Skeletal muscle satellite cells and adult myogenesis (original) (raw)
. Author manuscript; available in PMC: 2008 Dec 1.
Published in final edited form as: Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2007 Nov 8;19(6):628–633. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2007.09.012
Abstract
Research focusing on the canonical adult myogenic progenitor, the skeletal muscle satellite cell, is still an ever-growing field 46 years from their initial description. Recent publications revealed numerous new aspects of satellite cell biology, starting from their developmental life to their role as the principal self-renewing myogenic stem cell in the adult skeletal muscle and finally their loss during aging. The myogenic potential of satellite cells is under the molecular control of specific Paired-box and bHLH transcription factors which tightly orchestrated balance during adult skeletal muscle regeneration account for their effectiveness. New reports also demonstrated satellite cells’ continuous relationships with blood vessels and the high myogenic potential of new stem cell subsets related to both lineages.
Introduction
In this review, we discuss recent achievements in the studies of adult myogenesis and, specifically, on publications that carried major advances in our understanding of the cellular and molecular regulation of the muscle fibers’ satellite cells biology. We focused on the major mechanisms responsible for the maintenance and homeostasis of satellite cell during the whole life of a mammal, from the birth of their precursors in the embryonic paraxial mesoderm, through their implication in senescence of the muscle tissue. The last years provided a first overview of the hierarchy within this lineage and numerous research teams are currently trying to find which muscle-derived cell population harbors the most potent regenerative and self-renewal potential and, in parallel, which signals direct the self-renewal of satellite cells. In addition, recent advances clarified the intrinsic and extrinsic signals leading the quiescent satellite cells to become activated and subsequent timing of activation and repression of muscle-specific transcription factors enabling the progeny of activated satellite cells to efficiently regenerate damaged skeletal muscle fibers.
Developmental origin of satellite cells
All the skeletal muscles of the body and the limbs derive from the somites, segmental derivatives of the paraxial mesoderm. As the somite matures, myogenic progenitor cells become confined to the dorso-lateral part of the somite: the dermomyotome. Skeletal myogenesis is then initiated in myogenic cells originating form the dermomyotome lips that differentiate to form primary muscle fibers (see [1] for review). Subsequently, a progenitor population that expresses Pax3 and Pax7 arise from the central portion of the dermomyotome and is maintained throughout embryogenesis within the developing skeletal muscles [2–4]. Late in fetal development, the resident progenitor population generates cells in a satellite position around myofibers, which are marked by the expression of Pax7 [2–4]. Lineage tracing experiments using the Cre/LoxP recombination system further demonstrated that limb muscle satellite cells arise from hypaxial cells expressing Pax3. In parallel, it is an interesting fact that a significant number of limb muscle Side Population stem cells are also derived from the hypaxial somite and perhaps share a common ancestor with satellite cells [5].
Still little is known about the molecular signals that regulate the resident progenitor cells embryonic life, but recent reports highlighted the importance of Notch signaling (one the most recurrent signaling pathway directing stem cells expansion and fate determination) in satellite cell ontogenesis. Manipulation of either the Notch ligand Delta1 (Dll1) or the Notch downstream transcription factor RBP-J (Rbpsuh) in mice embryo demonstrated an essential role for Notch in the survival of the Pax3/7+ve cells during embryogenesis. In the context of mice heteroallelic for a null mutation and an hypomorphic Dll1 allele [6•], or when floxed RBP-J alleles are conditionally recombined under the control of myogenic genes [7•], resident progenitor cells are formed initially, but they undergo an uncontrolled myogenic differentiation. This precocious differentiation leads to a progressive depletion of the progenitor pool and a subsequent absence of progenitor cells and/or satellite cells at the beginning of fetal life [6•,7•]. The recent discovery of satellite cell embryonic origin brought a lot of interesting questions to the field, and studies concerning the implication of well-known signaling pathways previously described as major regulators of embryonic myogenesis, such as Wnt signals or Myostatin/Follistatin antagonism in the regulation of satellite cell development will, without any doubts, be of critical interests in the next few years.
