publications – ENCODE (original) (raw)

THE ENCYCLOPEDIA AT A GLANCE
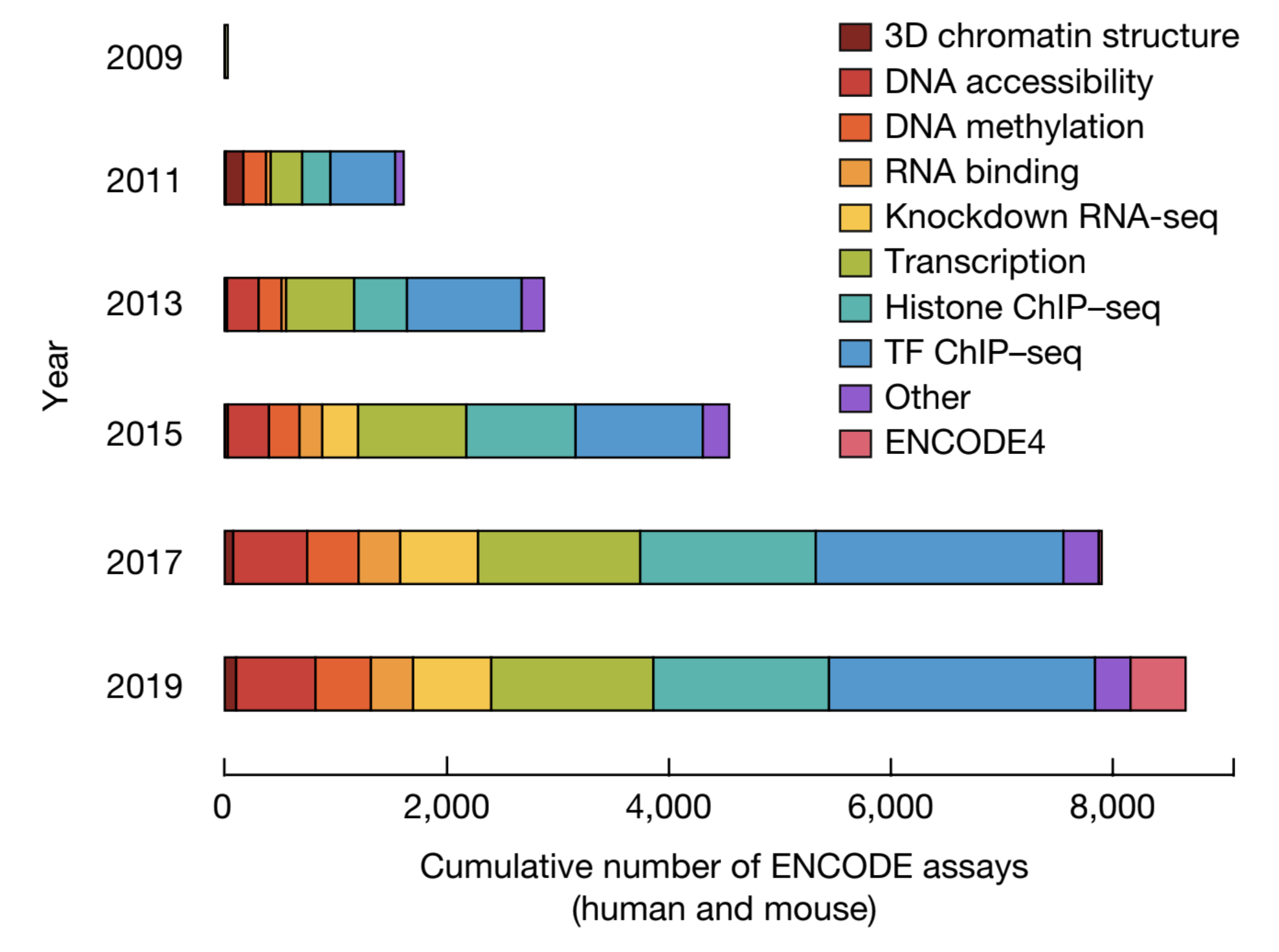
The human and mouse genomes contain instructions that specify RNAs and proteins and govern the timing, magnitude, and cellular context of their production. To better delineate these elements, phase III of the Encyclopedia of DNA Elements (ENCODE) Project has expanded analysis of the cell and tissue repertoires of RNA transcription, chromatin structure and modification, DNA methylation, chromatin looping, and occupancy by transcription factors and RNA-binding proteins...
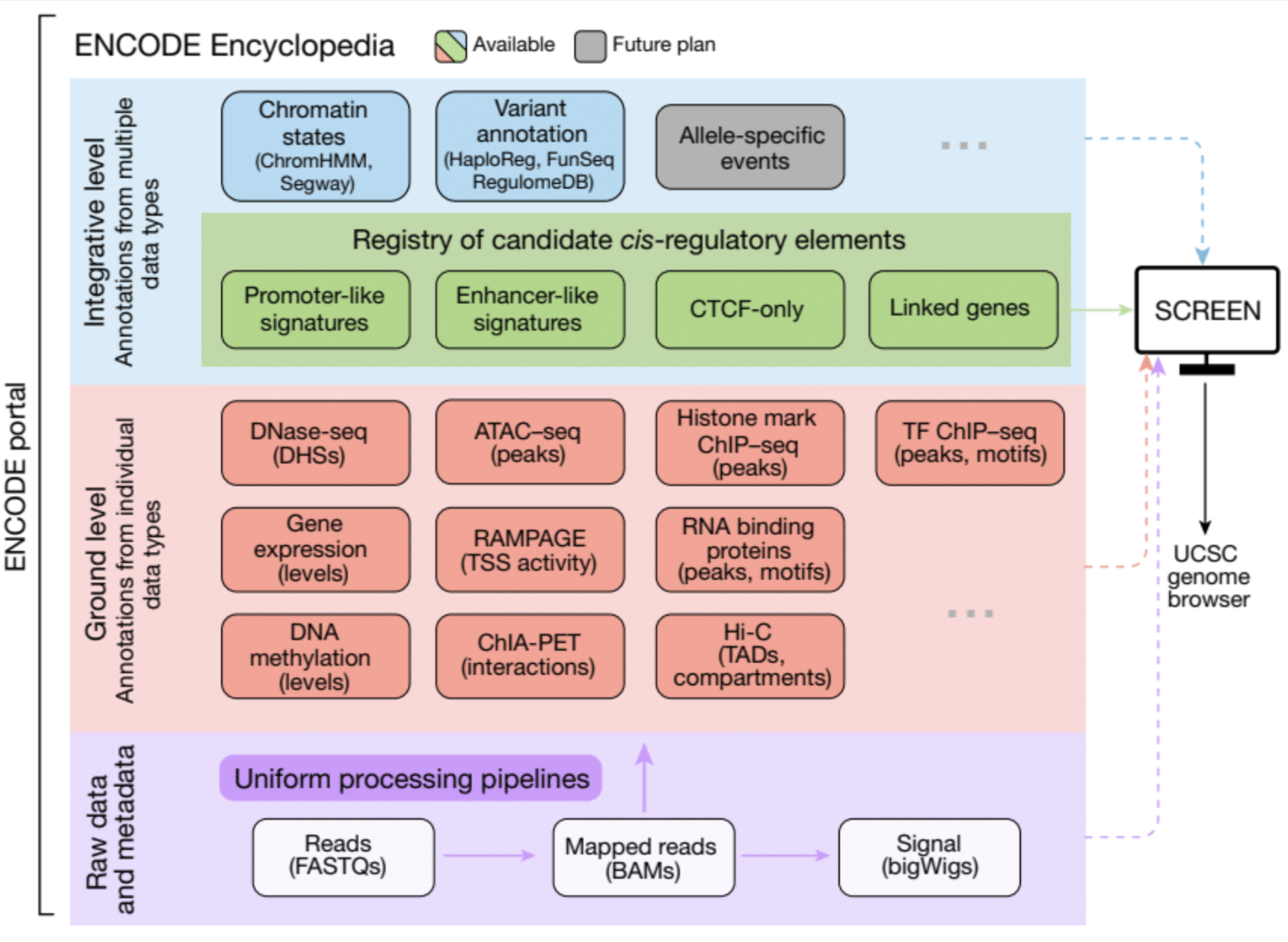
The Encylopedia of DNA Elements (ENCODE) Project launched in 2003 with the long-term goal of developing a comprehensive map of functional elements in the human genome. These included genes, biochemical regions associated with gene regulation (for example, transcription factor binding sites, open chromatin, and histone marks) and transcript isoforms. The marks serve as sites for candidate cis-regulatory elements (cCREs) that may serve functional roles in regulating gene expression...
MOUSE EPIGENETICS AND GENE EXPRESSION
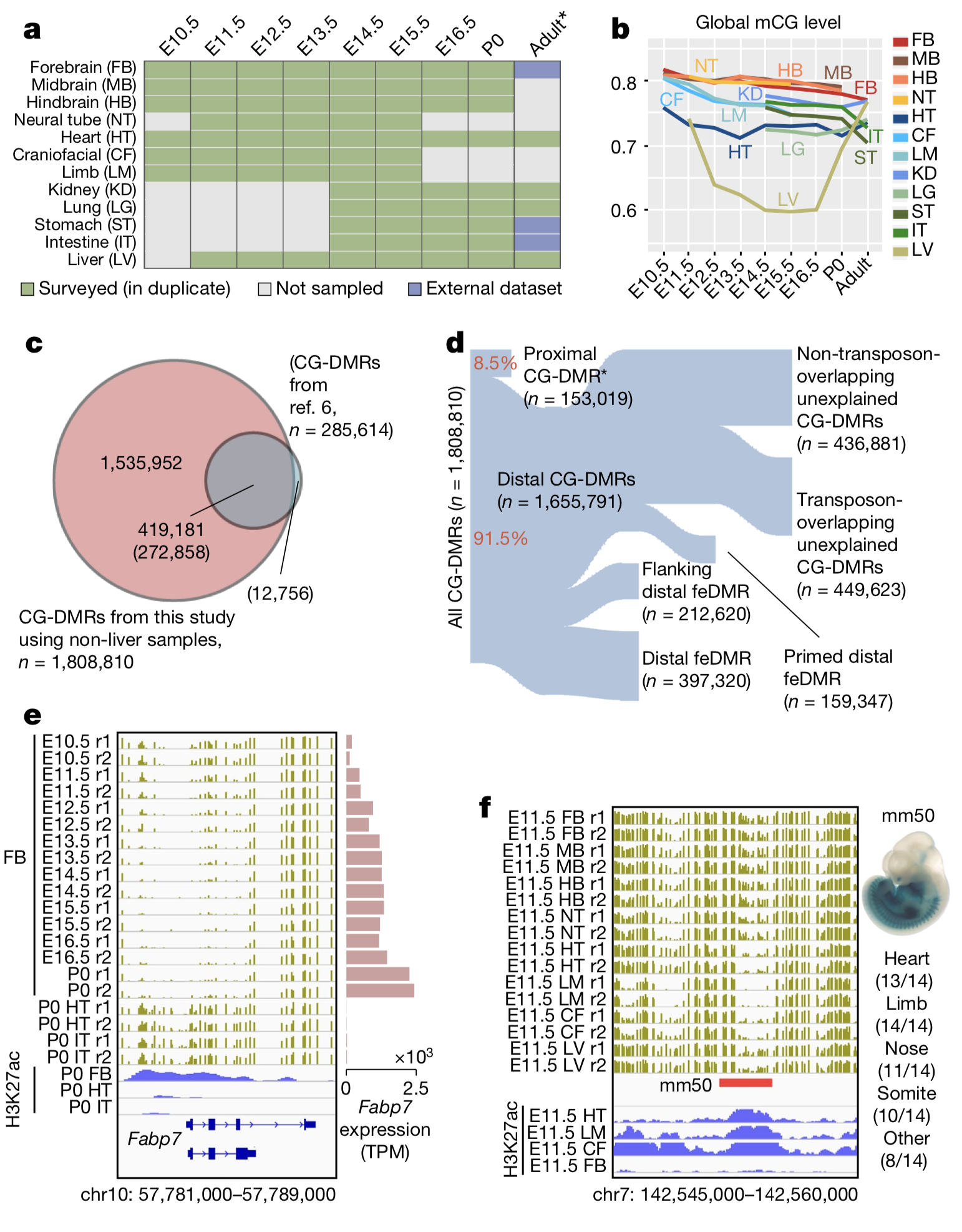
Cytosine DNA methylation is essential for mammalian development but understanding of its spatiotemporal distribution in the developing embryo remains limited. Here, as part of the mouse Encyclopedia of DNA Elements (ENCODE) project, we profiled 168 methylomes from 12 mouse tissues or organs at 9 developmental stages from embryogenesis to adulthood. We identified 1,808,810 genomic regions...
