Impact of Pirfenidone on arrhythmic and clinical outcomes in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (original) (raw)
Abstract
Background/Introduction
Atrial fibrosis is an important substrate in atrial fibrillation (AF), particularly in the setting of structural heart disease. Previous study reported that Pirfenidone, an antifibrotic agent, was beneficial at reducing myocardial fibrosis.
Purpose
The objective of the present study is to evaluate the effects of Pirfenidone on arrhythmic and clinical outcomes in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF).
Methods
Our database of patients diagnosed with IPF from 2008 to 2023 was used to obtain echocardiography, electrocardiogram, and 24hr-holter monitoring data. Inclusion criteria were all IPF patients with/without Pirfenidone. And we compared arrhythmic events including atrial fibrillation, atrial premature complex, atrial tachycardia, ventricular arrhythmia and clinical outcomes according to use of Pirfenidone.
Results
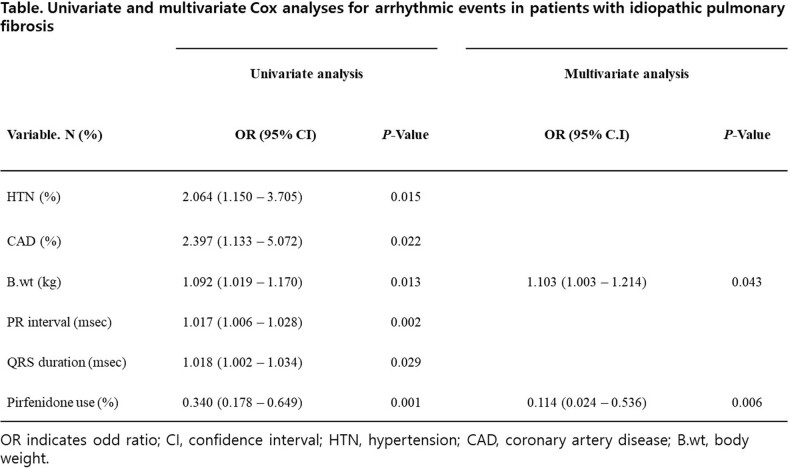
Among 257 patients with IPF (74.0±8.9 years), 106 (41.2%) patients took Pirfenidone. Difference in the baseline characteristics was not observed. During the median 36-month follow-up, a lower incidence of arrhythmic events (P=0.001) and diastolic dysfunction (P=0.025) was observed in the Pirfenidone group. In univariate analysis, hypertension, coronary artery disease, higher body weight, longer PR interval, QRS duration, and less use of Pirfenidone were associated with arrhythmic events. In multivariate analysis, higher body weight and less Pirfenidone use were independent risk factors for arrhythmic events.
Conclusion(s)
The use of Pirfenidone was associated with less arrhythmic events and lower diastolic dysfunction compared with no use of Pirfenidone in the long-term follow-up. And obesity was associated with higher incidence of arrhythmic events in IPF patients.
Table