Activation from quiescence
In the adult, satellite cells are mitotically quiescent and reside in a niche between the basal lamina and the sarcolemma of their associated muscle fibers. In that particular state, they exhibit limited gene expression and protein synthesis but they can become activated in response to stress that is induced by weight bearing or by trauma, such as injury or in the context of a myo-degenerative disease (see [8] for review). What control the transition between quiescence and proliferation, the “activation trigger”, remains largely unknown. A signal intrinsic to the cell itself is the production of sphingosine-1-phosphate from the inner leaflet of the plasma membrane. Sphingosine-1-phosphate is required for satellite cell entry in the cell cycle and inhibition of its synthesis dramatically abrogates muscle regeneration [9•].
Extrinsic mechanical stretch to the fiber also triggers numerous intracellular signals, including nitric oxide synthesis, which results in hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) release and satellite cell activation, this suggesting that the HGF receptor c-Met may be an early gene in satellite cell activation [10]. Nitric oxide also induces expression of Follistatin [11], a fusigenic secreted molecule, known to antagonize Myostatin, a negative regulator of myogenesis expressed by quiescent satellite cells thus maybe contributing to satellite cells exit from quiescence.
Microenvironment-secreted growth factors are third stimulus for satellite cell activation. As a matter of fact, fibroblasts growth factors (FGF) are known to induce pro-myogenic MAPK signaling cascades and the p38α/β MAPK is required for satellite cell activation and regulates the quiescent state of satellite cells [12]. Analysis of p38α mutant showed that p38α abrogation induces delayed cell-cycle exit and altered expression of cell-cycle regulators in cultured myoblasts. As a result of continuous proliferation, and lack of growth arrest feed-back, p38α mutants showed increased myoblast proliferation in the neonatal period [13]. An important question that now remains to be elucidated is whether adult satellite cells that have been activated during regeneration can return to quiescence in p38α mutant muscles. An alternative way p38α /β can be activated during myogenesis is through the surface protein Cdo via interaction with the scaffold protein JLP [14], this predicting a still unknown helper cell to satellite cell activation mechanism.
Self-renewal and stem cell potential
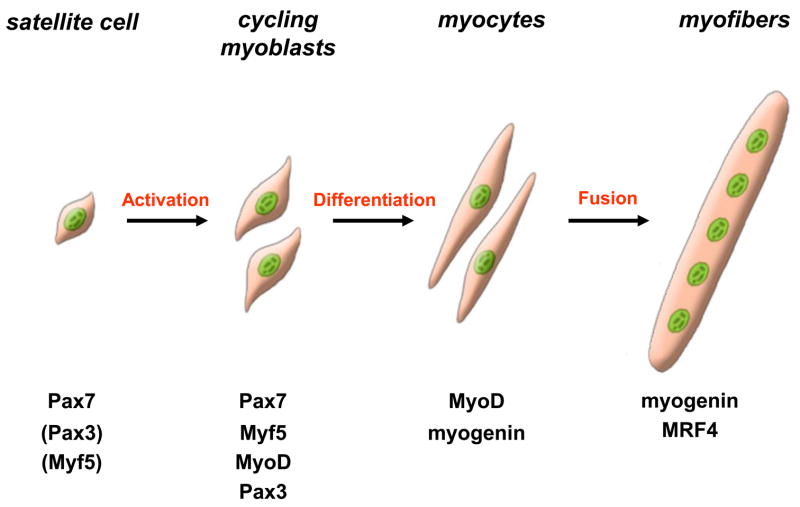
Following activation, satellite cell will leave their niche and move outside of the basal lamina, start to cycle and coexpress Pax7 and MyoD. The descendants of activated satellite cells, the skeletal myoblasts, undergo multiple rounds of division and most of them will downregulate Pax7, express myogenin and differentiate to fuse and form multinucleated myofibers (Figure 1).
Figure 1. Schematic representation of adult myogenesis.
Quiescent skeletal muscle satellite cell can become activated following stimuli originating from their associated fiber or from the micro-environment. Their proliferating progeny, the skeletal myoblasts, express the paired-box transcriptions factors Pax7 and Pax3, as well as the myogenic regulatory factors Myf5 and MyoD. Once committed to differentiation, myoblasts stop cycling and loose expression of Pax7, Pax3 and Myf5. Differentiating myogenin+ve myocytes will then align and fuse to form multinucleated myofibers. MRF4 is further required for hypertrophy of the new fibers.
A fraction of these myoblasts will maintain Pax7, loose expression of myogenic markers and eventually leave the cell cycle [15,16]. These {Pax7+ve, MyoD-ve} cells have thus been postulated to represent a self-renewing fraction and further transplantation of freshly isolated satellite cells or intact myofibers with their associated satellite cells in irradiated hosts proved that satellite cells can self-renew, replenish a depleted niche, and that their progeny is capable of efficient regeneration [17,18].
