data collection (original) (raw)
What is data collection?
Data collection is the process of gathering data for use in business decision-making, strategic planning, research and other purposes. It's a crucial part of data analytics applications and research projects. Effective data collection provides the information that's needed to answer questions; analyze business performance or other outcomes; and predict future trends, actions and scenarios.
In businesses, data collection happens on multiple levels. IT systems regularly collect data on customers, employees, sales and other aspects of business operations when transactions are processed and data is entered. Companies also conduct surveys and track social media to get feedback from customers. Data scientists, other analysts and business users then collect relevant data to analyze from internal systems, plus external data sources if needed. The latter task is the first step in data preparation, which involves gathering data and preparing it for use in business intelligence and analytics applications.
For research in science, medicine, higher education and other fields, data collection is often a more specialized process in which researchers create and implement measures to collect specific sets of data. In both the business and research contexts, however, the collected data must be accurate to ensure analytics findings and research results are valid.
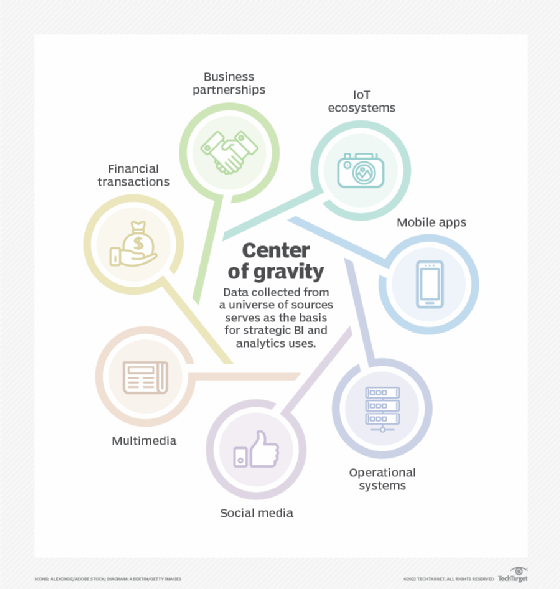
Organizations collect data from a variety of systems and other data sources.
What are different methods of data collection?
Data can be collected from one or more sources as needed to provide the information that's being sought. For example, to analyze sales and the effectiveness of its marketing campaigns, a retailer might collect customer data from transaction records, website visits, mobile applications, its loyalty program and online surveys.
The methods used to collect data vary based on the type of application. Some involve the use of technology, while others are manual procedures. The following are some common data collection methods:
- Automated data collection functions built into business applications, websites and mobile apps.
- Sensors that collect operational data from industrial equipment, vehicles and other machinery.
- Data collected from information services providers and other external data sources.
- Social media, discussion forums, reviews sites, blogs and other online channels.
- Surveys, questionnaires and forms completed online; in person; or by phone, email or mail.
- Focus groups and one-on-one interviews.
- Direct observation of participants in a research study.
Primary and secondary data collection methods
Data collection methods tend to fall into two categories: primary data collection and secondary data collection.
Primary data collection refers to data that's gathered firsthand through direct interaction with respondents; that is, it's original to the project for which it's being gathered. Primary data collection methods include questionnaires and surveys, interviews, focus groups, and observation.
Secondary data collection involves data that has been collected previously. Secondary data collection is done from established data sources, which can include published sources, online databases, public data, government data, institutional records and published research studies.

Organizations use various methods to collect customer data.
What are common challenges in data collection?
The challenges often faced when collecting data include the following:
- Data quality issues. Raw data typically includes errors, inconsistencies and other concerns. Ideally, data collection measures are designed to avoid or minimize such problems. However, in most cases, that isn't foolproof. As a result, collected data usually needs to be put through data profiling to identify issues and data cleansing to fix them.
- Finding relevant data. With a wide range of systems to navigate, gathering data to analyze can be a complicated task for data scientists and other users in an organization. The use of data curation techniques can help make it easier to find and access data. For example, that might include creating a data catalog and searchable indexes.
