Rapid Identification of Bacteria with a Disposable Colorimetric Sensing Array (original) (raw)
. Author manuscript; available in PMC: 2012 May 18.
Published in final edited form as: J Am Chem Soc. 2011 Apr 27;133(19):7571–7576. doi: 10.1021/ja201634d
Abstract
Rapid identification of both species and even specific strains of human pathogenic bacteria grown on standard agar have been achieved from the volatiles they produce using a disposable colorimetric sensor array in a Petri dish imaged with an inexpensive scanner. All ten strains of bacteria tested, including E. faecalis and S. aureus and their antibiotic resistant forms, were identified with 98.8% accuracy within 10 h, a clinically important timeframe. Furthermore, the colorimetric sensor arrays also prove useful as a simple research tool for the study of bacterial metabolism and as an easy method for the optimization of bacterial production of fine chemicals or other fermentation processes.
INTRODUCTION
The detection and identification of bacteria are pressing problems in both medicine and industry.1,2 A patient may present to the physician with symptoms consistent with a bacterial infection, but the physician may be unable to address the infection with the appropriate antibiotic until the identity or antibiotic susceptibility of the bacteria has been determined; as a consequence sepsis remains one of the leading causes of death even among first world nations.1 In industry, many products must be screened after manufacture for bacterial contamination before they may be released and as a consequence regulation of the food industry must be particularly stringent.2 Existing methods for identification of pathogenic bacteria are severely limited by the necessity of long culturing times, the need for highly trained laboratory personnel, and the requirement of expensive and high-maintenance equipment.3–5
Bacteria stink: that is, they produce volatile organic compounds (VOCs) to which the mammalian olfactory system is highly responsive. Consequently, an experienced microbiologist can readily identify many bacteria by smell. We have previously developed a simple colorimetric sensing array6 for the detection of VOCs7 and discrimination among complex mixtures;8 we report here that these arrays provide a rapid and quantitative method for the identification not only of the bacterial species, but even of the specific strain of a single species, based on volatile metabolites produced by the bacteria. We find that a disposable sensor array placed in a standard Petri dish and imaged with an ordinary flatbed scanner is capable of identifying human pathogenic bacterial strains in less than ten hours, which represents a substantial improvement over current clinical techniques in terms of speed, ease of use, and cost.
Traditional techniques for both manual and automated bacterial identification are based on the biochemical characteristics of each microorganism as defined by yes/no answers to a series of biochemical tests. In essence, these tests differentiate and identify bacteria by identifying specific bacterial metabolites as a function of available nutrients. A much less explored alternative, however, would be to identify bacteria by monitoring their metabolic output from growth on a single complex nutrient mixture. This strategy arises from the well-established knowledge that different species of bacteria consuming the same nutrients produce different metabolites. Different species, even different strains of the same species, emit distinct profiles of enzymatic reaction products such as amines, sulfides, and fatty acids.9–11 Given the high sensitivity of colorimetric sensors to numerous VOCs, we expected that the various volatile metabolites produced by different bacterial strains might provide identifying fingerprints in the response of the sensor arrays.
Towards that end, we have used a cross-responsive colorimetric sensor array to monitor the complex composite of volatile compounds produced by ten bacterial strains grown in replicate on solid media in closed Petri dishes. The sensor arrays consist of 36 chemically responsive dyes, including metalloporphyrins, pH indicators, metal salts, and solvatochromic dyes, that change color when exposed to a broad range of volatile analytes. Given the wide range of VOCs produced by bacteria,9–11 the chemical diversity of the sensor elements present in our array is critical to its capability to respond to broad classes of individual analytes and its ability to distinguish among complex mixtures.
EXPERIMENTAL SECTION
Bacteria
Bacterial strains were purchased from the American Type Culture Collection (Manassas, VA) and were cultured following manufacturer protocols before use. Bacteria were grown in tryptic soy broth (TSB) and plated during log phase growth on tryptic soy agar containing 5% sheep blood (Becton Dickinson, Franklin Lakes, NJ). Bacterial suspensions were prepared by inoculating 5 mL of TSB with a single colony and allowing it to grow overnight. A subculture then was prepared in 5 mL of fresh TSB and shaken at 37 °C for 3 h to achieve the desired inoculum density of 0.5 to 5 on the McFarland turbidity scale. This equates to ~3.0 × 108 to 1.5 × 109 CFU/mL. 10–250 μL of the subculture was then spread onto a 60 mm TSA/sheep blood Petri dish. A control (10–250 μL of TSB broth without the bacterial inoculum) was conducted in parallel for each experiment.