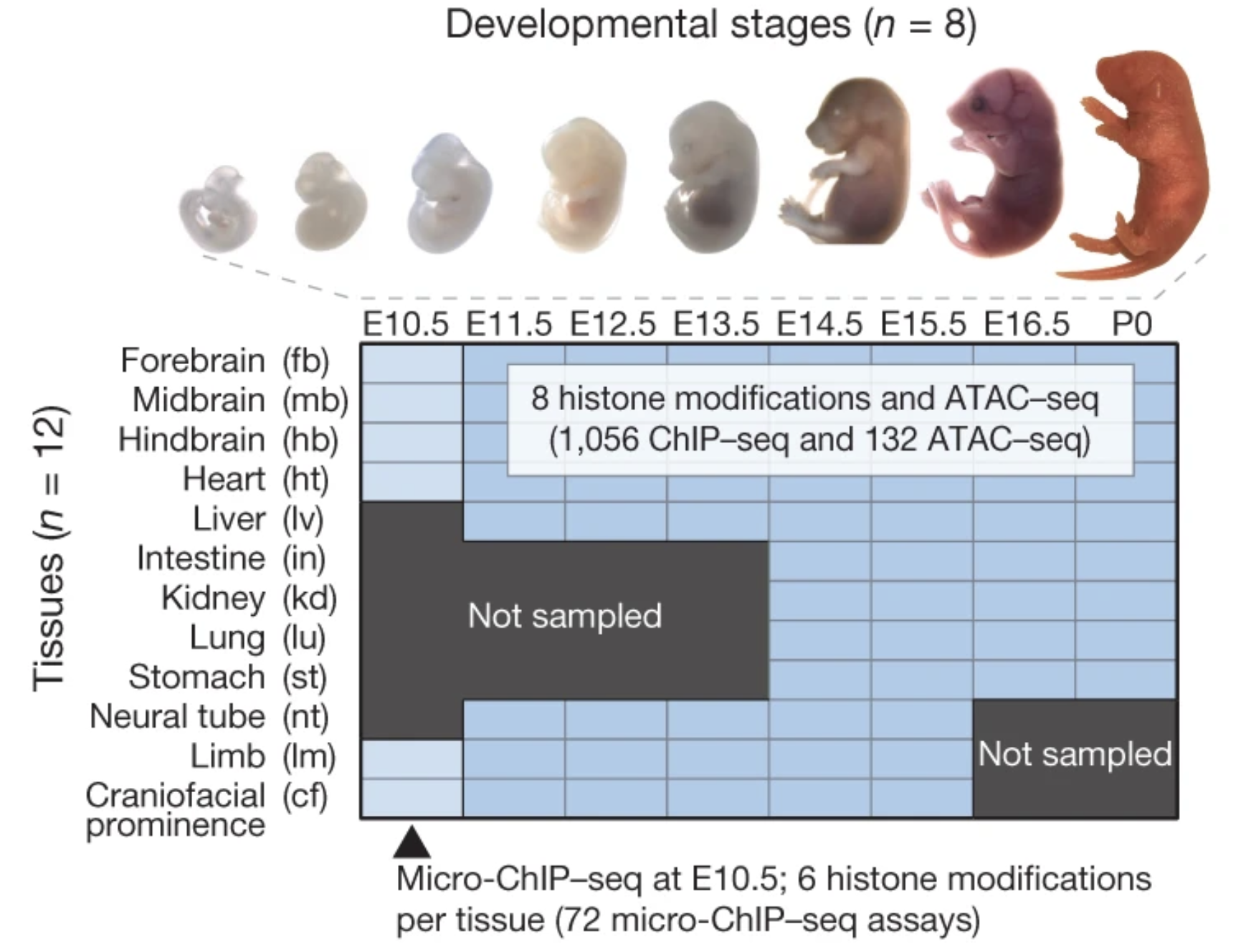
The Encyclopedia of DNA Elements (ENCODE) project has established a genomic resource for mammalian development, profiling a diverse panel of mouse tissues at 8 developmental stages from 10.5 days after conception until birth, including transcriptomes, methylomes and chromatin states. Here we systematically examined the state and accessibility of chromatin in the developing mouse fetus...
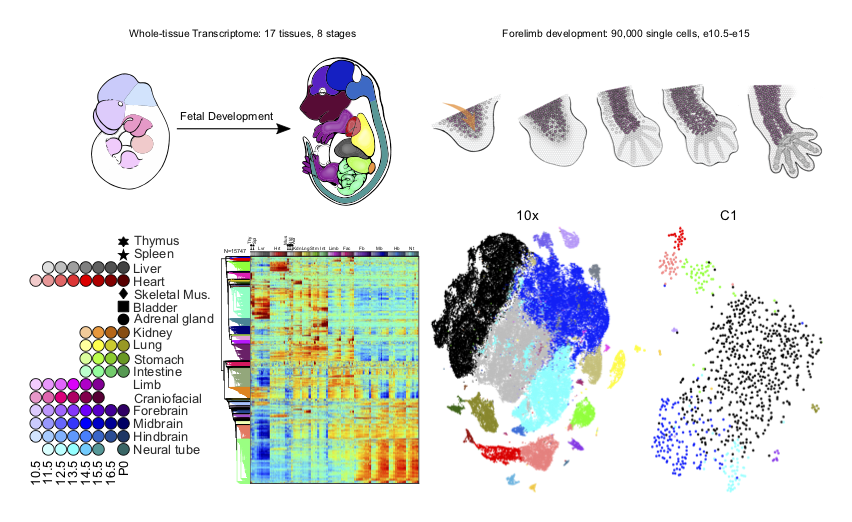
During mammalian embryogenesis, differential gene expression gradually builds the identity and complexity of each tissue and organ system. Here we systematically quantified mouse polyA-RNA from day 10.5 of embryonic development to birth, sampling 17 tissues and organs. The resulting developmental transcriptome is globally structured by dynamic cytodifferentiation, body-axis and cell-proliferation gene sets that were further characterized by the transcription factor motif codes of their promoters...
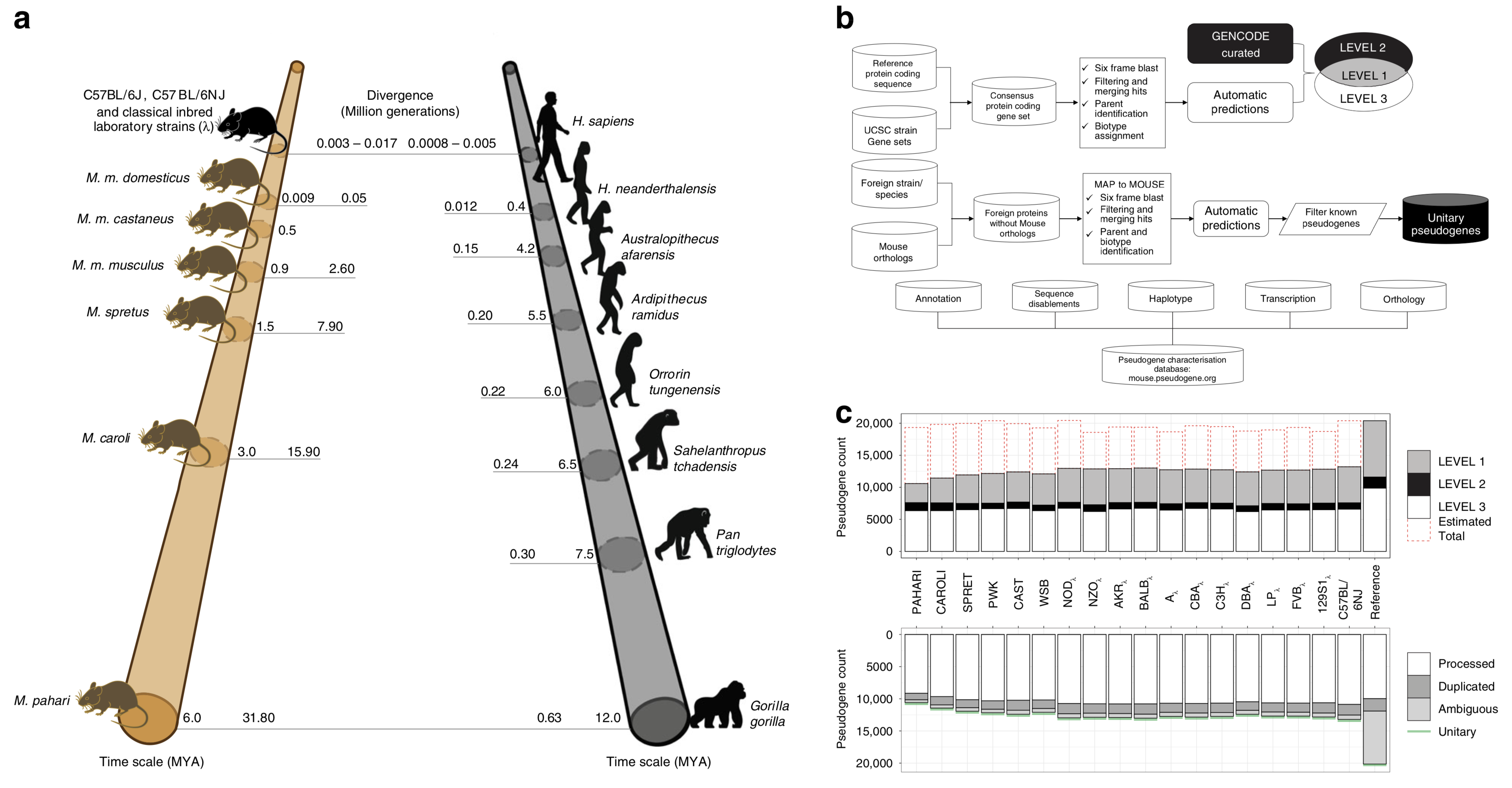
Pseudogenes are ideal markers of genome remodelling. In turn, the mouse is an ideal platform for studying them, particularly with the recent availability of strain-sequencing and transcriptional data. Here, combining both manual curation and automatic pipelines, we present a genome-wide annotation of the pseudogenes in the mouse reference genome and 18 inbred mouse strains...
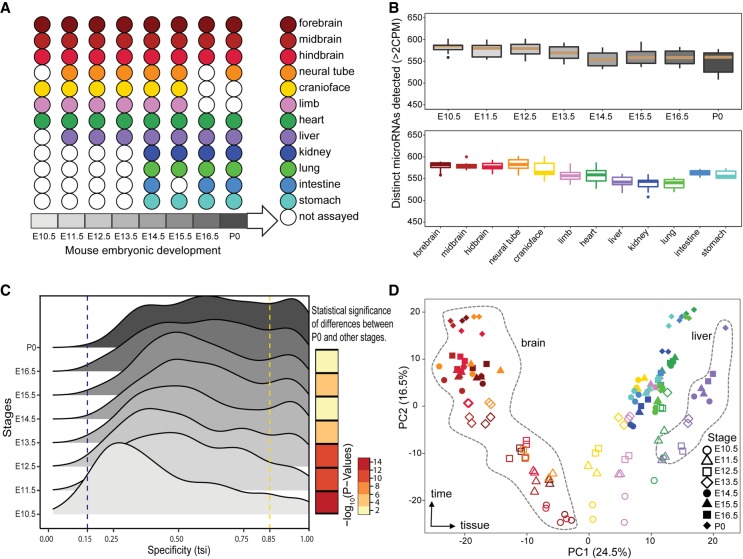
microRNAs (miRNAs) are a class of small non-coding RNA that are critical post- transcriptional regulators of gene expression. The ENCODE project profiled the expression of miRNAs in various tissues during a time-course of embryonic development in mouse and several human prenatal...
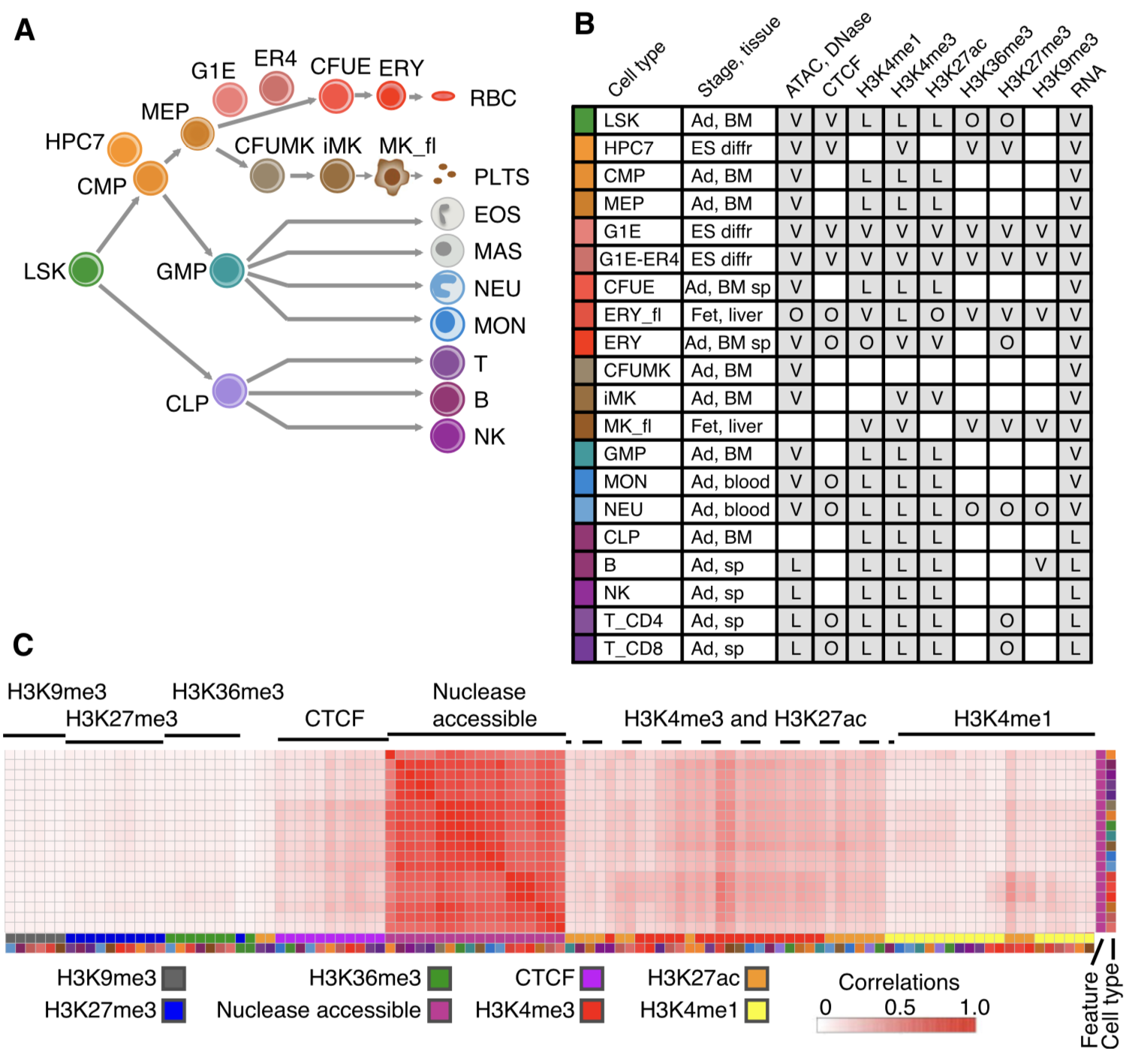
Thousands of epigenomic data sets have been generated in the past decade, but it is difficult for researchers to effectively use all the data relevant to their projects. Systematic integrative analysis can help meet this need, and the VISION project was established for validated systematic integration of epigenomic data in hematopoiesis...
