PlanarGraph—Wolfram Language Documentation (original) (raw)
BUILT-IN SYMBOL
PlanarGraph
PlanarGraph[{e1,e2,…}]
yields a planar graph with edges ej.
PlanarGraph[{v1,v2,…},{e1,e2,…}]
yields a planar graph with vertices vi and edges ej.
PlanarGraph[{…,wi[vi],…},{…,wj[ej],…}]
yields a planar graph with vertex and edge properties defined by the symbolic wrappers wk.
PlanarGraph[{vivj,…}]
uses rules vivj to specify a planar graph.
Examples
open allclose all
Basic Examples (2)
A planar graph:
The three-dimensional HypercubeGraph is planar:
A planar drawing:
Scope (25)
Connectivity (6)
Create an undirected planar graph using characters; enter the character as  ue
ue :
:
Create a directed planar graph using characters; enter the character as  de
de :
:
Create a directed planar graph from a list of rules:
Create an undirected planar graph from a list of rules:
Use VertexList and EdgeList to get vertices and edges:
The ordering for edges is the order in which they were entered:
The ordering for vertices is the order in which they were entered in the edges:
Use an explicit vertex list to control the ordering used by VertexList:
The input vertex list controls the resulting vertex order:
Any expression can be used as vertices:
Wrappers (5)
Use wrappers on vertices or edges:
Wrappers can be nested:
Add interactive behavior by wrappers such as Tooltip:
Any object can be used in the tooltip:
Use Button to trigger actions when clicking an edge or vertex:
Use PopupWindow to provide information drilldown:
Styling (8)
Set the style for all vertices or edges:
Style individual vertices or edges using options:
Use wrappers for individual styling:
Adjust the size of vertices using symbolic sizes:
Or use sizes in terms of the smallest distance between vertex centers:
Use built-in collections for VertexShapeFunction:
Rounded shapes:
Concave shapes:
Draw individual vertices:
Combine with a default vertex function:
Use any Graphics, Image, or Graphics3D as a vertex shape:
Use built-in collections for EdgeShapeFunction:
Directed edges including solid arrows:
Line arrows:
Open arrows:
Specify an edge function for an individual edge:
Combine with a different default edge function:
Labeling (6)
Label any edge or vertex:
Use any expression as a label:
Control the placement of vertex labels using Placed, including symbolic inside positions:
Symbolic outside positions:
Coordinate-based positions:
Place multiple labels using Placed in a wrapper:
Any number of labels can be used:
Place multiple labels using VertexLabels:
Use Placed with symbolic locations to control label placement along an edge:
Use explicit coordinates to place labels:
Place multiple labels using Placed in a wrapper:
Any number of labels can be used:
Place multiple labels using EdgeLabels:
Options (80)
AnnotationRules (3)
Specify an annotation for vertices:
Edges:
Graph itself:
DirectedEdges (2)
By default, a directed planar graph is generated when giving a list of rules:
Use DirectedEdges->False to interpret rules as undirected edges:
Use DirectedEdge or UndirectedEdge to directly specify whether a graph is directed or not:
EdgeLabels (7)
Label the edge 12:
Label all edges:
Use any expression as a label:
Use Placed with symbolic locations to control label placement along an edge:
Use explicit coordinates to place labels:
Vary positions within the label:
Place multiple labels using Placed in a wrapper:
Any number of labels can be used:
Place multiple labels using EdgeLabels:
Use automatic labeling by values through Tooltip and StatusArea:
EdgeShapeFunction (6)
Get a list of built-in settings for EdgeShapeFunction:
Undirected edges including the basic line:
Lines with different glyphs on the edges:
Directed edges including solid arrows:
Line arrows:
Open arrows:
Specify an edge function for an individual edge:
Combine with a different default edge function:
Draw edges by running a program:
EdgeShapeFunction can be combined with EdgeStyle:
EdgeShapeFunction has higher priority than EdgeStyle:
EdgeStyle (2)
Style all edges:
Style individual edges:
EdgeWeight (2)
Specify the weight for all edges:
Use any numeric expression as a weight:
GraphHighlight (3)
Highlight the vertex 1:
Highlight the edge 12:
Highlight vertices and edges:
GraphHighlightStyle (2)
GraphLayout (2)
By default, the layout is chosen automatically:
Specify layouts on planar graphs:
PlotTheme (4)
Base Themes (2)
Use a common base theme:
Use a monochrome theme:
Feature Themes (2)
Use a large graph theme:
Use a classic diagram theme:
VertexCoordinates (3)
By default, any vertex coordinates are computed automatically:
Extract the resulting vertex coordinates using AbsoluteOptions:
Specify a layout function along an ellipse:
Use it to generate vertex coordinates for a graph:
VertexCoordinates has higher priority than GraphLayout:
VertexLabels (13)
Use vertex names as labels:
Label individual vertices:
Label all vertices:
Use any expression as a label:
Use Placed with symbolic locations to control label placement, including outside positions:
Symbolic outside corner positions:
Symbolic inside positions:
Symbolic inside corner positions:
Use explicit coordinates to place the center of labels:
Place all labels at the upper-right corner of the vertex and vary the coordinates within the label:
Place multiple labels using Placed in a wrapper:
Any number of labels can be used:
Place multiple labels using VertexLabels:
Use the argument to Placed to control formatting including Tooltip:
Or StatusArea:
Use more elaborate formatting functions:
VertexShape (5)
VertexShapeFunction (10)
VertexSize (8)
By default, the size of vertices is computed automatically:
Specify the size of all vertices using symbolic vertex size:
Use a fraction of the minimum distance between vertex coordinates:
Use a fraction of the overall diagonal for all vertex coordinates:
Specify size in both the 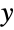 and
and  directions:
directions:
Specify the size for individual vertices:
VertexSize can be combined with VertexShapeFunction:
VertexSize can be combined with VertexShape:
VertexStyle (5)
VertexWeight (3)
Set the weight for all vertices:
Specify the weight for individual vertices:
Use any numeric expression as a weight:
Wolfram Research (2016), PlanarGraph, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/PlanarGraph.html.
Text
Wolfram Research (2016), PlanarGraph, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/PlanarGraph.html.
CMS
Wolfram Language. 2016. "PlanarGraph." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/PlanarGraph.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (2016). PlanarGraph. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/PlanarGraph.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_planargraph, author="Wolfram Research", title="{PlanarGraph}", year="2016", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/PlanarGraph.html}", note=[Accessed: 06-May-2025 ]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_planargraph, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={PlanarGraph}, year={2016}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/PlanarGraph.html}, note=[Accessed: 06-May-2025 ]}