Colorimetric Sensor Array
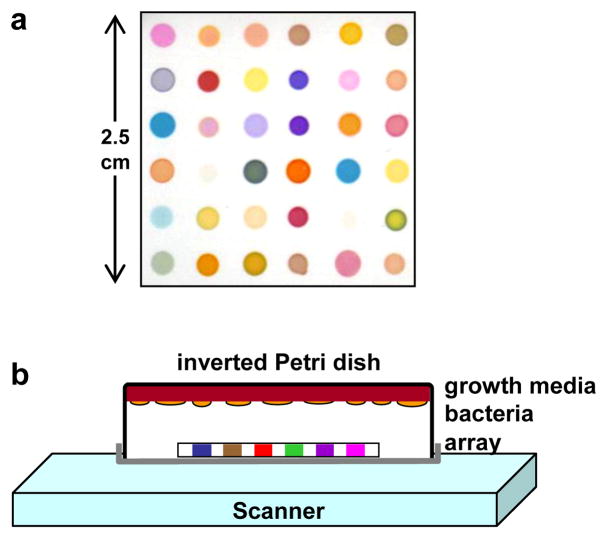
The disposable colorimetric sensor array and its construction have been previously described7 and the specific dyes used for this study are given in Supporting Information, Table S1. An array was mounted in an inert platform that was inserted into the lid of the Petri dish. The Petri dish was closed and inverted onto an ordinary flatbed scanner (as shown in Figure 1) housed in an incubator at 35–37 °C; the printed side of the array faced towards the scanner. Data was collected using an Epson Perfection 3490 scanner every 30 min. Color difference maps were generated by averaging the RGB color values for the center of each spot and subtracting from them the RGB averages for the baseline image: ΔR, ΔG, ΔB, i.e. red value after exposure minus red value at 90 min, etc. Substantial sensor array color changes arising from the media occur upon exposure as the media equilibrates to the incubator temperature of 37 °C, so the baseline image was taken at 90 min, which was sufficient for complete equilibration but before any significant bacterial growth had occurred. A complete database is available in the Supporting Information.
Figure 1.
(a) Colorimetric sensor array used for bacterial identification experiments; details provided in Supporting Information Table S1. (b) Schematic of the experimental apparatus consisting of an inverted closed Petri dish containing growth media (tryptic soy agar (TSA) with 5% sheep blood) upon which was spread the appropriate liquid bacterial culture, an array positioned in the headspace, and an ordinary flatbed scanner. The array was scanned and images collected as a function of time.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Current Clinical Bacterial Detection
Bloodstream infections by bacteria (i.e., bacteremia) are among the most serious medical problems because of their significant morbidity and mortality.1 In the U.S., an estimated 750,000 patients annually develop bloodstream infections with associated mortality rates ranging from 14 to 50%. Sepsis and septic shock are the tenth leading cause of death in the U.S. and the third most common cause of death in Germany; furthermore, sepsis and related complications represent a significant economic burden, with an estimated annual cost beyond $17 billion in the U.S. alone.1
There remain major unmet needs to shorten and improve current clinical and laboratory methods for the detection and identification of bloodstream infections, and molecular diagnostic methods (ranging from mass spectral analysis to PCR to peptide-nucleic acid fluorescent probes, etc.) have yet to have a major impact on such diagnoses.3d Blood cultures remain the “gold standard” for the diagnosis of bacteremia.1,2 Current standard clinical procedures2 start with culturing (generally in liquid growth media), for example of blood samples, which generally takes 24 to 48 hours to confirm the presence of bacteria, but can take much longer for slow growing bacteria (e.g., tuberculosis generally requires more than a week). Microorganisms taken from positive blood cultures are then subjected to rapid gram staining (~10 min), but then must be sub-cultured and analyzed by culture based systems such as the Analytical Profile Index (API) test or antibiotic susceptibility tests (e.g., bioMérieux’s automated VITEK system), which require another 18 to 48 hours.3 The reader is referred to an excellent recent review of clinical procedures by Riedel and Carroll.1a Nucleic-acid based identification,4,5 such as fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH), can be performed directly from positive blood cultures that require only 6 hours, although identification by culture based systems is needed for confirmation.4d,5e,f
Bacterial Detection by Electronic Nose
There have been various studies using “electronic nose” technologies12–13 (i.e., electronic sensor arrays made from conductive polymers, metal oxides, etc.) for headspace analysis in attempts to identify bacterial strains.14–16 Most such studies use a single time sampling of the headspace over a mature bacterial culture.15 The temporal profile of the gases produced in a closed culture environment, however, provides valuable additional information for bacterial identification. In addition, the VOCs produced by bacteria in a closed environment approximate an integral of growth and may therefore improve the rapidity of analysis. In those few studies in which the headspace was sampled at multiple time points,16 bacterial discrimination was generally still quite limited. In part, this is due to the inherent limitations6 in low dimensionality of prior array technology,12–13 which relies primarily on weak and non-selective analyte-sensor interactions: in general, prior electronic nose technology needs only two dimensions, or at most three, to capture >95% of the total dataset variance. As such, previous bacterial identification efforts with traditional electronic nose technology have typically required complex pattern recognition algorithms in order to achieve modest success, even when attempting to classify small numbers of bacterial species.14–16
Colorimetric Sensor Arrays
The colorimetric sensor arrays are disposable, one-time use sensors that are simply placed in the headspace of bacterial cultures and imaged with an ordinary flatbed scanner at multiple time points during bacteria growth (Figure 1). The responses of the chemically responsive dyes used in the array are in general reversible. As shown below, the array can therefore monitor changes in the volatile metabolites evolved by each bacterial strain over time and thereby differentiate one bacterial species from another.
