured what he learned in Kochi into Muso Shinden Ryu (夢想神伝流) using the Chinese characters for dream or vision. The Yushinkan once a training hall exclusively for Shindo Munen Ryu and Gekiken under Negishi Shingoro; became a dojo for several martial arts. Students of the Yushinkan (under Hakudo) were selected to learn specific styles. Men like Nakayama Zendo and Hashimoto Toyo learned everything while others like Nakakura Kiyoshi, Danzaki Tomoaki and Nakajima Gozoro learned only Muso Shinden Ryu Iaido and Kendo.
In his time Hakudo had seen the death of stylized Gekiken and the birth of modern Kendo. In 1934 he and his contemporary Takano Sasaburo demonstrated the Dai Nippon Teikoku Kendo Kata at the Tenranjiai while Emperor Hirohito watched on. Both Hakudo and Takano were highly commended for their performances.
Kendo gained popularity and Hakudo along with Takano Sasaburo became among (if not) the most requested teachers in Japan. They traveled the country teaching at universities, police stations, military bases, Japanese Government installations, and even the Imperial Palace. Hakudo’s students ran into the tens of thousands. In fact over two thirds of those who held the rank of kyoshi with the Nippon Butokukai had studied with Hakudo to some effect.
World War II was a desperate time for Japan. The proud Japanese Military was being pushed back by Allied Forces. Japan had now become a target to American firebombing. Japanese buildings largely made of wood and built in close proximity to other residences became mere kindle for Allied bombs. Tokyo and other cities were decimated. This accompanied by the destruction Hiroshima and Nagasaki via Atomic Weapons brought about Japan’s formal surrender on September 2nd, 1945. Hakudo was quick to use his influence, using the Japanese idiom “a samurai never talks (bad mouths) about what is finished” Hakudo asked people to meet their American occupiers with dignity.
“In fencing we call ‘ohen‘ (応変_)_ the spirit or ability to adapt one’s self to the change. What this means is in a condition where after understanding and acknowledging the natural tide of affairs (what has happened), all past ambitions (or goals) must be given up. In doing so one can reach the state of nothingness. This requires noble heart. It (nothingness) is the ultimate goal of fencing. We must meet the Allied Army with such a spirit. Yesterday they were our enemies, but today they are not. If we fail not to think of them as enemies, then it cannot be said that we (the Japanese) truly understand Bushido. If there is even the smallest feeling of ill will remaining in our hearts and if we cannot take a broader outlook, it will to show in our faces and attitude, giving reason for them (Allied soldiers) to think of us as cowardly. I am of the personal belief that the greatness of a nation lies in its open-mindedness.”
 Hakudo demonstrating proper Nukitsuke
Hakudo demonstrating proper Nukitsuke
The end of the war brought on many hardships. In an effort to pacify the Japanese people Japanese martial arts were banned. This brought Hakudo in cooperation with his compatriots to fight for the right to practice martial arts in Japan. Eventually through the help of Sasamori Junzo, Kuroda Yasuji, and Kunii Zenya the ban on martial arts as a whole was eventually lifted. Japanese could practice martial arts again.
Hakudo’s victory brought about harsh realities however. Many of his most dedicated students died in the war, with even fewer of the surviving returned to train. Budo fell into decline. Hakudo felt a change was needed.
Hakudo restructured Muso Shinden Ryu for the general populous. The attempt was to reduce the aggressive nature of the kata and emphasize the more spiritual side of the ryu. Certain aspects of the kata were changed to reflect this. Omori Ryu’s Gyakuto for example, pre-war ended with stabbing the teki in the back of the head. Hakudo later changed the stab into Muso Jikiden Eishin Ryu’s todome, which was considered a more merciful coup de grâce.
(Authors note the Pre-War Gyakuto Todome was done far differently than what most iaido-ka do it today. The sword was raised high in the air and caught on the mune of the blade with the middle finger. Then after flattening the palm against back of the blade, it was thrust into the part of the head where the spine meets the skull [US. Marine Scout Snipers were taught to shoot the same spot]. The Yushinkan preserved this method).
