Prime—Wolfram Language Documentation (original) (raw)
BUILT-IN SYMBOL
Prime
Prime[n]
gives the n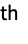 prime number
prime number ![TemplateBox[{n}, Prime]](http://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Files/Prime.en/2.png) .
.
Details

Examples
open allclose all
Basic Examples (3)
Compute the 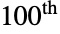 prime:
prime:
Plot the sequence of primes:
Find the leading asymptotic term for Prime at Infinity:
Scope (10)
Numerical Evaluation (4)
Prime works over positive integers:
Large numbers:
Prime works over large integers:
Prime threads over lists:
Symbolic Manipulation (6)
TraditionalForm formatting:
Find a solution instance of equalities with Prime:
Sum involving prime numbers:
Product:
Recognize the Prime sequence:
Simplify an expression:
Find the leading asymptotic term for Prime as 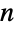 approaches Infinity:
approaches Infinity:
The ratio of the sequence and its leading asymptotic approaches 1 as 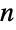 approaches Infinity:
approaches Infinity:
Applications (38)
Basic Applications (9)
Highlight prime numbers:
Visualize the primes with a parabolic sieve:
Visualize the sieve of Eratosthenes for the first 5 primes:
Spiral of primes:
Hexagonal prime spiral:
Find the lowest-divisor pair for an integer 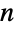 :
:
Find the factorization for an integer 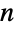 :
:
Construct a factorization tree for an integer 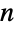 :
:
Divisibility graph:
Visualize prime numbers with periodic curves. Prime numbers are those where only two curves cross—its own and the curve of 1:
Visualize an array of primes:
Approximations (3)
Approximation to ![TemplateBox[{n}, Prime]](http://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Files/Prime.en/16.png) with
with 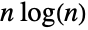 :
:
Plot Prime compared with an estimate:
Cesàro approximation of ![TemplateBox[{n}, Prime]](http://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Files/Prime.en/18.png) :
:
The relative error is small:
Compute Prime using the aliquot sum 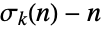 , which is equal to 1 when
, which is equal to 1 when 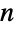 is prime:
is prime:
Number Theory (14)
Prime numbers modulo 10:
Prime numbers modulo 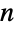 :
:
Plot of the first 50 primes modulo 6:
Fraction of the first million primes greater than 3 of the form 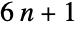 :
:
With the exception of 2 and 3, all primes are of the form 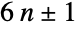 :
:
Define a residue number system:
Choose two numbers and represent them in the residue system:
Multiplying and recovering in the residue system:
Adding and recovering:
An approximation to the zeta function:
Calculate the probability that a number is relatively prime to the first 25primes:
Differences between the first 100 primes:
Find the jumping champion, i.e. the most frequently occurring difference between consecutive primes:
Calculate the sum of prime factors:
Plot the sum of prime factors for the first 25 integers:
Find Goldbach partitions, i.e. pairs of primes (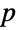 ,
, 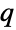 ) such that
) such that 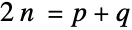 :
:
Graph Goldbach's conjecture/comet:
Calculate the primorial up to the _nth_prime, i.e. a function that multiplies successive primes, similar to the factorial:
Compare the primorial to the factorial up to 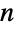 :
:
Plot the differences between the factorial and the primorial up to 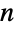 :
:
Plot the Chebyshev theta function:
Calculate the prime powers up to 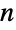 :
:
Count all the prime powers up to 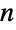 :
:
Graph the sequence of prime powers:
It is conjectured that for any integer 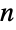 , there is a prime
, there is a prime 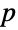 with
with 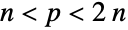 :
:
Verify this for a range of integers:
Plot Andrica's conjecture, which states that √pn+1_-√_pn<1 for every pair of consecutive prime numbers pn and pn+1:
Plot Brocard's conjecture, which states that if pn and pn+1 are consecutive primes greater than 2, then between (pn _)_2 and (pn+1 _)_2 there are at least four prime numbers:
Plot polynomials for 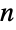 -gons, i.e. Chebyshev polynomials of the second kind, such that
-gons, i.e. Chebyshev polynomials of the second kind, such that 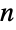 is prime:
is prime:
Special Sequences (12)