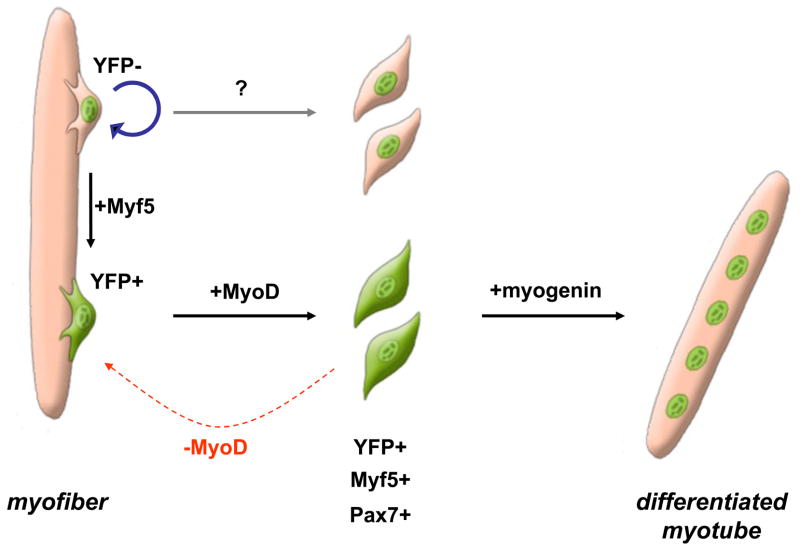
In the last couple years, researchers aimed to discover which signals direct the self-renewal of satellite cells, and if it is a potential that all satellite cell posses or only a minority of them. A first insight came from lineage tracing experiments using Myf5-reporter mice, which showed that muscle satellite cells are a heterogeneous mixture of stem cells and committed progenitors. In fact, satellite “stem” cells which never expressed Myf5 can asymmetrically divide, and give rise to a Myf5+ve daughter committed to myogenesis as well as a self-renewing Myf5-ve daughter (Figure 2). Prospective isolations and transplantations of both cell sub-types then demonstrated that Myf5-ve stem cells can extensively contribute to the satellite cell reservoir [19••].
Figure 2. Satellite cell hierarchy and self-renewal.
During regeneration, satellite stem (Myf5YFP-ve) cells can asymmetrically divide and give rise to a self-renewing daughter (blue arrow) and a committed (Myf5YFP+ve) daughter. Committed cells become activated, leave the sub-laminar niche and proliferate. Myf5+ve cycling myoblasts mainly differentiate and contribute to new fiber formation., Some Myf5+ve myoblasts can also downregulate MyoD and return to quiescence (red arrow), thus replenishing the niche. Myf5-ve stem cells arealso postulated as being able to give rise to uncommitted progenitors which will participate in regeneration of the tissue (grey arrow).
More than 30 years ago, the Cairns hypothesis of the “immortal strand” proposed that stem cell that divide asymmetrically can retain the oldest DNA strand in the less committed cell, thus limiting mutations in the self-renewing pool [20]. That hypothesis was recently tested in the muscle system, and using pulse-chase labeling of stem cells with halogenated thymidine analogs, researchers were able to demonstrate co-segregation of template DNA strands in dividing skeletal myoblasts [21••,22•]. Further to that point, the label-retaining cells were shown to co-segregate with the immature cell determinants Numb and/or Sca1, while the non-retaining cells are proposed to follow a myogenic pathway. However, the Cairns hypothesis does not appear to be commonly accepted as a common stem cell feature, since only a few cell types show asymmetric strand segregation. Hence, haematopoietic stem cells were recently reported as to not asymmetrically segregate chromosomes or retain BrdU [23]. Another interesting explanation is that asymmetric cell divisions and cell fate are codirected by epigenetic differences between sister chromatids and that the DNA strands bearing the more “active” stem cell genes are co-segregated for the maintenance of self-renewal properties [24].
