Searching in Binary Search Tree (BST) (original) (raw)
Last Updated : 14 Jun, 2025
Given a **BST, the task is to search a node in this **BST. For searching a value in BST, consider it as a sorted array. Now we can easily perform search operation in BST using **Binary Search Algorithm.
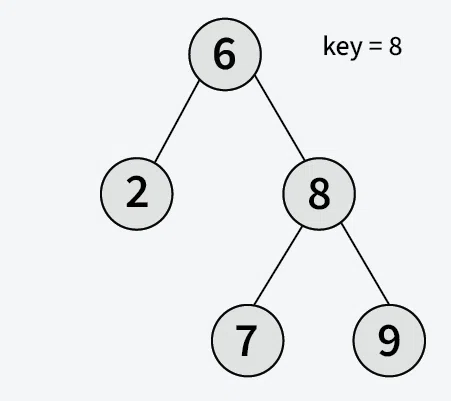
**Input: Root of the below BST
**Output: True
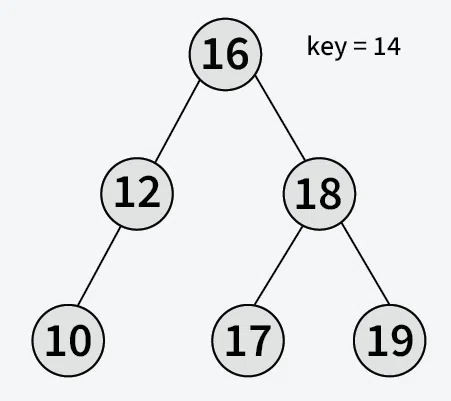
**Explanation: 8 is present in the BST as right child of root**Input: Root of the below BST
**Output: False
**Explanation: 14 is not present in the BST
**Algorithm to search for a key in a given Binary Search Tree:
Let's say we want to search for the number **X, We start at the root. Then:
- We compare the value to be searched with the value of the root. If it's equal we are done with the search if it's smaller we know that we need to go to the left subtree because in a binary search tree all the elements in the left subtree are smaller and all the elements in the right subtree are larger.
- Repeat the above step till no more traversal is possible
- If at any iteration, key is found, return True. Else False.
Illustration of searching in a BST:
See the illustration below for a better understanding:
Recursive Program to implement search in BST:
C++ `
#include using namespace std;
struct Node { int key; Node* left; Node* right; Node(int item) { key = item; left = right = NULL; } };
// function to search a key in a BST Node* search(Node* root, int key) {
// Base Cases: root is null or key
// is present at root
if (root == NULL || root->key == key)
return root;
// Key is greater than root's key
if (root->key < key)
return search(root->right, key);
// Key is smaller than root's key
return search(root->left, key);}
// Driver Code int main() {
// Creating a hard coded tree for keeping
// the length of the code small. We need
// to make sure that BST properties are
// maintained if we try some other cases.
Node* root = new Node(50);
root->left = new Node(30);
root->right = new Node(70);
root->left->left = new Node(20);
root->left->right = new Node(40);
root->right->left = new Node(60);
root->right->right = new Node(80);
(search(root, 19) != NULL)? cout << "Found\n":
cout << "Not Found\n";
(search(root, 80) != NULL)? cout << "Found\n":
cout << "Not Found\n";
return 0;}
C
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h>
struct Node { int key; struct Node* left; struct Node* right; };
// Constructor to create a new BST node struct Node* newNode(int item) { struct Node* temp = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); temp->key = item; temp->left = temp->right = NULL; return temp; }
// function to search a key in a BST struct Node* search(struct Node* root, int key) {
// Base Cases: root is null or key is
// present at root
if (root == NULL || root->key == key)
return root;
// Key is greater than root's key
if (root->key < key)
return search(root->right, key);
// Key is smaller than root's key
return search(root->left, key);}
// Driver Code int main() { // Creating a hard coded tree for keeping // the length of the code small. We need // to make sure that BST properties are // maintained if we try some other cases. struct Node* root = newNode(50); root->left = newNode(30); root->right = newNode(70); root->left->left = newNode(20); root->left->right = newNode(40); root->right->left = newNode(60); root->right->right = newNode(80);
printf(search(root, 19) != NULL ? "Found\n"
: "Not Found\n");
printf(search(root, 80) != NULL ? "Found\n"
: "Not Found\n");
return 0;}
Java
class Node { int key; Node left, right;
public Node(int item)
{
key = item;
left = right = null;
}} class GfG {
// function to search a key in a BST
static Node search(Node root, int key)
{
// Base Cases: root is null or key is present at
// root
if (root == null || root.key == key)
return root;
// Key is greater than root's key
if (root.key < key)
return search(root.right, key);
// Key is smaller than root's key
return search(root.left, key);
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating a hard coded tree for keeping
// the length of the code small. We need
// to make sure that BST properties are
// maintained if we try some other cases.