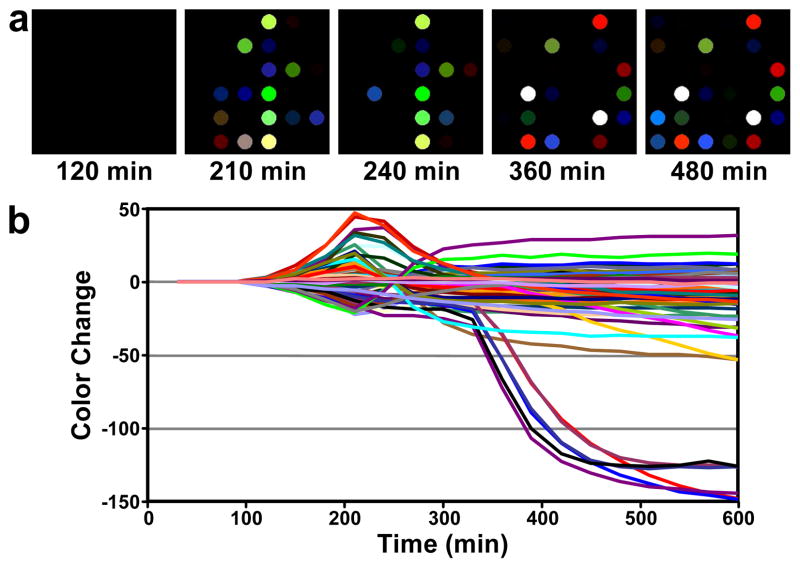
Representative data arising from exposure of the sensor array to E. coli are shown in Figure 2, as both color difference maps and as a time response profile that show the change in spot colors as a function of bacterial growth time. Several notable features are readily apparent in Figure 2. First, there is a time lag (~150 min in this case) before appreciable signal is observed above baseline. As will be shown below, the duration of this lag is species and strain dependent. Once signal is observed, it evolves through several stages; different volatile analytes appear to be generated at different points during growth. Note, for example, the steeply negative color changes occurring between 300 and 400 min. In addition, several color channels pass through a maximum or minimum and then reverse direction, returning to their baseline values or crossing the baseline to change sign. This too implies changes in the nature of volatiles emitted over time.
Figure 2.
Color difference maps and time response profile resulting from colorimetric sensor array exposure to a growing culture of E. coli, American Type Culture Collection (ATCC) #25922. a. The color difference maps (i.e., ΔR, ΔG, ΔB) at select times were generated by subtracting the average RGB of each spot from a baseline image (taken at 90 min). For the purpose of effective visualization only, the color range shown in the color range maps is expanded from RGB values of 0–31 to 0–255. b. The color change values versus time plotted for all color channels (ΔR, ΔG, and ΔB values for each spot, i.e., 108 color channels) at each time point.
Time response profiles were collected in multiple replicates for nine additional bacterial strains (6 to 24 replicates per strain, cf. Supporting Information Table S2). Representative color difference maps and time response profiles for each strain are shown in Figure 3 and Figure 4, respectively. All quantitative analyses were based on the full digital data, which are provided in Supporting Information Table S3.
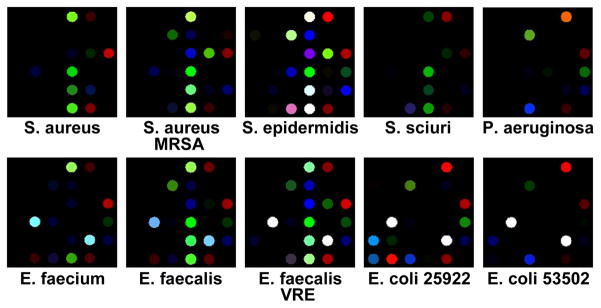
Figure 3.
Color difference maps for 10 different bacterial strains resulting from colorimetric sensor array exposure to Petri dish growing cultures after 480 min. The color range shown is the same as Figure 2a.
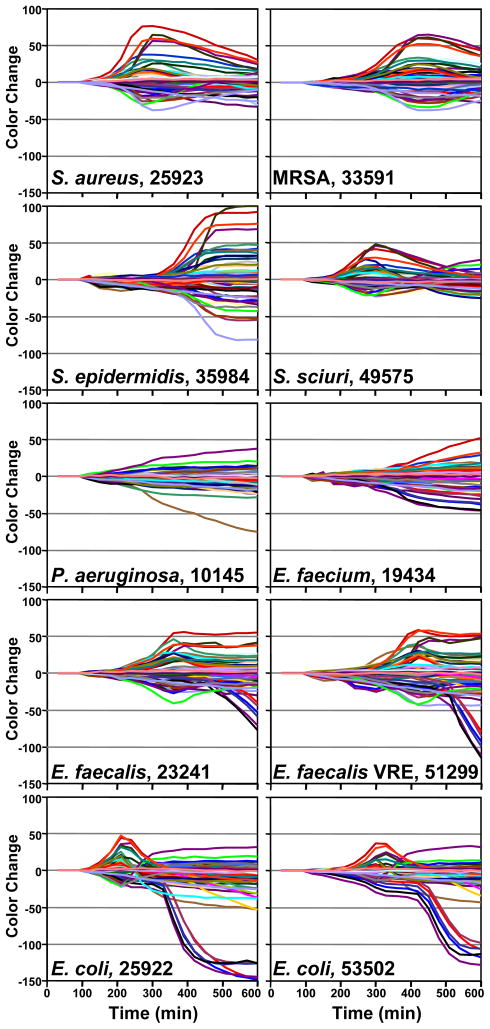
Figure 4.