Molecular regulation of satellite cell proliferation and differentiation
Satellite cell myogenic potential mostly relies on the expression of Pax genes and Myogenic Regulatory Factors (MRFs; MyoD, Myf5, myogenin, MRF4), sequential activation and repression of Pax3/7 and MRFs is required for the progression of skeletal myoblasts through myogenesis. Pax7 is essential for the post-natal maintenance and self-renewal of satellite cells [25,26•]. At birth, satellite cell numbers are close to normal in Pax7 mutant mice, but they are progressively lost, mainly because of cell death in the absence of Pax7. Remnant satellite cells can be detected in the absence of Pax7, but they are defective, and unable to support efficient regeneration [26•]. Pax3 is also expressed in a subset of quiescent satellite cells and can be detected after activation in most skeletal myoblasts [27•]. Its roles in muscle regeneration are not well defined, since Pax3-null mice dies in utero and still no adult conditional mutation of Pax3 has been described. Pax3 and Pax7 play similar roles in the activation of myogenic genes, such as MyoD, but only Pax7 possess a survival and anti-apoptotic function [27•].
Recent works demonstrated the importance of Pax proteins regulation during adult myogenesis. Pax3 is regulated by monoubiquitination and proteasomal degradation during satellite cell activation. Sustained expression of stable mutant form Pax3 inhibited myogenic differentiation, demonstrating that control of Pax3 degradation is an essential step for the progression of myogenic program beyond commitment [28•]. Pax7 induces myoblast proliferation and delay their differentiation, thus not by blocking myogenin expression [29] but by regulation of MyoD [30], in parallel, myogenin directly affects Pax7 protein expression and is postulated as being a regulator of Pax7 down-regulation during differentiation [30].
In contrast with the Pax3/7 genes, MyoD and Myf5 possess clearly defined specific roles in satellite cell biology. MyoD is required for the differentiation potential of skeletal myoblasts [31,32] whereas Myf5 regulates their proliferation rate and homeostasis [33•,34•]. Interestingly, while both Myf5 and MyoD can each compensate for the loss of the other during embryogenesis [35], they cannot efficiently compensate for each other in an adult context. When MyoD-null and Myf5-null mice were crossed with mdx mutants both compound showed constant regeneration and aggravation of the dystrophic phenotype [33•,34•,36]. Myf5 deficiency leading to a lack of myoblast amplification and loss of MyoD induced an increased propensity for self-renewal rather than progression through the myogenic differentiation.
The differentiation factors myogenin and MRF4 are not involved in satellite cell development or maintenance [33] but induction of myogenin is necessary and sufficient for the formation of myotubes and fibers. As a proof of the latter, mice with a conditional post-natal recombination of myogenin show a reduced muscle mass, thus suggesting that the absence of myogenin prevented the skeletal myoblasts from contributing to post-natal muscle growth [37].
Satellite cells depletion and inhibition during aging
Sarcopenia, the degenerative loss of skeletal muscle mass and strength, occurs during senescence and results in a reduction in the performance of muscles in old age (see [38] for review). The regenerative potential of skeletal muscle itself diminishes with aging, this related to a decline in satellite cells activity. Impairment in satellite cell function as a source of new myonuclei can be related to a diminution of the satellite cell pool, in fact, the abundance of resident satellite cells declines with age in myofibers from both fast-and slow- twitch muscles, but the down-sized population is still able to support effective myogenesis in vitro [39]. To this extend, transplantation experiments showed that satellite cells associated with aged fibers, can mediate extensive regeneration, and provide new satellite cell to the host muscle pool, thus demonstrating that the self-renewal and myogenic potential of young and old satellite cells is similar [40•]. The changes in the extrinsic microenvironment inhibit satellite cells competences and increase in tissue fibrosis. As a demonstration of the latter, regenerative capacity and proliferation of satellite cells within old skeletal muscle were restored when exposed to a young systemic environment by parabiotic pairings of old and young animals [41]. Further lineage tracing experiments showed that cells that once were Pax7+ve satellite cells can loose Pax7 expression during muscle aging in mice, and differentiate into fibroblasts in old muscle, hence contributing to fibrosis. This loss of stem cell phenotype, results from an elevated canonical Wnt signalling induced by component of the old serum [42••].
