Browse Articles
| Nature Geoscience (original) (raw)
Article Type
- All
- Article (1273)
- Author Correction (63)
- Backstory (78)
- Books & Arts (48)
- Comment (36)
- Commentary (107)
- Correspondence (134)
- Corrigendum (33)
- Editorial (224)
- Feature (23)
- In the press (32)
- Letter (965)
- Matters Arising (27)
- News & Views (828)
- Perspective (61)
- Progress Article (32)
- Publisher Correction (37)
- Research Briefing (62)
- Research Highlights (226)
- Review Article (80)
Year
All
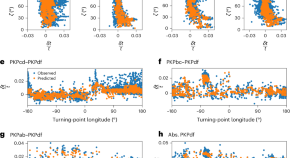
Tilted transverse isotropy in Earth’s inner core
A seismic tomographic model shows that the directional dependence of the travel time of seismic waves through Earth’s inner core can be explained by a spatially varying orientation of the transverse isotropy symmetry axis, which is simpler than other proposed structures.
Article27 Sept 2024
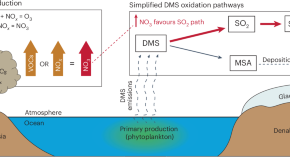
Pollution drives multidecadal decline in subarctic methanesulfonic acid
Multidecadal declines in methanesulfonic acid in arctic ice cores reflect increasing anthropogenic pollution in the industrial era rather than declining marine primary production, according to analyses of a multi-century record of methanesulfonic acid from Alaska and atmospheric modelling.
- Jacob I. Chalif
- Ursula A. Jongebloed
- Jihong Cole-Dai
Article23 Sept 2024 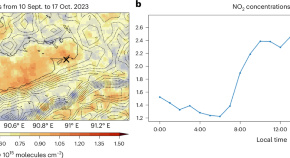
Matters Arising20 Sept 2024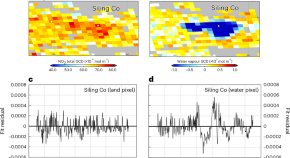
Matters Arising20 Sept 2024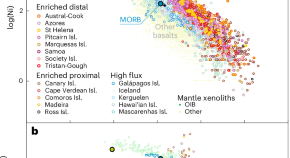
A common precursor for global hotspot lavas
An investigation of global trace-element data suggests that the parental melts of hotspot lavas are uniform in their elemental composition, consistent with derivation from a common depleted and outgassed mantle reservoir.
- Matthijs A. Smit
- Ellen Kooijman
ArticleOpen Access19 Sept 2024 - ArticleOpen Access12 Sept 2024
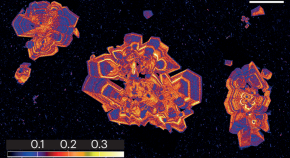
Volcanic crystal balls
Clinopyroxene offers clues about the inner workings of volcanic systems, as Teresa Ubide explains. Its ability to track where and when magma is stored may also help forecast eruptions.
- Teresa Ubide
All Minerals Considered10 Sept 2024 
Finite sand resource needs better governance
Sand is an overlooked resource and is being depleted at an alarming rate. Improved management of sand extraction and consumption is imperative to protect sand resources and reduce the impacts of extraction.
Editorial10 Sept 2024
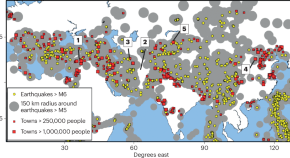
Correspondence10 Sept 2024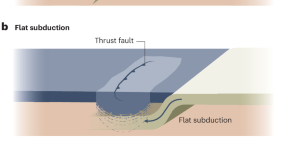
The oldest parts of continents are falling apart
The processes that control the deformation and eventual destruction of Earth’s oldest continental crust are unclear. Mantle flow models suggest subduction played a role in the deformation of the North China Craton.
- Jolante van Wijk
News & Views06 Sept 2024 - ArticleOpen Access06 Sept 2024
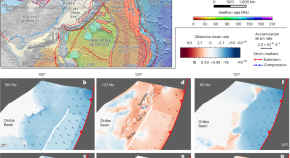
Craton deformation from flat-slab subduction and rollback
Mesozoic deformation of the North China Craton occurred via lithospheric thickening followed by thinning and extension triggered by flat-slab subduction and rollback, according to four-dimensional mantle flow models of the plate–mantle system.
- Shaofeng Liu
- Bo Zhang
- Michael Gurnis
ArticleOpen Access06 Sept 2024 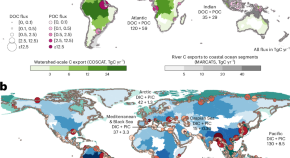
An ensemble assessment to improve estimates of land-to-ocean carbon fluxes
A re-evaluation of global land-to-ocean carbon exports using a multi-model ensemble and a database of observations reveals that the export of carbon by rivers is 20% higher than that reported in the 2021 Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) assessment. These findings underscore the important contribution of riverine carbon to the carbon budget.
Research Briefing05 Sept 2024
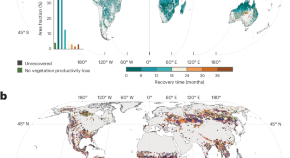
Spatial heterogeneity in post-fire vegetation productivity recovery and its drivers
A global analysis of post-fire vegetation productivity recovery reveals that the recovery time shows spatial variations across vegetation types and regions. The dominant factors that influence the recovery time in the majority of the global burned area are the post-fire climate conditions, such as soil moisture, vapour pressure deficit and air temperature.
Research Briefing03 Sept 2024
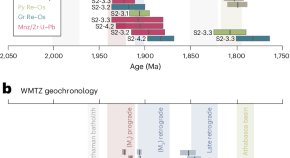
Graphite preserved in ancient mountain belts linked to supercontinent assembly
This study investigates the history of graphitic carbon in two ancient North American mountain belts related to Nuna supercontinent assembly. Using rhenium–osmium and uranium–lead dating, the research reveals that biogenic graphite was hydrothermally remobilized in shear zones during late orogenesis, indicating periodic carbon cycling over 200 million years.
Research Briefing02 Sept 2024