 Nakayama Hakudo (right), Hashimoto Toyo (left), HasegawaEishin Ryu: Oroshi
Nakayama Hakudo (right), Hashimoto Toyo (left), HasegawaEishin Ryu: Oroshi
Hakudo did have several regrets. In his Kendo Koshutsujyu (剣道口述集) or Collection of Oral dictations on Kendo, Hakudo talked about his regret over a style he kept in secrecy from most of his students. The style of Hayashizaki Jinsuke Minamoto no Shigenobu.
Hakudo intended all of his serious students to learn all of his arts. Only those students who pursued and progress in all of Hakudo’s arts had access to what Hakudo called Hayashizaki Hon Ryu (林崎本流) or the real teachings of Hayashizaki Jinsuke Shigenobu. According to Hakudo only nine people learned the first inner tier of the school; they were:
- Otuska Iwao (Menkyo)
- Hasegawa Minoshiro (Menkyo)
- Ohayashi Jungo (Menkyo)
- Sakonji Tadaichi (Menkyo)
- Nakayama Zendo (Menkyo)
- Aoki Eizou (Menkyo)
- Hashimoto Toyo (Menkyo)
- Mukuta Kozou (Menkyo)
- Suhara Sugematsu (Menkyo)
Hakudo added that only four individuals surpassed them by learning all the kata and in effect achieving Menkyo Kaiden, their names were:
- Nakayama Zendo (Menkyo Kaiden)
- Hashimoto Toyo (Menkyo Kaiden)
- Mukuta Kozou (Menkyo Kaiden)
- Sakonji Tadaichi (Menkyo Kaiden)
 Hakudo demonstrates the kata Junto
Hakudo demonstrates the kata Junto
Hakudo said, it was his intention to teach the Hayashizaki Hon Ryu (林崎本流) school more, but by the end of the war he lacked the proper time and suitable candidates to do so.
This is not to say that Hakudo did not foster or teach his other students. Less than a handful of outstanding students ever received any traditional ranking (ie. Densho) from Hakudo. The most notable of them were perhaps Matsuo Kenpu and Kimura Eijyu, who received Menkyo Kaiden in Muso Shinden Ryu Iaido (夢想神伝流居合道).
The man called “_The Last (True) Martial Artist_” (最後の武芸者) died in 1958 at the age of eighty-five. Hakudo was survived by his son Nakayama Zendo to whom he passed all of his knowledge onto.
_[_おい乙吉、男にほれられるような男になるんだぞう_]:_高沢藤吉
“Otsuyoshi, you’ll be a man, who other men fall in love with” :Takazawa Toyoshi
To be Continued………..
**(**Part three will serve as a clairification of Muso Shinden Ryu and Hayashizaki Hon Ryu. It will explore the origin, past, present, technicalities, and curriculum of the school and it’s derivative sects).
(Special Thanks to: Richard Stonell !!! to whom without this article would not have been possible)
Glossary:
Teachers/Influences:
- Takazawa Toyoshi: former head of the Toyama Inn and former student of the Shin-Shintakuma Ryu Jujutsu school. He was a father figure to Hakudo.
- Saito Michinori: last known Shihan of Yamaguchi Ha Itto Ryu; he was Hakudo’s first sword instructor. Unfortunately little information on him survived.
- Hosoda Kenzo: Educator and influential sempai of Hakudo. Shindo Munen Ryu Kenjutsu Menkyo under Negishi Shingoro.
- Negishi Shingoro: 6th Generation Shihan of Shindo Munen Ryu Kenjutsu and Hakudo’s most influential
teacher. - Takano Sasaburo: Ono Ha Itto Ryu Kenjutsu Menkyo Kaiden, and a Hanshi in Kendo. He was one of Hakudo greatest sempai and confidants.
- Uchida Ryogoro: A contemporary of Shirashi Hanjiro. Ryogoro received Menkyo Kaiden in Haruyoshi Ha (Haruyoshi branch) of Shinto Muso Ryu and Ikkaku Ryu Torite from Hirano Kichizo Yoshinobu. He also received Menkyo Kaiden in Ono Ha Itto Ryu (from Ikuoka Heitaro), Hozoin Ryu (via the Takeda Family), and Kushin Ryu. He was the founder of Uchida Ryu Tanjojutsu.