- Deciding which data to collect. This is a fundamental issue both for upfront collection of raw data and when users gather data for analytics applications. Collecting data that isn't needed adds time, cost and complexity to the process. But leaving out useful data can limit a data set's business value and affect analytics results.
- Dealing with big data. Big data environments typically include a combination of large volumes of structured, unstructured and semistructured data. That makes the initial data collection and processing stages more complex. In addition, data scientists often need to filter sets of raw data stored in a data lake for specific analytics applications.
- Low response and other research issues. In research studies, a lack of responses or willing participants raises questions about the validity of the data that's collected. Other research challenges include training people to collect the data and creating sufficient quality assurance procedures to ensure the data is accurate.
What are the key steps in the data collection process?
Well-designed data collection processes include the following steps:
- Identify a business or research issue that needs to be addressed and set goals for the project.
- Gather data requirements to answer business questions or deliver research information.
- Identify the data sets that can provide the desired information.
- Set a plan for collecting the data, including the collection methods that will be used.
- Collect the available data and begin working to prepare it for analysis.
What are data collection tools?
Beyond data collection methods and steps in the data collection process, many specific data collection tools are routinely used. These include the following:
- In-person surveys. Respondents provide data face to face.
- Online surveys. Respondents provide data over the internet.
- Mobile surveys. Online surveys are deployed on the respondent's smartphone or tablet.
- Telephone surveys. Data is collected through question-and-answer interactions over the phone.
- Observation. Data is collected by observing the behavior of participants, without direct interaction.
- Sentence completion. Respondents are asked to complete sentences to determine their mindset, opinions or level of knowledge.
- Role-playing. Respondents are asked how they would respond to a given situation or scenario.
- Word association. Respondents are asked to offer words that occur to them when they're presented with a cueing word.
There are many different products on the market for collecting data, including survey software or marketing automation software that lets users develop forms or collect data for graphs, charts or other types of reports. Dedicated data collection tools can help businesses save time and money, ensure data accuracy, and consolidate data in one location.
Data collection considerations and best practices
Two primary types of data can be collected: quantitative data and qualitative data. The former is numerical -- for example, prices, amounts, statistics and percentages. Qualitative data is descriptive in nature -- for example, color, smell, appearance and opinion.
Organizations also use secondary data from external sources to help drive business decisions. For example, manufacturers and retailers might use U.S. Census Bureau data to aid in planning their marketing strategies and campaigns. Companies might also use government health statistics and outside healthcare studies to analyze and optimize their medical insurance plans.
The European Union's General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and other privacy laws enacted in recent years make data privacy and security major considerations when collecting data, particularly if it contains personal information about customers. An organization's data governance program should include policies to ensure data collection practices comply with laws such as the GDPR.
Other data collection best practices include the following:
- Know the questions you're trying to answer. Understand why data is being collected to ensure the right data is obtained to meet business or research needs.
- Employ data validation procedures. Ensure the data is accurate, either as it's collected or as part of the data preparation process.
- Only gather the necessary data. Don't waste time and resources collecting irrelevant data.
- Reduce human error. Using automated data collection techniques can help reduce the possibility of human error.
Learn which methods and best practices companies use to collect massive amounts of information -- or big data -- from a variety of sources to gain insight to make business decisions.
This was last updated in June 2024
Continue Reading About data collection
- ESG data collection: Beginning steps and best practices
- Ways to collect customer data that keep you compliant
- Standardized data collection methods can help fight cybercrime
- IoT data collection: When time is of the essence
- Top data preparation challenges and how to overcome them
 customer insight (consumer insight)
customer insight (consumer insight)  By: Katie Terrell Hanna
By: Katie Terrell Hanna  How to collect customer feedback
How to collect customer feedback  By: Beth Schultz
By: Beth Schultz  How to create a customer journey map -- with template
How to create a customer journey map -- with template  By: Andrew Froehlich
By: Andrew Froehlich  How to gather and evaluate customer sentiment
How to gather and evaluate customer sentiment  By: Scott Sachs
By: Scott Sachs