Nature Genetics (original) (raw)

Genomic analysis of brain volumes
A genome-wide association analysis of intracranial and subcortical brain volumes identifies 254 loci and yields polygenic scores accounting for brain variation across ancestries.
Featured
- ArticleOpen Access04 Oct 2024
Announcements
The field of spatial omics is developing rapidly, with a potentially transformative effect across many areas of biology. Nature Genetics invites authors to submit papers that use these techniques to answer questions of broad interest to researchers working in genetics and genomics.
Nature Genetics, along with other Springer Nature journals, will publish a collection of genetic studies focusing on diverse human populations, including but not limited to complex trait association studies, rare variant studies, population genetics and bioinformatic methods. We will also consider Reviews, Perspectives, and Comments addressing these topics.
Open for submissions
Latest Research articles
- ArticleOpen Access05 Nov 2024
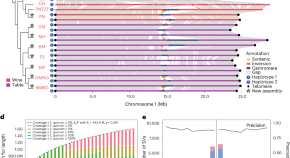
Grapevine pangenome facilitates trait genetics and genomic breeding
By constructing a graph-based grapevine pangenome reference (Grapepan v.1.0) and incorporating structural variations and phenotypic maps, the study investigates the genetic basis of agronomic traits, empowering grapevine genomic breeding.
- Zhongjie Liu
- Nan Wang
- Yongfeng Zhou
ArticleOpen Access04 Nov 2024 - ArticleOpen Access04 Nov 2024

Convergence and divergence of diploid and tetraploid cotton genomes
High-quality assemblies of 15 diploid and 35 allotetraploid cotton accessions are analyzed in graph-based pan-genomes, providing insights into genome dynamics and regulatory control of fiber transcriptomes under varying ploidy and selection pressures.
- Jianying Li
- Zhenping Liu
- Maojun Wang
Article29 Oct 2024
Latest Reviews & Analysis
The kinase ZmCPK39 regulates foliar disease resistance in maize plants
The calcium-dependent protein kinase ZmCPK39 is identified as a key immune component in maize infected with foliar pathogens. Its expression is lower in resistant maize lines than in susceptible lines, leading to stabilization of the transcription factor ZmDi19, elevated expression of the anti-microbial protein ZmPR10 and enhanced resistance to multiple foliar diseases.
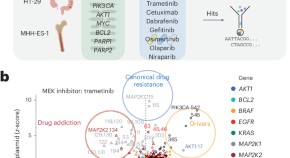
Mapping drug resistance variants in cancer, one base at a time
DNA variants arising in the genome of cancer cells are a major cause of therapy failure, but for most variants, their effects on drug response are unknown. Base-editing screens provide a systematic approach to uncover the functions of cancer variants at scale, which might help to inform the use of precision cancer therapies.
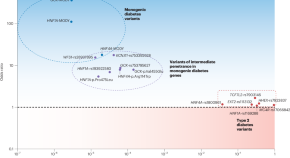
Parsing the spectrum of allelic architectures in diabetes
Distinguishing ordinary diabetes from its monogenic forms has been one of the challenges in optimally managing the disease. Using high-quality imputation of rare variants and large databases, a study now defines the gray zone between the two and lays down a blueprint for objectively evaluating the related variants.