- Takeda Kohachi: former Kuroda Clansmen, he was also a contemporary of Shirashi Hanjiro. He received Menkyo Kaiden in Haruyoshi branch of Shinto Muso Ryu. Kohachi died only a few years after Hakudo began training with him.
- Itagaki Taisuke: famous Japanese statesmen from Kochi: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Itagaki_Taisuke
- Oe Masamichi: former Shihan of Muso Jikiden Eishin Ryu and Muso Shinden Eishin Ryu, he was a former samurai of the Tosa/Yamauchi clan.
- Morimoto Tokumi: former samurai of the Tosa/Yamauchi clan. Tokumi received his Menkyo Kaiden in Muso Jikiden Eishin Ryu from Goto Magobei Masasuke making him Oe Masamichi’s contemporary.
- Hosokawa Yoshimasa: former samurai of the Yamauchi clan. He was a Shihan of Muso Shinden Eishin Ryu and teacher of Hakudo.
- **Noma Seiji:**Kendo enthusiast and founder of Kodansha Publishing Ltd. He established Noma Dojo in 1925.
- Sasamori Junzo: educator and Hanshi in Kendo and Iaido. He received Menkyo Kaiden in Tsuguru Den and Yamashika Den (collectively together they made up Hirosaki Han Den) Ono Ha Itto Ryu, Muraku Ryu, Hirosaki Han Den Shinmuso Hayashizaki Ryu, and Chokugen Ryu.
- Kuroda Yasuji: famous swordsmen and Shihan of Kogagawa Kaishin Ryu, Tamiya Ryu, Shin-Shintakuma Daiken-Nichi Ryu, Tsubaki Kotengu Ryu, and Setama Oguri Ryu. He was an activist who fought for the right to practice Japanese martial arts while under American occupation.
- Kunii Zenya: former Maniwa Nen Ryu Shihan and revisor (disputed creator) of Kashima Shin Ryu. He was recruited by Sasamori Junzo to participate in a bout against an American soldier armed with a rifle and live bayonet. He won the match without killing the soldier. Junzo used this as evidence that weapon based martial arts were as much about preserving life as they were about taking it. The ban on martial arts in Japan was soon after lifted.
Ryu-Ha or Schools Mentioned:
- Toyama Han Den Yamaguchi Ha Itto Ryu (富山藩傳山口派一刀流): Founded by Yamaguchi Bokushinsai it was a synthesis of several styles. Most famously studied by Mugai Ryu founder Tsuji Gettan. It was a ryu or school that unfortunately fell into obscurity. Hakudo earned a Mokuroku in the style prior to leaving for Tokyo at eighteen. Upon receiving Menkyo, Inkyo in Shindo Munen Ryu Kenjutsu from Negishi Shingoro, Saito Michinori awarded Hakudo the Zukai Densho (図解伝書) the highest-level scroll in the school. The school died with Michinori.
- Shindo Munen Ryu(神道無念流): Founded by Fukui Hyoemon Yoshihira was school of Kenjutsu and Iaijutsu. It became one of the most popular and wide spread martial arts schools in Japanese history. Shingoro and Hakudo’s particular version was Kanto Ha Shindo Munen Ryu: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Shind%C5%8D_Munen-ry%C5%AB
- Ono Ha Itto Ryu (小野派一刀流): Founded by Ono Tadaaki a student of legendary swordsmen Itto Ittosai, it was Ono’s version of Itto Ryu. The ryu or school was widely transmitted having countless branches all over Japan. The family line was transmitted through the ages until Yamaoka Tesshu received mastery of it. He then formed his Itto Shoden Muto Ryu, effectively ending the Ono family line.
- Hokushin Itto Ryu (北辰一刀流): Founded by Chiba Shusaku Narimasa; Shusaku first learned Hokushin Muso ryu from his father and later Nakanishi Ha Itto Ryu from Asari Matashichiro Yoshinobu. He later combined the teachings by reducing the eight sets of Itto Ryu into three, while adding iaijutsu and later a naginata techniques. The style became one of the most popular styles in the country spreading across Japan.
