GraphData—Wolfram Language Documentation (original) (raw)
BUILT-IN SYMBOL
- See Also
- Graph
- GraphPlot
- GraphPlot3D
- PolyhedronData
- KnotData
- LatticeData
- Entity Types
- Graph
- Interpreter Types
- Graph
- GraphClass
- ComputedGraph
- Related Guides
GraphData
GraphData[name]
gives a graph with the specified name.
GraphData[entity]
gives the graph corresponding to the graph entity.
GraphData[entity,property]
gives the value of the property for the specified graph entity.
GraphData[class]
gives a list of available named graphs in the specified graph class.
GraphData[n]
gives a list of available named graphs with n vertices.
Details
- The specified entity in GraphData can be an Entity, a list of entities or an entity canonical name such as such as "PetersenGraph" or "FosterCage".
- GraphData[entity] gives a Graph object.
- The specified property can be an EntityProperty, a property canonical name or a list of properties.
- GraphData[patt] gives a list of all graph standard names that match the string pattern patt.
- GraphData[] gives a list of all standard named graphs.
- GraphData[All] gives all available graphs.
- GraphData[;;n] gives a list of available standard named graphs with ≤n vertices.
- GraphData[m;;n] gives a list of available standard named graphs with m through n vertices.
- GraphData[class,nspec] gives a list of available graphs with nspec vertices in the specified class.
- GraphData["Classes"] gives a list of all supported classes.
- GraphData["Properties"] gives a list of properties available for graphs.
- GraphData[{n,i},…] gives data for the i
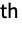 simple graph with n vertices.
simple graph with n vertices. - GraphData[{"type",id},…] gives data for the graph of the specified type with identifier id. The type is typically a string and the identifier is typically an integer or lists of integers.
- Basic graph properties include:
"AdjacencyMatrix" adjacency matrix "EdgeCount" total number of edges "Edges" edges "FaceCount" total number of faces (for a planar graph) "Faces" faces "IncidenceMatrix" incidence matrix "VertexCount" total number of vertices "Vertices" vertices - Properties related to graph connectivity include:
"AdjacencyLists" adjacency lists "ArticulationVertexCount" number of articulation vertices "ArticulationVertices" list of vertices whose removal would disconnect the graph "BlockCount" number of blocks "Blocks" minimal 2-connected components "BridgeCount" number of bridges "Bridges" list of edges whose removal would disconnect the graph "Connected" connected "ConnectedComponentCount" number of connected components "ConnectedInducedSubgraphCount" connected induced subgraph count "ConnectedComponents" connected components "CyclicEdgeConnectivity" cyclic edge connectivity "Disconnected" disconnected "EdgeConnectivity" minimum edge deletions to disconnect the graph "EdgeCutCount" number of edge cuts "EdgeCuts" edge cuts "IncidenceLines" indices of collinear vertices in a configuration graph "LambdaComponents" lambda components "LuccioSamiComponents" Luccio–Sami components "MinimalEdgeCutCount" number of minimal edge cuts "MinimalEdgeCuts" minimal edge cuts "MinimalVertexCutCount" number of minimal vertex cuts "MinimalVertexCuts" minimal vertex cuts "MinimumCyclicEdgeCutCount" minimum cyclic edge cut count "MinimumCyclicEdgeCuts" minimum cyclic edge cuts "MinimumEdgeCutCount" number of minimum edge cuts "MinimumEdgeCut" minimum edge cuts "MinimumVertexCutCount" minimum vertex cut count "MinimumVertexCuts" minimum vertex cuts "MinorCount" graph minor count "SpanningTrees" spanning trees "Strength" graph strength "Toughness" graph toughness "Triangulated" triangulated (maximally planar) "VertexConnectivity" minimum vertex deletions to disconnect the graph - Properties related to graph minors include:
"HadwigerNumber" Hadwiger number "MinorCount" graph minor count - Properties related to graph display include:
"EmbeddingClasses" list of embedding class tags, one to an embedding "Embeddings" vertex coordinates for all available layouts "Graph" graph object "Graphics" graphic "Graphics3D" 3D graphics "Image" image "MeshRegion" mesh region "Polyhedron" polyhedron "VertexCoordinates" vertex coordinates for the default layout - Annotatable properties related to list-type output include:
"AdjacencyMatrix","outputtype" one or all adjacency matrices or count of all possible adjacency matrices "ConnectedComponents","outputtype" connected components as a graph, list, count, list of edge counts, or list of vertex counts "Cycles","outputtype" undirected, directed, or count of cycles "Edges","outputtype" edges as a list, edge list, index pair list, rule list, graphic, or count of edges "EulerianCycles","outputtype" undirected, directed, or count of Eulerian cycles "Faces","outputtype" faces as a list, index list, graphic, or count of faces "HamiltonianCycles","outputtype" undirected, directed, or count of Hamiltonian cycles "HamiltonianPaths","outputtype" undirected, directed, or count of Hamiltonian paths "HamiltonianWalks","outputtype" undirected, directed, or count of Hamiltonian walks "VertexCoordinates","outputtype" one or all vertex coordinates or embedding count "Vertices","outputtype" vertices as a list, indexed coordinate rule list, graphic, or count of vertices - Properties giving pure functions representing graph polynomials include:
"CharacteristicPolynomial" characteristic polynomial of the adjacency matrix "ChordlessCyclePolynomial" polynomial encoding the counts of chordless cycles by length "ChromaticPolynomial" chromatic polynomial "CliquePolynomial" clique polynomial "CoboundaryPolynomial" coboundary polynomial "ComplementChordlessCyclePolynomial" polynomial encoding the counts of chordless cycles in the graph complement by length "ComplementOddChordlessCyclePolynomial" polynomial encoding the counts of odd chordless cycles in the graph complement by length "ConnectedDominationPolynomial" connected domination polynomial "ConnectedInducedSubgraphPolynomial" polynomial encoding the counts of connected induced subgraphs by size "CyclePolynomial" cycle polynomial "DetourPolynomial" characteristic polynomial of the detour matrix "DistancePolynomial" distance polynomial "DominationPolynomial" domination polynomial "EdgeCoverPolynomial" edge cover polynomial "EdgeCutPolynomial" edge cut polynomial "FlowPolynomial" flow polynomial "IdiosyncraticPolynomial" Tutte's idiosyncratic polynomial "IndependencePolynomial" independence polynomial "IrredundancePolynomial" irredundance polynomial "LaplacianPolynomial" Laplacian polynomial "MatchingGeneratingPolynomial" matching generating polynomial "MatchingPolynomial" matching polynomial "MaximalCliquePolynomial" polynomial encoding the counts of maximal cliques by size "MaximalIndependencePolynomial" polynomial encoding the counts of maximal independent vertex sets by size "MaximalIrredundancePolynomial" polynomial encoding the counts of maximal irredundant sets by size "MaximalMatchingGeneratingPolynomial" polynomial encoding the counts of maximal independent edge sets by size "MinimalConnectedDominationPolynomial" polynomial encoding the counts of minimal connected dominating sets by size "MinimalDominationPolynomial" polynomial encoding the counts of minimal dominating sets by size "MinimalEdgeCoverPolynomial" polynomial encoding the counts of minimal edge covers by size "MinimalEdgeCutPolynomial" polynomial encoding the counts of minimal edge cuts by size "MinimalTotalDominationPolynomial" polynomial encoding the counts of minimal total dominating sets by size "MinimalVertexCoverPolynomial" polynomial encoding the counts of minimal vertex covers by size "MinimalVertexCutPolynomial" polynomial encoding the counts of minimal vertex cuts by size "OddChordlessCyclePolynomial" polynomial encoding the counts of odd chordless cycles by length "PathPolynomial" path polynomial "QChromaticPolynomial" _Q_-chromatic polynomial "RankPolynomial" rank polynomial "ReliabilityPolynomial" reliability polynomial "SigmaPolynomial" chromatic polynomial in falling factorial basis "TotalDominationPolynomial" polynomial encoding the counts of total dominating sets by size "TuttePolynomial" Tutte polynomial "VertexCoverPolynomial" polynomial encoding the counts of vertex covers by size "VertexCutPolynomial" polynomial encoding the counts of vertex cuts by size - Coloring‐related graph properties include:
"ChromaticInvariant" chromatic invariant "ChromaticNumber" chromatic number "ChromaticPolynomial" chromatic polynomial "ChromaticRoots" chromatic roots "CyclicChromaticNumber" cyclic chromatic number "EdgeChromaticNumber" edge chromatic number "FractionalChromaticNumber" fractional chromatic number "FractionalEdgeChromaticNumber" fractional edge chromatic number "MinimumVertexColoringCount" number of minimum vertex colorings "MinimumVertexColorings" minimum vertex colorings "MinimumEdgeColoring" minimum edge coloring "MinimumWeightFractionalColoring" minimum weight fractional coloring "QChromaticPolynomial" _Q_‐chromatic polynomial "WeisfeilerLemanDimension" Weisfeiler–Leman dimension - Graph index properties include:
"ABCIndex" atom-bond connectivity index "ArithmeticGeometricIndex" arithmetic-geometric index "BalabanIndex" Balaban index "CircuitRank" minimum number of edges to remove to turn acyclic "DetourIndex" detour index "HararyIndex" Harary index "HosoyaIndex" Hosoya index "KirchhoffIndex" Kirchhoff index "KirchhoffSumIndex" Kirchhoff sum index "MolecularTopologicalIndex" molecular topological (second Schultz) index "RandicIndex" Randić index "SomborIndex" Sombor index "StabilityIndex" stability index "TopologicalIndex" topological (first Schultz) index "WienerIndex" Wiener index "WienerSumIndex" Wiener sum index "ZagrebIndex1" first Zagreb index "ZagrebIndex2" second Zagreb index - Matrix graph properties include:
"ABCMatrix" atom-bond connectivity matrix "AdjacencyMatrix" adjacency matrix "ArithmeticGeometricMatrix" arithmetic-geometric matrix "DetourMatrix" matrix of longest path distances "DistanceMatrix" distance matrix "IncidenceMatrix" incidence matrix "LaplacianMatrix" Laplacian matrix "MaximumFlowMatrix" matrix flow matrix "MinimumCostFlowMatrix" minimum cost flow matrix "NormalizedLaplacianMatrix" normalized Laplacian matrix "RandicMatrix" Randić matrix "ResistanceMatrix" resistances between pairs of vertices for unit‐resistance edges "SomborMatrix" Sombor matrix - Local graph properties include:
"ChordCount" number of chords "Chords" chords "Curvatures" curvatures "IsolatedPointCount" number of isolated points "IsolatedPoints" vertices of degree 0 "LeafCount" number of leaves "Leaves" vertices of degree 1 - Global graph properties include:
"Anarboricity" maximum number of edge‐disjoint nonacyclic subgraphs whose union is the original graph "ApexCount" apex count "Apices" list of vertices whose removal renders the graph planar "Arboricity" minimum number of edge‐disjoint acyclic subgraphs whose union is the original graph "Center" indices of vertices with graph eccentricity equal to radius "Circumference" circumference of the graph "Coarseness" maximum number of line‐disjoint nonplanar subgraphs "Corank" edge count minus vertex count plus connected component count "Degeneracy" graph degeneracy "DegreeSequence" vertex degrees in monotonic nonincreasing order "DeterminedByResistance" no other graph shares the same multiset of resistances "DeterminedBySpectrum" no other graph shares the spectrum "Diameter" diameter of the graph "Eccentricities" eccentricities of each vertex "FractionalArboricity" fractional arboricity "IntersectionArray" intersection array "LinearArboricity" linear arboricity "MaximumLeafNumber" largest number of tree leaves in any spanning trees "MaximumVertexDegree" largest vertex degree "MeanCurvature" mean curvature "MeanDistance" mean distance between vertices "MinimumLeafNumber" smallest number of tree leaves in any spanning trees "MinimumVertexDegree" smallest vertex degree "Periphery" indices of vertices with graph eccentricity equal to diameter "Pseudoarboricity" pseudoarboricity "QuadraticEmbeddingConstant" quadratic embedding constant "Rank" vertex count minus connected component count "RegularParameters" parameters describing common neighbor counts of vertices "Skewness" minimum number of edges whose removal would result in a planar graph "SpanningTreeCount" number of spanning trees "StarArboricity" star arboricity "Thickness" minimum number of planar subgraphs whose union is the original graph "TreeNumber" minimal number of trees covering the edges of a graph "Triameter" graph triameter (generalization of graph diameter) "VertexDegrees" vertex degeres - Spectral graph properties include:
"ABCEnergy" atom-bond connectivity energy "ABCSpectralRadius" atom-bond connectivity spectral radius "AlgebraicConnectivity" second smallest eigenvalue of the Laplacian matrix "ArithmeticGeometricEnergy" arithmetic-geometric energy "ArithmeticGeometricSpectralRadius" arithmetic-geometric spectral radius "Energy" graph energy "LaplacianSpectralRadius" Laplacian spectral radius "LaplacianSpectralRatio" Laplacian spectral ratio "LaplacianSpectrum" eigenvalues of the Laplacian matrix "RandicEnergy" Randić energy "SomborEnergy" Sombor energy "SomborSpectralRadius" Sombor spectral radius "SpectralRadius" spectral radius "Spectrum" eigenvalues of the adjacency matrix "SpectrumSignature" tallies of adjacency matrix eigenvalues - Labeled graph properties include:
"AverageDisorderNumber" average disorder number "DisorderNumber" disorder number "ErdosSequence" Erdős sequence "GracefulLabelingCount" number of fundamentally distinct graceful labelings "GracefulLabelings" fundamentally distinct graceful labelings "IrregularityStrength" irregularity strength "PinnacleSetCount" number of pinnacle sets "PinnacleSets" pinnacle sets "RadioLabelingCount" number of fundamentally distinct optimal radio labelings "RadioLabelings" fundamentally distinct optimal radio labelings "RadioNumber" radio number - Graph construction properties include:
"AssemblyNumber" assembly number "ConstructionNumber" construction number - Topological graph properties include:
"CrossingNumber" minimum crossings in an embedding of the graph "Dimension" graph dimension "Genus" minimum number of handles yielding a non-edge-crossing embedding "KleinBottleCrossingNumber" minimum crossings in a Klein bottle embedding "LocalCrossingNumber" local crossing number "MapNumber" map number "MetricDimension" metric dimension "ProjectivePlaneCrossingNumber" minimum crossings in a projective plane embedding "RectilinearCrossingNumber" minimum crossings in a straight‐line embedding "RectilinearLocalCrossingNumber" rectilinear local crossing number "ToroidalCrossingNumber" minimum crossings in a toroidal embedding - Clique‐related properties include:
"CliquePolynomial clique polynomial "Cliques cliques "BicliqueNumber" biclique number "BipartiteDimension" bipartite dimension "CliqueCount" number of cliques "CliqueCoveringNumber" minimum number of maximum cliques needed to cover the vertex set "CliqueNumber" number of vertices in a maximum clique "DelsarteCliqueCount" number of Delsarte cliques "DelsarteCliques cliques in a distance-regular graph for which the Delsarte bound is achieved "FractionalCliqueNumber" fractional clique number "LowerCliqueNumber" size of smallest maximal clique "MaximalCliqueCount" number of distinct maximal cliques "MaximalCliquePolynomial" polynomial encoding tallies of maximal clique sizes "MaximalCliques" maximal cliques "MaximumCliqueCount" number of maximum cliques "MaximumCliques" maximum cliques "MinimumCoveringsByMaximalCliques" smallest coverings by maximal cliques "MinimumCoveringsByMaximalCliquesCount" number of smallest coverings by maximal cliques "SimplexGraph" simplex graph - Cover‐related properties include:
"CliqueCoveringNumber" minimum number of maximum cliques needed to cover the vertex set "EdgeCoverCount" number of edge covers "EdgeCoverNumber" size of the minimum edge cover "EdgeCoverPolynomial" edge cover polynomial "EdgeCovers" edge covers "MinimalEdgeCoverCount" number of minimal edge covers "MinimalEdgeCoverPolynomial" polynomial encoding tallies of minimal edge cover sizes "MinimalEdgeCovers" minimal edge covers "MinimalVertexCoverCount" number of minimal vertex covers "MinimalVertexCoverPolynomial" polynomial encoding tallies of minimal vertex cover sizes "MinimalVertexCovers" minimal vertex covers "MinimumCliqueCoveringCount" number of minimum clique coverings "MinimumCliqueCoverings" minimum clique coverings "MinimumEdgeCoverCount" number of minimum edge covers (matchings) "MinimumEdgeCovers" minimum edge covers (matchings) "MinimumPathCoveringCount" number of minimum path coverings "MinimumPathCoverings" minimum path coverings "MinimumVertexCoverCount" number of minimum vertex covers "MinimumVertexCovers" minimum vertex covers "PathCoveringNumber" path covering number "VertexCoverCount" number of vertex covers "VertexCoverNumber" size of a minimum vertex cover "VertexCoverPolynomial" vertex cover polynomial - Independent set‐related properties include:
"BipartiteDimension" bipartite dimension "EdgeIndependenceNumber" tallies of independent edge set sizes "FractionalIndependenceNumber" fractional independence number "IndependenceNumber" size of the largest independent vertex set "IndependencePolynomial" independence polynomial "IndependenceRatio" independence ratio "IndependentEdgeSetCount" number of independent edge sets "IndependentEdgeSets" independent edge sets "IndependentVertexSetCount" number of independent vertex sets "IndependentVertexSets" independent vertex sets "IntersectionNumber" intersection number "LowerIndependenceNumber" size of the smallest maximal independent vertex set "LowerMatchingNumber" size of the smallest maximal independent edge set "MatchingGeneratingPolynomial" matching‐generating polynomial "MatchingNumber" degree of the matching‐generating polynomial "MatchingPolynomial" matching‐generating polynomial "MaximalIndependencePolynomial" polynomial encoding the numbers of maximal independent vertex sets by size "MaximalIndependentEdgeSetCount" number of maximal independent edge sets (matchings) "MaximalIndependentEdgeSets" maximal independent edge sets (matchings) "MaximalIndependentVertexSetCount" number of maximal independent vertex sets "MaximalIndependentVertexSets" maximal independent vertex sets "MaximalMatchingGeneratingPolynomial" polynomial encoding the numbers of maximal independent edge sets by size "MaximumIndependentEdgeSetCount" number of maximum independent edge sets (matchings) "MaximumIndependentEdgeSets" maximum independent edge sets (matchings) "MaximumIndependentVertexSetCount" number of maximum independent vertex sets "MaximumIndependentVertexSets" maximum independent vertex sets - Irredundant set‐related properties include:
"IrredundanceNumber" (lower) irredundance number "IrredundancePolynomial" irredundance polynomial "IrredundantSetCount" number of irredundant sets "IrredundantSets" irredundant sets "MaximalIrredundancePolynomial" polynomial encoding tallies of maximal irredundant set sizes "MaximalIrredundantSetCount" number of maximal irredundant sets "MaximalIrredundantSets" maximal irredundant sets "MaximumIrredundantSetCount" number of maximum irredundant sets "MaximumIrredundantSets" maximum irredundant sets "UpperIrredundanceNumber" upper irredundance number - Dominating set‐related properties include:
"ConnectedDominatingSetCount" connected dominating set count "ConnectedDominatingSets" connected dominating sets "ConnectedDominationNumber" size of smallest possible connected dominating set "ConnectedDominationPolynomial" polynomial encoding tallies of connected dominating set sizes "DomaticNumber" maximum number of disjoint dominating sets in a domatic partition of a graph "DominatingSetCount" number of dominating sets "DominatingSets" dominating sets "DominationNumber" size of smallest possible dominating set "DominationPolynomial" polynomial encoding tallies of dominating set sizes "MinimalConnectedDominatingSetCount" number of minimal connected dominating sets "MinimalConnectedDominatingSets" minimal connected dominating sets "MinimalConnectedDominationPolynomial" polynomial encoding tallies of minimal connected dominating set sizes "MinimalDominatingSetCount" number of minimal dominating sets "MinimalDominatingSets" minimal dominating sets "MinimalDominationPolynomial" polynomial encoding tallies of minimal dominating set sizes "MinimalTotalDominatingSetCount" number of minimal total dominating sets "MinimalTotalDominatingSets" minimal total dominating sets "MinimalTotalDominationPolynomial" polynomial encoding tallies of minimal total dominating set sizes "MinimumConnectedDominatingSetCount" minimum connected dominating set count "MinimumConnectedDominatingSets" minimum connected dominating sets "MinimumDominatingSetCount" number of minimum dominating sets "MinimumDominatingSets" minimum dominating sets "MinimumTotalDominatingSetCount" number of minimum total dominating sets "MinimumTotalDominatingSets" minimum total dominating sets "TotalDominatingSetCount" number of total dominating sets "TotalDominatingSets" total dominating sets "TotalDominationNumber" size of smallest possible total dominating set "TotalDominationPolynomial" polynomial encoding the tallies of total dominating set sizes "UpperDominationNumber" size of the largest maximal dominating set - Symmetry‐related properties include:
"ArcTransitivity" maximal order s of an s‐arc-transitive graph "AutomorphismCount" order of the vertex automorphism group "AutomorphismGroup" graph automorphism permutation group "CanonicalPolyhedronDistinctEdgeLengthCount" number of distinct edge lengths in the corresponding canonical polyhedron "CayleyGraphGeneratingGroupNames" names of groups that generate the graph as a Cayley graph "CayleyGraphGeneratingGroups" groups that generate the graph as a Cayley graph "DistinguishingNumber" distinguishing number "FixingNumber" fixing number "MinimumDistinguishingLabelingCount" number of minimum distinguishing labelings "MinimumDistinguishingLabelings" minimum distinguishing labelings "PlanarEmbeddingCount" number of planar embeddings "SymmetricallyDistinctFaceCount" number of symmetrically distinct faces "SymmetricallyDistinctFaces" list of symmetrically distinct face representatives "SymmetricallyDistinctVertexPairCount" number of symmetrically distinct vertex pairs "SymmetricallyDistinctVertexPairSignature" signature of symmetrically distinct vertex pairs "SymmetricallyDistinctVertices" list of symmetrically distinct vertex representatives "SymmetricallyDistinctVertexCount" number of symmetrically distinct vertices "SymmetricallyEquivalentFaces" lists of symmetrically equivalent faces "SymmetricallyEquivalentVertices" lists of symmetrically equivalent vertices - Information‐related properties include:
"Bandwidth" graph bandwidth "BroadcastTime" graph broadcast time "BroadcastTimes" list of vertex broadcast times "BurningNumber" burning number "CheegerConstant" Cheeger constant "Conductance" graph conductance "CoolingNumber" cooling number "Gonality" gonality "Likelihood" probability for graph to be generated by random number and corresponding vertex 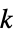 -subset picking
-subset picking"LovaszNumber" Lovász number (estimate of Shannon capacity) "Pathwidth" graph pagewidth "PebblingNumber" pebbling number "ScrambleNumber" scramble number "ShannonCapacity" effective alphabet size in a graph‐represented communication model "TreeDepth" tree depth "Treewidth" graph treewidth - Path‐ and cycle‐related properties include:
"ChordlessCycleCount" number of chordless cycles of length at least 4 "ChordlessCyclePolynomial" polynomial encoding tallies of chordless cycle by length "ChordlessCycles" cycles of length at least 4 with no chords "ComplementChordlessCycleCount" number of chordless cycles in the graph complement "ComplementChordlessCyclePolynomial" polynomial encoding tallies of chordless cycles of the graph complement by length "ComplementChordlessCycles" chordless cycles of length at least 4 in the graph "ComplementOddChordlessCycleCount" number of odd chordless cycles in the graph complement "ComplementOddChordlessCyclePolynomial" polynomial encoiding tallies of odd chordless cycles of the graph complement by length "ComplementOddChordlessCycles" odd chordless cycles of length at least 4 in the graph complement "CubeGraph" graph cube "CycleCount" number of distinct cycles "CyclePolynomial" cycle polynomial "Cycles" lists of cycles "EulerianCycleCount" number of distinct Eulerian cycles "EulerianCycles" lists of Eulerian cycles "FaceSignature" tallies of face lengths "Girth" length of the shortest cycle "HamiltonDecompositionCount" number of Hamilton decompositions "HamiltonDecompositions" partitions of edge set into Hamiltonian cycles "HamiltonianCycleCount" number of distinct Hamiltonian cycles "HamiltonianCycles" lists of Hamiltonian cycles "HamiltonianNumber" length of a shortest Hamiltonian walk "HamiltonianPathCount" number of distinct Hamiltonian paths "HamiltonianPaths" lists of Hamiltonian paths "HamiltonianWalkCount" number of distinct Hamiltonian walks "HamiltonianWalks" lists of Hamiltonian walks "HexagonCount" number of 6-cycles "KCyclicIndices" indices 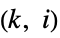 that label the graph as the
that label the graph as the 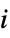 th
th 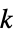 -cyclic graph
-cyclic graph"LCFSignature" tally of the orders of all possible LCF signatures "LongestCycleCount" number of longest cycles "LongestCycles" longest cycles "LongestPathCount" number of longest paths "LongestPathLength" length of longest path "LongestPaths" longest paths "MinimumPathCoveringCount" number of minimum path coverings "MinimumPathCoverings" minimum path coverings "OddChordlessCycleCount" number of odd chordless cycles of length greater than 3 "OddChordlessCyclePolynomial" polynomial encoding tallies of numbers of odd chordless cycles by length "OddChordlessCycles" chordless cycles of odd length greater than 3 "PathCount" number of distinct paths "PathCoveringNumber" path covering number "PathPolynomial" path polynomial "PathPolynomialMatrix" matrix function of path polynomials "Paths" lists of paths "PentagonCount" number of 5-cycles "Radius" radius of the graph "SquareCount" number of 4-cycles "SquareGraph" square graph "TriangleCount" number of 3-cycles - Graph centralities include:
"BetweennessCentralities" betweenness centralities "ClosenessCentralities" closeness centralities "DegreeCentralities" vertex degrees "EccentricityCentralities" reciprocal of vertex eccentricities "EdgeBetweennessCentralities" edge betweenness centralities "EigenvectorCentralities" eigenvector centralities "HITSCentralities" hub centralities "KatzCentralities" Katz centralities "LinkRankCentralities" link rank centralities "PageRankCentralities" page rank centralities "RadialityCentralities" radiality centralities "StatusCentralities" status centralities - Graph clustering coefficients include:
"GlobalClusteringCoefficient" global clustering coefficient "LocalClusteringCoefficients" local clustering coefficients "MeanClusteringCoefficient" mean clustering coefficient - Naming‐related properties include:
"AlternateNames" alternate English names "AlternateStandardNames" alternate standard Wolfram Language names "Entity" graph entity "Name" English name "Names" English name and alternate names "StandardName" standard Wolfram Language name "StandardNames" standard and alternate Wolfram Language names - Notation‐related properties include:
"HouseOfGraphID" House of Graphs identifier "LCFNotations" graph notations for embeddings based on Hamiltonian cycles "Notation" primary notation used for graph "NotationRules" rules for notations specifying the graph "WikidataID" Wikidata identifier - GraphData["class"] gives a list of named graphs in the specified class. GraphData[name,"class"] gives True or False, depending on whether the graph corresponding to name is in the specified class.