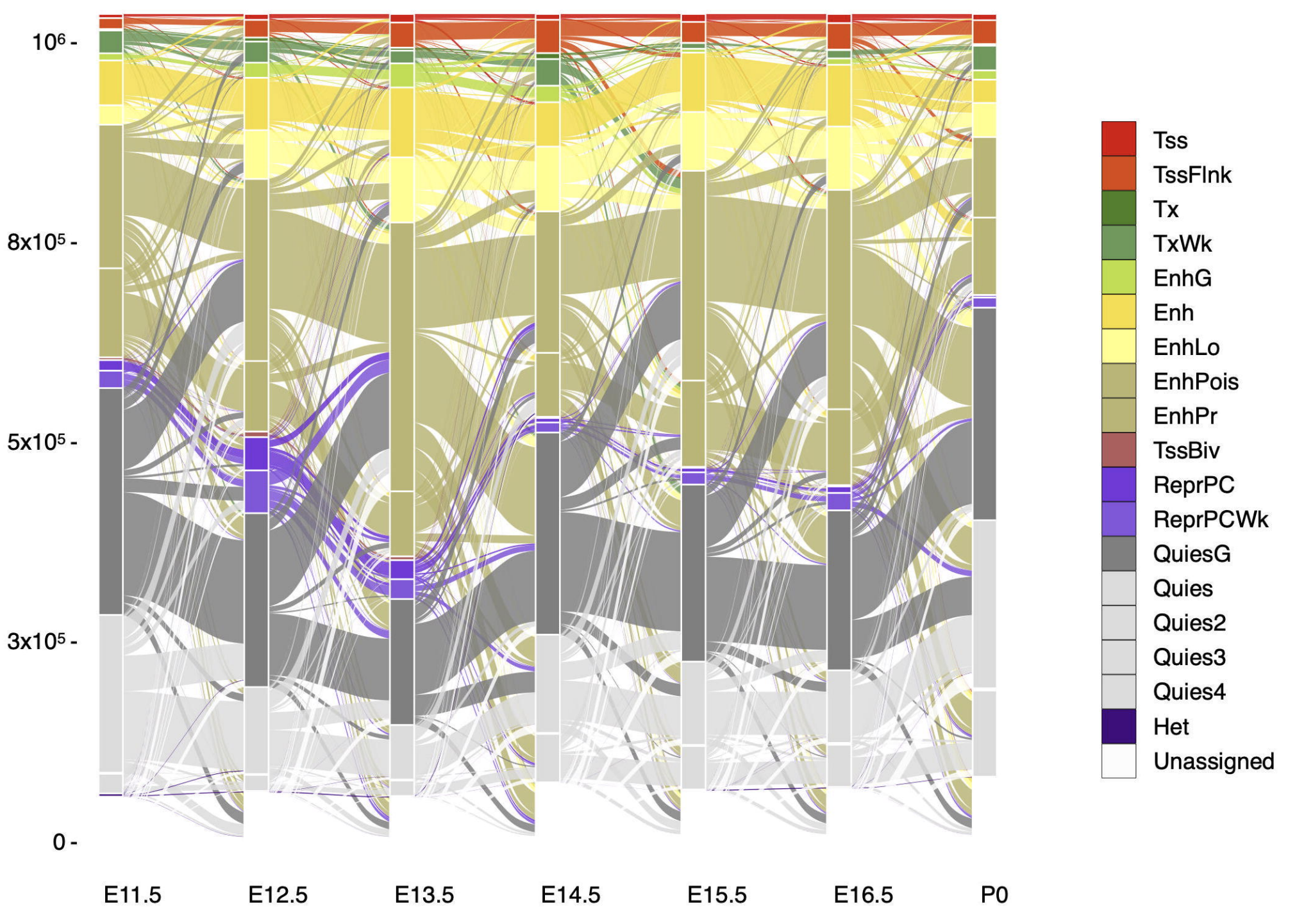
The morphologically and functionally distinct cell types of a multicellular organism are maintained by epigenomes and gene expression programs. Phase III of the ENCODE Project profiled 66 mouse epigenomes across twelve tissues at daily intervals from embryonic day 10.5 to birth. Applying the ChromHMM algorithm to these epigenomes, we annotated...
HUMAN GENE EXPRESSION AND RNA EXPRESSION
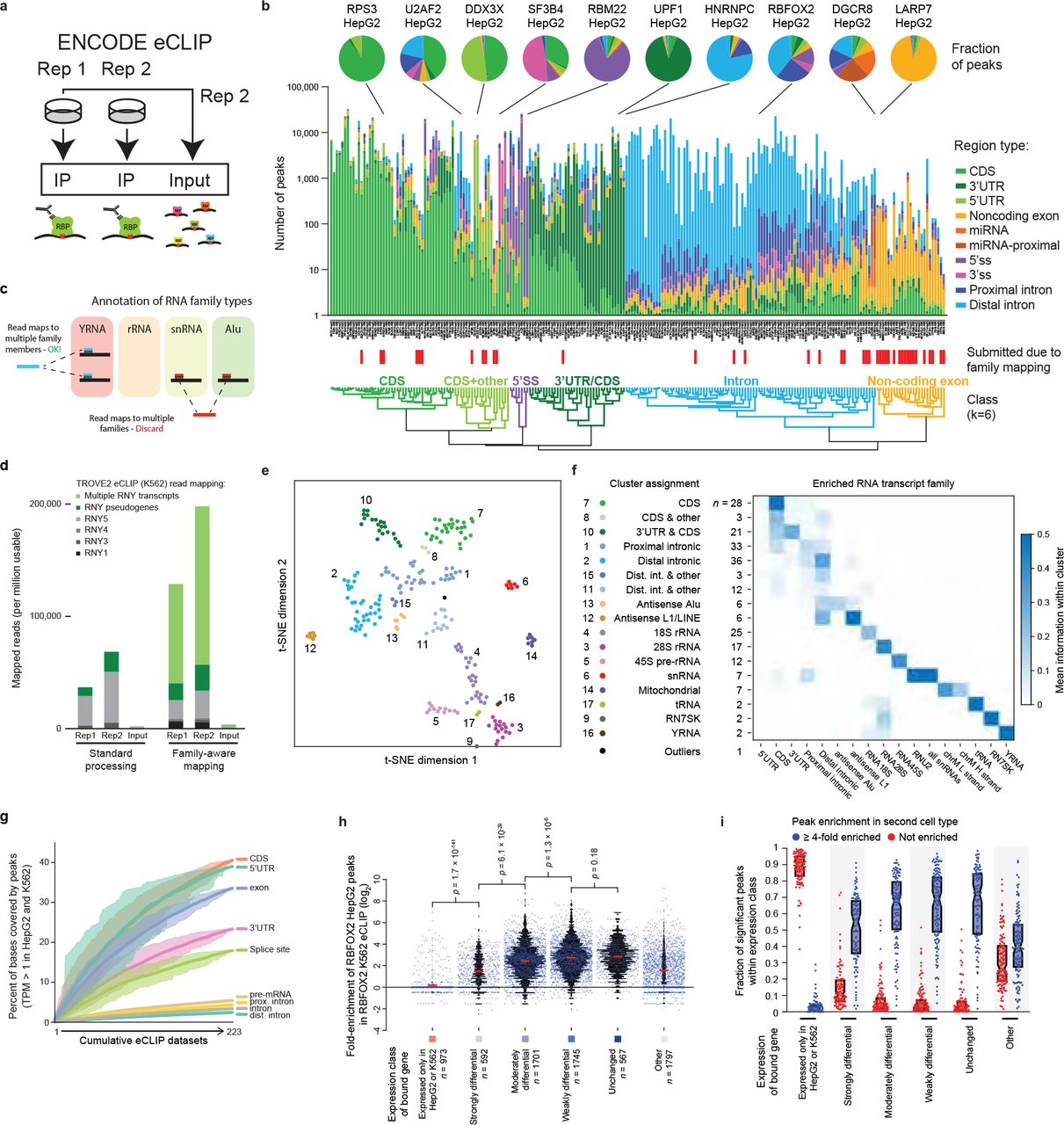
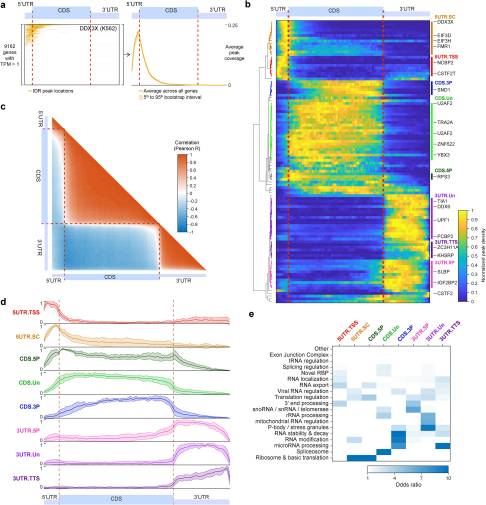
Many proteins regulate the expression of genes by binding to specific regions encoded in the genome1. Here we introduce a new data set of RNA elements in the human genome that are recognized by RNA-binding proteins (RBPs), generated as part of the Encyclopedia of DNA Elements (ENCODE) project phase III. This class of regulatory elements functions only when transcribed into RNA, as they serve as the binding sites for RBPs...
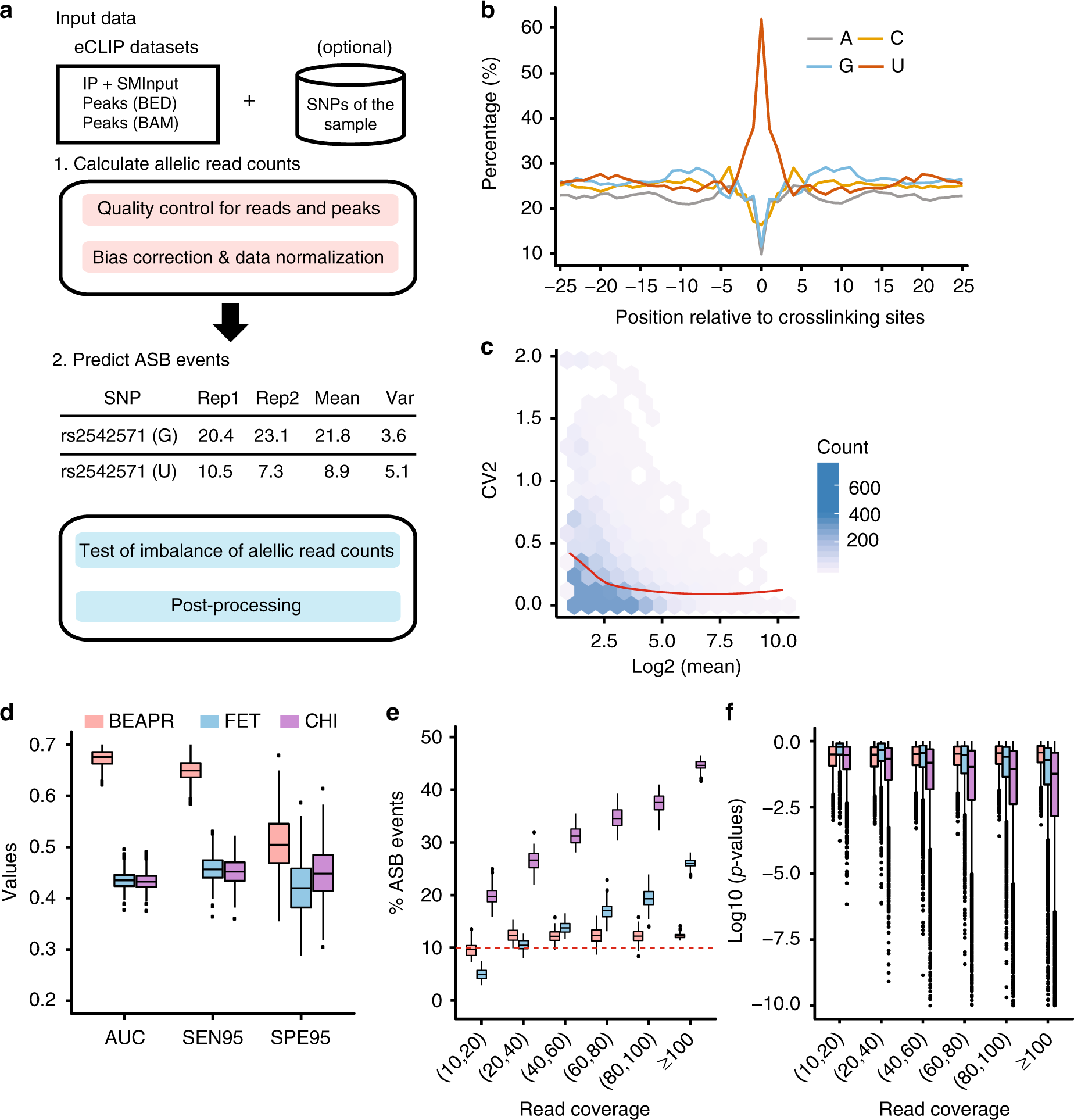
Allele-specific protein-RNA binding is an essential aspect that may reveal functional genetic variants (GVs) mediating post-transcriptional regulation. Recently, genome-wide detection of in vivo binding of RNA-binding proteins is greatly facilitated by the enhanced crosslinking and immunoprecipitation (eCLIP) method. We developed a new computational approach, called BEAPR...