- Suifu Ryu(水府流): Founded by Tokugawa Nariaki; a synthesis of the three main sword arts of the Mito Clan (Mito Han Den): Shindo Munen Ryu, Hokushin Itto Ryu, and Togun Ryu. It was one of Nariaki’s most ambitious projects. Sasaki Masanobu was the last shihan of the system. He trained at the Tobukan along with Ozawa Jiro. After his death, Jiro attempted to resurrect the style, but failed.
- Shinto Muso Ryu (神道夢想流): Founded by Musō Gonnosuke Katsuyoshi; Gonnosuke integrated the spear, naginata, sword, and bo staff into a single versatile weapon. A Otome Ryu (御留流) of the Kuroda domain the art split into several factions. By the late Edo Period only two branches survived; the Haruyoshi and Jigyo. Both Uchida Ryogoro and Takeda Kohachi received Menkyo Kaiden in the Haruyoshi branch and taught their versions of Shinto Muso Ryu to the masses. Shirashi Hanjiro (another Kuroda retainer) received Menkyo Kaiden in the Haruyoshi branch and Mokuroku in the Jigyo branch. He later combined and re-codified the schools using the characters for divine (神道). His line was succeeded by Shimizu Takaji and under went even more revisions. Takaji’s Jodo(杖道) was passed to many individuals throughout the world. Uchida’s line unaffected by both Hanjiro and Takaji’s changes was passed on through his son Ryohei and student Nakayama Hakudo. Another line of the Haruyoshi branch survived though one of Hakudo’s students Matsuo Kenpu who received Menkyo Kaiden from Shirashi Tokugoro.
- Tosa Eishin Ryu (土佐英信流): is a collective reference to Muso Jikiden Eishin Ryu/Muso Shinden Eishin Ryu as taught within the Yamauchi Domain. It was one of several Otome Ryu (御留流) of the Yamauchi Domain and as such meant exclusively for Yamauchi clansmen.
- Muso Shinden Eishin Ryu (無双神傳英信流): Founded by Hayashizaki Jinsuke Shigenobu and revised by Hasegawa Chikaranosuke Eishin. Shimomura Mōichi Sadamasa was licensed in Tosa Eishin Ryu by Yamakawa Kyūzō Yukikatsu. He (Mochi) was said to have devised several innovative changes in the school and passed them on to his students. Both Yoshimasa and (Oe) Masamichi received Menkyo Kaiden in the school and transmitted it to several people. Yoshimasa issued Menkyo Kaiden to Ueda Heitaro Chubu and Menkyo to Nakayama Hakudo. Ueda’s and a few other lines of Muso Shinden Eishin Ryu survive and are being taught today.
- Goto Ha Muso Jikiden Eishin Ryu (五藤派無双直傳英信流): Founded by Hayashizaki Jinsuke Shigenobu and revised by Hasegawa Chikaranosuke Eishin. The style was transmitted throughout the years to Tanimura Kamenojō Takakatsu. Kamenojō passed Menkyo Kaiden onto several students including Gotō Magobei Masasuke. One of many shihan of Muso Jikiden Eishin Ryu, his line became known as Goto Ha or Goto version. He had several talented students and issued Menkyo Kaiden to a few of them. Among those awarded were Oe Masamichi and Morimoto Tokumi.
- Toyama Ryu Gunto Soho (戸山流軍刀操法): was developed in 1925 was a military art devised for Japanese soldiers. It consisted of Kumitachi, Iaijutsu, Sojutsu (meant to represent a Bayonet), Happo Giri (八法切) or “_Eight Methods of Cutting_”, Shigeki (射撃) or Marksmanships, Tameshigiri (試し切り) or “_Test Cutting_”, and Military Music (used for marching and cadence).
- Hayashizaki Hon Ryu (林崎本流): Founded by Hayashizaki Jinsuke Shigenobu; it was a style passed down to Nakayama Hakudo via Hosokawa Yoshimasa. The only remaining teacher of the style is Ogawa Takeshi (current headmaster of the Yushinkan Dojo).
Glossary of Terms:
- Shiai Geiko (試合稽古)- lit: “Contest”, “practice”; it is used to express the idea of a sparing match.
- Kumitachi (組太刀)- lit: “Grouped swords”; is a type of paired form usually found in Japanese weapon arts.
