Nature Medicine (original) (raw)

When politics trumps patients
Elected to make America healthy again, the actions of the Trump administration have undermined health globally.
Year in Review 05 December 2025
Featured

Year in Review01 Dec 2025
Advancing equitable and sustainable urban health
Cities are often at the forefront of creative thinking on policy opportunities; this Perspective outlines an agenda for urban health research that promotes a virtuous cycle by which population health and environmental sustainability support and reinforce each other.
- Ana V. Diez Roux
- Usama Bilal
Perspective12 Nov 2025 
Determining the value of genomics in healthcare
Assessing the value of genomics is key to informing evidence-based policies; this Review outlines how current approaches to health technology assessment, implementation and data management can be adapted to suit the rapidly evolving technology and evidence base.
- Ilias Goranitis
- Robin Z. Hayeems
- Zornitza Stark
Review Article27 Nov 2025 - Correspondence25 Nov 2025
Announcements
30th Anniversary Series on the Future of Medicine
As Nature Medicine celebrates the 30th anniversary of its launch, we reflect on what the future holds for medicine and for our journal. In this Series, we spotlight key challenges and opportunities as we look to the next 30 years of biomedical innovation.
Series: Women’s health throughout the lifecourse
Women’s health has been underfunded and underprioritized for too long, leading to delays in diagnosis and poor health outcomes. This series will bring together a range of viewpoints and new research focusing on the causes of ill health in women and the barriers to their health and wellbeing in the 21st Century.
Diversity, equity and inclusion in medical research
This ongoing series brings together a range of viewpoints on DEI in medical research, covering topics such as funding biases, workforce diversity and how to fix the lack of diversity of health data. Reach out to us to contribute your perspective.
Latest Research articles
- ArticleOpen Access08 Dec 2025
- ArticleOpen Access08 Dec 2025
- ArticleOpen Access01 Dec 2025
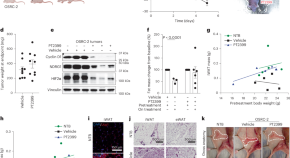
Targeting of HIF2-driven cachexia in kidney cancer
In vivo experiments and clinical cohort analyses show that hypoxia-inducible factor 2 (HIF2)-induced parathyroid hormone-related protein (PTHrP) expression contributes to cachexia in the context of renal cell carcinoma (RCC). The pathway can be targeted by HIF2 inhibitors, including belzutifan, which may reduce cachexia in patients with RCC.
- Muhannad Abu-Remaileh
- Laura A. Stransky
- William G. Kaelin Jr
ArticleOpen Access28 Nov 2025 
A therapeutic peptide vaccine for fibrolamellar hepatocellular carcinoma: a phase 1 trial
In this phase 1 trial, treatment of patients with fibrolamellar hepatocellular carcinoma with a therapeutic peptide vaccine targeting the fusion kinase DNAJB1–PRKACA, which is the driver of the disease, together with nivolumab and ipilimumab, was safe and led to encouraging preliminary clinical responses, and translational analysis showed activation of immune responses.
- Marina Baretti
- Allison M. Kirk
- Mark Yarchoan
ArticleOpen Access24 Nov 2025 - ArticleOpen Access20 Nov 2025
Latest Reviews & Analysis
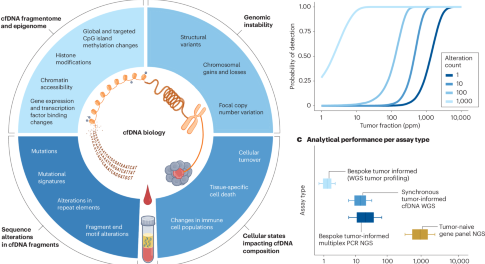
Liquid biopsies across the cancer care continuum
This Review summarizes current and emerging liquid biopsy methods, together with their clinical validity and utility, and highlights opportunities to support their implementation throughout the cancer care continuum.
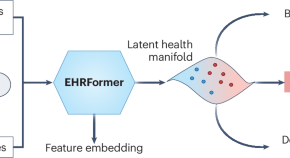
A lifespan clock tells the biology of time
A full‑lifecycle clock derived from millions of routine clinical records reveals that human development and aging form a continuous physiological trajectory, enabling early disease detection and mechanistic insights for preventive and precision health.
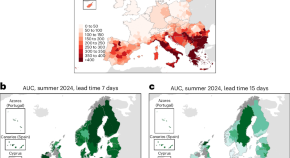
Reliable forecasts of heat-health emergencies at least one week in advance
We estimate that there were more than 181,000 heat-related deaths in Europe during the three exceptionally hot summers of 2022–2024, with 62,775 deaths during 2024 alone. Our assessment of a new generation of impact-based early warning systems shows that these emergencies can be reliably forecast at least one week ahead, enabling provision of tailored information for vulnerable populations.