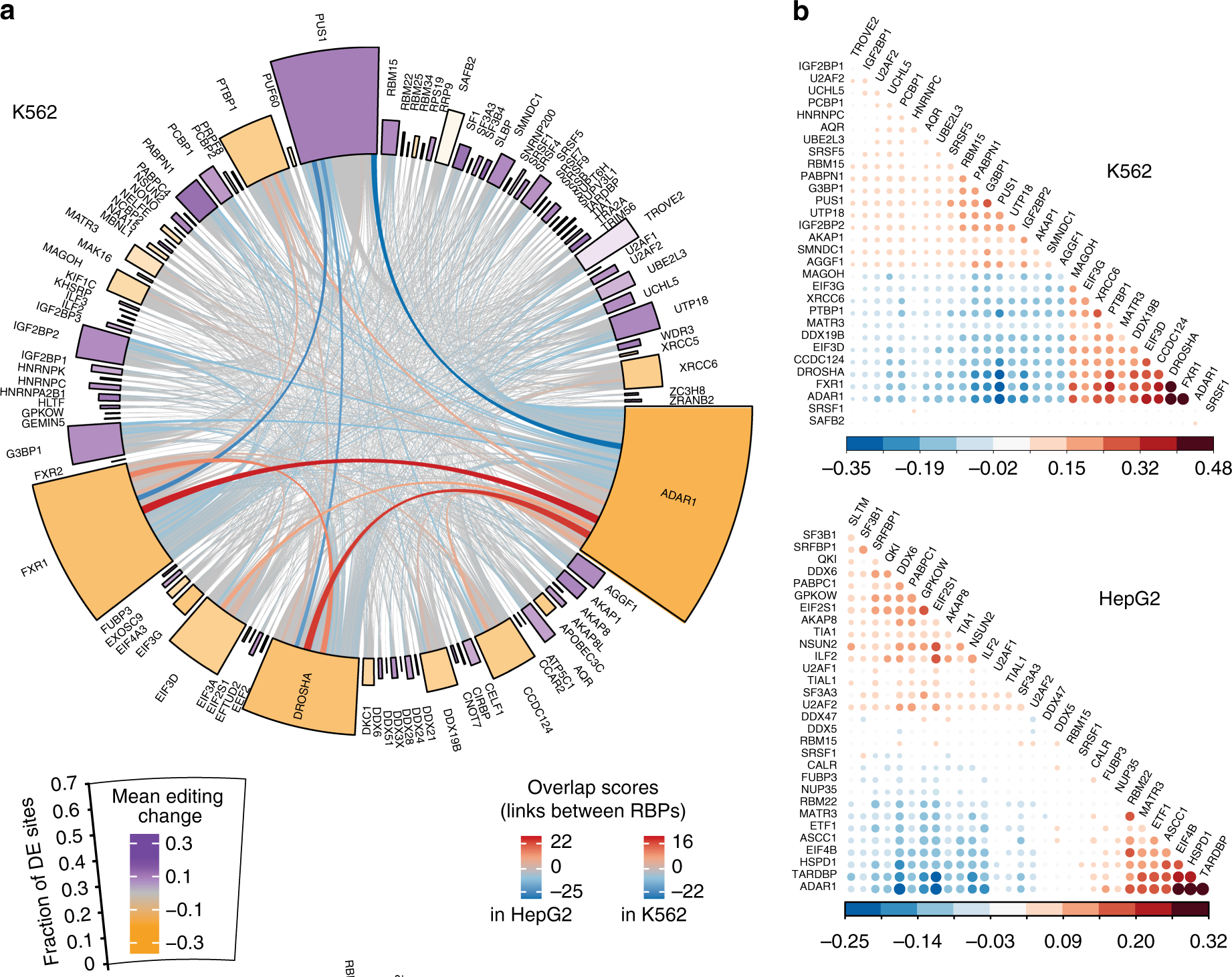
Adenosine-to-inosine (A-to-I) editing, mediated by the ADAR enzymes, diversifies the transcriptome by altering RNA sequences. Recent studies reported global changes in RNA editing in disease and development. Such widespread editing variations necessitate an improved understanding of the regulatory mechanisms of RNA editing. Here, we study the roles of >200 RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) in mediating RNA editing in two human cell lines...
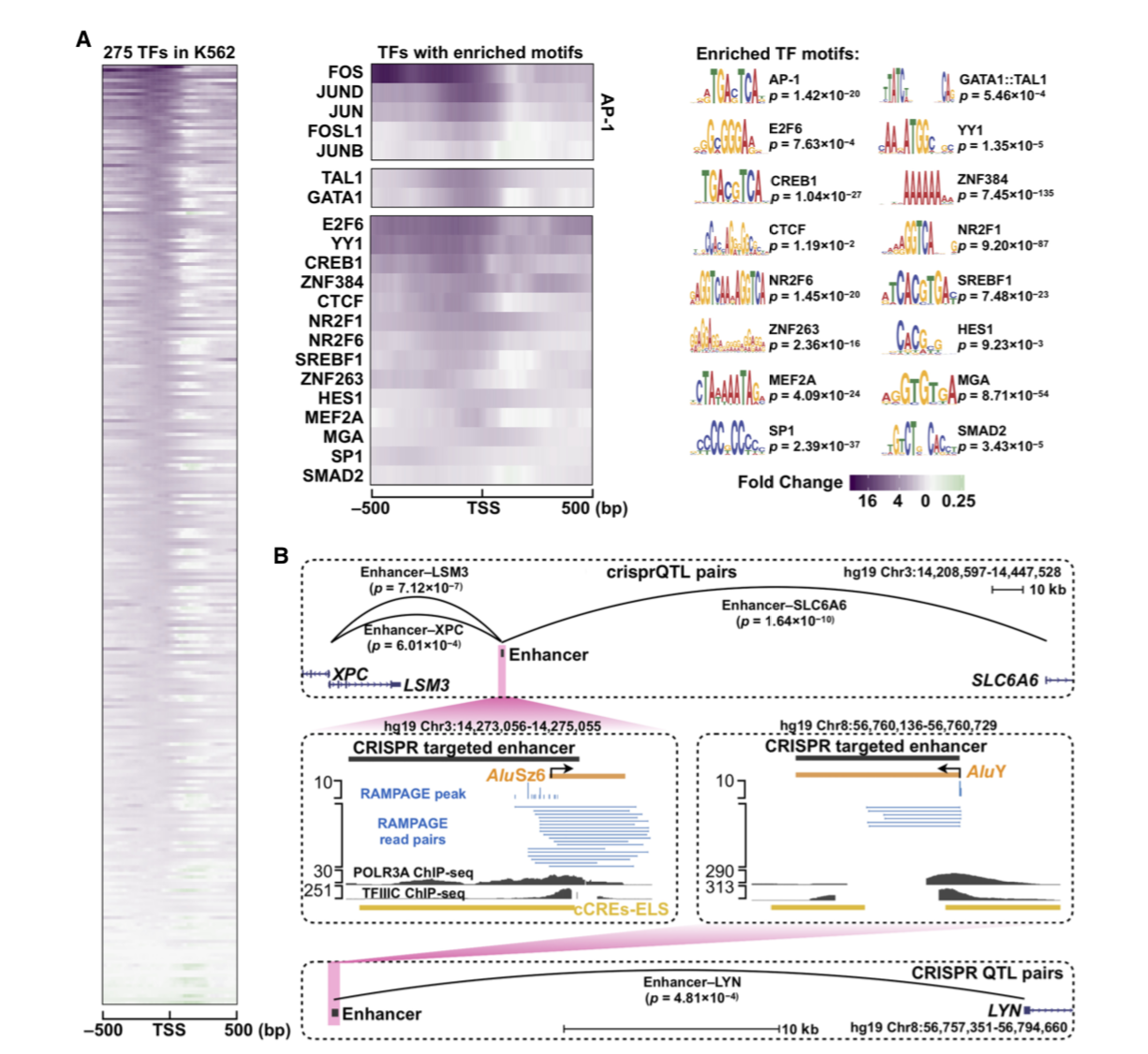
Transcription factors are DNA-binding proteins that have key roles in gene regulation. Genome-wide occupancy maps of transcriptional regulators are important for understanding gene regulation and its effects on diverse biological processes. However, only a minority of the more than 1,600 transcription factors encoded in the human genome has been assayed...

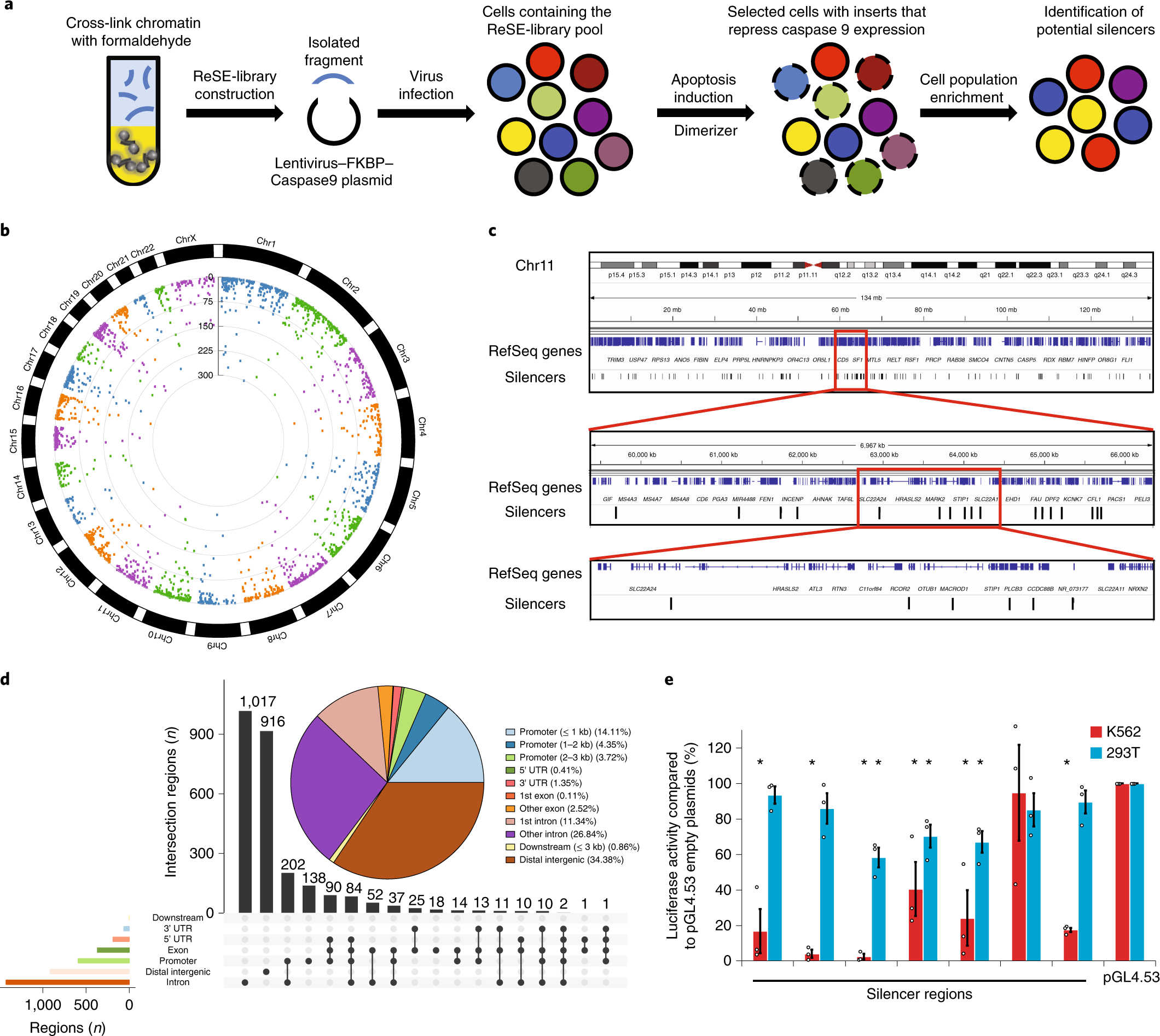
The majority of the human genome does not encode proteins. Many of these noncoding regions contain important regulatory sequences that control gene expression. To date, most studies have focused on activators such as enhancers, but regions that repress gene expression—silencers—have not been systematically studied...
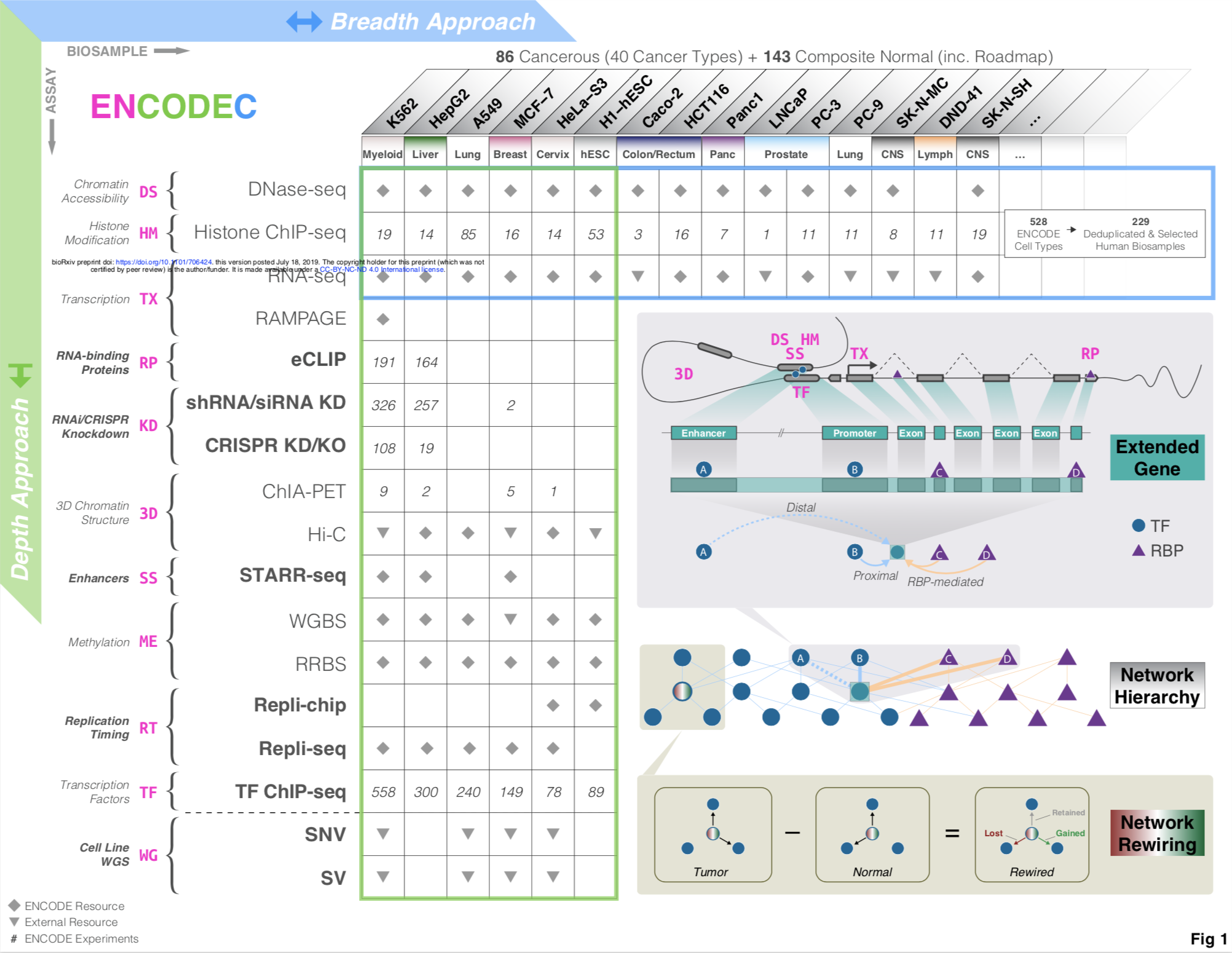
ENCODE comprises thousands of functional genomics datasets, and the encyclopedia covers hundreds of cell types, providing a universal annotation for genome interpretation. However, for particular applications, it may be advantageous to use a customized annotation...