Time response profiles for 10 different bacterial strains (names and ATCC number given in each panel).
Array Response to Bacterial Growth
As illustrated in Figs. 3 and 4, each strain of bacterium has its own individual color change fingerprint. Even by simple visual examination of the color difference map (Figure 3) or of the time response profiles (Figure 4), all ten of the bacterial strains are readily differentiated; quantitative classification (discussed below) is highly accurate using standard statistical methods. This includes the differentiation of S. aureus from a methicillin resistant S. aureus (MRSA), as well as E. faecalis from a vancomycin resistant E. faecalis (VRE). There are, moreover, genera- and species-based resemblances. This is most apparent in the two strains of E. coli and E. faecalis, respectively, which show the greatest inter-pair similarity in the time response profiles (Figure 4).
There are at least three possible closely-related contributions to the changes and reversal of color features in the array each of which reflect the relationship between the chemical input and output of bacteria. The dominant contributor is likely to be conventional diauxie, in which the bacteria consume one nutrient first and then switch to alternate nutrients when the first is exhausted:17 as the input nutrients change, so too would the evolved volatiles. Consistent with this, the response profiles do depend strongly on the type of solid media (such as TSA, TSA/sheep blood or Luria-Bertani) used as a nutrient source. A second contributor to the temporal changes in the array response (which is generally reversible7) may be the bacterial consumption of a previously excreted product. For example, many bacteria ferment rich nutrients (e.g., glucose) and excrete acetate; acetate can then, upon the exhaustion of better carbon sources, be consumed and oxidized to carbon dioxide.18 A third possibility is a transition from aerobic to anaerobic growth, itself a form of diauxie.19 Chemical analysis of the complex mixture of volatiles produced during bacterial growth presents a significant challenge for conventional component by component analyses (e.g., GC-MS):9–11 fortunately, one need not know the identities of the individual volatile products for the identification of the bacteria using a sensor array approach, which gives a composite response to the complex mixture of bacterial metabolites.
The complex structures observed in the bacterial response profiles underscore the importance of incorporating broad chemical diversity in a single sensor array. These structures also emphasize the value in having a reversible, real-time sensor continuously positioned in the headspace of growing bacterial cultures. The additional advantage of having a disposable, inexpensive sensor array allows for the facile monitoring of bacterial cultures individually and continuously.
Quantitative Classification
Classification of specific bacterial strains based on the colorimetric sensor array data was successfully accomplished using a variety of independent techniques. For quantitative analysis, the color change values for each experiment were analyzed as “time stacked” vectors in order to capture the temporal behavior of the response profiles. The entire time-stacked vector, ν, from a single experiment is given by equation 1, using images collected every 30 min for 10 h, with the 90 min image as the baseline for evolution of differences in red, green and blue values for all 36 spots:
| ν=ΔR1,120min,ΔG1,120min,ΔB1,120min,ΔR2,120min,ΔG2,120min,ΔB2,120min,…ΔR36,120min,ΔG36,120min,ΔB36,120min,ΔR1,150min,ΔG1,150min,ΔB1,150min,……ΔR36,600min,ΔG36,600min,ΔB36,600min | (1) |
|---|
Surprisingly, accurate identification was possible even using simple Euclidean distances, which compares only the overall total response of the array. Average time-stacked vectors were calculated for each strain of bacteria, and the Euclidean distance between each of the 164 individual experimental vectors and each of the average vectors was determined. Each input experimental vector was classified as the strain whose average vector was nearest. Using the time stack data from 90 to 600 min post innoculation, the correct classification was achieved for 162 of the 164 experiments (i.e., 98.8% accuracy); the only two misclassifications were between E. faecalis and its vancomycin resistant mutant (VRE). For the same experiments, the classification accuracy was 95% at 420 min culturing time and 85% at 300 min.