- GraphData[name,"Classes"] gives a list of the classes in which the graph corresponding to name appears.
- Basic classes of graphs include:
"Bipartite" bipartite (two components connected by every edge) "Nonplanar" nonplanar (requires crossings) "Nonsimple" nonsimple graph "Planar" planar (no crossings) "Simple" simple graph (unlabeled, undirected) "Tree" tree (no cycles) - Classes based on crossings include:
"Apex" apex graph "CriticalNonplanar" nonplanar and removal of any vertex gives a planar graph "Doublecross" crossing number 2 "DoubleToroidal" genus 2 "IntrinsicallyLinked" intrinically linked "LinklesslyEmbeddable" linklessly embeddable "Map" map graph "Nonplanar" crossing number ≥ 1 "Planar" crossing number 0 "Pretzel" genus 3 "Singlecross" crossing number 1 "Toroidal" minimally embeddable on a torus - Classes based on vertex degrees include:
"Cubic" each vertex is of degree 3 "HighlyIrregular" neighbors of each vertex have distinct vertex degrees "Multigraphic" one or more other graphs share the degree sequence "Octic" each vertex is of degree 8 "Quartic" each vertex is of degree 4 "QuasiRegular" each vertex is of the same degree except a single one with degree one larger than the others "Quintic" each vertex is of degree 5 "Regular" each vertex is of the same degree "Septic" each vertex is of degree 7 "Sextic" each vertex is of degree 6 "Switchable" can be reduced to another graph with the same degree sequence by edge switching "TwoRegular" each vertex is of degree 2 "Unigraphic" no other graph shares the degree sequence "Unswitchable" not switchable - Classes based on traversals include:
"Acyclic" free of cycles "AlmostHamiltonian" 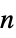 -node graph with Hamiltonian number
-node graph with Hamiltonian number 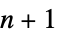
"AlmostHypohamiltonian" almost Hamiltonian "Antipodal" each vertex has exactly one maximum-distance vertex "Bridged" contains at least one bridge "Bridgeless" free of bridges "Chordal" free of chordless cycles of length at least 4 "Chordless" free of chords "Cyclic" contains at least one cycle "Eulerian" has a closed cycle containing every edge once "Geodetic" has a unique shortest path between any two vertices "HamiltonConnected" every pair of vertices bounds a Hamiltonian path "HamiltonDecomposable" has a partition of its edge set into Hamiltonian cycles "Hamiltonian" has a closed cycle containing every vertex once "HamiltonLaceable" Hamilton‐connected with bipartitioned endpoints "HStarConnected" either Hamilton‐connected or Hamilton‐laceable "Hypohamiltonian" one‐vertex‐removed graphs are Hamiltonian "Hypotraceable" one‐vertex‐removed graphs are traceable "KempeCounterexample" counterexample to Kempe's 4‐coloring algorithm "MaximallyNonhamiltonian" maximally nonhamiltonian "Median" median graph "Meyniel" every odd cycle of length ≥5 has at least 2 chords "Noneulerian" not Eulerian "Nonhamiltonian" not Hamiltonian "Pancyclic" contains cycles of all lengths from 3 to vertex count "SquareFree" free of 4‐cycles "Traceable" contains a Hamiltonian path "TriangleFree" free of 3‐cycles "Unicyclic" possesses a unique cycle "UniquelyHamiltonian" possessing a unique Hamiltonian cycle "UniquelyPancyclic" uniquely pancyclic "Untraceable" not traceable - Classes based on chess boards include:
"Antelope" moves of an antelope generalized chess piece "Bishop" moves of two (white and black) chess bishops "BlackBishop" moves of a chess black bishop "Fiveleaper" moves of a fiveleaper generalized chess piece "Camel" moves of a (1,3)-leaper graph "Giraffe" moves of a (1,4)-leaper graph "King" moves of a chess king "Knight" moves of a chess knight "Queen" moves of a chess queen "Rook" moves of a chess rook "RookComplement" graph complement of a rook graph "TriangularHoneycombAcuteKnight" moves of an acute knight on a triangular honeycomb chess board "TriangularHoneycombBishop" moves of a bishop on a triangular honeycomb chess board "TriangularHoneycombKing" moves of a king on a triangular honeycomb chess board "TriangularHoneycombObtuseKnight" moves of an obtuse knight on a triangular honeycomb chess board "TriangularHoneycombQueen" moves of a queen on a triangular honeycomb chess board "TriangularHoneycombRook" moves of a rook on a triangular honeycomb chess board "WhiteBishop" moves of a chess white bishop "Zebra" moves of a (2,3)-leaper graph - Classes based on symmetry and regularity include:
"ArcTransitive" ordered pairs of adjacent vertices have identical environments "Asymmetric" not symmetric "Chang" strongly regular on 28 vertices "ConformallyRigid" conformally rigid "DistanceRegular" all vertices have identical distance sets "DistanceTransitive" all pairs of vertices have identical distance environments "EdgeTransitive" all edges have identical environments "Geometric" every edge of a distance-regular graph lies in a unique Delsarte clique "Identity" automorphism group is of order unity "LocallyPetersen" locally Petersen "Nongeometric" nongeometric "Paulus" strongly regular on 25 or 26 vertices "Semisymmetric" regular and edge transitive but not vertex transitive "StronglyRegular" strongly regular "Symmetric" both edge transitive and vertex transitive "Taylor" distance regular with intersection array of form 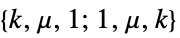
"UniquelyEmbeddable" uniquely embeddable "VertexTransitive" all vertices have identical environments "WeaklyRegular" regular, but not strongly regular "ZeroSymmetric" vertex‐transitive cubic with edges partitioned into three orbits "ZeroTwo" every two vertices have either 0 or 2 common neighbors - Spectral classes include:
"Integral" spectrum consists of integers "Line" line graph "Maverick" maverick graph - Classes based on forbidden graphs include:
"Beineke" Beineke graph (line graph forbidden induced subgraph) "Kuratowski" Kuratowski graph (planar graph forbidden induced subgraph) "Metelsky" Metelsky graph (ine graph forbidden if 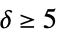 induced subgraph)
induced subgraph)"Pathwidth1ForbiddenMinor" pathwidth 1 forbidden minor "Pathwidth2ForbiddenMinor" pathwidth 2 forbidden minor "PetersenFamily" linklessly embeddable forbidden minor "ProjectivePlanarForbiddenMinor" projective planar forbidden minor "ProjectivePlanarForbiddenTopologicalMinor" projective planar forbidden topological minor "ToroidalForbiddenMinor" toroidal graph forbidden minor "UnitDistanceForbiddenSubgraph" minimal unit-distance forbidden subgraph - Special classes include:
"DistanceHereditary distance-hereditary graph "AlmostControllable" almost-controllable graph "Bicolorable" two or fewer vertex colors needed "Bicubic" bipartite and cubic "Biplanar" biplanar "Block" block graph "BracedPolygon" braced regular polygon graph "Cage" smallest graph of a given girth "Cayley" Cayley graph "ChromaticallyUnique" no other graph shares the chromatic polynomial "ClawFree" free of the claw graph "Conference" conference graph "Configuration" graph represents a point-line configuration "Controllable" controllable graph "Flexible" infinitesimally flexible graph "Fullerene" planar cubic with all bounded faces pentagons or hexagons "Fusene" planar 2‐connected with all bounded faces hexagons "Graceful" graceful graph "Imperfect" imperfect (i.e. not perfect) graph "Incidence" incidence graph of a configuration "Laman" minimal rigid (Laman) graph "LCF" describable in LCF notation (regular Hamiltonian) "Local" graph is locally a particular graph for all vertices "Matchstick" embeddable with a planar drawing having unit edge lengths "Moore" graphs with the Moore property "Nonempty" nonempty graph "NoPerfectMatching" has no perfect matching "Nuciferous" nuciferous graph "Nut" adjacency matrix has rank 1 and contains no 0 element "Ore" Ore graph "Outerplanar" outerplanar graph "Perfect" perfect graph "PerfectMatching" has a matching with 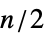 vertices
vertices"Polyhex" polyhex graph "Polyiamond" polyiamond graph "Polyomino" polyomino graph "ProjectivePlanar" graph can be drawn on the real projective plane "Ptolemaic" Ptolemaic graph "QuadraticallyEmbeddable" quadratically embeddable graph "Rigid" infinitesimally rigid graph "SelfComplementary" isomorphic to its complement "SelfDual" isomorphic to its dual "Split" split graph "StronglyPerfect" every induced subgraph 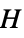 has an independent set meeting all maximal cliques of
has an independent set meeting all maximal cliques of 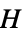
"UniquelyColorable" vertex-colorable in a single way modulo graph symmetry and permutation of colors "UnitDistance" embeddable with edges of unit length "WeaklyPerfect" clique number equals chromatic number "WellCovered" every minimal vertex cover has the same size - Classes associated with polyhedra include:
"Antiprism" skeleton of an antiprism "Archimedean" skeleton of one of the 13 Archimedean solids "ArchimedeanDual" skeleton of one of the 13 Archimedean duals "Dipyramid" skeleton of a dipyramid "JohnsonSkeleton" skeleton of one of the 92 Johnson solids "Platonic" skeleton of one of the five Platonic solids "Polyhedral" skeleton of a polyhedron "Prism" skeleton of a prism "RegularPolychoron" skeleton of one of the six regular four‐dimensional solids "Trapezohedron" skeleton of a trapezohedron "UniformSkeleton" skeleton of a uniform polyhedron "Wheel" skeleton of a pyramid - Snark-related classes include:
"Flower" flower graph (snark for n5, 7, …) "Goldberg" Goldberg graph (snark for n5, 7, …) "Snark" snark (cyclically 4-edge connected cubic graph with edge chromatic number 4 and girth at least 5) "WeakSnark" weak snark (cyclically 4-edge connected cubic graph with edge chromatic number 4 and girth at least 4) - Special classes of trees and their generalization include:
"Cactus" connected graph in which any two cycles have no edge in common "Caterpillar" vertices are on a central stalk or only one edge away from a stalk "Centipede" vertices and edges correspond to the configuration of a comb "Forest" a collection of trees (same as "Acyclic") "FullyReconstructibleC1" determined from its 1‐dimensional measurement variety "FullyReconstructibleC2" determined from its 2‐dimensional measurement variety "FullyReconstructibleC3" determined from its 3‐dimensional measurement variety "Halin" Halin graph "KTree" 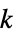 -tree
-tree"Lobster" removal of leaves gives a caterpillar "Pseudoforest" contains at most one cycle per connected component "Pseudotree" a connected pseudoforest "SeriesReduced" series-reduced tree (no vertices of degree 2) "Spider" one vertex of degree at most 3 and all others ≤2 "Tripod" a tree having exactly three tree leaves - Classes of graphs indexed by one or more integers include:
"Accordion" accordion graph "Alkane" n alkane graph "Apollonian" connectivity graph of a 2D Apollonian gasket "BipartiteKneser" vertices represent k subsets and n‐k subsets of 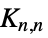
"Book" graph Cartesian product of a star and a two‐path graph "Bouwer" regular graphs including members that are symmetric but not arc transitive "Bruhat" graph whose vertices are permutations on n symbols with edges for permutations differing by an adjacent transposition "Caveman" caveman graph "Circulant" n vertices each with identical relative adjacencies "Complete" all pairs of vertices are connected "CompleteBipartite" all pairs connected across two disjoint sets of vertices "CompleteKPartite" all pairs connected across 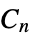 disjoint sets of vertices
disjoint sets of vertices"CompleteTripartite" all neighboring pairs connected across three disjoint sets of vertices "Cone" graph join of a cycle graph and empty graph "Crown" complete bipartite 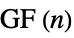 with horizontal edges removed
with horizontal edges removed"Cycle" a single cycle through n vertices "CycleComplement" complement graph of the cycle graph 
"Cyclotomic" graph with vertices adjacent if their difference is a cube in 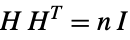
"DiagonalIntersection" graph with vertices formed from the vertices of a regular n-gon and the intersection of its diagonals "Dipyramid" skeleton graph of an n-dipyramid "Doob" Cartesian product of Shrikhande graphs and a Hamming graph "DorogovtsevGoltsevMendes" Dorogovtsev-Goltsev-Mendes graph "DoubleCone" double cone graph with n-gonal bases "Egawa" Egawa graph "Empty" n vertices with no edges "Fan" graph join of an empty graph with a path graph "FibonacciCube" a Fibonacci cube graph "Flower" flower graph (snark for n5, 7, …) "FoldedCube" folded n‐hypercube graph "Gear" a wheel with vertices added between the vertices of the outer cycle "GeneralizedPolygon" an incidence plane based on a symmetric binary relation "GoethalsSeidelBlockDesign" Goethals–Seidel block design graph "Goldberg" Goldberg graph (snark for n5, 7, …) "Grassmann" Grassmann graph "Grid" an array of points with grid connectivity "Haar" Haar (regular bipartite) graph of index n "Hadamard" graph corresponding to a 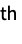 matrix satisfying
matrix satisfying 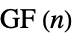
"HalvedCube" halved n‐hypercube graph "Hamming" direct product of m complete graphs of size n "Hanoi" a Hanoi graph "Harary" a Harary graph "Helm" a wheel with a pendant edge adjoined at each cycle vertex "HexagonalGrid" hexagonal grid graph "HoneycombToroidal" honeycomb toroidal graph "Hypercube" an n‐dimensional hypercube "IGraph" generalization of a generalized Petersen graph "Jahangir" Jahangir graph "Johnson" graph describing adjacencies in the m‐subsets of an n‐set "JohnsonSkeleton" skeleton graph of the n 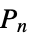 Johnson solid
Johnson solid"KayakPaddle" kayak paddle graph "Keller" Keller graph "KleinBottleTriangulation" a regular triangulation of a Klein bottle "Kneser" vertices represent k‐subsets of {1,…,n} "Ladder" a 2n‐vertex ladder graph "LadderRung" graph union of n two‐paths "LindgrenSousselier" Lindgren-Sousselier graphs "LucasCube" Lucas cube graph "Mathon" Mathon graph "MengerSponge" connectivity graph of a Menger sponge "MiddleLayer" middle layer graph "MoebiusLadder" an n‐sided prism graph with a half‐twist "Mycielski" a triangle‐free graph with chromatic number n "Odd" an odd graph "Paley" graph with vertices adjacent if their difference is a square in 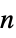