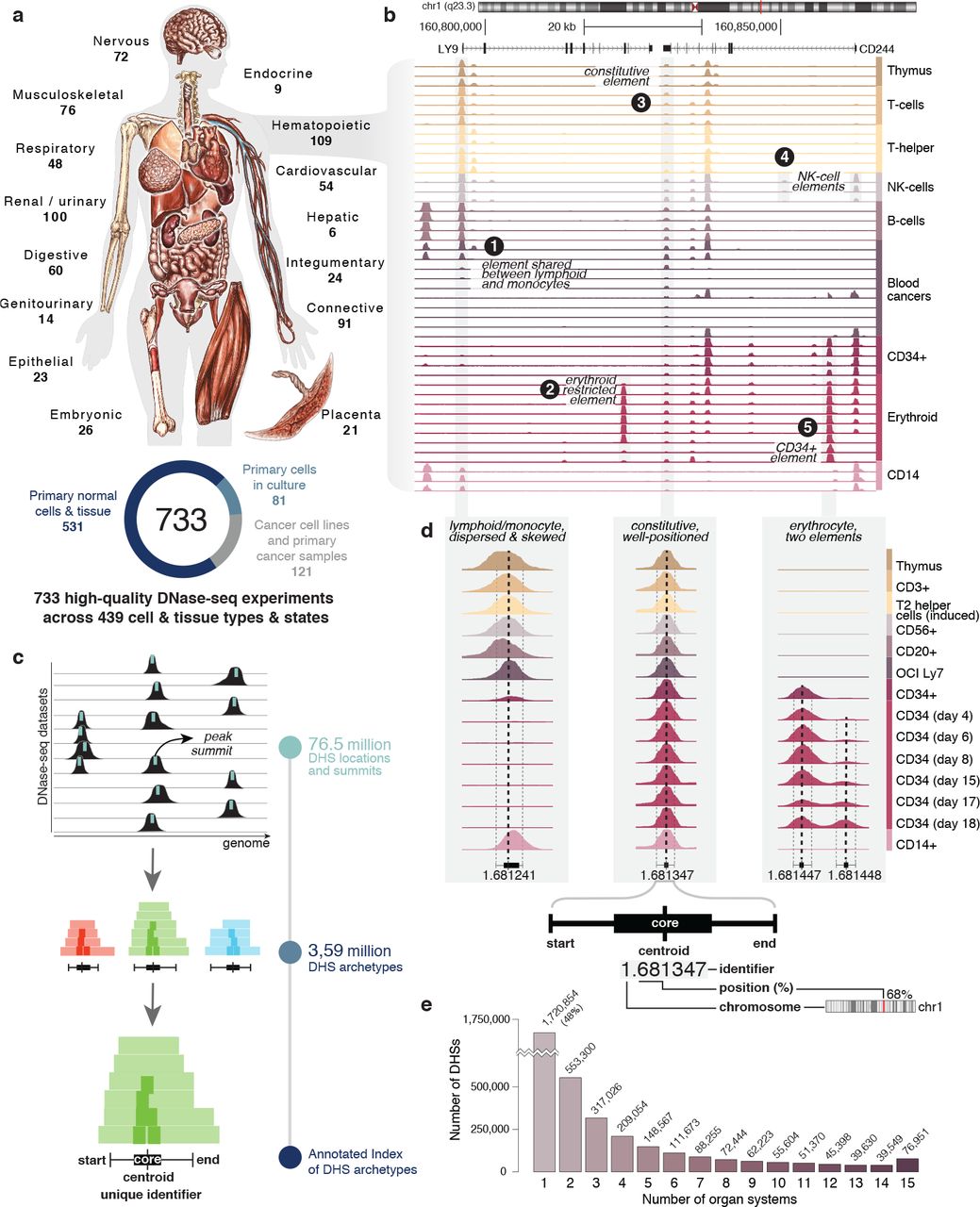
DNase I hypersensitive sites (DHSs) are generic markers of regulatory DNA and contain genetic variations associated with diseases and phenotypic traits. We created high-resolution maps of DHSs from 733 human biosamples encompassing 438 cell and tissue types and states, and integrated these to delineate and numerically index approximately 3.6 million DHSs within the human genome sequence, providing a common coordinate system for regulatory DNA...
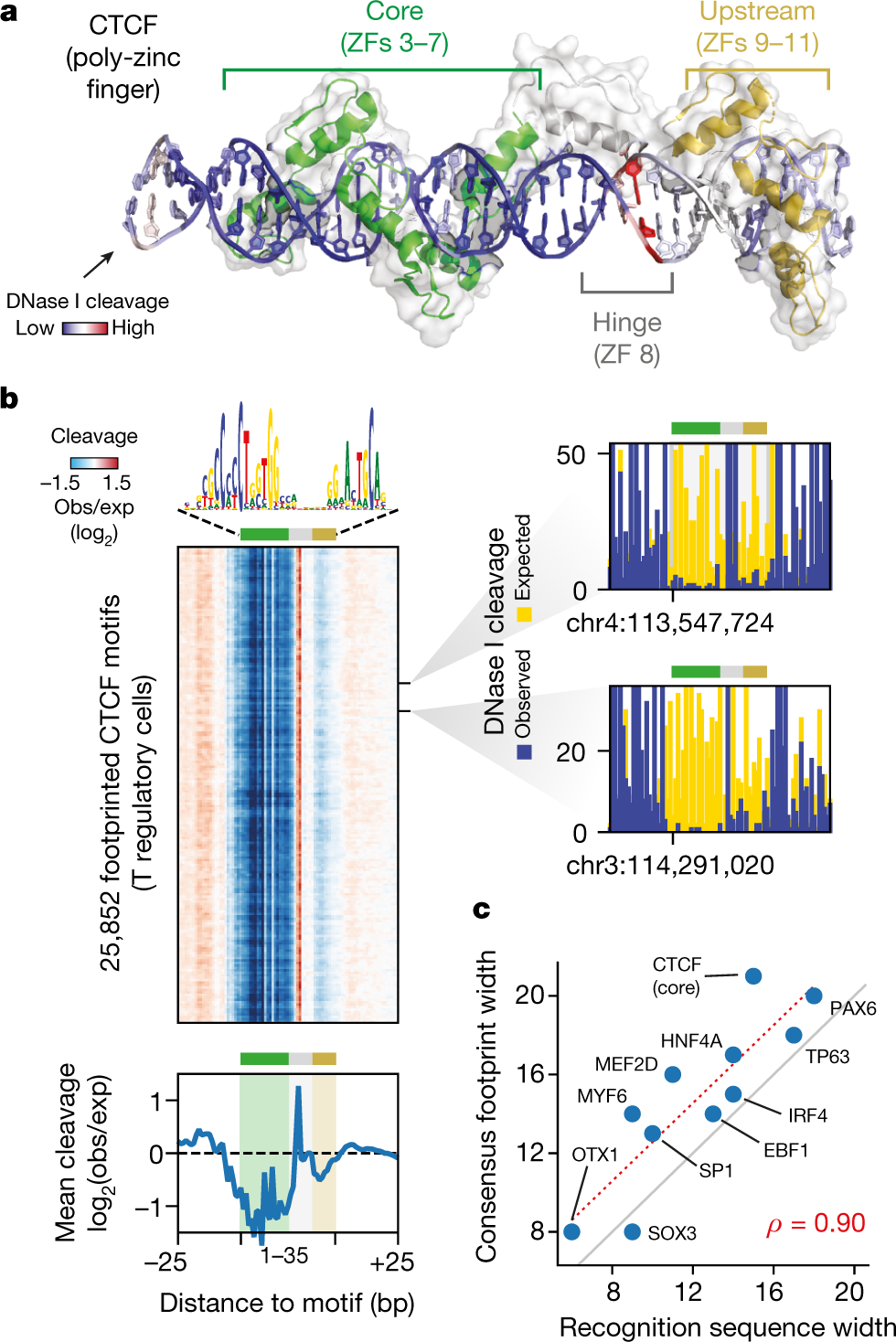
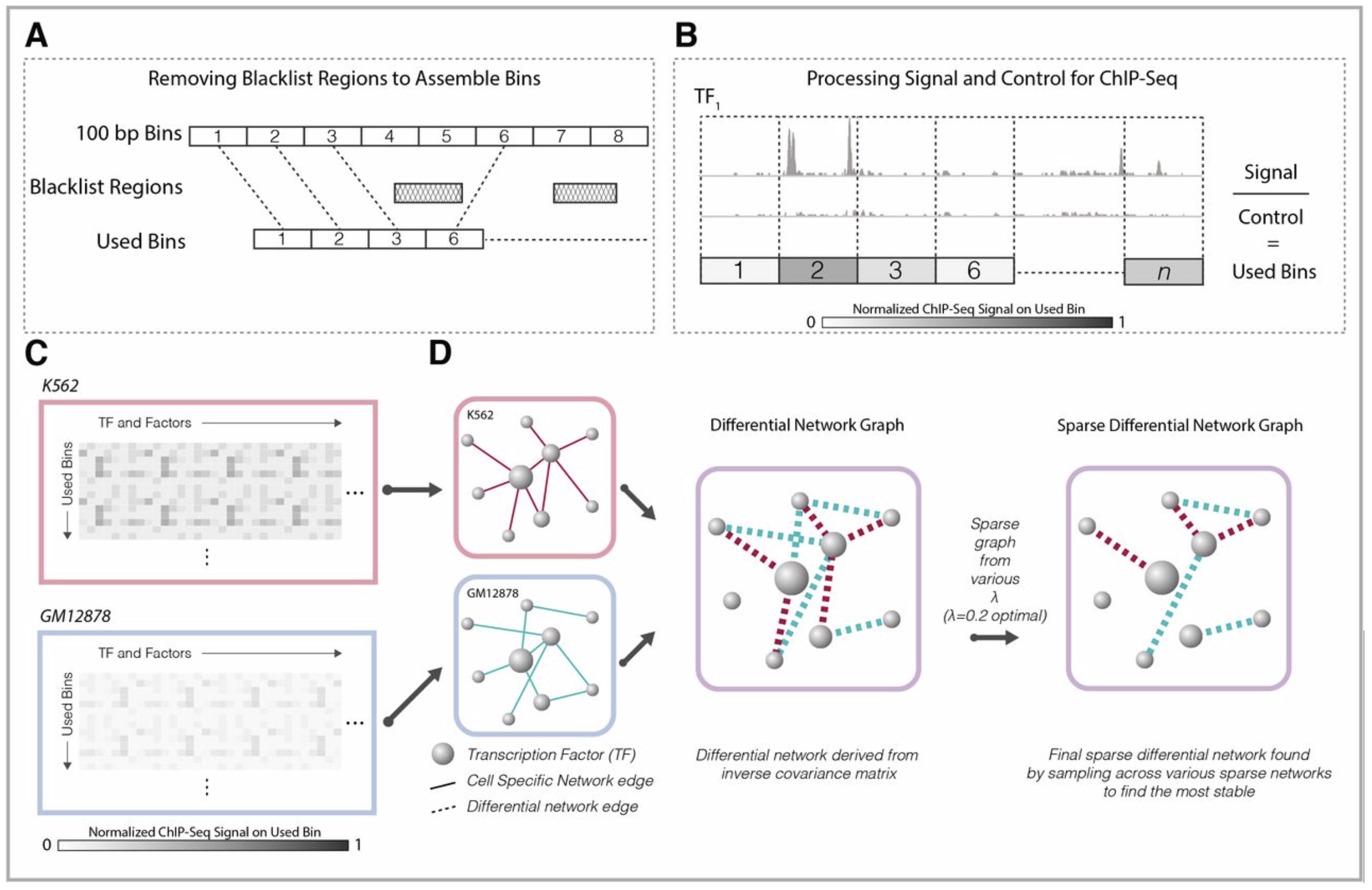
Combinatorial binding of transcription factors to regulatory DNA underpins gene regulation in all organisms. Genetic variation in regulatory regions has been connected with diseases and diverse phenotypic traits, but it remains challenging to distinguish variants that affect regulatory function. Genomic DNase I footprinting enables the quantitative, nucleotide-resolution delineation of sites of transcription factor occupancy within native chromatin...
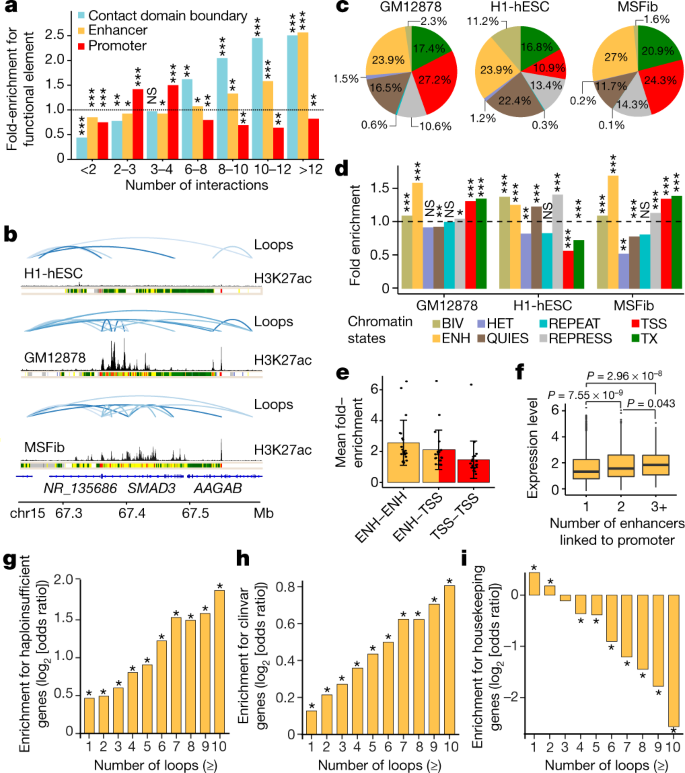
Physical interactions between distal regulatory elements have a key role in regulating gene expression, but the extent to which these interactions vary between cell types and contribute to cell-type-specific gene expression remains unclear. Here, to address these questions as part of phase III of the Encyclopedia of DNA Elements (ENCODE), we mapped cohesin-mediated chromatin loops, using chromatin interaction analysis by paired-end tag sequencing (ChIA-PET), and analysed gene expression in 24 diverse human cell types, including core ENCODE cell lines...
