Experimental Models of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases (original) (raw)
Abstract
The understanding of the intestinal inflammation occurring in the inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) has been immeasurably advanced by the development of the now numerous murine models of intestinal inflammation. The usefulness of this research tool in IBD studies has been enabled by our improved knowledge of mucosal immunity and thus our improved ability to interpret the complex responses of mice with various causes of colitis; in addition, it has been powered by the availability of models in which the mice have specific genetic and/or immunologic defects that can be related to the origin of the inflammation. Finally, and more recently, it has been enhanced by our newly acquired ability to define the intestinal microbiome under various conditions and thus to understand how intestinal microorganisms impact on inflammation. In this brief review of murine models of intestinal inflammation, we focus mainly on the most often used models that are, not incidentally, also the models that have yielded major insights into IBD pathogenesis.
Keywords: Cell Transfer Colitis, DSS Colitis, IL10 Deficiency, Murine Colitis Models, NKT Cells, Oxazolone Colitis, TNBS Colitis, TH1 Cells, TH17 Cells, Tregs
Abbreviations used in this paper: bp, binding-protein; DSS, dextran sulfate sodium; Foxp3, forkhead box P3; IBD, inflammatory bowel disease; IFN-γ, interferon-γ; IL, interleukin; LAP, latency-associated protein; NKT, natural killer T; PSA, polysaccharide A; PTEN, phosphatase and tensin homolog on chromosome 10; TGF-β, transforming growth factor-β; TH, T helper cell; TLR, Toll-like receptor; TNBS, 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α; Treg, regulatory T cell
Summary.
Experimental models of inflammatory bowel diseases have provided valuable insights into the complex mechanisms operative in the development and pathogenesis of these diseases. This review describes widely used models and how they help us understand the immunology of intestinal inflammation.
For more than two decades, animal models of intestinal inflammation have provided a wealth of information about mucosal immunology, particularly as the latter relates to the maintenance of intestinal homeostasis or the disruption of such homeostasis and the intestinal inflammation encountered in the inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD). No single model captures the complexity of human IBD, but each model provides valuable insights into one or another major aspect of disease, and together they have led to the establishment of now a generally accepted set of principles of human IBD pathogenesis. Chief among these are that (1) different causes of induced or genetically based inflammation give rise to a finite number of common pathways of immunopathogenesis; (2) normal resident gut microbiota can drive intestinal inflammation; (3) loss of oral tolerance and disruption of the epithelial barrier contribute to the development of intestinal inflammation; and (4) polarized T helper (TH) cell responses as well as defects in innate immunity mediate disease. In this review, we focus on selected experimental models of intestinal inflammation that amply verify these principles and in doing so provide important contributions to our understanding of the immune dysregulation that characterizes IBD. In addition, we provide a brief summary (Table 1) of less common mouse models that are based on genetic defects that lead to increased susceptibility to gut inflammation.
Table 1.
Experimental Models of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Due to Specific Genetic Defects
| Model | Underlying Defect | Major Consequences | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Muc2 | |||
| Colitis147, 148 | Deficiency of Muc2, the main gastrointestinal mucin. | Spontaneous colitis (severe in the distal colon) that is enhanced by DSS administration and develops into colorectal cancer. Inflammation is associated with increases in intestinal lymphocytes, TNF-α, and IL-1β. | Loss of epithelial barrier function resulting from Muc2 deficiency causes inflammation. |
| Related models149, 150 | Lack of C3GnT (β1,3-_N_-acetylglucosaminyltransferase), an enzyme involved in the synthesis of core 3-derived _O_-glycans that are components of colonic mucins.149 | Increased susceptibility to DSS colitis and DSS/AOM-induced tumorigenesis; TH1 and TH7 proinflammatory cytokine production is elevated. | Enhanced intestinal permeability due to deficiency in core 3-derived _O_-glycans and reduced Muc2 levels increases susceptibility to colitis and colorectal cancer. |
| Targeted deletion of core 1-derived _O_-glycans, also components of mucins.150 | Spontaneous colitis (severe in the distal colon and rectum) driven by TNF-α-producing macrophages and granulocytes rather than lymphocytes. Inflammation is independent of TLR signaling. | Core 1-derived _O_-glycans deficiency leading to a reduced inner mucus layer and decreased Muc2 enhances intestinal permeability to both proteins and bacteria and causes inflammation, that is associated with epithelial cell expression of the Tn antigen, observed in some UC patients. | |
| MDR1a colitis151 | Lack of P-gp, the product of the MDR1a gene alters epithelial barrier function. | Spontaneous colitis driven by TH1 cytokines. | A barrier defect arising from P-gp deficiency causes increased intestinal permeability and translocation of bacteria into the lamina propria, and the development of colitis.152, 153 |