Alternative source of regeneration; myogenesis from blood vessels
Myogenic and angiogenic cells are closely related during embryonic development. To that extend, a recent study demonstrated that cells of the dorsal aorta and of the myotome derive from a common precursor during early embryogenesis [43]. In fact, developing blood vessels and myogenic precursors are in close vicinity during embryonic development and interact with each others [44]. It has also been demonstrated that fetal myogenic progenitors and muscle fiber-associated endothelial cells share myogenic potential [45]. In post-natal life, satellite cells and endothelial cells are close neighbors and interact with each others during physiological processes and muscle regeneration [46]. In parallel, the mesoangioblast, an adult vessel-derived stem cell, possess high myogenic potential and is highly effective vector for muscle reconstruction in the context of muscular dystrophy [47]. Recent experiments carried out from human muscle tissue have maybe shaken the position of satellite cells as the major effectors of muscle regeneration and homeostasis. Indeed, pericytes associated with microvasculature walls are myogenic precursor [48••] as well as multipotent myogenic cells related to the endothelial cell lineage [49•] can efficiently contribute to myogenic regeneration. It is still unknown, at the moment, if human mesoangioblasts/pericytes and myo-endothelial cells are actually part of the normal homeostasis and regeneration during normal life. These cells possess a high myogenic potential in vitro and after transplantation in a dystrophic host, but they represent a very smaller progenitor population compared to satellite cells [48••,49•].
Conclusion
Skeletal muscle satellite cells are a heterogeneous population of stem and progenitor cells which are necessary for skeletal muscle embryonic development, repair, homeostasis and senescence. Satellite cells are the main source for myofibers repair in the adult, and once woken-up from quiescence, they can generate differentiated cells and self-renewing stem cells by asymmetric division. Other vessel-related progenitors can also contribute to myofibers reconstruction, but our current opinion, without impeding any of the considerable impact for cell-mediated therapy of the latest studies, is that muscle satellite cells represent the major source of myogenic cells in the adult, and that vessel-related progenitor cells account for a secondary source of myogenesis as well as being able to contribute to neoangiogenesis in human muscle. From discussing with the researchers in our field, we can say that the study of satellite cells, their niche and regenerative capacities, is accelerating, and clearly, there will numerous breakthrough advances in the next few years in both developmental and molecular biology as well as medicine.
Acknowledgments
Michael A Rudnicki and Fabien Le Grand acknowledge support from NIAMS, HHMI, MDA, CIHR, the CRC Program, and Jesse’s Journey Foundation.
Footnotes
Publisher's Disclaimer: This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final citable form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
References and recommended reading
- 1.Buckingham M, Bajard L, Chang T, Daubas P, Hadchouel J, Meilhac S, Montarras D, Rocancourt D, Relaix F. The formation of skeletal muscle: from somite to limb. J Anat. 2003;202:59–68. doi: 10.1046/j.1469-7580.2003.00139.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Gros J, Manceau M, Thome V, Marcelle C. A common somitic origin for embryonic muscle progenitors and satellite cells. Nature. 2005;435:954–958. doi: 10.1038/nature03572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Kassar-Duchossoy L, Giacone E, Gayraud-Morel B, Jory A, Gomes D, Tajbakhsh S. Pax3/Pax7 mark a novel population of primitive myogenic cells during development. Genes Dev. 2005;19:1426–1431. doi: 10.1101/gad.345505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Relaix F, Rocancourt D, Mansouri A, Buckingham M. A Pax3/Pax7-dependent population of skeletal muscle progenitor cells. Nature. 2005;435:948–953. doi: 10.1038/nature03594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Schienda J, Engleka KA, Jun S, Hansen MS, Epstein JA, Tabin CJ, Kunkel LM, Kardon G. Somitic origin of limb muscle satellite and side population cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103:945–950. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0510164103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.•.Schuster-Gossler K, Cordes R, Gossler A. Premature myogenic differentiation and depletion of progenitor cells cause severe muscle hypotrophy in Delta1 mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104:537–542. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0608281104. This work demonstrates that the Notch ligand Delta1 provides essential signals that regulate myogenic precursors balance between proliferation and differentiation. Embryonic satellite cell precursors are gradually lost in the context of defective Notch signaling. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.