HUMAN TRANSCRIPTS AND RNA REGULATION
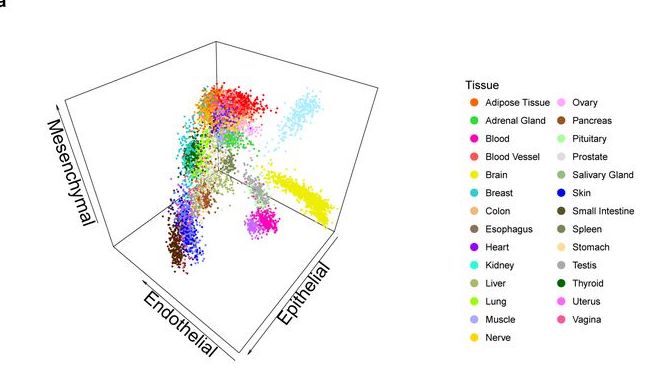
We have produced RNA sequencing data for 53 primary cells from different locations in the human body. The clustering of these primary cells reveals that most cells in the human body share a few broad transcriptional programs, which define five major cell types: epithelial, endothelial, mesenchymal, neural, and blood cells. These act as basic components of many tissues and organs...
A critical step in uncovering rules of RNA processing is to study the in vivo regulatory networks of RNA binding proteins (RBPs). Crosslinking and immunoprecipitation (CLIP) methods enable mapping RBP targets transcriptome-wide, but methodological differences present challenges to large-scale analysis across datasets...
Alu elements are one of the most successful families of transposons in the human genome. A portion of Alu elements is transcribed by RNA Pol III, whereas the remaining ones are part of Pol II transcripts. Because Alu elements are highly repetitive, it has been difficult to identify...
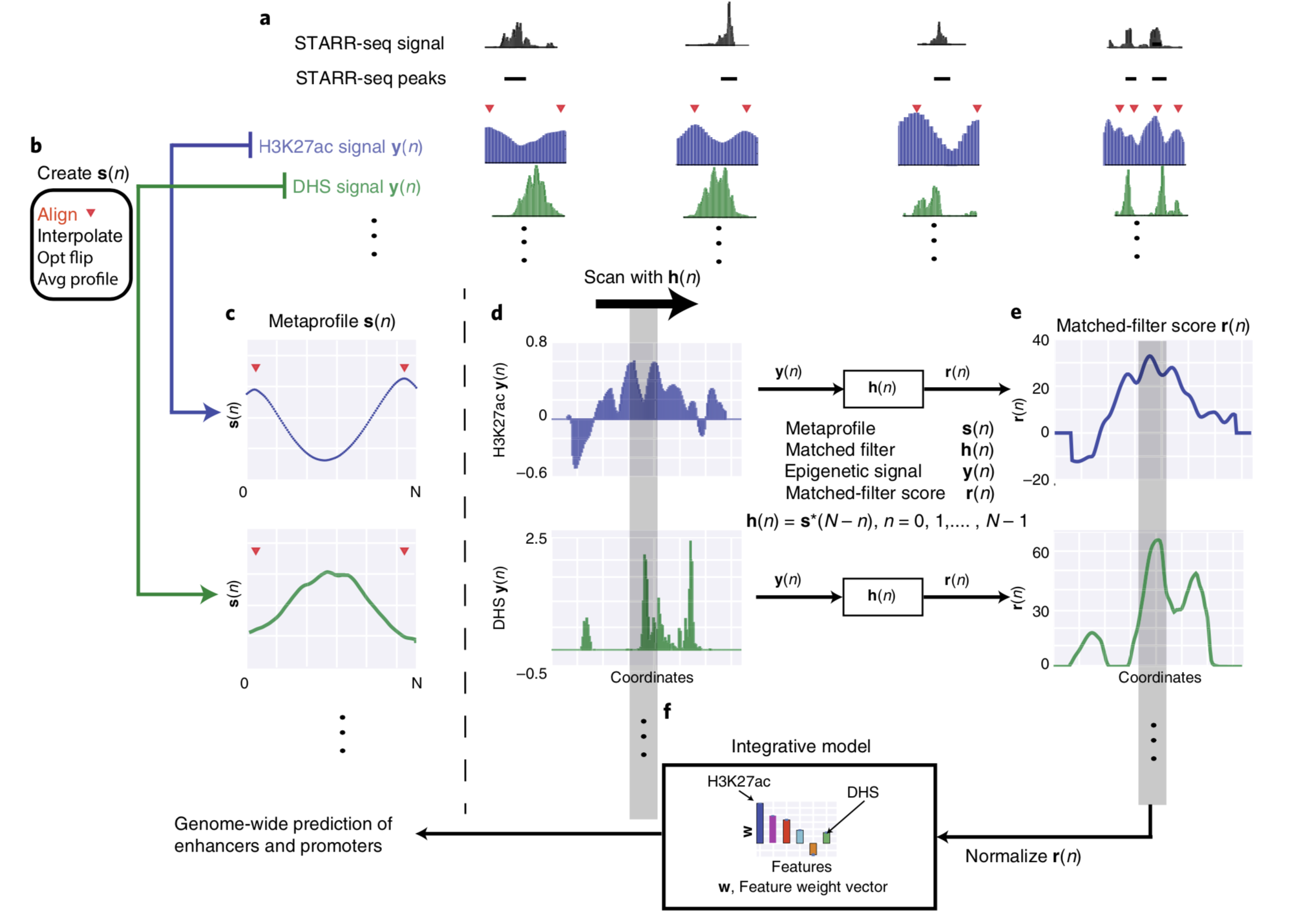
Enhancers are important non-coding elements, but they have traditionally been hard to characterize experimentally. The development of massively parallel assays allows the characterization of large numbers of enhancers for the first time. Here, we developed a framework using Drosophila STARR-seq to create shape-matching filters based on meta-profiles of epigenetic features...
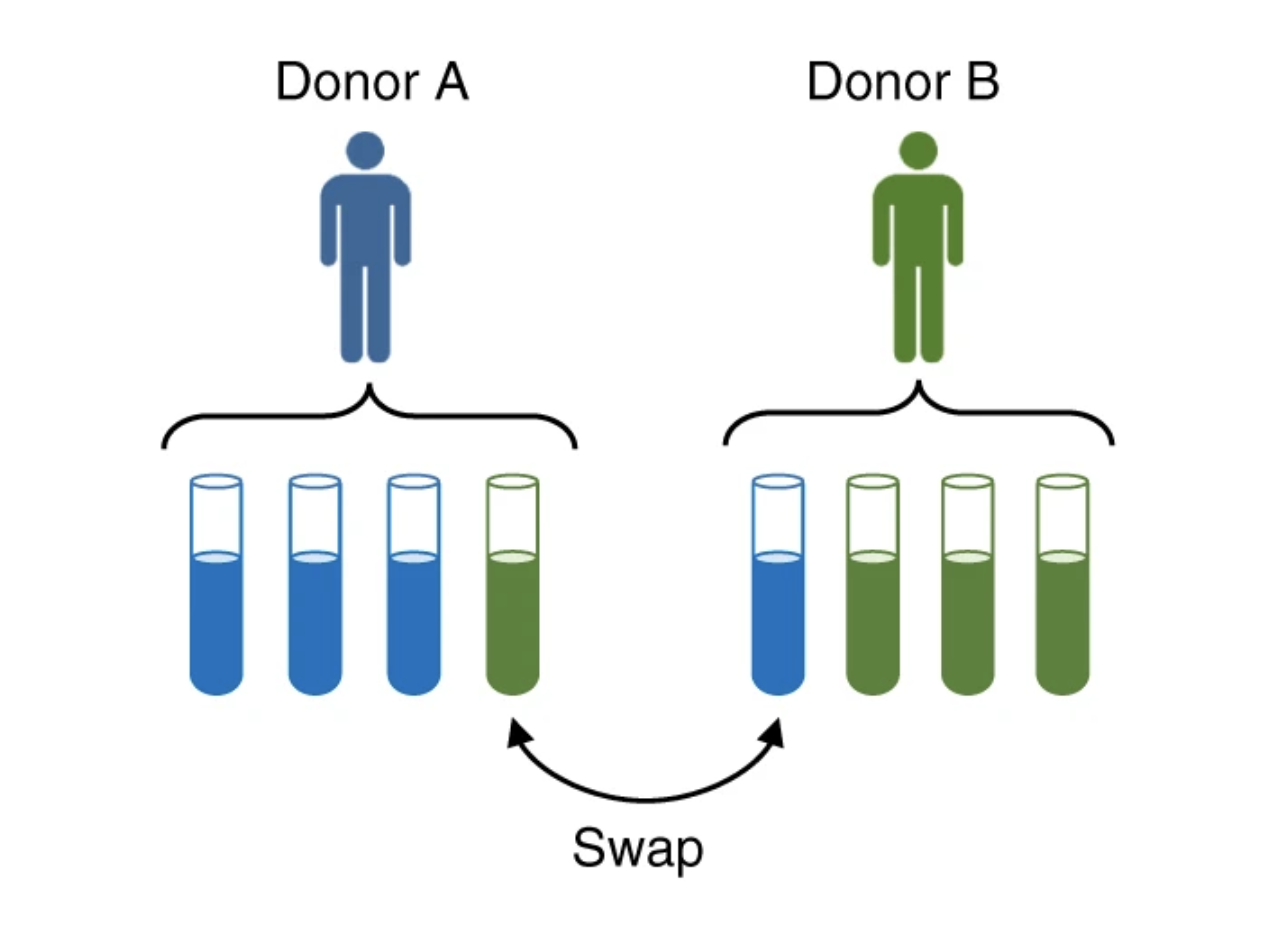
As the number of genomics datasets grows rapidly, sample mislabeling has become a high stakes issue. We present CrosscheckFingerprints (Crosscheck), a tool for quantifying sample-relatedness and detecting incorrectly paired sequencing datasets from different donors. Crosscheck outperforms similar methods and is effective even when data are sparse or from different assays...
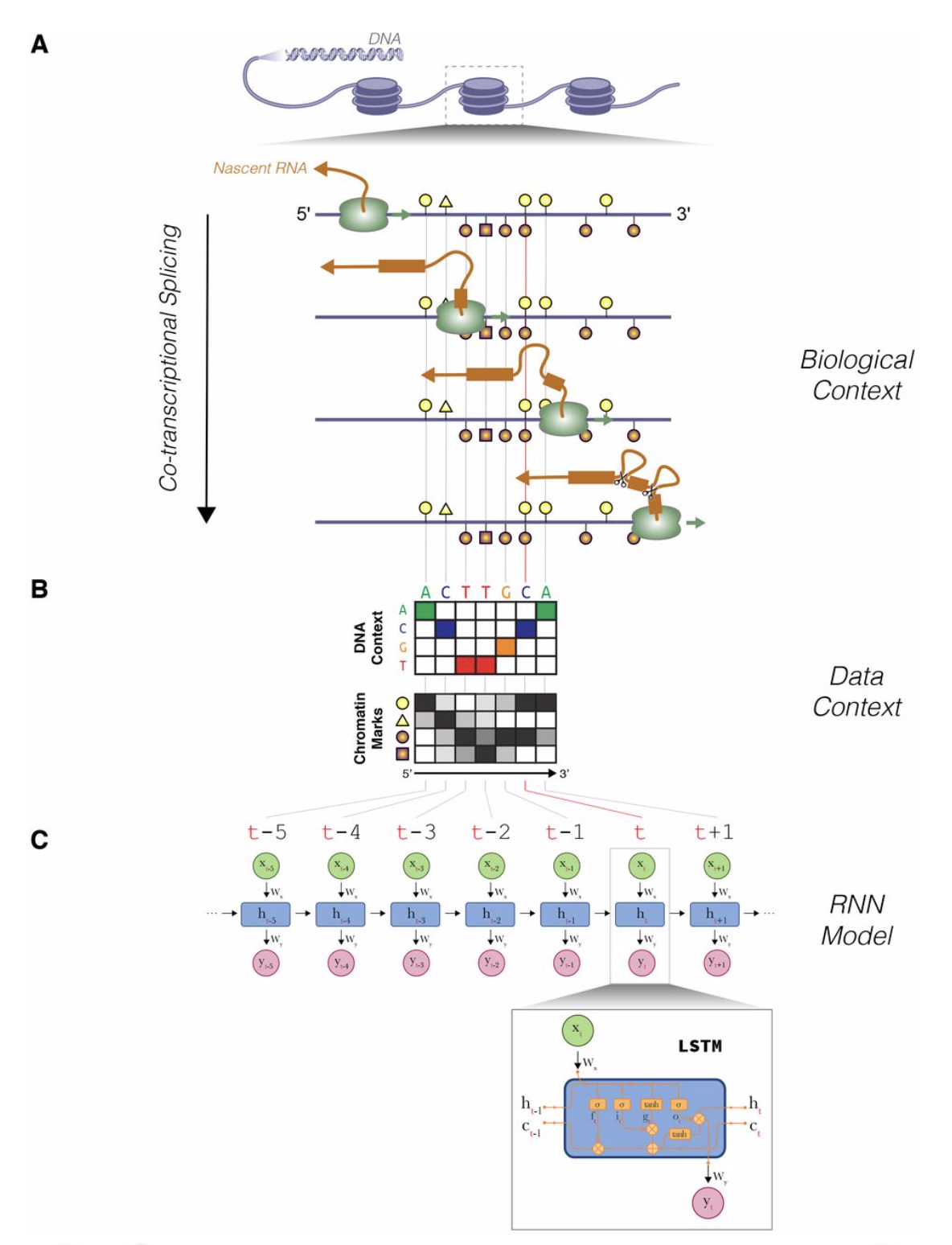
Alternative RNA splicing provides an important means to expand metazoan transcriptome diversity. Contrary to what was accepted previously, splicing is now thought to predominantly take place during transcription. Motivated by emerging data showing the physical proximity of the spliceosome to Pol II, we surveyed the effect of epigenetic context on co-transcriptional splicing...