- Gekiken (撃剣)- lit: “_Conquering the Sword_” or “_Fencing_“; it was the pre-cursor to modern Kendo. Often _ryu_or school specific, it was a practice that allowed swordsmen of particular schools to apply learned techniques or concepts in a relatively controlled environment. Unlike modern Kendo; it contained the use of several or multiple weapons, grappling, striking, and physical duress that brought students to a new level of endurance and understanding.
- Otome Ryu (御留流)- lit: that “_which flows but remains at home_” was a ryu-ha or school that was either sponsored by or kept secret by a feudal clan.
- Densho (伝書)- lit: “Written Teachings” are scrolls normally awarded to students of Japanese koryu or “Old Japanese Martial Arts”. Densho act as a both a text on martial arts and certification (having the names of the author, recipient, and date issued).
- Mokuroku (目録)- lit: “Catalog” is a type of scroll usually awarded to students after several years of dedication. The details differ from school to school, but a mokuroku consists of a (partial or complete) list of kata, fighting strategy, military strategy, esoteric or religious teachings, philosophy, or other facets of learning.
- Jun-Menkyo (順免許) lit: “Orderly License”; it is a scroll issued by several ryu or schools, usually prior to the Menkyo scroll.
- Menkyo (免許)- lit: “License/Permit”; differs from school to school, but is normally a scroll of high level awarded to those who have attained a profound level of skill or understanding in their respective
school. - Menkyo Kaiden (免許皆伝)- lit: License of Full-Transmission; it is a scroll that normally denotes that the receiver has attained a superior command or even mastery of their ryu or school.
- Inkyo (允許)- lit: “Certificate of Proficiency”; is a license given to those who have either finished their training or have been given permission to establish their own dojo.
- Inka (印可)- lit: “Certificate of Proficiency”; is a license given to those who have either finished their training or have been given permission to establish their own dojo. (Same as Inkyo)
- Shihan (師範)- lit: “Instructor”; is a term often misused today. A Shihan is a person who was fully licensed in their respective _ryu_or school and by the grace of their teachers, allowed to run or operate their own dojo or training hall.
- Soke (宗家)- lit: “Head of Family”; it is a term that has been widely misused and misunderstood (especially within the last eighty years). Soke or Patriarch is the head of a family house hold. Japanese families were traditionally extremely hierarchical. Families following Confucian doctrine were divided into households based solely on ones age or importance in the family. The patriarch of the family (normally belonging to the highest house of the family) had the power to make final decisions on behalf of the entire family, issue or cut off financial support to lower households, or in extreme cases hamon (破門) or excommunicate a family relative. It was a very powerful position. Though the principle has existed in Japanese martial systems for sometime, but it has became more or less exaggerated in the 20th and 21st century. It has become a way for a Shihan to consolidate power as well as preserve the integrity of his/her martial art.
- Hanshi (範士)- lit: “Instructor of Warriors”; it is an honorary title issued by a number of organizations in Japan.
- San-Dou-no-Hanshi (三道の藩士): was a honorary title given to those that received Hanshi in Kendo, Iaido, and Jodo from Nippon Butokukai or Zen Nippon Kendo Renmei (All Japan Kendo Federation).
- Dai Nippon Teikoku Kendo Kata (大日本帝国剣道形)- lit: “The Greater Kendo Kata of Imperial Japan” was the pre-cursor to the Nippon Kendo Kata (日本剣道形).
- Tenranjiai (天覧試合)- lit: match [game] held while in the presence of the Emperor; a Tenranjiai is not just related to a martial art contest, but in any contest where the Emperor is watching. The martial art related Tenranjiai(s) occurred in 1895 and 1940. Nakayama Hakudo and Takano Sasaburo demonstrated at the Showa Tenranjiai (昭和天覧試合) or the Tenranjiai of the Showa Emperor. Since that time the Tenranjiai have occurred in modern sports like baseball and more traditional sport like Sumo.
References:
- 乙藤市蔵監修/松井健二:天真正傳神道夢想流杖術
- 中山博道:剣道口述集
- 中山博道:剣道手引層
- 中山博道や中山善道:日本剣道と西洋剣技
- 壇崎友厭彰:居合道-その理合と神髄
- Tony Cundy: Kendo World vol 2 No. 4, 2004