Node root = new Node(50);
root.left = new Node(30);
root.right = new Node(70);
root.left.left = new Node(20);
root.left.right = new Node(40);
root.right.left = new Node(60);
root.right.right = new Node(80);
// Searching for keys in the BST
System.out.println(search(root, 19) != null
? "Found"
: "Not Found");
System.out.println(search(root, 80) != null
? "Found"
: "Not Found");
}}
Python
class Node: def init(self, key): self.key = key self.left = None self.right = None
function to search a key in a BST
def search(root, key):
# Base Cases: root is null or key
# is present at root
if root is None or root.key == key:
return root
# Key is greater than root's key
if root.key < key:
return search(root.right, key)
# Key is smaller than root's key
return search(root.left, key)Creating a hard coded tree for keeping
the length of the code small. We need
to make sure that BST properties are
maintained if we try some other cases.
root = Node(50) root.left = Node(30) root.right = Node(70) root.left.left = Node(20) root.left.right = Node(40) root.right.left = Node(60) root.right.right = Node(80)
Searching for keys in the BST
print("Found" if search(root, 19) else "Not Found") print("Found" if search(root, 80) else "Not Found")
C#
using System;
public class Node { public int Key; public Node Left, Right;
public Node(int item)
{
Key = item;
Left = Right = null;
}}
public class GfG { // function to search a key in a BST public static Node Search(Node root, int key) { // Base Cases: root is null or key is // present at root if (root == null || root.Key == key) return root;
// Key is greater than root's key
if (root.Key < key)
return Search(root.Right, key);
// Key is smaller than root's key
return Search(root.Left, key);
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main()
{
// Creating a hard coded tree for keeping
// the length of the code small. We need
// to make sure that BST properties are
// maintained if we try some other cases.
Node root = new Node(50);
root.Left = new Node(30);
root.Right = new Node(70);
root.Left.Left = new Node(20);
root.Left.Right = new Node(40);
root.Right.Left = new Node(60);
root.Right.Right = new Node(80);
// Searching for keys in the BST
Console.WriteLine(Search(root, 19) != null ? "Found" : "Not Found");
Console.WriteLine(Search(root, 80) != null ? "Found" : "Not Found");
}}
JavaScript
class Node { constructor(key) { this.key = key; this.left = null; this.right = null; } }
// function to search a key in a BST function search(root, key) {
// Base Cases: root is null or key is
// present at root
if (root === null || root.key === key)
return root;
// Key is greater than root's key
if (root.key < key)
return search(root.right, key);
// Key is smaller than root's key
return search(root.left, key);}
// Creating a hard coded tree for keeping // the length of the code small. We need // to make sure that BST properties are // maintained if we try some other cases. let root = new Node(50); root.left = new Node(30); root.right = new Node(70); root.left.left = new Node(20); root.left.right = new Node(40); root.right.left = new Node(60); root.right.right = new Node(80);
// Searching for keys in the BST console.log(search(root, 19) !== null ? "Found" : "Not Found"); console.log(search(root, 80) !== null ? "Found" : "Not Found");
`
**Time complexity: O(h), where h is the height of the BST.
**Auxiliary Space: O(h) This is because of the space needed to store the recursion stack.
We can avoid the auxiliary space and recursion overhead withe help of iterative implementation. Below is link for the iterative implementation that works in O(h) time and O(1) auxiliary space.