Next generation sequencing data highlights comprehensive and dynamic changes in the human gene regulatory network. Moreover, changes in regulatory network connectivity (network “rewiring”) manifest different regulatory programs in multiple cellular states...
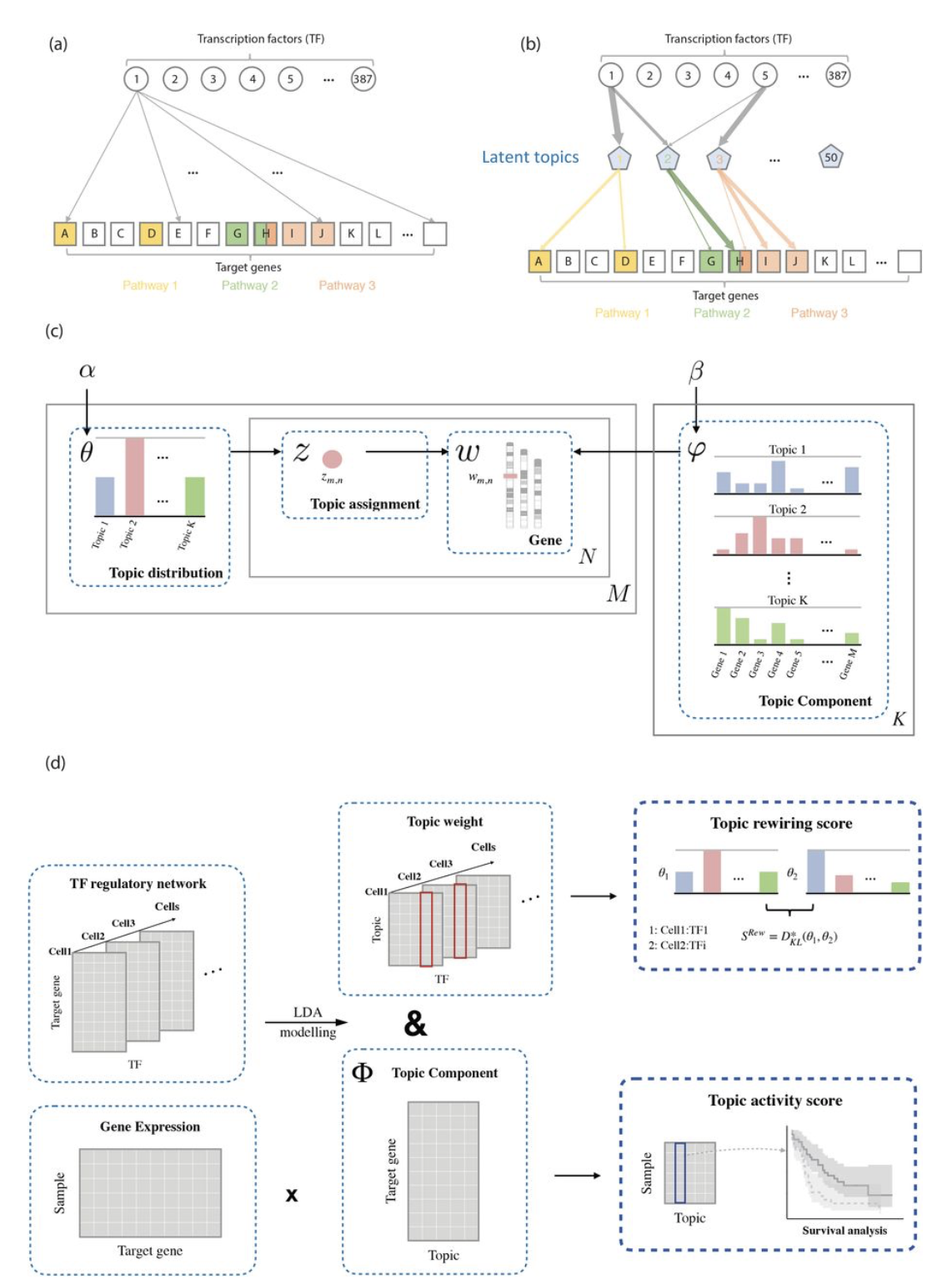
During transcription, numerous transcription factors (TFs) bind to targets in a highly coordinated manner to control the gene expression. Alterations in groups of TF-binding profiles (i.e. “co-binding changes”) can affect the co-regulating associations between TFs (i.e. “rewiring the co-regulator network”)...
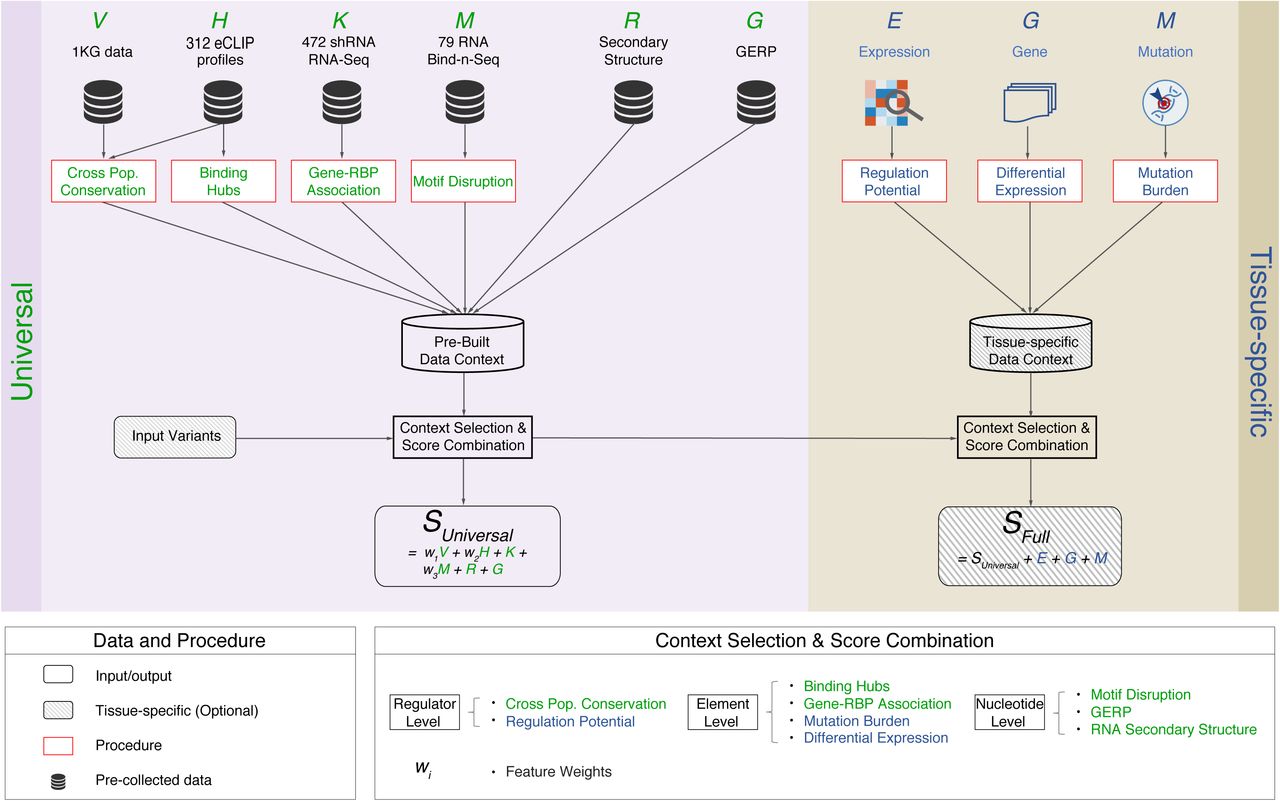
RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) play key roles in post-transcriptional regulation and disease. Their binding sites cover more of the genome than coding exons; nevertheless, most noncoding variant-prioritization methods only focus on transcriptional regulation. Here, we integrate the portfolio of ENCODE-RBP experiments to develop RADAR, a variant-scoring framework...
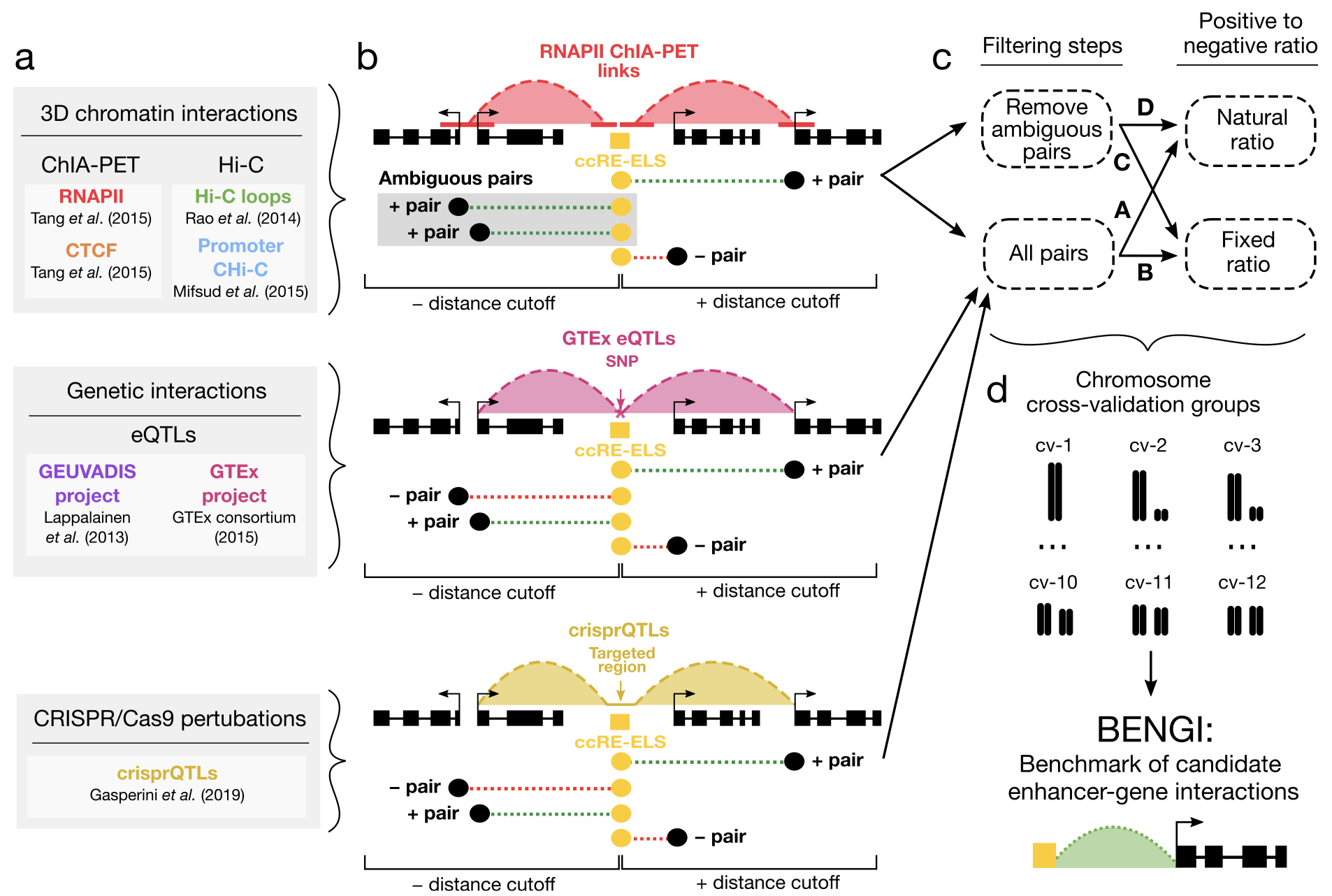
Many genome-wide collections of candidate cis-regulatory elements (cCREs) have been defined using genomic and epigenomic data, but it remains a major challenge to connect these elements to their target genes. To facilitate the development of computational methods for predicting target genes, we develop a Benchmark of candidate Enhancer-Gene Interactions (BENGI) by integrating the recently developed Registry of cCREs with experimentally derived genomic interactions...
The human epigenome has been experimentally characterized by thousands of measurements for every basepair in the human genome. We propose a deep neural network tensor factorization method, Avocado, that compresses this epigenomic data into a dense, information-rich representation...