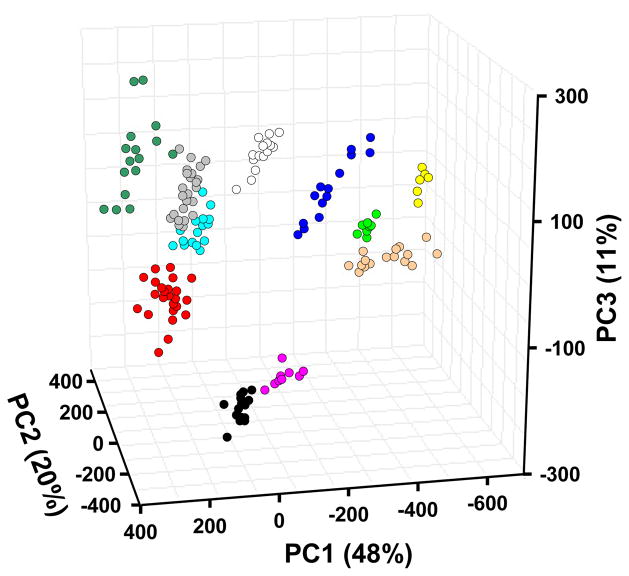
Beyond using just the Euclidean distance of the array response, there is much greater information available in the variance of the specific spots of the array. The ability of the colorimetric sensor array to discriminate among different bacteria is due, in part, to the high dimensionality of the data. Principal component analysis (PCA) uses the variance in the array response to evaluate the relative contributions of independent dimensions and generates optimized linear combinations of the original 108 dimensions so as to maximize the amount of variance in as few dimensions as possible (46–49). Using standard PCA, the data from 164 experiments were analyzed. As we have observed with colorimetric sensor arrays applied to many other systems,6–8 the data has exceptionally high dispersion, requiring 7 and 23 dimensions to capture 90% and 95% of the total variance, respectively (SI Figure S1 provides the PCA scree plot). The first three dimensions in PCA space account for only 79% of the total variance. Nonetheless, a three-dimensional PCA score plot (Figure 5) shows very good clustering of 164 experimental trials on the ten bacteria.
Figure 5.
PCA score plot using the three most important principal components based on all 164 trials of 10 bacterial strains and controls. The resolution between bacterial classes is in fact much better than can be shown by any three-dimensional PCA plot because the first three principal components account for only 79% of the total variance. ● S. aureus;  MRSA;
MRSA;  S. epidermidis;
S. epidermidis;  S. sciuri;
S. sciuri;  P. aeruginosa; ○ E. faecium;
P. aeruginosa; ○ E. faecium;  E. faecalis;
E. faecalis;  E. faecalis VRE;
E. faecalis VRE;  E. coli 25922;
E. coli 25922;  E. coli 53502;
E. coli 53502;  Control.
Control.
The extremely high dispersion of our colorimetric sensor array data reflects the wide range of chemical-property space being probed by the choice of 36 chemically responsive dyes. Consequently, chemically diverse mixtures of volatiles produced by bacteria are easily recognizable, and even closely related bacteria can be distinguished. In contrast, data from most prior electronic nose technologies are dominated by only two or three independent dimensions (one of which, analyte hydrophobicity, generally accounts for >90% of total variance); this is the inherent result of relying on van der Waals and other weak interactions for molecular recognition.
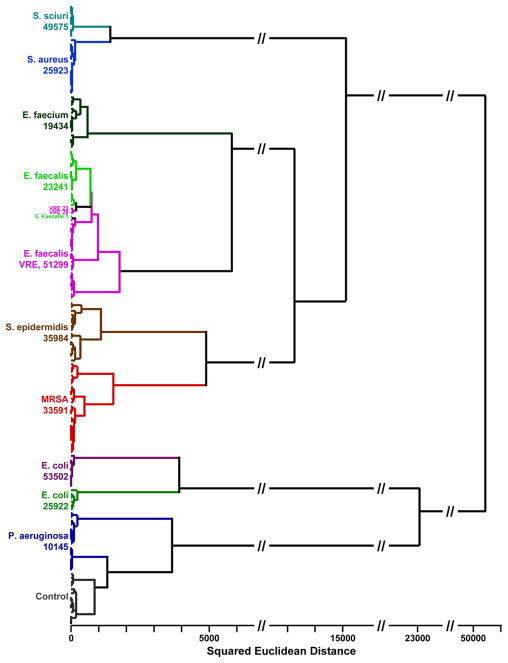
Given the high dimensionality of data from the colorimetric sensor array, the usual two or three dimensional PCA plots (e.g., Figure 5) cannot adequately represent the discrimination among experimental trials. Instead, we prefer the use of another quite standard chemometric approach, hierarchical cluster analysis (HCA), which is based on the grouping of the analyte vectors according to their spatial distances in their full vector space.20 HCA has the advantages of being model-free (unlike, for examples, linear discriminant analysis or neural nets) and of using the full dimensionality of the data. As shown in Figure 6, HCA generates dendrograms based on clustering of the array response data. Excellent classification is observed, with three misclassifications among the 164 trials (all three confusions are between E. faecalis and its vancomycin resistant mutant, VRE).
Figure 6.
HCA dendrogram of 164 trials of 10 human pathogenic bacteria and control, using minimum variance (Ward’s method). The dendrogram is based on the 23 dimensions from PCA that capture 95% of the total variance. The ATCC number is given below the name of each bacterial strain.
