Gene delivery - Latest research and news (original) (raw)
Gene delivery articles from across Nature Portfolio
Gene delivery is a process by which foreign DNA is transferred to host cells for applications such as genetic research or gene therapy. Gene delivery methods can be mechanical (e.g. microinjection, electroporation or biolistics), chemical (e.g. lipid or nanoparticle carriers) or biological (e.g. viral or bacterial vectors).
Featured
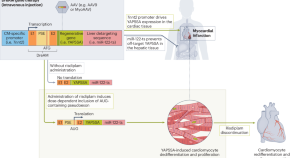
A tunable gene therapy for heart regeneration
AAV-based gene therapies hold promise for treating disease, but their long-lasting gene expression limits their use in regenerative medicine. A study now presents DreAM, a drug-inducible AAV system that enables tunable tissue-specific gene activation via the splicing modulator risdiplam, and its potential application in myocardial infarction.
- Gabriele D’Uva
News & Views13 Jun 2025 Nature Cardiovascular Research
P: 1-3
Related Subjects
Latest Research and Reviews
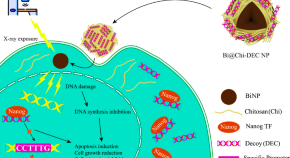
Combined treatment using bismuth sulfide nanoparticles loaded with NANOG decoy oligodeoxynucleotides under X-ray radiation for breast cancer cells
- Sara Heidari
- Mahmoud Gharbavi
- Behrooz Johari
ResearchOpen Access02 Jul 2025 Scientific Reports
Volume: 15, P: 23131 
Evaluation of transduction efficiency in pancreatic beta and alpha cells utilizing various AAV serotypes
- Vishal Ahuja
- Sanjeev Jeyabalan
- Emmanuel S. Tzanakakis
ResearchOpen Access01 Jul 2025 Scientific Reports
Volume: 15, P: 20927 
Induction of flowering in Arabidopsis through functional peptide-mediated FT mRNA delivery
- Masaki Odahara
- Maai Mori
- Keiji Numata
ResearchOpen Access01 Jul 2025 Scientific Reports
Volume: 15, P: 22088 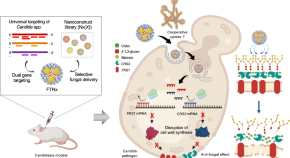
Effective treatment of systemic candidiasis by synergistic targeting of cell wall synthesis
In this work, authors generate nanoconstructs that synergistically target cell wall synthesis in Candida pathogens, which induce potent antifungal effects and prolonged survival in candidiasis, providing an alternative treatment option to conventional drugs.
- Ju Yeon Chung
- Yoon-Kyoung Hong
- Hyun Jung Chung
ResearchOpen Access01 Jul 2025 Nature Communications
Volume: 16, P: 5532 
Transgene- and tissue culture-free heritable genome editing using RNA virus-based delivery in wheat
Efficient delivery systems are urgently needed for genome editing in monocot plants. Here, this study develops a system of virus-induced genome editing in tillers (ViGET) to achieve heritable editing in wheat bypassing transgene and tissue culture.
- Ji-Hui Qiao
- Ying Zang
- Xian-Bing Wang
Research25 Jun 2025 Nature Plants
P: 1-8 
AAV for ovarian cancer gene therapy
- Hee Chan Yoo
- Sangkil Lee
- Eun-Ju Lee
ReviewsOpen Access20 Jun 2025 Cancer Gene Therapy
P: 1-14
News and Comment
A tunable gene therapy for heart regeneration
AAV-based gene therapies hold promise for treating disease, but their long-lasting gene expression limits their use in regenerative medicine. A study now presents DreAM, a drug-inducible AAV system that enables tunable tissue-specific gene activation via the splicing modulator risdiplam, and its potential application in myocardial infarction.
- Gabriele D’Uva
News & Views13 Jun 2025 Nature Cardiovascular Research
P: 1-3 AAV vector engineering for human aorta transduction: becoming a smooth operator
- Kleopatra Rapti
- Dirk Grimm
Comments & Opinion17 Mar 2025 Gene Therapy
P: 1-2
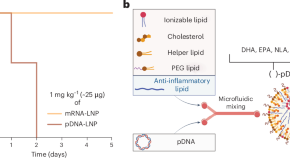
Improving the safety of lipid nanoparticle-based DNA delivery for extended gene expression
DNA delivery using lipid nanoparticles results in severe toxicity in mice. However, we find that the incorporation of endogenous anti-inflammatory lipids into the lipid nanoparticles mitigates this toxicity and enables prolonged gene expression.
News & Views03 Mar 2025 Nature Biotechnology
P: 1-2
A preprint by Xu et al. shows that MHC-pseudotyped retroviruses can reprogramme, activate and expand tumour-specific T cell populations in vivo.
- Hugo Kwong
- Persephone Borrow
Research Highlights08 Jan 2025 Nature Reviews Immunology
Volume: 25, P: 76 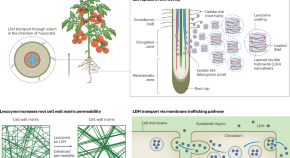
Lysozyme-coated LDHs boost trait control
Coating RNA- or DNA-loaded layered double hydroxide nanosheets with lysozyme enhances their uptake by loosening the plant cell wall and stimulating endocytosis and membrane trafficking — with promising implications for both fundamental research and agricultural applications.
- Karl-Heinz Kogel
News & Views02 Jan 2025 Nature Plants
Volume: 11, P: 9-10 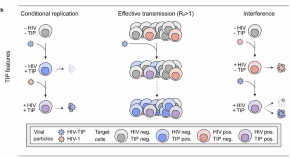
Therapeutic interfering particles against HIV: molecular parasites reducing viremia
- Henning Gruell
- Stanley Odidika
- Philipp Schommers
Research HighlightsOpen Access14 Oct 2024 Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy
Volume: 9, P: 287