"Pan" an n‐cycle connected to a singleton graph by a bridge "Pasechnik" Pasechnik graph "Path" an n‐vertex tree with no branches "PathComplement" complement graph of the path graph 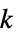
"Pell" Pell graph "PermutationStar" a "star graph" on permutations of {1,…,n} with edges at swaps "PlummerToft" Plummer-Toft graphs "SierpinskiCarpet" connectivity graph of the Sierpiński carpet "SierpinskiSieve" connectivity graph of the Sierpiński sieve "SierpinskiTetrahedron" connectivity graph of the Sierpiński tetrahedron (tetrix) "Spoke" spoke graph with 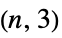 arms and
arms and 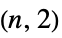 vertices per arm
vertices per arm"StackedBook" graph Cartesian product of a star and a path graph "StackedPrism" a stacked prism graph "Star" a center vertex connected to n‐1 vertices "Sun" a complete graph with erected triangles on outer edges "Sunlet" a cycle with pendant edges "Tetrahedral" an 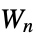 ‐Johnson graph
‐Johnson graph"TorusGrid" grid graph on a torus "TorusTriangulation" a regular triangulation of a torus "Transposition" a transposition graph "Triangular" an 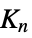 ‐Johnson graph
‐Johnson graph"TriangularGrid" a triangular grid graph "TriangularSnake" triangular snake graph "Turan" a Turán graph on n vertices that is (k+1)‐clique free "Wheel" a cycle with all vertices connected to a center "WheelComplement" complement of a wheel graph 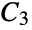
"Windmill" m copies of the complete graph 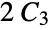 with a vertex in common
with a vertex in common"Wreath" n collections of k nodes arranged around a circle such that all nodes in adjacent collections are connected - GraphData[name,"property","type"] gives a set of specific graphs, images, or embeddings, where in 2D "type" may include "3D", "All", "Circulant", "Circular", "Degenerate", "Gear", "GeneralizedPetersen", "Grid", "Halin", "IGraph", "IntegerCoordinates", "Integral", "LCF", "Linear", "Matchstick", "MinimalCrossing", "MinimalIntegral", "MinimalLocalCrossing", "MinimalPlanarIntegral", "MinimalRectilinearCrossing", "MinimalRectilinearLocalCrossing", "Perspective", "Planar", "Polyiamond", "Polyomino", "Primary", "Torus", "TriangularGrid", "UnitDistance", and "XYZ"; and in 3D "type" may include "Grid", "IntegerCoordinates", "Integral", "Polyhedron", "Primary", "TetrahedralGrid", "UnitDistance", and "XYZ".
- Type properties related to graph display include:
"Embeddings" embeddings of a given type "EmbeddingClasses" list of embedding classifications "Graph" graph of a given type "Graphics" graphics "Graphics3D" 3D graphics "Image" images of a given type "MeshRegion" mesh region - GraphData[name,"property","outputtype"] gives graph properties in the format specified by "outputtype", which, depending on "property", may be "All", "Count", "Directed", "Edge", "Entity", "Graph", "Graphics", "Group", "Image", "Labeled", "List", "Name", "Pair", "Polyhedron", "Rule", or "Undirected".
- Output type properties related to graph output include:
"BipartiteDoubleGraph" bipartite double graph "CanonicalGraph" canonical version of graph that is isomorphic to the original "CayleyGraphGeneratingGroups" groups generating corresponding to graph as a Cayley graph as groups, entities, or entity names "CochromaticGraphs" cochromatic graphs as graphs, entities, entity names, 3D graphs, graphics, or images "CodegreeSequenceGraphs" codegree sequence graphs as graphs, entities, entity names, 3D graphs, graphics, or images "ComplementGraph" complement graph as a graph, entity, entity name, graphics, or image "ConnectedComponents" connected components as graphs, entities, entity names, 3D graphs, graphics, or images "CoresistanceGraphs" coresistance graphs as graphs, entities, entity names, 3D graphs, graphics, or images "CospectralGraphs" cospectral graphs as graphs, entities, entity names, 3D graphs, graphics, or images "CubeGraph" cube graph as a graph, entity, entity name, graphics, or image "DualGraph" dual graph as a graph, entity, entity name, graphics, or image "LeviGraph" Levi graph as a graph, entity, entity name, graphics, or image "LineGraph" line graph as a graph, entity, entity name, graphics, or image "LocalGraph" local graph as a graph, entity, entity name, graphics, or image "OrdinaryLineGraph" ordinary line graph "PolyhedralEmbeddings" polyhedra having given graph as a skeleton as polyhedra, entities, or entity names "RootGraph" root graph as a graph, entity, entity name, graphics, or image "SimplexGraph" simplex graph as a graph, entity, entity name, graphics, or image "SquareGraph" square graph as a graph, entity, entity name, graphics, or image - GraphData[name,"property","ann"] or GraphData["property","ann"] gives various annotations associated with a property. Typical annotations include:
"Description" short textual description of the property "Information" hyperlink to additional information "LongDescription" longer textual description of the property "Note" additional information about the property "Value" the value of the property - Using GraphData may require internet connectivity.
Examples
open allclose all
Basic Examples (4)
Return a list of standard names for all simple graphs on 5 vertices:
Give the corresponding Graph objects:
Do the same without explicitly specifying the default "Graph" property:
Return the Pappus graph:
Show all available 2D embeddings of the graph:
Show the spectrum of the icosahedral graph:
Generate a list of named snark graphs:
Visualize the snarks:
Scope (741)
Names and Classes (7)
Obtain a list of all standard implemented graphs:
Obtain a list of all implemented graphs:
Find the English name of a graph:
A list of alternate names can also be found:
Additional names acceptable as input can be found:
Find the list of graph classes:
Find the list of named graphs belonging to a class:
Test whether a graph belongs to a class:
Properties and Annotations (2)
Get a list of properties for a particular graph:
Get a short textual description of a property:
Get a longer textual description:
Property Values (4)
The values of properties may take a variety of forms as Wolfram Language expressions:
A property that is not available for a graph has the value Missing["NotAvailable"]:
Some graph properties may be Missing but still include partial information:
A property whose value is too large to include has the value Missing["TooLarge"]:
Detailed Properties (728)
Basic Graph Properties (9)
Give the adjacency matrix, returned as a SparseArray object:
Convert to an explicit matrix:
Plot the matrix using ArrayPlot:
Verify that the positions of 1s in the adjacency matrix correspond to graph edges:
List the number of distinct adjacency matrices possible for the cubical graph:
Return the number of edges of the octahedral graph:
Compare with taking the length of the edge list:
Return the edges of the octahedral graph:
Give the face count of the octahedral graph:
Give the faces of the octahedral graph:
Give the incidence matrix of the octahedral graph:
Give it in expanded form:
Plot the matrix:
Give the number of vertices of the octahedral graph:
Return the vertices of the octahedral graph:
Properties Related to Graph Connectivity (30)
Give the block count of the butterfly graph:
Show the blocks:
Give the blocks of the butterfly graph:
Show the original graph:
Show the bridges of the 3-barbell graph:
List all connected graphs:
List connected graphs on five vertices:
Check if the graph 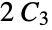 is connected:
is connected:
Check if the graph 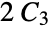 is connected:
is connected:
Return the number of connected components in the 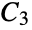 graph:
graph:
Do the same using the "Count" annotation:
Return the connected components of the 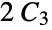 graph:
graph:
List the names of the connected components:
List the indices of connected components:
Give the number of connected induced subgraphs of the diamond graph:
Compare with the value obtained from the connected induced subgraph polynomial:
Display the diamond graph and compare the above counts with those computed from scratch:
Give the connected induced subgraph polynomial of the diamond graph:
Compare to the actual subgraphs:
Give the cyclic edge connectivity of the Petersen graph:
Show the two cyclic components of a edge cut set of size 5:
List disconnected graphs on five vertices:
Check if the graph 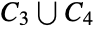 is disconnected:
is disconnected:
Check if the graph 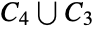 is disconnected:
is disconnected:
Find the edge connectivity of a complete binary tree of order 4:
Return the number of edge cuts in the triangle graph:
Do the same with the "Count" annotation:
Compare with the length of edge cuts:
Show the edge cuts in the triangle graph:
Visualize how the cuts disconnect the graph:
Give the incidence lines that generate the Pappus graph:
Show the Levi graph generated by these incidences:
Identify the resulting graph:
Give a realization of the Pappus configuration showing the incidences:
Give the lambda components of the domino graph:
Give the Luccio–Sami components of the domino graph:
Return the number of minimal edge cuts in the triangle graph:
Do the same with the "Count" annotation:
Compare with the length of edge cuts:
Show the minimal edge cuts in the triangle graph:
Visualize how the cuts disconnect the graph:
Return the number of minimal vertex cuts in the butterfly graph:
Do the same with the "Count" annotation:
Compare with the length of edge cuts:
Show the minimal edge cuts in the butterfly graph:
Visualize how the cuts disconnect the graph:
Return the number of minimum vertex cuts of the square graph with triangles erected on two opposite sides:
Return as an annotation:
Compare with the cuts:
Give the number of minimum cyclic edge cuts of the Petersen graph:
Do the same as an annotation to "MinimumCyclicEdgeCuts":
Compare with the number of minimum cyclic edge cuts:
Return the minimum cyclic edge cuts of the Petersen graph:
Compare with the cyclic edge connectivity:
Visualize the cuts to reveal the resulting two cyclic components:
Give the minimum vertex cuts of the square graph with triangles erected on two opposite sides:
Show the disconnected graphs resulting from these cuts:
Give spanning trees for the tetrahedral graph:
Give the strength of the butterfly graph:
Compute using edge cuts:
Give the toughness of the butterfly graph:
Compute using edge cuts:
Give the vertex connectivity of Tietze's graph:
Return the number of vertex cuts in the butterfly graph:
Do the same with the "Count" annotation:
Compare with the length of edge cuts:
Show the vertex cuts of the butterfly graph:
Visualize how the cuts disconnect the graph:
Properties Related to Graph Minors (2)
Show the number of graph minors the octahedral graph:
Give the Hadwiger number of a wheel complement graph:
Properties Related to Graph Display (12)
Show the default embedding of the octahedral graph:
Show classes of tabulated 2D embeddings of the cubical graph:
Show classes of known 3D embeddings of the cubical graph:
List the known 2D embeddings of the octahedral graph:
List the known 3D embeddings of the octahedral graph:
Show the default embedding of the octahedral graph:
Show the default 3D embedding of the octahedral graph:
Show a labeled version:
Give all cataloged 3D embeddings of the cubical graph:
Show a graphic of the octahedral graph:
Show a labeled version:
Give all cataloged embeddings of the octahedral graph as graphics:
Show a 3D graphic of the octahedral graph:
Show a labeled version:
Give all cataloged embeddings of the cubical graph as 3D graphics:
Show an image of the default embedding of the octahedral graph:
Show the three-dimensional embedding of the cubical graph as an image:
Show the Nauru graph as a mesh region:
Label the mesh:
Show all available embeddings as mesh regions:
Show a mesh region embedded in 3D:
Show the icosahedral graph as a polyhedron:
Return the vertex coordinates for the default embedding of the octahedral graph:
Plot the vertices:
Show vertex coordinates for all cataloged embeddings:
Annotatable Properties Related to Graph Output (20)
Return the bipartite double graph of the Clebsch graph:
Give the standard name of the bipartite double graph:
Return the cubical graph in canonical form:
The edge lists are not necessarily the same:
Verify the graphs are isomorphic:
Return groups whose Cayley graphs generate the cubical graph using the default output type:
Return them explicitly as groups:
Return FiniteGroupData standard names whose Cayley graphs generate the cubical graph:
Return FiniteGroupData entities whose Cayley graphs generate the cubical graph:
Give cochromatic graphs of the claw graph:
Return the names of the cochromatic graphs:
Verify these share the same chromatic polynomial:
Show graph names for graphs that are cochromatic with the 5-star graph:
Give the names of graphs cochromatic with the bull graph:
Return the co-degree sequence graphs of the 5-path graph:
Since this graph shares a degree sequence, it is not unigraphic:
Return the graph complement of the icosahedral graph:
Do the same using the annotation "Graph":
Return as an Image:
Return as a Graphics object:
Give the name of the complement graph:
Return the entity corresponding to the complement graph:
Show the graph names for the complement of graphs on four or fewer vertices:
The complement graph name of a self-complementary graph is identical to the StandardName:
Show graph and complement names (should be the same) for "interesting" small self-complementary graphs:
Return the connected components graph of the 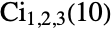 graph:
graph:
Do the same using the "Graph" annotation:
Return the indices of the connected components:
Return the names of the connected components:
Return the number of connected components:
Do the same using the "Count" annotation:
Give the vertex counts of the connected components:
Do the same using the "List" annotation:
Do the same using the "VertexCount" annotation:
Show coresistance graphs:
Do the same using the "Graph" annotation:
Get the names of the coresistance graphs:
Show the graph and its coresistance graph together:
Verify that the graphs in question have the same resistance sets:
Show graphs that share a resistance multiset with at least one other distinct graph:
List the names of graphs sharing the same multiset of resistances with a given graph:
Display these graphs:
Show graph names for graphs that are equivalent with a particular 20-vertex graph:
Return the cospectral graphs of the tesseract graph using the default output type:
Return the cospectral graphs of the tesseract graph explicitly as a graph:
Return the standard names:
Return graphics:
Return entities:
Return images:
Give the names of graphs cospectral with the Shrikhande graph:
Show graph names for graphs that are cospectral with the tesseract graph:
Return a graph object for the cube graph of the 7-antiprism graph:
Compare with an explicit computation:
Return the name:
Return a graph object for the dual graph of the icosahedral graph:
Return the name:
Not all graphs have unique duals:
Show the graph name for the graph that is dual to the icosahedral graph:
It is in turn dual to the icosahedral graph:
List graphs with a tabulated graph dual:
Display the Johnson solid J8 skeleton:
Verify that it is dual to itself:
Tabulate cataloged self-dual graphs:
Return the Levi graph of the Desargues configuration graph:
Return the name of the Levi graph of the Desargues configuration graph:
Visualize the Desargues configuration:
Return the lines:
Compute the Levi graph explicitly:
Return the line graph of the icosahedral graph:
Return the name of the line graph:
Give the name of the line graph for the Petersen graph:
Give the names of the line graphs of the Platonic graphs:
Show the Platonic graphs and their line graphs:
Show the graph names for the line graphs of non-empty graphs on four or fewer vertices:
Taking the line graph twice does not in general give back the original graph:
The line graph of a graph is isomorphic to itself only for cycle graphs or unions of identical cycle graphs:
Return the local graph of the Conway–Smith graph:
Return the name of the local graph:
Return the name of the ordinary line graph of the pentagram configuration:
Return the ordinary line graph of the pentagram configuration:
Compute by finding the extraordinary lines of the pentagram configuration:
Complement with all possible pairs of points to get the ordinary lines:
Build the ordinary line graph:
Identify using ToEntity:
Return polyhedra whose skeletons are isomorphic to the cubical graph using the default output type:
Return explicitly as PolyhedronData standard names:
Return them as polyhedra:
Return them as entities:
Return the root graph of the icosahedral line graph:
Return the name of the line graph:
Return a graph object for the simplex graph of the complete graph K4:
Return the name:
Return a graph object for the square graph of the 7-antiprism graph:
Compare with an explicit computation:
Return the name:
Annotatable Properties Related to List-Type Output (10)
Give the adjacency matrix of the default embedding for the square graph:
Give the number of possible adjacency matrices:
Return the same using the "Count" annotation:
Give all possible adjacency matrices:
Give (undirected) cycles of the house graph:
Do the same using the explicit "Undirected" annotation:
Give directed cycles:
Give count of undirected cycles:
Compare with the direct property:
Return the edges of the octahedral graph:
Verify the above agrees with the "EdgeCount" property:
Return the edges as a set of rules, suitable for plotting in GraphPlot:
Return a graphic of the edges:
Give (undirected) Eulerian cycles of the butterfly graph:
Compare with the output of FindEulerianCycle:
Do the same using the explicit "Undirected" annotation:
Give directed cycles:
Give count of undirected cycles:
Compare with the direct property:
Give the faces of the octahedral graph:
Verify the above agrees with the "FaceCount" property:
Show the faces of the octahedral graph:
Give (undirected) Hamiltonian cycles of the house X graph:
Do the same using the explicit "Undirected" annotation:
Give directed Hamiltonian cycles:
Give count of undirected Hamiltonian cycles:
Compare with the direct property:
Give (undirected) Hamiltonian paths of the butterfly graph:
Do the same using the explicit "Undirected" annotation:
Give directed Hamiltonian paths:
Give count of undirected Hamiltonian paths:
Compare with the direct property:
Give (undirected) Hamiltonian walks of the butterfly graph:
Do the same using the explicit "Undirected" annotation:
Give directed Hamiltonian paths:
Give count of undirected Hamiltonian paths:
Compare with the direct property:
Give the vertex coordinates of the default embedding of the octahedral graph:
Specify the "All" annotation:
This is equivalent to the "Embeddings" property:
Plot the vertex positions:
Return the vertices of the octahedral graph:
Verify the above agrees with the "VertexCount" property:
Annotatable Properties Related to Graph Display (7)
Give all tabulated embeddings of the cubical graph:
Show classes for each embedding:
Display all embeddings:
Return the primary embedding of a graph:
Return all tabulated planar embeddings of the graph:
Return all tabulated LCF embeddings of the graph:
Give all tabulated 3D embeddings of the cubical graph:
Show classes for each 3D embedding:
Return all tabulated Polyhedron embeddings of the graph:
Return the cubical graph as a graph object:
Show a labeled version:
Return tabulated planar embeddings:
Return the cubical graph as a 3D graph object:
Show a labeled version:
Return tabulated polyhedron embeddings:
Return the cubical graph as a graphics object:
Show a labeled version:
Return tabulated planar embeddings:
Return the cubical graph as a 3D graph object:
Show a labeled version:
Return tabulated polyhedron embeddings as graphics objects:
Return an image of the primary embedding of a graph:
Show a labeled version:
Give all cataloged embeddings of the octahedral graph:
Show the three-dimensional embedding of the cubical graph as an image:
Show a labeled version:
Give all cataloged 3D embeddings of the cubical graph as images:
Properties Representing Graph Polynomials (43)
Display the characteristic polynomial of the Coxeter graph as a pure function:
As a function of a variable x:
Compare with the directly computed value:
Give the chordless cycle polynomial of the cubical graph as a pure function:
Extract tallies by cycle length:
Extract tallies by cycle length a different way:
Compare with the tallies of chordless cycle lengths:
Give the chromatic polynomial of the cubical graph as a pure function:
As a function of a variable x:
The chromatic polynomial is a special case of the rank polynomial:
Give the chromatic polynomial of the icosahedral graph in terms of a variable x:
Give the clique polynomial of the utility graph as a pure function:
Compare to the explicit cliques:
Give the complement chordless cycle polynomial of the 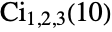 circulant graph as a pure function:
circulant graph as a pure function:
Extract tallies by cycle length:
Extract tallies by cycle length a different way:
Compare with the tallies of complement chordless cycle lengths:
Give the complement odd chordless cycle polynomial of the 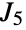 circulant graph as a pure function:
circulant graph as a pure function:
Extract tallies by cycle length:
Extract tallies by cycle length a different way:
Compare with the tallies of complement odd chordless cycle lengths:
Give the coboundary polynomial of the complete graph K5 as a pure function:
As a function of a variables q and t:
The coboundary polynomial is a special case of the Tutte polynomial:
Give the connected domination polynomial of the fish graph:
Compare with the connected dominating set count:
Compare with connected dominating set tallies:
Give the connected induced subgraph polynomial of the Eiffel Tower graph:
Compare with the count of connected induced subgraphs:
Give the cycle polynomial of the cubical graph as a pure function:
Compare to cycle tallies:
Give the detour polynomial of the cubical graph as a pure function:
As a function of a variable x:
Give the distance polynomial of the cubical graph as a pure function:
As a function of a variable x:
Compute from distance matrix:
Give the domination polynomial of the Coxeter graph as a pure function:
As a function of a variable x:
Give the edge cover polynomial of the utility graph as a pure function:
As a function of a variable x:
Compare to the explicit covers:
Give the edge cut polynomial of the utility graph as a pure function:
As a function of a variable x:
Compare to the explicit cuts:
Give the flow polynomial of the cubical graph as a function of a variable u:
The flow polynomial is a special case of the rank polynomial:
Give the idiosyncratic polynomial of the cubical graph:
Compare with a direct computation:
Give the independence polynomial of the cubical graph:
Give the irredundance polynomial of the cubical graph:
Compute from the irredundant sets:
Give the Laplacian polynomial of the cubical graph as a pure function:
As a function of a variable x:
Compute from Laplacian polynomial:
Give the matching generating polynomial of the cubical graph:
Give the matching polynomial of the cubical graph:
Give the maximal clique polynomial of the house graph as a pure function:
Extract tallies by maximal clique size:
Extract tallies by maximal clique size a different way:
Compare with the tallies of maximal clique sizes:
Give the maximal independence polynomial of the cricket graph as a pure function:
Extract tallies by maximal independent vertex set size:
Extract tallies by maximal independent vertex set size a different way:
Compare with the tallies of maximal independent edge sets:
Give the maximal irredundance polynomial of the cricket graph as a pure function:
Extract tallies by maximal irredundant set size:
Extract tallies by maximal irredundant set size a different way:
Compare with the tallies of maximal irredundant sets:
Give the maximal matching generating polynomial of the cricket graph as a pure function:
Extract tallies by maximal independent edge set size:
Extract tallies by maximal independent edge set size a different way:
Compare with the tallies of maximal independent edge sets:
Give the minimal connected domination polynomial of the 5-wheel graph as a pure function:
Extract tallies by minimal connected dominating set size:
Extract tallies by minimal connected dominating set size a different way:
Compare with the tallies of minimal connected dominating sets:
Give the minimal domination polynomial of the cricket graph as a pure function:
Extract tallies by minimal dominating set size:
Extract tallies by minimal dominating set size a different way:
Compare with the tallies of minimal dominating sets:
Give the minimal edge cover polynomial of the cricket graph as a pure function:
Extract tallies by minimal edge cover size:
Extract tallies by minimal edge cover size a different way:
Compare with the tallies of minimal edge covers:
Give the minimal edge cut polynomial of the utility graph as a pure function:
As a function of a variable x:
Compare to the explicit cuts:
Give the minimal total domination polynomial of the butterfly graph as a pure function:
Extract tallies by total dominating set size:
Extract tallies by total dominating set size a different way:
Compare with the tallies of total dominating sets:
Give the minimal vertex cover polynomial of the cricket graph as a pure function:
Extract tallies by minimal vertex cover size:
Extract tallies by minimal vertex cover size a different way:
Compare with the tallies of minimal vertex covers:
Give the minimal vertex cut polynomial of the utility graph as a pure function:
As a function of a variable x:
Compare to the explicit cuts:
Give the odd chordless cycle polynomial of the Golomb graph as a pure function:
Extract tallies by odd chordless cycle lengths:
Extract tallies by odd chordless cycle lengths in a different way:
Compare with the tallies of odd chordless cycle lengths:
Give the path polynomial of the cubical graph as a pure function:
Compare to cycle tallies:
Give the _Q_-chromatic polynomial of the Chvátal graph:
Give the rank polynomial of the cubical graph:
Give the reliability polynomial of the cubical graph:
The reliability polynomial is a special case of the Tutte polynomial:
Give the sigma polynomial of the cubical graph:
Give the total domination polynomial of the 5-wheel graph as a pure function:
Extract tallies by total dominating set size:
Extract tallies by total dominating set size a different way:
Compare with the tallies of total dominating sets:
Give the Tutte polynomial of the cubical graph:
The Tutte polynomial is a special case of the rank polynomial:
Give the vertex cover polynomial of the utility graph as a pure function:
Compare to the explicit covers:
Give the vertex cut polynomial of the utility graph as a pure function:
As a function of a variable x:
Compare to the explicit cuts:
Coloring-Related Graph Properties (13)
Give the chromatic invariant cubical graph:
Give the chromatic number of the cubical graph:
Compare with the built-in function:
Visualize the chromatic number:
Give the edge chromatic number of the cubical graph:
Compare with the built-in function:
Visualize the edge chromatic number:
Give the fractional chromatic numbers of the Mycielski graphs:
Compare with the closed form known for this fractional chromatic number:
Return the chromatic roots of the first Harvey–Royle graph:
Verify equality with the roots of the chromatic polynomial:
Return the cyclic chromatic number of of 2-Plummer–Toft graph:
Give the fractional edge chromatic numbers of the flower snark 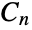 :
:
Give a minimum edge coloring of the octahedral graph:
Visualize the coloring:
Give the number of minimum vertex colorings of the octahedral graph:
Do the same using an annotation:
Compare with the number of actual colorings:
Give the minimum vertex colorings of the octahedral graph:
Verify the colorings are consistent with the chromatic number:
Visualize the colorings:
Show a minimum-weight fractional coloring of the Petersen graph:
Compute the fractional chromatic number:
Compare with the direct property:
Give the _Q_-chromatic polynomial of the Chvátal graph:
The _Q_-chromatic polynomial has smaller degree and coefficients than the usual chromatic polynomial for graphs with chromatic number at least 3:
The _Q_-chromatic polynomial is not defined for graphs with chromatic number less than 3:
Give the Weisfeiler–Leman dimension of the tetrahedral graph:
Graph Index Properties (18)
Give the ABC index of the butane graph:
Compare with the sum of ABC matrix elements:
Give the arithmetic-geometric index of the propane graph:
Compare with the sum of arithmetic-geometric matrix elements:
Display the Balaban index of the Coxeter graph:
Give the Balaban index of the isobutane graph:
Give the circuit rank of the Coxeter graph:
Display the circuit rank of the icosahedral graph:
Compare with the value obtained from other properties:
Give the detour index of the cubical graph:
Give the Harary index of the cubical graph:
Give the Hosoya index of the cubical graph:
The Hosoya index is identical to the independent edge set count:
Give the Kirchhoff index of the cubical graph:
Give the Kirchhoff index of the isobutane graph:
Give the Kirchhoff sum index of the cubical graph:
Give the Kirchhoff sum index of the isobutane graph:
Give the molecular topological index of the cubical graph:
Give the stability index of the cubical graph:
Give the Randić index of the octahedral graph:
Compare with the sum of Randić matrix elements:
Give the Sombor index of the octahedral graph:
Compare with the sum of Sombor matrix elements:
Give the topological index of the cubical graph:
Give the Wiener index of the cubical graph:
Give the Wiener index of the isobutane graph:
Give the Wiener sum index of the cubical graph:
Give the Wiener sum index of the isobutane graph:
Give the first Zagreb index of the cubic graph:
The first Zagreb index is defined as the sum of squared vertex degrees:
Give the second Zagreb index of the cubic graph:
The second Zagreb index is defined as the sum of squared vertex degrees:
Matrix Graph Properties (12)
Give the ABC matrix of the propane graph:
Give the arithmetic-geometric matrix of the propane graph:
Give the adjacency matrix, returned as a SparseArray object:
Convert to an explicit matrix:
Plot the matrix using ArrayPlot:
Verify that the positions of 1s in the adjacency matrix correspond to graph edges:
Give the detour matrix of the cubical graph:
Return the distance matrix of the octahedral graph:
Give the incidence matrix of the octahedral graph:
Give it in expanded form:
Plot the matrix:
Give the Laplacian matrix of the octahedral graph:
Give it in expanded form:
Plot the matrix:
Show the maximum flow matrix for the E graph:
Show the minimum cost flow matrix for the E graph:
Give the normalized Laplacian matrix of the octahedral graph:
Give the matrix in expanded form:
Plot the matrix:
Give the Randić matrix of the propane graph:
Give the resistance matrix of the cubical graph:
Give the Sombor matrix of the propane graph:
Local Graph Properties (6)
Find graphs having bridges:
List the bridges of the Walther graph:
Number of bridges:
Do the same using the "Count" annotation:
Give the number of chords in the house graph:
Give the chord:
List the chords of the house graph:
Number of chords:
Do the same using the "Count" annotation:
Display the curvatures of the A graph:
Show isolated points:
Find leaves:
Show number of leaves directly:
Do the same using the "Count" annotation:
Visualize:
Global Graph Properties (29)
Show the anarboricity of the cycle graph 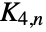 :
:
Give the number of apices of the Wagner graph:
Do the same as an annotation:
Compare with the length of the list of apices:
List named connected (nonplanar) apex graphs:
Find all apices of the Wagner graph:
Delete apices and verify planarity of the resulting graphs:
Show the arboricity of the complete graphs:
Compare with the value form theory:
Give the number of articulation vertices in the A-graph:
Compare with the list of articulation vertices:
Find graphs having articulation vertices:
Give the indices of the articulation vertices of the isobutane graph:
Visualize the articulation vertices:
Display the center of a tree:
Visualize the center:
Display the circumference of the icosahedral graph:
Verify that this corresponds to the length of the longest cycle:
Display the corank of the icosahedral graph:
Compute the corank from other graph properties:
Give the graphs on four or fewer vertices that are determined by resistance:
Check if the cubical graph is determined by spectrum:
Check if the tesseract graph is determined by spectrum:
Give the names of the graphs with the same spectrum as the tesseract graph:
Give the diameter of the Pappus graph:
Give the eccentricities of the Pappus graph:
Give the intersection array of the cubical graph:
Display the maximum leaf number of the A graph:
The maximum leaf number is the maximum possible leaf count of a spanning tree:
Give the maximum vertex degree of the E graph:
Display the mean curvature of the A graph:
The mean curvature is the mean of the curvatures associated with individual vertices:
Display the mean distance of the Petersen graph:
Display the minimum leaf number of the A graph:
The maximum leaf number is the minimum possible leaf count of a spanning tree:
Give the minimum vertex degree of the E graph:
Display the periphery of a tree:
Visualize the periphery:
Display the quadratic embedding constant of the icosahedral graph:
For graphs whose distance matrices have constant row sums, the quadratic embedding constant equals the second largest eigenvalue of the distance matrix:
Display the rank of the icosahedral graph:
Compute the rank from other graph properties:
Display the regular parameters of the cubical graph:
Display the skewness of the tesseract graph:
Compare with the result from theory:
Display the number of spanning trees in the 120-cell graph:
Show the triameter of the Coxeter graph:
Compare with the directly computed value:
Show the vertex degrees of the claw graph:
Give the toroidal crossing numbers for complete graphs:
Spectral Graph Properties (13)
Give the ABC energy of isobutane:
Compare with the sum of absolute values of the eigenvalue of the ABC matrix:
Give the ABC spectral radius of isobutane:
Compare with the largest eigenvalue of the ABC matrix:
Give the algebraic connectivity of isobutane:
Algebraic connectivity is defined as the second smallest member of the Laplacian spectrum:
Compare with the second smallest eigenvalue of the Laplacian matrix:
Give the arithmetic-geometric energy of methane:
Compare with the sum of absolute values of the eigenvalue of the arithmetic-geometric matrix:
Give the arithmetic-geometric spectral radius of isobutane:
Compare with the largest eigenvalue of the arithmetic-geometric matrix:
Display the Laplacian spectral radius of the tesseract graph:
The Laplacian spectral radius is the largest eigenvalue of the Kirchhoff matrix:
Display the Laplacian spectral ratio of the tesseract graph:
The Laplacian spectral ratio is defined as the ratio of the Laplacian spectral radius to the algebraic connectivity:
Display the Laplacian spectrum of the 600-cell graph:
Display a nicely formatted version:
Give the Randić energy of isobutane:
Compare with the sum of absolute values of the eigenvalue of the Randić matrix:
Give the Sombor energy of isobutane:
Compare with the sum of absolute values of the eigenvalue of the Sombor matrix:
Give the Sombor spectral radius of isobutane:
Compare with the largest eigenvalue of the Sombor matrix:
Give the spectral radius of the 600-cell graph:
Compare with the graph spectrum:
Display the spectrum of the 600-cell graph:
Display a nicely formatted version:
Labeled Graph Properties (11)
Return the average disorder number of the cubical graph:
Compare with the Wiener index:
Return the disorder number of the cubical graph:
Return the Erdős sequence of the 2-triangular grid graph:
Construct the corresponding Erdős graph:
Identify the graph:
Return the number of fundamentally distinct graceful labelings for the tetrahedral graph:
Do the same using the "Count" annotation:
Compare with the number of distinct labelings:
Show the fundamentally distinct graceful labelings of the tetrahedral graph:
Visualize the first labeling:
Verify the labeling is graceful:
Give the irregularity strength of the 5-star graph:
Return the connected graphs for which the irregularity strength equals one less than the vertex count:
Give the number of pinnacle sets in the banner graph:
Do the same with the "Count" annotation:
Compare with the length of actual sets:
Return the pinnacle sets of the banner graph:
Show labelings of the graph corresponding to these pinnacle sets:
Show the fundamentally distinct optimal radio labelings of the 5-path graph:
Visualize the first labeling:
Return the number of fundamentally distinct optimal radio labelings for the 5-path graph:
Do the same using the "Count" annotation:
Compare with the number of distinct optimal labelings:
Give the radio number of the 5-path graph:
Compare again the maximum label of all distinct optimal radio labelings:
Graph Construction Properties (2)
Display the assembly number of the pentatope graph:
Display the construction number of the pentatope graph:
Topological Graph Properties (10)
Display the crossing number of the icosahedral graph:
The crossing number is 0 since the graph is planar:
Return the dimension of the cubical graph:
Show unit-distance embeddings in the plane corresponding to dimension 2:
Give the genus of the cubical graph:
Give the genus of the unique graph that triangulates the torus and Klein bottle:
Give the Klein bottle crossing number of the unique graph that triangulates the torus and Klein bottle:
Display the local crossing number of the complete graph K6:
Display embeddings with this number of crossings:
The crossed dodecahedral graph has a unique 2-planar embedding, but does not admit a straight-line 2-planar drawing:
Return the metric dimension of the cubical graph:
Give the projective plane crossing numbers of the complete bipartite graphs  :
:
Compare with the known closed-form values:
Give the rectilinear crossing numbers for complete graphs:
Display the rectilinear local crossing number of the complete graph K6:
Display embeddings with this number of rectilinear crossings:
Give the toroidal crossing number of the unique graph that triangulates the torus and Klein bottle:
Clique‐Related Graph Properties (15)
Return the clique count of the octahedral graph:
Compare with the explicit listing of cliques:
Return the clique number of the icosahedral graph:
Compare with the lengths of the maximum cliques:
Give the clique polynomial of the utility graph:
Compare to the explicit cliques:
Return the cliques of the octahedral graph:
Return the Delsarte cliques of the octahedral graph:
Compare with number of cliques directly:
Return the Delsarte cliques of the octahedral graph:
Verify the graph is distance-regular:
Verify these cliques achieve the Delsarte bound:
Return the fractional clique number of the Heawood graph:
Return the lower clique number of the Krackhardt kite graph:
Compare with the size of the smallest maximal clique:
Return the number of maximal cliques of the cubical graph:
Compare with the number of maximal cliques:
Return the maximal clique polynomial of the cubical graph:
Return the maximal cliques of the bull graph:
Return the maximum cliques of the bull graph:
Give the smallest covers of the cubical graph by maximal cliques:
Give the number of smallest covers of the cubical graph by maximal cliques:
Give the name of the simplex graph of the cycle graph C5, i.e. the graph with vertices given by the cliques of the base graph and edges between pairs of cliques that differ by insertion/deletion of exactly one vertex:
Return the graph:
Cover‐Related Graph Properties (20)
Give the biclique cover of the cubical graph:
Return the clique covering number of the icosahedral graph:
Verify it is the chromatic number of the graph complement:
Give the number of edge covers of the cubical graph:
Compare to the length of the list of edge covers:
Return the edge cover number of the icosahedral graph:
Compare with the length of a minimum edge cover:
Give the edge cover polynomial of the utility graph:
Compare to the explicit covers:
Give the edge covers of the utility graph:
Return the number of minimal edge covers for the cubical graph:
Compare to the length of the list:
Use the "Count" annotation:
Return the minimal edge cover polynomial of the tetrahedral graph:
Compute from the minimal edge covers:
Return the minimal edge covers of the tetrahedral graph:
Return the number of minimal vertex covers for the cubical graph:
Compare to the length of the list:
Use the "Count" annotation:
Return the minimal vertex cover polynomial of the tetrahedral graph:
Compute from the minimal vertex covers:
Return the minimal vertex covers of the tetrahedral graph:
Return the number of minimum clique coverings for the cubical graph:
Compare to the length of the list:
Give the number of minimum path coverings of the 4-star graph:
Return using a "Count" qualifier:
Compare with minimum path coverings:
Show the minimum path coverings of the 4-star graph:
Give the path covering number of the cross graph:
Append "paths" of length 0 to the paths on the graph:
The path covering number is the smallest number of vertex-disjoint paths that cover the given graph:
Compare with the minimum path coverings:
Give the number of vertex covers of the cubical graph:
Compare to the length of the list of edge covers:
Return the vertex cover number:
Compare with the size of a minimum vertex cover:
Give the vertex cover polynomial of the utility graph:
Compare to the explicit covers:
Give the vertex covers of the cubical graph:
Independent Set‐Related Graph Properties (27)
Give the biclique cover of the cubical graph:
Give the bipartite dimension of the cubical graph:
Return the fractional independence number of the Petersen graph:
Compare with the usual independence number:
Return the independence number of the Heawood graph:
Compare with the size of a maximum independent vertex set:
Return the independence polynomial of the utility graph:
Compare to the explicit independent sets:
Return the independence ratio of the Petersen graph:
Compare to the direct ratio of properties:
Return the number of independent edge sets of the Heawood graph:
Compare to the explicit independent sets:
Return the independent edge sets of the utility graph:
Return the number of independent vertex sets of the cubical graph:
Compare to the explicit independent sets:
Return the independent vertex sets of the Heawood graph:
Return the intersection number of the Heawood graph:
Give the lower independence number of the Petersen graph:
Compare with the smallest exponent of the maximal independence polynomial:
Give the lower matching number of the Coxeter graph:
Compare with the smallest exponent of the maximal matching-generating polynomial:
Return the matching-generating polynomial of the utility graph:
Compare to the explicit independent edge sets:
Return the matching number of the cubical graph:
Compare with the matching-generating polynomial:
Return the maximal independence polynomial for the Heawood graph:
Compare with the numbers of maximal independent vertex sets:
Return the number of maximal independent edge sets for the cubical graph:
Compare with the number of maximal independent edge sets:
Return the maximal independent edge sets for the cubical graph:
Return the maximal matching-generating polynomial for the Heawood graph:
Compare with the explicit edge sets:
Return the number of maximal independent vertex sets for the Heawood graph:
Compare with the number of maximal independent vertex sets:
Return the maximal independent vertex sets for the cubical graph:
Return the maximal independence polynomial for the cubical graph:
Compare with the explicit edge sets:
Return the maximal matching generating polynomial for the cubical graph:
Compare with the numbers of maximal independent edge sets:
Return the number of maximum independent edge sets for the Heawood graph:
Do the same with the "Count" annotation:
Return the maximum independent edge sets for the Heawood graph:
Return the number of maximum independent vertex sets for the Heawood graph:
Do the same with the "Count" annotation:
Return the maximum independent vertex sets for the Heawood graph:
Irredundant Set‐Related Graph Properties (9)
Give the irredundance number of the Petersen graph:
Compare with the smallest exponent of the maximal irredundance polynomial:
Give the number of irredundant sets in the cubical graph:
Compare with the length of the list of sets:
Use the "Count" annotation:
Give the irredundant sets in the cubical graph:
Give the maximal irredundant polynomial of the cubical graph:
Compute from the maximal irredundant sets:
Give the number of maximal irredundant sets in the cubical graph:
Compare with the length of the list of sets:
Use the "Count" annotation:
Give the maximal irredundant sets in the cubical graph:
Give the number of maximum irredundant sets in the cubical graph:
Compare with the length of the list of sets:
Use the "Count" annotation:
Give the maximum irredundant sets in the cubical graph:
Give the upper irredundance number of the Petersen graph:
Compare with the largest exponent of the maximal irredundance polynomial:
Dominating Set‐Related Graph Properties (29)
Return the connected dominating set count of the cubical graph:
Compare with the connected domination polynomial:
Compare with the connected dominating sets:
Give the connected dominating sets of the square graph:
Return the connected domination number of the cubical graph:
Compare with the connected domination polynomial:
Compare with the connected dominating sets:
Return the connected domination polynomial of the cubical graph:
Compare with the sizes of connected dominating sets:
Give the domatic numbers of the first several hypercube graphs:
Return the number of dominating sets of the cubical graph:
Compare with the domination polynomial:
Compare with the dominating sets:
Return the dominating sets of the cubical graph:
Return the domination number of the cubical graph:
Return the domination polynomial of the cubical graph:
Compare with the sizes of dominating sets:
Give the number of minimal connected dominating sets in the Nauru graph:
Compute from the minimal connected dominating sets:
Use the "Count" annotation:
Return the minimal connected dominating sets in the Nauru graph:
Give the minimal connected domination polynomial of the Nauru graph:
Compute from the minimal connected dominating sets:
Give the number of minimal dominating sets in the cubical graph:
Compute from the minimal dominating sets:
Use the "Count" annotation:
Return the minimal dominating sets in the cubical graph:
Give the minimal domination polynomial of the cubical graph:
Compute from the minimal dominating sets:
Give the minimal total dominating set count of the cubical graph:
Compute from the minimal total dominating sets:
Use the "Count" annotation:
Give the minimal total dominating sets in the cubical graph:
Give the minimal total domination polynomial of the cubical graph:
Compute from the minimal total dominating sets:
Return the minimum connected dominating set count of the cubical graph:
Compare with the connected domination polynomial:
Compare with the minimum connected dominating sets:
Give the minimum connected dominating sets of the square graph:
Return the number of minimum dominating sets for the cubical graph:
Do the same using the "Count" annotation:
Compare to the value computed from the domination polynomial:
Return the minimum dominating sets for the cubical graph:
Compare to the number from the direct property:
Return the number of minimum total dominating sets for the cubical graph:
Do the same using the "Count" annotation:
Compare to the value computed from the total domination polynomial:
Return the minimum total dominating sets for the cubical graph:
Compare to the number from the direct property:
Return the number of total dominating sets of the cubical graph:
Compare with the total domination polynomial:
Compare with the total dominating sets:
Return the total dominating sets of the cubical graph:
Return the total domination number of the cubical graph:
Return the total domination polynomial of the cubical graph:
Compare with the sizes of total dominating sets:
Return the upper domination number of the cubical graph:
Compare with the largest exponent of the minimal domination polynomial:
Symmetry‐Related Graph Properties (18)
Display the arc transitivity of the Coxeter graph:
List arc-transitive graphs:
Produce a table of the arc transitivities of some small arc-transitive graphs:
Give the order of the automorphism group of the octahedral graph:
Directly compute from the group:
Give the number of distinct edge lengths in the 4-trapezohedron:
Show the corresponding polyhedron:
List the names of groups generating the cubical graph as an (undirected) Cayley graph:
Visualize the (directed) Cayley graphs:
Verify the undirected graphs are isomorphic with the cubical graph:
List group representations (not necessarily corresponding to distinct groups) that generate the cubical graph as an (undirected) Cayley graph:
Verify these all generate the cubical graph:
Give the distinguishing number of the Petersen graph:
Give the fixing number of the Petersen graph:
Give the number of minimum distinguishing labelings of the Petersen graph:
Do the same using the "Count" annotation:
Give minimum distinguishing labelings of the Petersen graph:
Compare with the value from the direct property:
Give the number of planar embeddings in the Eiffel Tower graph:
Give the number of planar embeddings of a nonplanar graph:
Give the number of planar embeddings of a uniquely embeddable graph:
Give the number of symmetrically distinct faces in the truncated cubical graph:
Give representatives of the symmetrically distinct faces in the truncated cubical graph:
Give the number of symmetrically distinct vertices in the butterfly graph:
Give representatives of symmetrically distinct vertices:
Visualize:
Give the number of symmetrically distinct vertex pairs in the Petersen graph:
Compare with the signature of symmetrically distinct vertex pairs:
Give the signature of symmetrically distinct vertex pairs in the Petersen graph:
This means that there are 30 vertex pairs symmetrically equivalent to 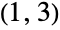 and 15 equivalent to
and 15 equivalent to 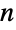 :
:
Compare the number of symmetrically distinct vertex pairs with the count:
Give representatives of symmetrically distinct vertices in the butterfly graph:
Visualize:
List all symmetrically equivalent faces in the truncated tetrahedral graph:
Visualize via the graph's polyhedral embedding:
List the symmetrically equivalent vertices in the butterfly graph:
Visualize:
Information‐Related Graph Properties (12)
Give the bandwidth of the 5-hypercube graph:
Compare to the known closed form:
Give the burning number of the 5-star graph:
Give the cooling number of the 5-cycle graph:
The cooling number of the 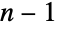 -cycle is given by
-cycle is given by ![TemplateBox[{{{(, {n, +, 2}, )}, /, 3}}, Ceiling]](http://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Files/GraphData.en/45.png) :
:
Give the gonality of the 5-star graph:
Return the likelihood of the Petersen graph:
Likelihoods are normalized for fixed node count:
Return the Lovász number of the 5-cycle graph:
Give the pathwidths of the hypercube graphs:
Compare to the known closed form:
Give the pebbling number of the cubical graph:
Give the scramble number of the cubical graph:
Display the Shannon capacity of the cubical graph:
Give the tree depth of a complete graph:
Give the treewidth of a complete graph:
Give the treewidth of a complete bipartite graph:
Path‐ and Cycle‐Related Properties (45)
Return the number of chordless cycles in the Petersen graph:
Verify against the chordless cycle polynomial:
Verify against the chordless cycles:
Return the chordless cycle polynomial of the Petersen graph:
Give the chordless cycles of the Petersen graph:
Visually verify the returned cycles are chordless:
Return the number of chordless cycles in the complement of the Petersen graph:
Verify against the chordless cycle polynomial:
Verify against the chordless cycles:
Return the chordless cycle polynomial in the complement of the Petersen graph:
Compare with the property computed from the complement:
Return the chordless cycles of the complement of the Petersen graph:
Return the number of chordless cycles in the complement of the Petersen graph:
Verify against the chordless cycle polynomial:
Verify against the chordless cycles:
Return the odd chordless cycle polynomial in the complement of the Petersen graph:
Compare with the property computed from the complement:
Return the odd chordless cycles of the complement of the Petersen graph:
Give the name of the cube graph of the 7-Möbius ladder:
Return the cube graph itself:
Compare with the third graph power:
Verify the graph property and computed graphs are isomorphic:
Return the number of cycles of the cubical graph:
Do the same using the "Count" annotation:
Return the cycles:
Give the cycle polynomial of the cubical graph as a pure function:
Compare to cycle tallies:
Return the cycles in the cubical graph:
Return the number of Eulerian cycles of the butterfly graph:
Return the cycles:
Visualize the Eulerian cycles:
Give the tally of cubical graph face sizes:
Compute directly from faces:
Display the girth of the Petersen graph:
Return the number of Hamilton decompositions of the octahedral graph:
Do the same using the "Count" annotation:
Return Hamilton decompositions of the octahedral graph:
Return the number of Hamiltonian cycles of the cubical graph:
Do the same using the "Count" annotation:
List the Hamiltonian cycles of the cubical graph:
Display the Hamiltonian cycles:
Return the Hamiltonian number of the octahedral graph:
Return the number of Hamiltonian paths of the tetrahedral graph:
Do the same using the "Count" annotation:
Return the Hamiltonian paths of the cubical graph:
Display the Hamiltonian paths:
Return the number of Hamiltonian walks of the cubical graph:
Do the same using the "Count" annotation:
List the Hamiltonian walks of the cubical graph:
Give the hexagon count of the truncated tetrahedral graph:
Compare with the value from the cycle polynomial:
Return the k-cyclic indices of the butterfly graph:
Give the longest cycle count of the (3,4)-cone graph:
Do the same using the "Count" annotation:
Give the longest cycles of the (3,4)-cone graph:
Compare to the value from the direct property:
Compare to the number of hexagons:
Give the longest path count of the (3,4)-cone graph:
Do the same using the "Count" annotation:
Give the longest path length of the (3,4)-cone graph:
Compare to the value obtained from the paths themselves (adjusting for the fact that a path specified by 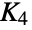 vertices has length
vertices has length 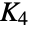 ):
):
Give the longest paths of the (3,4)-cone graph:
Compare to the value from the direct property:
Give the number of minimum path coverings of the 5-wheel graph:
Give the minimum path coverings of the 5-wheel graph:
View some of the edge coverings:
Since this graph is traceable, the minimum path coverings correspond to Hamiltonian paths:
Return the number of odd chordless cycles in the Petersen graph:
Verify against the chordless cycle polynomial:
Verify against the chordless cycles:
Give the odd chordless cycle polynomial of the 9-antiprism graph:
Compare with the length tallies of all odd chordless cycles:
Give the odd chordless cycles of the Petersen graph:
Compare with the set of cycles extracted from all chordless cycles:
Return the number of paths of the butterfly graph:
Do the same using the "Count" annotation:
Return the cycles:
Give the path polynomial of the butterfly graph as a pure function:
Compare to path length tallies:
Give the path covering number of the cross graph:
Exhibit a path covering consisting of two paths:
Return the paths in the butterfly graph:
Give the pentagon count of the snub cubical graph:
Compare with the value from the cycle polynomial:
Give the square count of the snub cubical graph:
Compare with the value from the cycle polynomial:
Graphs with nonzero square count should not be square-free:
Give the name of the square graph of the 7-Möbius ladder:
Return the cube graph itself:
Compare with the second graph power:
Verify the graph property and computed graphs are isomorphic:
Give the square count of the snub cubical graph:
Compare with the value from the cycle polynomial:
Graphs with nonzero triangle count should not be triangle-free:
Graph Centralities (11)
Closeness centralities:
Degree centralities:
Identical to degrees:
Eccentricity centralities:
Identical to reciprocal of vertex eccentricities for a connected graph:
Edge betweenness centralities:
Eigenvector centralities:
HITS centralities:
Katz centralities:
Link rank centralities:
Page rank centralities:
Return using explicit variables:
Radiality centralities:
Status centralities:
Graph Clustering Coefficients (3)
Give the global clustering coefficient of the house graph:
Compare with the value computed from the graph by the built-in function:
Give the local clustering coefficients of the house graph:
Compare with the value computed from the graph by the built-in function:
Give the mean clustering coefficient of the house graph:
Compare with the value computed from the graph by the built-in function:
Naming‐Related Properties (7)
List the alternate English names of the tesseract graph:
Show the alternate standard names for the tesseract graph:
Give the entity for the Petersen graph:
Give the textual name of the octahedral graph:
Give the name of the complete graph  :
:
Verify the standard name for this graph:
Give all textual names of the octahedral graph:
Query the standard name of the 4-hypercube graph:
Show other alternate standard names corresponding to this standard name:
Give the standard name of the complete graph 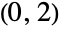 :
:
Give all standard names of the octahedral graph:
Notation‐Related Properties (3)
Give LCF notations for the octahedral graph (sorted by exponents):
Tally the LCF notation exponents:
Display the nontrivial LCF embeddings:
Give the primary notation of the cubical graph:
Display the notation with traditional typesetting:
Give a list of rules for notations associated with the complete graph 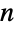 :
:
Give rules for various notations for the octahedral graph:
Basic Classes (4)
Bipartite graphs:
Nonplanar graphs:
Planar graphs:
Trees:
Classes Based on Crossings (11)
Apex graphs:
Critical nonplanar graphs:
List the doublecross graphs on 7 or fewer graphs:
Compare with the crossing numbers:
Double-toroidal graphs:
List intrinsically linked graphs:
List linklessly embeddable graphs:
Map graphs:
List the planar graphs on 5 or fewer graphs:
Verify:
Compare with the crossing numbers:
Pretzel graphs:
List the singlecross graphs on 6 or fewer graphs:
Compare with the crossing numbers:
Toroidal graphs:
Classes Based on Vertex Degrees (14)
Cubic graphs:
Highly irregular graphs:
Multigraphic graphs:
Octic graphs:
Quartic graphs:
Quasi-regular graphs:
Quintic graphs:
Regular graphs:
Septic graphs:
Sextic graphs:
Switchable graphs:
Two-regular graphs:
Unigraphic graphs:
Unswitchable graphs:
Classes Based on Traversals (32)
Acyclic graphs:
Almost Hamiltonian graphs:
Almost hypohamiltonian graphs:
Antipodal graphs:
Bridged graphs:
Bridgeless graphs:
Chordal graphs:
Chordless graphs:
Cyclic graphs:
Eulerian graphs:
Geodetic graphs:
Hamilton‐connected graphs:
Hamilton‐decomposable graphs:
Hamilton‐laceable graphs:
Hamiltonian graphs:
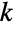 ‐connected graphs:
‐connected graphs:
Hypohamiltonian graphs:
Hypotraceable graphs:
Graphs that provide counterexamples to Kempe's purported proof of the four-color theorem:
Maximally nonhamiltonian graphs:
Median graphs:
Non-tree median graphs:
Meyniel graphs:
Noneulerian graphs:
Nonhamiltonian graphs:
Pancyclic graphs:
Square-free graphs:
Traceable graphs:
Triangle-free graphs:
Unicyclic graphs:
Pseudotrees that are not trees are equivalent to unicyclic graphs:
Uniquely Hamiltonian graphs:
Uniquely pancyclic graphs:
Untraceable graphs:
Classes Based on Chess Boards (19)
Antelope graphs:
Bishop graphs:
Black bishop graphs:
Camel graphs:
Fiveleaper graphs:
Giraffe graphs:
King graphs:
Knight graphs:
Queen graphs:
Rook graphs:
Rook complement graphs:
Triangular honeycomb acute knight graphs:
Triangular honeycomb bishop graphs:
Triangular honeycomb king graphs:
Triangular honeycomb obtuse knight graphs:
Triangular honeycomb queen graphs:
Triangular honeycomb rook graphs:
White bishop graphs:
Zebra graphs:
Classes Based on Symmetry and Regularity (21)
Arc-transitive graphs:
Asymmetric graphs:
Chang graphs:
Conformally rigid graphs:
Distance-regular graphs:
Distance-transitive graphs:
Edge-transitive graphs:
Geometric graphs:
Identity graphs:
Locally Petersen graphs:
Nongeometric graphs:
Paulus graphs:
Semisymmetric graphs:
Strongly regular graphs:
Symmetric graphs:
Taylor graphs:
Vertex-transitive graphs:
Weakly regular graphs:
Uniquely embeddable graphs:
Zero-symmetric graphs:
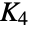 -graphs:
-graphs:
Spectral Classes (3)
Integral graphs:
Line graphs:
Maverick graphs:
Classes Based on Forbidden Graphs (10)
Beineke graphs:
Kuratowski graphs:
Metelsky graphs:
Forbidden minors for pathwidth 1:
Forbidden minors for pathwidth 2:
Forbidden minors for linkless embeddabiity:
Projective planar forbidden minors:
Projective planar forbidden topological minors (homeomorphic subgraphs):
Toroidal forbidden minors:
Unit-distance forbidden subgraphs:
Special Classes (50)
Almost-controllable graphs:
Bicolorable graphs:
Bicubic graphs:
Biplanar graphs:
Block graphs:
Braced polygon graphs:
Cage graphs:
Cayley graphs:
Claw-free graphs:
Chromatically unique graphs:
Chromatically unique graphs on six or fewer vertices:
The cubical graph is chromatically unique:
The antenna graph is not:
Find and show graphs that are cochromatic with the antenna graph:
Claw-free graphs:
Conference graphs:
Graph represents a configuration:
Controllable graphs:
Distance-hereditary graphs:
Flexible graphs:
Fullerenes:
Fully reconstructible in 1:
Fully reconstructible in 3:
Fusenes:
Graceful graphs:
Imperfect graphs:
Incidence graphs:
Laman graphs:
LCF (regular Hamiltonian) graphs:
Matchstick graphs:
Moore graphs:
No perfect matching graphs:
Nonempty graphs:
Nuciferous graphs:
Nut graphs:
Ore graphs:
Outerplanar graphs:
Perfect graphs:
Perfect matching graphs:
Polyhex graphs:
Ptolemaic graphs:
Projective planar graphs:
Quadratically embeddable graphs:
Rigid graphs:
Self‐complementary graphs:
Self‐dual graphs:
Snarks:
Named snarks:
Split graphs:
Strongly perfect graphs:
Triangulated graphs:
Uniquely colorable graphs:
Unit‐distance graphs:
Weakly perfect graphs:
Well‐covered graphs:
Classes Associated with Polyhedra (12)
Antiprism graphs:
Archimedean graphs:
Archimedean dual graphs:
Dipyramidal graphs:
Johnson skeleton graphs:
Platonic graphs:
Polyhedral graphs:
Prism graphs:
Regular polychoron graphs:
Trapezohedral graphs:
Uniform polyhedron skeleton graphs:
Wheel graphs:
Snark-Related Classes (4)
Flower graphs:
Goldberg graphs:
(Strong) snarks:
Weak snarks:
Special Classes of Trees and Their Generalizations (12)
Cacti:
Caterpillar trees:
Centipede trees:
Forests:
Halin graphs:
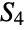 -trees:
-trees:
2-trees:
Lobster trees:
Pseudoforests:
Pseudotrees:
Series-reduced trees:
Spider trees:
Tripod trees:
Classes Indexed by One or More Integers (90)
Accordion graphs:
 -alkane graphs:
-alkane graphs:
Apollonian graphs:
Bipartite Kneser graphs:
Book graphs:
Bouwer graphs:
Bruhat graphs:
Caveman graphs:
Circulant graphs:
Complete graphs:
Complete bipartite graphs:
Complete  -partite graphs:
-partite graphs:
Complete tripartite graphs:
Cone graphs:
Crown graphs:
Cycle graphs:
Cycle complement graphs:
Cyclotomic graphs:
Diagonal intersection graphs:
Dipyramidal graphs:
Doob graphs:
Dorogovtsev–Goltsev–Mendes graphs:
Double cone graphs:
Egawa graphs:
Empty graphs:
Fan graphs:
Fibonacci cube graphs:
Flower graphs:
Folded cube graphs:
Gear graphs:
Generalized polygon graphs:
Goethals–Seidel block design graphs:
Goldberg graphs:
Grassmann graphs:
Grid graphs:
Haar graphs:
Hadamard graphs:
Halved cube graphs:
Hamming graphs:
Hanoi graphs:
Harary graphs:
Helm graphs:
Hexagonal grid graphs:
Honeycomb toroidal graphs:
Hypercube graphs:
I-graphs:
Jahangir graphs:
Johnson graphs:
Johnson skeleton graphs:
Kayak paddle graphs:
Keller graphs:
Klein bottle triangulation graphs:
Kneser graphs:
Ladder graphs:
Ladder rung graphs:
Lucas cube graphs:
Lindgren–Sousselier graphs:
Mathon graphs:
Menger sponge graphs:
Middle layer graphs:
Möbius ladder graphs:
Mycielski graphs:
Odd graphs:
Paley graphs:
Pan graphs:
Pasechnik graphs:
Path complement graphs:
Path graphs:
Pell graphs:
Permutation star graphs:
Sierpiński carpet graphs:
Sierpiński gasket graphs:
Sierpiński tetrahedron graphs:
Spoke graphs:
Stacked book graphs:
Stacked prism graphs:
Star graphs:
Sun graphs:
Sunlet graphs:
Tetrahedral graphs:
Torus grid graphs:
Torus triangulation graphs:
Transposition graphs:
Triangular graphs:
Triangular grid graphs:
Triangular snake graphs:
Turán graphs:
Wheel complement graphs:
Wheel graphs:
Windmill graphs:
Wreath graphs:
Generalizations & Extensions (1)
Find the list of graph names matching a string wildcard expression:
Find the list of graph names matching a string expression:
Find the list of graph names matching a regular expression:
Applications (8)
Generate a list of graphs on five nodes:
Generate a list of Hamiltonian graphs on five nodes:
Generate a list of Hamiltonian planar graphs on five nodes:
Generate a list of graphs on five or fewer nodes:
Generate an array of Cayley graphs:
Visualize families of graphs by plotting edge count against vertex count:
Plot the numbers of graphs with different numbers of nodes available:
Show the five known connected vertex-transitive nonhamiltonian graphs:
Properties & Relations (10)
FromEntity can be used to make a graph from an entity:
A graph can also be produced from an entity using the "Graph" property:
ToEntity can be used to construct an entity from a graph:
An entity is also returned using the GraphData "Entity" property:
Give the tesseract graph using GraphData directly:
Do the same using the explicit "Graph" property:
Construct a graph using FromEntity and the "Entity" property:
Construct a graph using an entity corresponding to its GraphData canonical name:
Use a member of an indexed graph family known to EntityValue:
Convert undirected graphs to graph entities using ToEntity:
Convert to the corresponding GraphData entity using CanonicalName:
Use GraphPlot and GraphPlot3D to construct graph drawings from connectivity:
Use the embedding provided by GraphData:
Use all embeddings available:
Show that the integral graphs have integer-valued spectra:
Show that the graphs classified as snarks satisfy their defining properties:
Construct an attractive symmetric embedding of the Gray graph from its LCF notation:
Verify that an antiprism graph is the skeleton of an antiprism:
Get the polyhedral embedding:
Display the corresponding PolyhedronData object:
Get the skeleton graph from the polyhedron object:
Show that the automorphism group of the complete graph  is the symmetric group
is the symmetric group  :
:
Possible Issues (4)
GraphData results are complete when the number of graphs is not too large:
For queries corresponding to a large number of graphs, the list returned by GraphData may not be exhaustive:
Using nonstandard graph names will not work:

Use string patterns directly in GraphData:
Or use general string-matching capabilities:
Using nonstandard property names will not work:

Use general string patterns to locate standard property names:
Arithmetical operations cannot be carried out on Missing entries:
Remove the Missing entries before performing operations:
Display the data as a formatted table using TextGrid:
Interactive Examples (1)
Create a simple graph explorer:
Neat Examples (3)
Display planar embeddings of the heptahedral graphs:
See the toric structure of some of the cubic symmetric graphs:
Construct the connectivity graph of the contiguous US states plus Washington, DC:
Make a list of rules representing adjacent states:
Visualize the resulting graph:
Check the vertex and edge counts:
Compare with the counts for the "ContiguousUSAGraph":
Exclude four pairs of states that either share only a single point in common or have a sea border but no land border:
Visualize the excluded borders:
Construct connectivity rules excluding these four edges:
Visualize:
Check the vertex and edge counts:
Verify this graph is isomorphic to the "ContiguousUSAGraph" using ToEntity:
Related Links
Wolfram Research (2007), GraphData, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/GraphData.html (updated 2025).
Text
Wolfram Research (2007), GraphData, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/GraphData.html (updated 2025).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2007. "GraphData." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2025. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/GraphData.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2007). GraphData. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/GraphData.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_graphdata, author="Wolfram Research", title="{GraphData}", year="2025", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/GraphData.html}", note=[Accessed: 20-June-2025 ]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_graphdata, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={GraphData}, year={2025}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/GraphData.html}, note=[Accessed: 20-June-2025 ]}