To test quantitatively the ability of a more sophisticated statistical model to classify new inputs (i.e., unknown cultures) as would be required in medical diagnostics, a randomized, strain-proportional 70% of the time stacks was used to train a Bayesian linear classifier in PCA space.21 This classifier was then given the remainder of the data, unlabeled, to be classified as one of the 11 strains, and the rate of correct classification was recorded. This was repeated 1000 times, randomizing the designated 70% each time. Analysis using the first seven principal components (which captured 90% of the total variance) produced 99.2% correct classification. Twenty-three principal components (capturing 95% of the variance) produced 99.5% correct classification.
The changes in the array response as a function of time for each bacterial strain imply that each strain of bacterium produces different volatile metabolic products at different rates. This suggests in turn that such arrays may also prove useful as an inexpensive research tool for the study of bacterial metabolism. In addition, the colorimetric sensor arrays are likely to provide an easy method for the optimization of bacterial production of fine chemicals or other fermentation processes.
The biomedical applications of this colorimetric sensing array technology are also potentially significant. The sensor arrays successfully identified all ten strains of bacteria tested, including E. faecalis and S. aureus together with their antibiotic resistant forms, by monitoring gases evolved during a 10 h growth of bacterial cultures. This time frame is clinically important: because we are able to quickly monitor growth rates (even after just 3 h as shown in Figure 4), parallel monitoring of bacterial growth in various antibiotic-doped media should provide physicians with valuable and timely information to guide treatment. Because the technology developed here is inexpensive and builds easily on conventional culturing, it may find widespread application in less economically developed regions.
The initial studies reported herein are being used to guide development of arrays with greater sensitivity and classification capabilities for bacteria. These arrays are currently being applied to blood culture systems using liquid growth media with very low initial inoculum concentrations. In addition, this colorimetric sensor array has also proven highly effective in point-of-care diagnosis of bacterial sinusitis22 and in lung cancer screening,23 and the possibility of other applications of colorimetric sensor arrays for medical diagnosis by breath are likely to emerge.
Supplementary Material
1_si_001
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Sandra McMasters and David Saper for support in experimental development and sample handling, Jeffrey D. Albarella for assistance in array printing, and Diana Biggs and Junho Pak for helpful discussions. At the time this work was done, JRC, KIH, AS and AEW were employees of ChemSensing, Inc. This work was supported in part by the through the NIH Genes, Environment and Health Initiative through award U01ES016011.
Footnotes
References
- 1.(a) Riedel S, Carroll KC. J Infect Chemother. 2010;16:301–306. doi: 10.1007/s10156-010-0069-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Martin GS, Mannino DM, Eaton S, Moss M. New Engl J Med. 2003;348:1546–1554. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa022139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Angus DC, Linde-Zwirble WT, Lidicker J, Clermont G, Carcillo J, Pinsky MR. Critical Care Medicine. 2001;29:1303–1310. doi: 10.1097/00003246-200107000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.(a) Schmidt RH, Rodrick GE, editors. Food Safety Handbook. Wiley; Hoboken, NJ: 2002. [Google Scholar]; (b) Jay JM, Loessner MJ, Golden DA. Modern Food Microbiology. 7. Springer; New York: 2005. [Google Scholar]; (c) Lazcka O, Del Campo FJ, Munoz FX. Biosens Bioelectron. 2007;22:1205–1217. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2006.06.036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (d) Savov AV, Kouzmanov GB. Biotechnol Biotechnol Equip. 2009;23:1462–1468. [Google Scholar]
- 3.(a) O’Hara CM. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2005;18:147–162. doi: 10.1128/CMR.18.1.147-162.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Carroll KC, Weinstein MP. In: Manual Of Clinical Microbiology. 9. Murray PR, Baron EJ, Jorgensen JH, Landry ML, Pfaller MA, editors. Am Soc Microbiol; Washington, D.C: 2007. pp. 192–217. [Google Scholar]; (c) Seng P, Drancourt M, Gouriet F, La Scola B, Fournier PE, Rolain JM, Raoult D. Clin Infect Dis. 2009;49:543–551. doi: 10.1086/600885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (d) Clerc O, Greub G. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2010;16:1054–1061. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2010.03281.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.(a) Raoult D, Fournier PE, Drancourt M. Nature Rev Microbio. 2004;2:151–159. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (a) Peters RPH, van Agtmael MA, Danner SA, Savelkoul PHM, Vandenbroucke-Grauls CMJE. The Lancet: Infectious Diseases. 2004;4:751–760. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(04)01205-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Peters RPH, Savelkoul PHM, Vandenbroucke-Grauls CMJE. Lancet. 2010;375:1779–1780. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60801-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (d) Ecker DJ, Sampath R, Li HJ, Massire C, Matthews HE, Toleno D, Hall TA, Blyn LB, Eshoo MW, Ranken R, Hofstadler SA, Tang YW. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2010;10:399–415. doi: 10.1586/erm.10.24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.(a) Klouche M, Schroder U. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2008;46:888–908. doi: 10.1515/CCLM.2008.157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Miller MB, Tang YW. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2009;22:611–633. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00019-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Boissinot M, Bergeron MG. Curr Op Microbio. 2002;5:478–482. doi: 10.1016/s1369-5274(02)00362-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (d) Weile J, Knabbe C. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2009;394:731–742. doi: 10.1007/s00216-009-2779-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (e) Peters RPH, Savelkoul PHM, Simoons-Smit AM, Danner SA, Vandenbroucke-Grauls CMJE, van Agtmael MA. J Clin Microbiology. 2006;44:119–123. doi: 10.1128/JCM.44.1.119-123.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (f) Forrest GN. Expert Rev Molec Diagn. 2007;7:231–236. doi: 10.1586/14737159.7.3.231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.(a) Suslick KS, Bailey DP, Ingison CK, Janzen M, Kosal MA, McNamara WB, III, Rakow NA, Sen A, Weaver JJ, Wilson JB, Zhang C, Nakagaki S. Quimica Nova. 2007;30:677. [Google Scholar]; (b) Suslick KS. MRS Bulletin. 2004;29:720. doi: 10.1557/mrs2004.209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Rakow NA, Suslick KS. Nature. 2000;406:710. doi: 10.1038/35021028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.(a) Rakow NA, Sen A, Janzen MC, Ponder JB, Suslick KS. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2005;44:4528. doi: 10.1002/anie.200500939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Janzen MC, Ponder JB, Bailey DP, Ingison CK, Suslick KS. Anal Chem. 2006;78:3591. doi: 10.1021/ac052111s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Lim SH, Feng L, Kemling JW, Musto CJ, Suslick KS. Nature Chem. 2009;1:562–567. doi: 10.1038/nchem.360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (d) Feng L, Musto CJ, Kemling JW, Lim SH, Suslick KS. Chem Commun. 2010;46:2037–2039. doi: 10.1039/b926848k. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (e) Feng L, Musto CJ, Kemling JW, Lim SH, Zhong W, Suslick KS. Anal Chem. 2010;82:9433–9440. doi: 10.1021/ac1020886. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.(a) Suslick BA, Feng L, Suslick KS. Discrimination of Complex Mixtures by a Colorimetric Sensor Array: Coffee Aromas. Anal Chem. 2010;82:2067–2073. doi: 10.1021/ac902823w. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Zhang C, Bailey DP, Suslick KS. J Agric Food Chem. 2006;54:4925. doi: 10.1021/jf060110a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Zhang C, Suslick KS. J Agric Food Chem. 2007;55:237. doi: 10.1021/jf0624695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.(a) Schulz S, Dickschat JS. Nat Prod Rep. 2007;24:814–42. doi: 10.1039/b507392h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Kai M, Haustein M, Molina F, Petri A, Scholz B, Piechulla B. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2009;81:1001–12. doi: 10.1007/s00253-008-1760-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.(a) Wang T, Smith D, Spanel P. Intl J Mass Spec. 2004;233:245–251. [Google Scholar]; (b) Demirev PA, Fenselau C. Annu Rev Anal Chem. 2008;1:71–93. doi: 10.1146/annurev.anchem.1.031207.112838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Zhu J, Bean HD, Kuo YM, Hill JE. J Clin Microbiol. 2010;48:4426–31. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00392-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (d) Ho YP, Reddy PM. Clin Chem. 2010;56:525–536. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2009.138867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.(a) Zechman JM, Aldinger S, Labows JNJ. Chromatogr. 1986;377:49–57. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)80760-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Elgaali H, Hamilton-Kemp TR, Newman MC, Collins RW, Yu KS, Archbold DD. J Basic Microbiol. 2002;42:373–380. doi: 10.1002/1521-4028(200212)42:6<373::AID-JOBM373>3.0.CO;2-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Sondag JE, Ali M, Murray PR. J Clin Microbiol. 1980;11:274–277. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.3.274-277.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Gardner JW, Bartlett PN. Electronic Noses: Principles and Applications. Oxford University Press; New York: 1999. [Google Scholar]; (b) Toko K. Biomimetic Sensor Technology. Cambridge University Press; Cambridge, UK: 2000. [Google Scholar]