Find twin primes, i.e. pairs of primes of the form 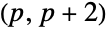 :
:
Plot the twin primes:
A prime 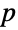 is a Sophie Germain prime if
is a Sophie Germain prime if 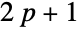 is also a prime:
is also a prime:
Find Mersenne primes:
There are 5 Fermat primes, i.e. Fermat numbers 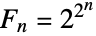 such that
such that 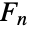 is prime:
is prime:
There are two Wieferich primes under 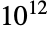 , i.e. a prime number
, i.e. a prime number 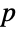 such that
such that  divides
divides 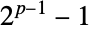 :
:
Construct prime Euclid numbers:
Find perfect numbers:
Pythagorean primes can be written as the sum of two squares, i.e. a prime number 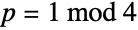 :
:
Ramanujan primes are the smallest number Rn such that π(x) - π(x/2) ≥ n for all x≥ Rn:
Differences in nth Ramanujan primes and Prime:
Primes of the form 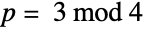 , i.e. prime elements of the Gaussian integers:
, i.e. prime elements of the Gaussian integers:
Array plot of the Gaussian primes, a Gaussian integer 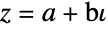 such that if
such that if 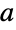 and
and 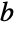 are nonzero, then
are nonzero, then 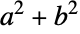 is prime or if
is prime or if 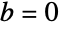 ,
, 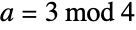 or if
or if 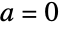 ,
, 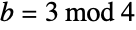 :
:
Emirp primes are primes 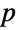 whose reversal is also prime but not a palindrome:
whose reversal is also prime but not a palindrome:
Find home primes of 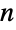 .
. 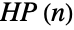 is found by concatenating the prime factors of
is found by concatenating the prime factors of 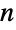 and repeating until a prime is reached:
and repeating until a prime is reached:
Properties & Relations (8)
The traditional mathematical notation for Prime:
Primes represents the domain of all prime numbers:
The largest domain of definitions of Prime:
Prime is asymptotically equivalent to 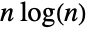 as
as 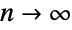 :
:
PrimePi is the inverse of Prime:
Use NextPrime to find the next prime above n:
PrimeOmega counts the number of prime divisors:
EulerPhi[n] counts numbers less than or equal to 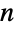 that are coprime to
that are coprime to 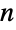 :
:
Possible Issues (1)
Evaluation timing increases exponentially:
Interactive Examples (2)
Visualize factorization diagrams:
The polar plot of primes:
Neat Examples (6)
Ulam spiral colored based on the difference in Prime values:
Visualize when 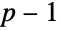 is divisible by primes. Each row of dots corresponds to the divisors of
is divisible by primes. Each row of dots corresponds to the divisors of 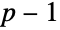 , which are labelled along the horizontal axis:
, which are labelled along the horizontal axis:
Generate a path based on the Prime sequence:
Construct polyhedra using directed graphs generated by primes less than 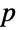 :
:
Visualize prime 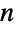 _-_sided polygons:
_-_sided polygons:
Fill the set of primes with primes:
Related Guides
▪
- Prime Numbers ▪
- Cryptographic Number Theory ▪
- Number Theoretic Functions ▪
- Analytic Number Theory ▪
- Mathematical Functions ▪
- Number Theory ▪
- Multiplicative Number Theory
Wolfram Research (1988), Prime, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Prime.html (updated 2020).
Text
Wolfram Research (1988), Prime, Wolfram Language function, https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Prime.html (updated 2020).
CMS
Wolfram Language. 1988. "Prime." Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Wolfram Research. Last Modified 2020. https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Prime.html.
APA
Wolfram Language. (1988). Prime. Wolfram Language & System Documentation Center. Retrieved from https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Prime.html
BibTeX
@misc{reference.wolfram_2025_prime, author="Wolfram Research", title="{Prime}", year="2020", howpublished="\url{https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Prime.html}", note=[Accessed: 10-June-2025 ]}
BibLaTeX
@online{reference.wolfram_2025_prime, organization={Wolfram Research}, title={Prime}, year={2020}, url={https://reference.wolfram.com/language/ref/Prime.html}, note=[Accessed: 10-June-2025 ]}