Matrix Operations—Wolfram Documentation (original) (raw)
- Functions
- Adjugate
- CharacteristicPolynomial
- ConjugateTranspose
- Det
- Diagonal
- Dot
- Eigensystem
- Eigenvalues
- Eigenvectors
- Inverse
- KroneckerProduct
- LinearSolve
- LowerTriangularize
- MatrixExp
- MatrixFunction
- MatrixLog
- MatrixMinimalPolynomial
- MatrixPower
- MatrixRank
- Minors
- Norm
- NullSpace
- Permanent
- PseudoInverse
- RangeSpace
- RowReduce
- Symmetrize
- Tr
- Transpose
- UpperTriangularize
- Related Guides
- Tech Notes
- Functions
* Adjugate
* CharacteristicPolynomial
* ConjugateTranspose
* Det
* Diagonal
* Dot
* Eigensystem
* Eigenvalues
* Eigenvectors
* Inverse
* KroneckerProduct
* LinearSolve
* LowerTriangularize
* MatrixExp
* MatrixFunction
* MatrixLog
* MatrixMinimalPolynomial
* MatrixPower
* MatrixRank
* Minors
* Norm
* NullSpace
* Permanent
* PseudoInverse
* RangeSpace
* RowReduce
* Symmetrize
* Tr
* Transpose
* UpperTriangularize - Related Guides
* Linear Systems
* Matrix-Based Minimization
* Matrix Decompositions
* Parts of Matrices
* Matrix Distributions - Tech Notes
* Vectors and Matrices
* Basic Matrix Operations
* Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors
* Tensors
- Functions
The Wolfram Language's matrix operations handle both numeric and symbolic matrices, automatically accessing large numbers of highly efficient algorithms. The Wolfram Language uses state-of-the-art algorithms to work with both dense and sparse matrices, and incorporates a number of powerful original algorithms, especially for high-precision and symbolic matrices.
+, *, ^, ... — all automatically work element-wise
Dot (.) — products of matrices, automatically handling row and column vectors
Inverse — matrix inverse (use LinearSolve for linear systems)
MatrixRank — rank of a matrix
NullSpace — vectors spanning the null space of a matrix
RangeSpace — vectors spanning the range space of a matrix
RowReduce — reduced row echelon form
PseudoInverse — pseudoinverse of a square or rectangular matrix
Transpose — transpose (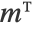 , entered with
, entered with  tr
tr )
)
ConjugateTranspose — conjugate transpose (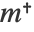 , entered with
, entered with  ct
ct )
)
LowerTriangularize, UpperTriangularize — extract the lower- or upper-triangular part of a matrix
Symmetrize — find the symmetric, antisymmetric, etc. part of a matrix
Diagonal — get the list of elements on the diagonal
Tr — trace
Det — determinant
Norm — operator norm, p-norms and Frobenius norm
Adjugate — adjugate
Minors — matrices of minors
Permanent — permanent
KroneckerProduct — matrix direct product (outer product)
MatrixPower — powers of numeric or symbolic matrices
MatrixExp— matrix exponential
MatrixLog — matrix logarithm
MatrixFunction — general matrix function
Eigenvalues, Eigenvectors — exact or approximate eigenvalues and eigenvectors
Eigensystem — eigenvalues and eigenvectors together
CharacteristicPolynomial — symbolic characteristic polynomial