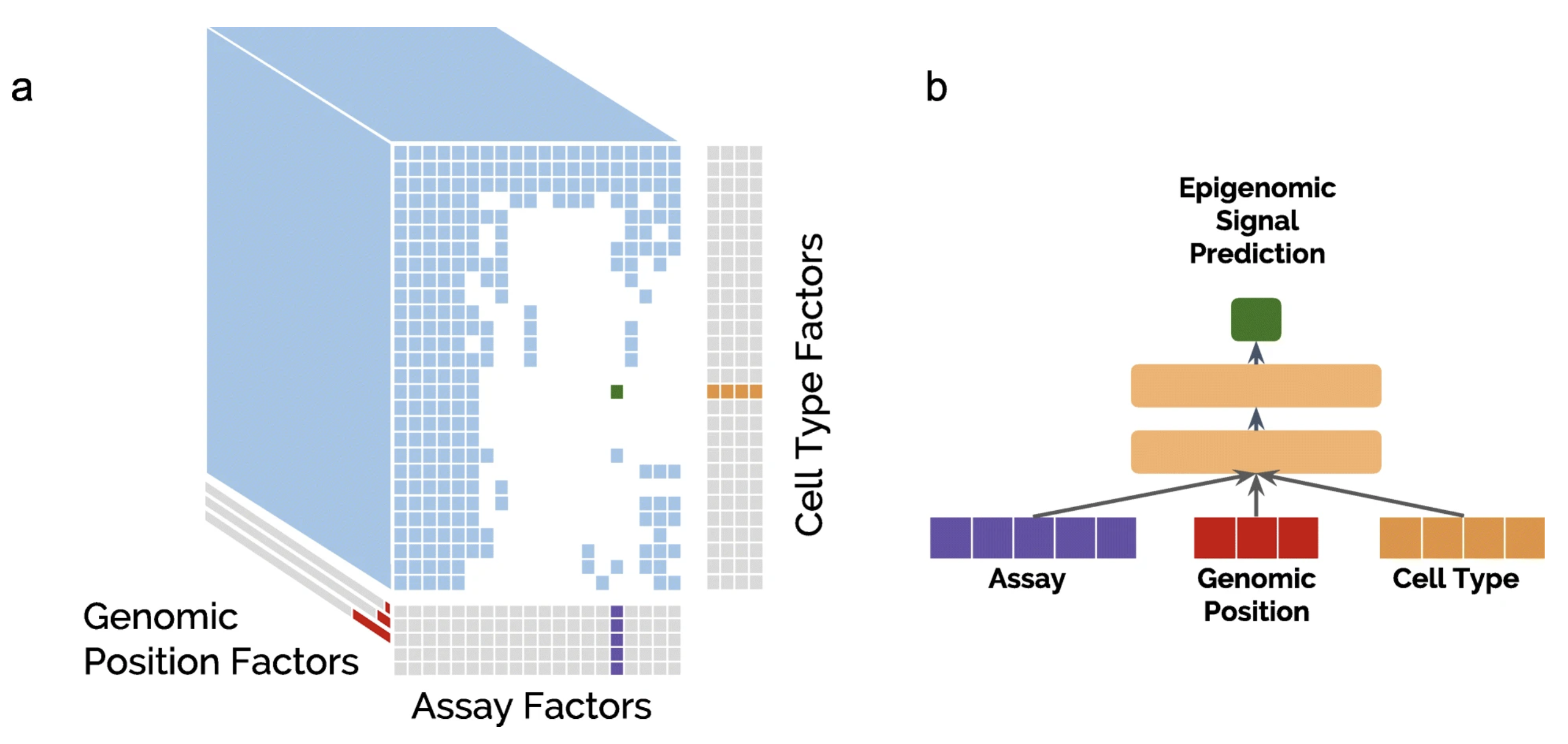
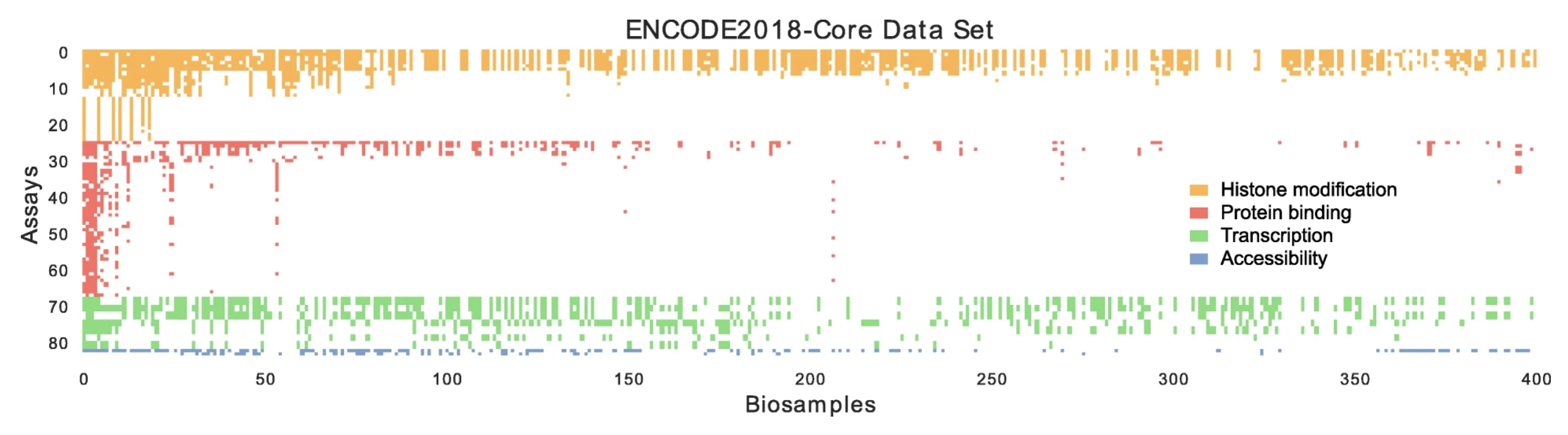
Recent efforts to describe the human epigenome have yielded thousands of epigenomic and transcriptomic datasets. However, due primarily to cost, the total number of such assays that can be performed is limited. Accordingly, we applied an imputation approach, Avocado, to a dataset of 3814 tracks of data derived from the ENCODE compendium, including measurements of chromatin accessibility, histone modification, transcription, and protein binding...
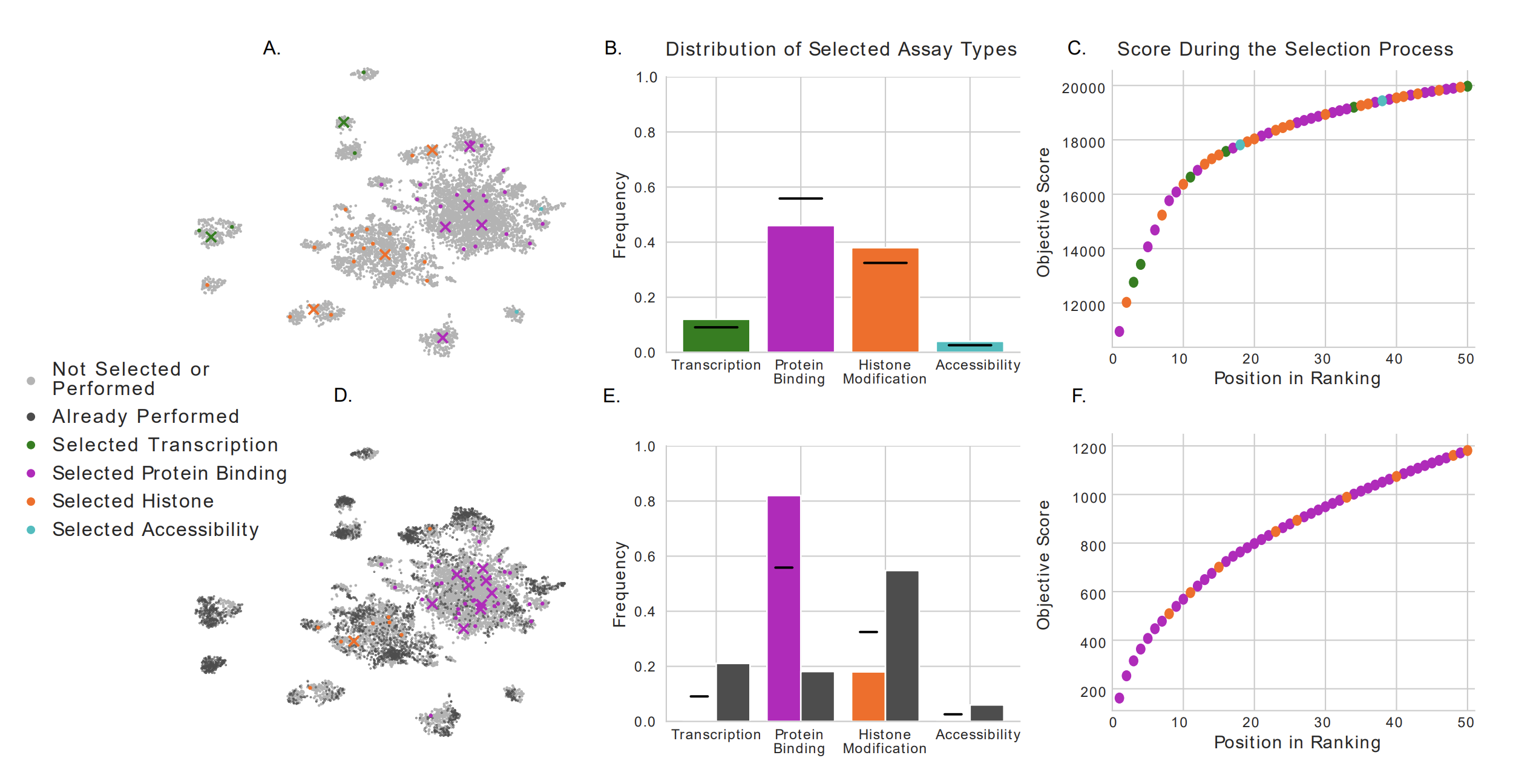
Successful science often involves not only performing experiments well, but also choosing well among many possible experiments. In a hypothesis generation setting, choosing an experiment well means choosing an experiment whose results are interesting or novel. In this work, we formalize this selection procedure in the context of genomics and epigenomics data generation...
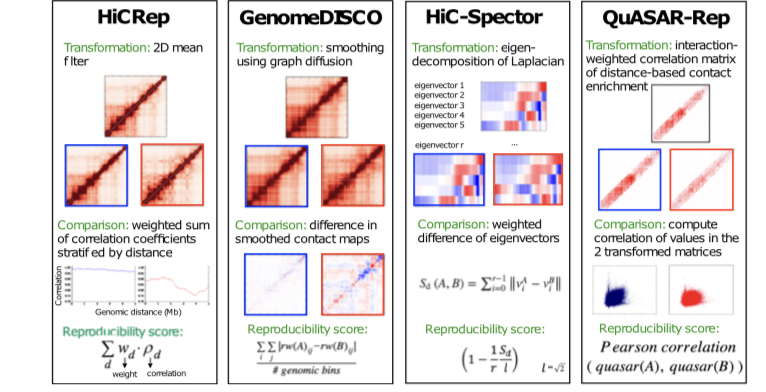
Hi-C is currently the most widely used assay to investigate the 3D organization of the genome and to study its role in gene regulation, DNA replication, and disease. However, Hi-C experiments are costly to perform and involve multiple complex experimental steps...
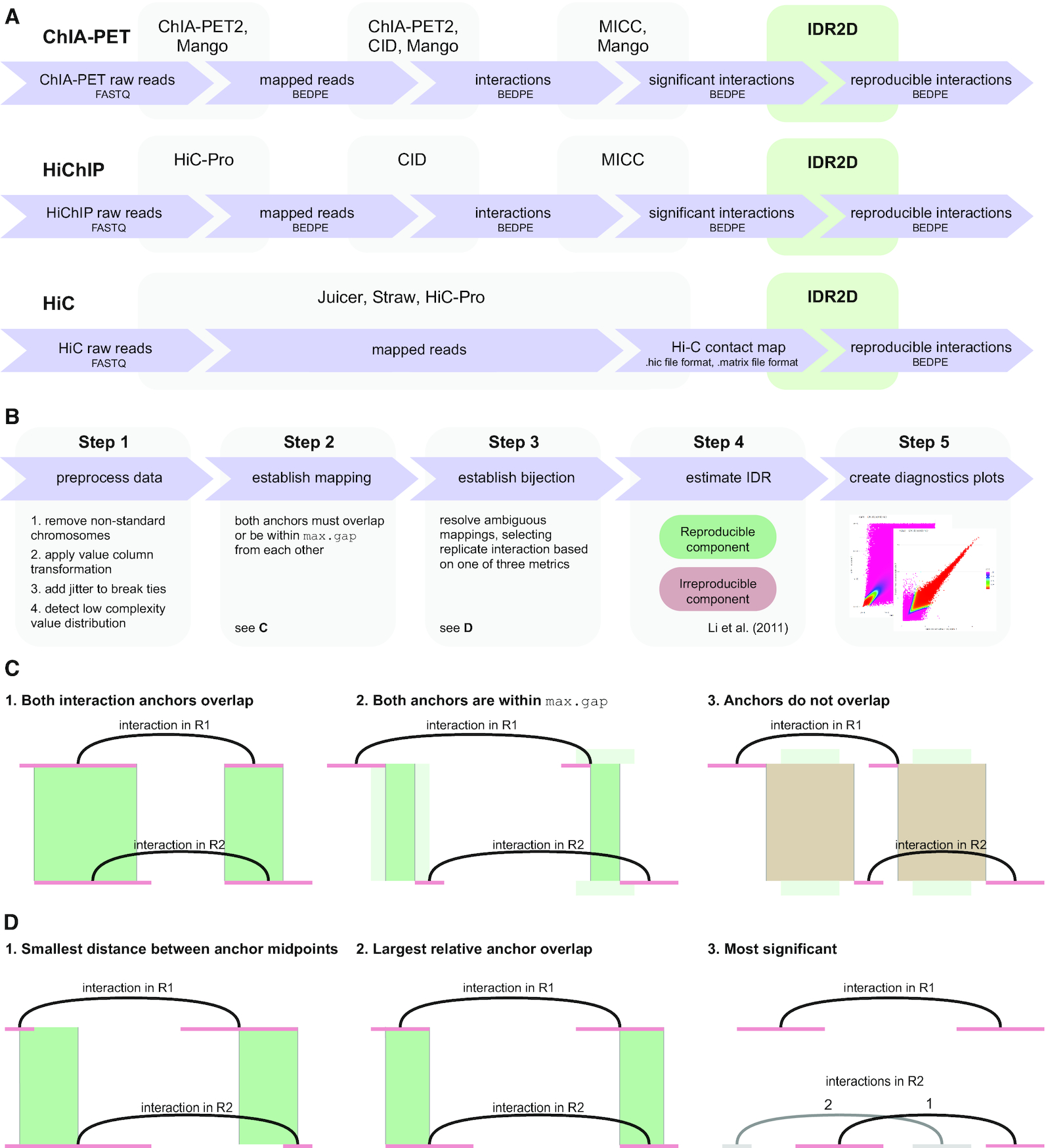
Chromatin interaction data from protocols such as ChIA-PET, HiChIP and Hi-C provide valuable insights into genome organization and gene regulation, but can include spurious interactions that do not reflect underlying genome biology. We introduce an extension of the Irreproducible Discovery Rate (IDR) method called IDR2D that identifies replicable interactions shared by chromatin interaction experiments...