- 13.(a) Janata J, Josowicz M. Nat Mater. 2003;2:19–24. doi: 10.1038/nmat768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Lewis NS. Acc Chem Res. 2004;37:663–672. doi: 10.1021/ar030120m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Hsieh MD, Zellers ET. Anal Chem. 2004;76:1885–1895. doi: 10.1021/ac035294w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (d) Walt DR. Anal Chem. 2005;77:45A. doi: 10.1021/ac0505270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (e) Anslyn EV. J Org Chem. 2007;72:687–699. doi: 10.1021/jo0617971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (f) Falconi C, Martinelli E, Di Natale C, D’Amico A, Maloberti F, Malcovati P, Baschirotto A, Stornelli V, Ferri G. Sens Actuator B-Chem. 2007;121:295–329. [Google Scholar]; (g) Röck F, Barsan N, Weimar U. Chem Rev. 2008;108:705–725. doi: 10.1021/cr068121q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (h) Hierlemann A, Gutierrez-Osuna R. Chem Rev. 2008;108:563–613. doi: 10.1021/cr068116m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (i) Janata J, Josowicz M. J Sol St Electrochem. 2009;13:41–49. [Google Scholar]; (j) Walt DR, Aernecke MJ, Guo J, Sonkusale S. Anal Chem. 2009;81:5281–5290. doi: 10.1021/ac900505p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (k) Wilson AD, Baietto M. Sensors. 2009;9:5099–5148. doi: 10.3390/s90705099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (l) Meier DC, Raman B, Semancik S. Annu Rev Anal Chem. 2009;2:463–484. doi: 10.1146/annurev-anchem-060908-155127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (m) Berna A. Sensors. 2010;10:3882–3910. doi: 10.3390/s100403882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (n) Walt DR. Chem Soc Rev. 2010;39:38–50. doi: 10.1039/b809339n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (o) Stich MIJ, Fischer LH, Wolfbeis OS. Chem Soc Rev. 2010;39:3102–3114. doi: 10.1039/b909635n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.(a) Thaler ER, Hanson CW. Expert Rev Med Dev. 2005;2:559–566. doi: 10.1586/17434440.2.5.559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Thaler ER, Hanson CW. Amer J Rhinology. 2006;20:170–172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Anand V, Kataria M, Kukkar V, Saharan V, Choudhury PK. Drug Discovery Today. 2007;12:257. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2007.01.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.(a) Gibson TD, Prosser O, Hulbert JN, Marshall RW, Corcoran P, Lowery P, Ruck-Keene EA, Heron S. Sens Actuators. 1997;B 44:413–422. [Google Scholar]; (b) Rossi V, Talon R, Berdague JL. J Microbiol Methods. 1995;24:183–190. [Google Scholar]; (c) Dutta R, Morgan D, Baker N, Gardner JW, Hines EL. Sens Actuators. 2005;B 109:355–362. [Google Scholar]; (d) Karasinski J, Andreescu S, Sadik OA, Lavine B, Vora MN. Anal Chem. 2005;77:7941–7949. doi: 10.1021/ac0512150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (e) Moens M, Smet A, Naudts B, Verhoeven J, Ieven M, Jorens P, Geise HJ, Blockhuys F. Lett Appl Microbiol. 2006;42:121–126. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-765X.2005.01822.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (f) Setkus A, Kancleris Z, Olekas A, Rimdeika R, Senulien D, Strazdien Z. Sens Actuator B-Chem. 2008;130:351–358. [Google Scholar]; (g) Thaler ER, Huang D, Giebeig L, Palmer J, Lee D, Hanson CW, Cohen N. Amer J Rhinol. 2008;22:29–33. doi: 10.2500/ajr.2008.22.3126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.(a) Dutta R. Sens Actuators B-Chem. 2006;120:156–165. [Google Scholar]; (b) McEntegart CM, Penrose WR, Strathmann S, Stetter JR. Sens Actuators B-Chem. 2000;70:170–176. [Google Scholar]; (c) Holmberg M, Gustafsson F, Hornsten EG, Winquist F, Nilsson LE, Ljung L, Lundstrom I. Biotechnol Tech. 1998;12:319–324. [Google Scholar]; (d) Gardner JW, Craven M, Dow C, Hines EL. Meas Sci Technol. 1998;9:120–127. [Google Scholar]
- 17.(a) Görke B, Stülke J. Nature Rev Microbiol. 2008;6:613–624. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro1932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Narang A, Pilyugin SS. J Theor Biol. 2007;244:326–48. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2006.08.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Mahadevan R, Edwards JS, Doyle FJ., III Biophys J. 2002;83:1331–1340. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(02)73903-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (d) Chang DE, Smalley DJ, Conway T. Mol Microbiol. 2002;45:289–306. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2002.03001.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Veit A, Polen T, Wendisch VF. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2007;74:406–421. doi: 10.1007/s00253-006-0680-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Thomas AD, Doelle HW, Westwood AW, Gordon GL. J Bacteriol. 1972;112:1099–1105. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.3.1099-1105.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.(a) Hasswell S. Practical Guide To Chemometrics. Dekker; New York: 1992. [Google Scholar]; (b) Scott SM, James D, Ali Z. Microchim Acta. 2007;156:183. [Google Scholar]; (c) Johnson RA, Wichern DW. Applied Multivariate Statistical Analysis. 6. Prentice Hall; New Jersey: 2007. [Google Scholar]; (d) Hair JF, Black B, Babin B, Anderson RE, Tatham RL. Multivariate Data Analysis. 6. Prentice Hall; New Jersey: 2005. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Liu J. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2004;43:7815–7825. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Thaler ER, Lee DD, Hanson CW. J Breath Res. 2008;2:37016-1–4. doi: 10.1088/1752-7155/2/3/037016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Mazzone PJ. J Thorac Oncol. 2008;3:774–80. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e31817c7439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
1_si_001