•.Vasyutina E, Lenhard DC, Wende H, Erdmann B, Epstein JA, Birchmeier C. RBP-J (Rbpsuh) is essential to maintain muscle progenitor cells and to generate satellite cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104:4443–4448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0610647104. Inhibition of Notch signaling, during embryonic development, within the expression domains of Lbx1 and Pax3 induce a precocious differentiation of muscle resident progenitor cells, and satellite cell depletion in fetal muscles. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Charge SB, Rudnicki MA. Cellular and molecular regulation of muscle regeneration. Physiol Rev. 2004;84:209–238. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00019.2003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.•.Nagata Y, Partridge TA, Matsuda R, Zammit PS. Entry of muscle satellite cells into the cell cycle requires sphingolipid signaling. J Cell Biol. 2006;174:245–253. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200605028. This work shows that shingolipid, generated from the inner leaflet of the plasma membrane, is involved in satellite cell activation from quiescence and efficient regeneration. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Wozniak AC, Anderson JE. Nitric oxide-dependence of satellite stem cell activation and quiescence on normal skeletal muscle fibers. Dev Dyn. 2007;236:240–250. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.21012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Pisconti A, Brunelli S, Di Padova M, De Palma C, Deponti D, Baesso S, Sartorelli V, Cossu G, Clementi E. Follistatin induction by nitric oxide through cyclic GMP: a tightly regulated signaling pathway that controls myoblast fusion. J Cell Biol. 2006;172:233–244. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200507083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- 12.Jones NC, Tyner KJ, Nibarger L, Stanley HM, Cornelison DD, Fedorov YV, Olwin BB. The p38alpha/beta MAPK functions as a molecular switch to activate the quiescent satellite cell. J Cell Biol. 2005;169:105–116. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200408066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Perdiguero E, Ruiz-Bonilla V, Gresh L, Hui L, Ballestar E, Sousa-Victor P, Baeza-Raja B, Jardi M, Bosch-Comas A, Esteller M, et al. Genetic analysis of p38 MAP kinases in myogenesis: fundamental role of p38alpha in abrogating myoblast proliferation. Embo J. 2007;26:1245–1256. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Takaesu G, Kang JS, Bae GU, Yi MJ, Lee CM, Reddy EP, Krauss RS. Activation of p38alpha/beta MAPK in myogenesis via binding of the scaffold protein JLP to the cell surface protein Cdo. J Cell Biol. 2006;175:383–388. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200608031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Olguin HC, Olwin BB. Pax-7 up-regulation inhibits myogenesis and cell cycle progression in satellite cells: a potential mechanism for self-renewal. Dev Biol. 2004;275:375–388. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2004.08.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Zammit PS, Golding JP, Nagata Y, Hudon V, Partridge TA, Beauchamp JR. Muscle satellite cells adopt divergent fates: a mechanism for self-renewal? J Cell Biol. 2004;166:347–357. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200312007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Collins CA, Olsen I, Zammit PS, Heslop L, Petrie A, Partridge TA, Morgan JE. Stem cell function, self-renewal, and behavioral heterogeneity of cells from the adult muscle satellite cell niche. Cell. 2005;122:289–301. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.05.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Montarras D, Morgan J, Collins C, Relaix F, Zaffran S, Cumano A, Partridge T, Buckingham M. Direct isolation of satellite cells for skeletal muscle regeneration. Science. 2005;309:2064–2067. doi: 10.1126/science.1114758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.••.Kuang S, Kuroda K, Le Grand F, Rudnicki MA. Asymmetric self-renewal and commitment of satellite stem cells in muscle. Cell. 2007;129:999–1010. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.03.044. The authors demonstrate that satellite cells are a heterogeneous population of Myf5-ve stem cell and Myf5+ve committed progenitors. Satellite stem cells give rise to committed progenitors by asymmetric division and extensively repopulate the satellite cell pool. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Cairns J. Mutation selection and the natural history of cancer. Nature. 1975;255:197–200. doi: 10.1038/255197a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.••.Shinin V, Gayraud-Morel B, Gomes D, Tajbakhsh S. Asymmetric division and cosegregation of template DNA strands in adult muscle satellite cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2006;8:677–687. doi: 10.1038/ncb1425. Along with [22•], this work demonstrates that satellite cells can undergo parental template DNA strand co-segregation during asymmetric division. Label-retaining cells express fate-determination markers and are postulated to retain the “immortal template” DNA. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.•.Conboy MJ, Karasov AO, Rando TA. High incidence of non-random template strand segregation and asymmetric fate determination in dividing stem cells and their progeny. PLoS Biol. 2007;5:e102. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0050102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Kiel MJ, He S, Ashkenazi R, Gentry SN, Teta M, Kushner JA, Jackson TL, Morrison SJ. Haematopoietic stem cells do not asymmetrically segregate chromosomes or retain BrdU. Nature. 2007;449:238–242. doi: 10.1038/nature06115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Lansdorp PM. Immortal strands? Give me a break. Cell. 2007;129:1244–1247. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.06.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Seale P, Sabourin LA, Girgis-Gabardo A, Mansouri A, Gruss P, Rudnicki MA. Pax7 is required for the specification of myogenic satellite cells. Cell. 2000;102:777–786. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)00066-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.•.Kuang S, Charge SB, Seale P, Huh M, Rudnicki MA. Distinct roles for Pax7 and Pax3 in adult regenerative myogenesis. J Cell Biol. 2006;172:103–113. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200508001. Along with [27•], this work describes the progressive post-natal loss of satellite cells in Pax7 mutants. They also report that remnant satellite cells found in pax7-null muscle are defective for myogenesis and they identified a novel interstitial Pax3+ve myogenic cell population. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.•.Relaix F, Montarras D, Zaffran S, Gayraud-Morel B, Rocancourt D, Tajbakhsh S, Mansouri A, Cumano A, Buckingham M. Pax3 and Pax7 have distinct and overlapping functions in adult muscle progenitor cells. J Cell Biol. 2006;172:91–102. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200508044. This study reports that Pax3, which is transcribed in some satellite cells in the adult, cannot compensate for the loss of Pax7. Pax3 and Pax7 are shown to induce MyoD expression and thus myogenic progression in myoblasts. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.•.Boutet SC, Disatnik MH, Chan LS, Iori K, Rando TA. Regulation of pax3 by proteasomal degradation of monoubiquitinated protein in skeletal muscle progenitors. Cell. 2007;130:349–362. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.05.044. This work demonstrates that Pax3, but not Pax7, is specifically regulated by proteasomal destruction during myogenesis. Pax3 degradation is postulated to be a pre-requirement for myoblasts differentiation. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Zammit PS, Relaix F, Nagata Y, Ruiz AP, Collins CA, Partridge TA, Beauchamp JR. Pax7 and myogenic progression in skeletal muscle satellite cells. J Cell Sci. 2006;119:1824–1832. doi: 10.1242/jcs.02908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Olguin HC, Yang Z, Tapscott SJ, Olwin BB. Reciprocal inhibition between Pax7 and muscle regulatory factors modulates myogenic cell fate determination. J Cell Biol. 2007;177:769–779. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200608122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Sabourin LA, Girgis-Gabardo A, Seale P, Asakura A, Rudnicki MA. Reduced differentiation potential of primary MyoD−/− myogenic cells derived from adult skeletal muscle. J Cell Biol. 1999;144:631–643. doi: 10.1083/jcb.144.4.631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Cornelison DD, Olwin BB, Rudnicki MA, Wold BJ. MyoD(−/−) satellite cells in single-fiber culture are differentiation defective and MRF4 deficient. Dev Biol. 2000;224:122–137. doi: 10.1006/dbio.2000.9682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.•.Gayraud-Morel B, Chretien F, Flamant P, Gomes D, Zammit PS, Tajbakhsh S. A role for the myogenic determination gene Myf5 in adult regenerative myogenesis. Dev Biol. 2007 doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2007.08.059. Along with [34•], this work analyzes Myf5 roles adult muscle regeneration. Myf5 deletion induces a reduction in skeletal myoblasts proliferation rate and a delayed transition from proliferation to differentiation. Myf5-null*mdx compound mutants exhibit constant regeneration, thus predicting a role for Myf5 in muscle homeostasis. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.•.Ustanina S, Carvajal J, Rigby P, Braun T. The myogenic factor Myf5 supports efficient skeletal muscle regeneration by enabling transient myoblast amplification. Stem Cells. 2007;25:2006–2016. doi: 10.1634/stemcells.2006-0736. See annotation to [33•] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Rudnicki MA, Schnegelsberg PN, Stead RH, Braun T, Arnold HH, Jaenisch R. MyoD or Myf-5 is required for the formation of skeletal muscle. Cell. 1993;75 :1351–1359. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90621-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Megeney LA, Kablar B, Garrett K, Anderson JE, Rudnicki MA. MyoD is required for myogenic stem cell function in adult skeletal muscle. Genes Dev. 1996;10:1173–1183. doi: 10.1101/gad.10.10.1173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Knapp JR, Davie JK, Myer A, Meadows E, Olson EN, Klein WH. Loss of myogenin in postnatal life leads to normal skeletal muscle but reduced body size. Development. 2006;133:601–610. doi: 10.1242/dev.02249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Grounds MD. Age-associated changes in the response of skeletal muscle cells to exercise and regeneration. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1998;854:78–91. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1998.tb09894.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Shefer G, Van de Mark DP, Richardson JB, Yablonka-Reuveni Z. Satellite-cell pool size does matter: defining the myogenic potency of aging skeletal muscle. Dev Biol. 2006;294:50–66. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2006.02.022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.•.Collins CA, Zammit PS, Ruiz AP, Morgan JE, Partridge TA. A population of myogenic stem cells that survives skeletal muscle aging. Stem Cells. 2007;25:885–894. doi: 10.1634/stemcells.2006-0372. This study demonstrate that satellite cell decrement contribute to the impairment in regeneration during aging. They further demonstrate that stem cell potential is still present in remnant satellite cell but inhibited by extrinsic influences. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Conboy IM, Conboy MJ, Wagers AJ, Girma ER, Weissman IL, Rando TA. Rejuvenation of aged progenitor cells by exposure to a young systemic environment. Nature. 2005;433:760–764. doi: 10.1038/nature03260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.••.Brack AS, Conboy MJ, Roy S, Lee M, Kuo CJ, Keller C, Rando TA. Increased Wnt signaling during aging alters muscle stem cell fate and increases fibrosis. Science. 2007;317:807–810. doi: 10.1126/science.1144090. In the elderly, satellite cells can loose Pax7 expression and differentiate into fibroblasts, thus impairing skeletal muscle fiber maintenance and increasing fibrosis. Canonical Wnt signaling, induced by old serum, is shown to be responsible for the loss of myogenic phenotype by a subset of satellite cells. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Esner M, Meilhac SM, Relaix F, Nicolas JF, Cossu G, Buckingham ME. Smooth muscle of the dorsal aorta shares a common clonal origin with skeletal muscle of the myotome. Development. 2006;133:737–749. doi: 10.1242/dev.02226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Tozer S, Bonnin MA, Relaix F, Di Savino S, Garcia-Villalba P, Coumailleau P, Duprez D. Involvement of vessels and PDGFB in muscle splitting during chick limb development. Development. 2007;134:2579–2591. doi: 10.1242/dev.02867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Le Grand F, Auda-Boucher G, Levitsky D, Rouaud T, Fontaine-Perus J, Gardahaut MF. Endothelial cells within embryonic skeletal muscles: a potential source of myogenic progenitors. Exp Cell Res. 2004;301:232–241. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2004.07.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Christov C, Chretien F, Abou-Khalil R, Bassez G, Vallet G, Authier FJ, Bassaglia Y, Shinin V, Tajbakhsh S, Chazaud B, et al. Muscle satellite cells and endothelial cells: close neighbors and privileged partners. Mol Biol Cell. 2007;18:1397–1409. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E06-08-0693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Sampaolesi M, Blot S, D'Antona G, Granger N, Tonlorenzi R, Innocenzi A, Mognol P, Thibaud JL, Galvez BG, Barthelemy I, et al. Mesoangioblast stem cells ameliorate muscle function in dystrophic dogs. Nature. 2006;444:574–579. doi: 10.1038/nature05282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.••.Dellavalle A, Sampaolesi M, Tonlorenzi R, Tagliafico E, Sacchetti B, Perani L, Innocenzi A, Galvez BG, Messina G, Morosetti R, et al. Pericytes of human skeletal muscle are myogenic precursors distinct from satellite cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2007;9:255–267. doi: 10.1038/ncb1542. The authors identify human pericytes as a source of skeletal myogenesis in vitro and in vivo. They demonstrate that transplanted pericyte-derived cells can efficiently colonize a host dystrophic mouse muscle and generate skeletal muscle fibers expressing human dystrophin. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.•.Zheng B, Cao B, Crisan M, Sun B, Li G, Logar A, Yap S, Pollett JB, Drowley L, Cassino T, et al. Prospective identification of myogenic endothelial cells in human skeletal muscle. Nat Biotechnol. 2007;25:1025–103. doi: 10.1038/nbt1334. In this study, human multipotent cells coexpressing myogenic and endothelial cell markers are shown to extensively regenerate myofibers after transplantation in an injured muscle of immunodeficient mice. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]