| TRUC model122 | Disruption of the transcriptional regulator T-bet in the innate immune system of _RAG2_−/− mice. | Spontaneous colitis driven by intestinal flora and increased production of TNF-α and IL-23. Cohousing of TRUC mice with wild-type mice demonstrate transmission of colitis to a normal host and thus reveal the existence of a “colitogenic” microflora (such as Proteus mirabilis and Klebsiella pneumonia or Helicobacter typhlonius).154 | First and only demonstration of the existence of a colitogenic intestinal microflora. However, treatment of TRUC mice with anti-TNF-α therapy prevents inflammation and bacterial populations from becoming “colitogenic,” indicating that the development of the latter requires an abnormal mucosal immune system. |
| NEMO | |||
| Colitis155 | Intestinal epithelial cell-specific disruption of NF-κB function via targeted deletion of NEMO, an essential regulatory subunit of NF-κB also known as IKK-γ. | Spontaneous and severe chronic intestinal inflammation. | Lack of NF-κB signaling results in heightened TNF-α sensitivity and apoptosis of colonic epithelial cells followed by inflammation caused by translocation of bacteria into the mucosa. Highlights role of TNF-α in maintenance of epithelial cell barrier function. |
| Related model156 | Specific deletion of the catalytic subunit of IKK-β in intestinal epithelial cells. | Severe intestinal inflammation after infection with the gut-dwelling parasite Trichuris muris and reduced expression of TSLP. | IKK-β in intestinal epithelial cells promotes TH2-cell dependent immunity and limits chronic inflammation. |
| SAMP1/Yit mouse157 | The SAMP1/Yit strain was established by selective breading of SAM (senescence accelerated mouse derived from AKR/J mice) P1 strain mice showing spontaneous skin ulcerations. | Spontaneous inflammation of the terminal ileum and caecum driven by a TH1 response; however, a TH2 response may develop at later stages of disease. Exhibit “skip lesions.” Inflammation originates from epithelial barrier defect. | One of the few models exhibiting severe inflammation of the terminal ileum, the primary location of Crohn’s disease lesions. |
| XBP1 model158, 159 | Epithelial cell-specific deletion of the transcription factor, XBP1, an important component of the ER stress response. | Spontaneous enteritis and enhanced susceptibility to DSS colitis. | Induction of ER stress through disruption of XPB1 causes small intestinal inflammation possibly due to absence of Paneth cell antibacterial mediators and reduction of goblet cells. |
| STAT3 | |||
| Colitis160, 161 | Macrophage/neutrophil-specific deficiency of the transcriptional regulator STAT3. | Spontaneous chronic enterocolitis associated with a polarized TH1 response dependent on overproduction of IL-12p40. Defective IL-10 signaling in macrophages. | IL-10 signaling in macrophages and neutrophils is necessary to prevent abnormal regulation of responses to the normal microflora. |
| Related model (IL-22 deficiency)162 | Targeted deletion of STAT3 in intestinal epithelial cells and associated IL-22 deficiency. | Enhanced susceptibility to DSS colitis. | In intestinal epithelial cells, STAT3 activity is critical for mucosal wound healing mediated by IL22 during acute colitis. |
| IL-7 transgenic mice163 | Systemic overexpression of IL-7. | Spontaneous chronic colitis associated with a TH1 response. | IL-7 acts as a critical survival factor for colitogenic CD4+ effector memory T cells.164 Bone marrow is the main source of IL-7 and a substantial population of colitogenic CD4+ memory T cells reside in the bone marrow.165, 166, 167, 168 |
DSS Colitis
Disruption of the intestinal epithelial barrier and thereby the entry of luminal bacteria or bacterial antigens into the mucosa has been clearly established as a disease mechanism in enterocolitis by the fact that intestinal inflammation can be more easily induced or may occur spontaneously in numerous murine models characterized by molecular abnormalities that cause massive barrier loss. The importance of an intact epithelium in the prevention of mucosal inflammation was initially demonstrated by Hermiston and Gordon1 in an influential study published in the 1990s. In this study, a chimeric mouse was created in which small intestinal epithelial cell adhesion mediated by E-cadherin was undermined by the introduction of an epithelial cell transgene expressing dominant negative N-cadherin. The small intestines of these mice contained patches of villi with poorly adherent and incompletely differentiated transgenic enterocytes adjacent to patches of normal enterocytes with normal adherence. The striking finding was that inflammation occurred in the lamina propria of these mice but only in areas subjacent to the defective epithelium, strongly suggesting that entry of commensal microorganisms into an otherwise normal lamina propria can induce an inflammatory response.
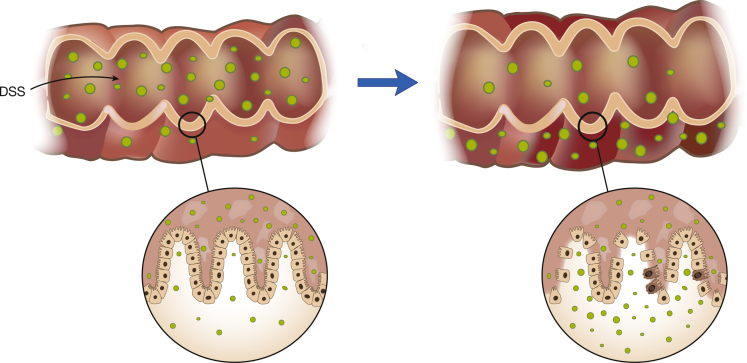
A similar phenomenon occurs in dextran sulfate sodium (DSS) colitis, but in this case a sulfated polysaccharide that is directly toxic to colonic epithelium causes epithelial cell injury and the resulting immune responses alter mucosal barrier function throughout the colonic epithelium (Figure 1). Thus, administration of DSS to mice in their drinking water for a short period of time results in the induction of a very reproducible acute inflammation limited to the colon and characterized by erosions/ulcers, loss of crypts, and infiltration of granulocytes.2, 3 Importantly, this inflammation develops in the absence of T cells mediating adaptive immunity, such as in SCID4 and _Rag1_−/− mice,5 indicating that effector cytokines produced by innate cells are sufficient to cause the inflammation. On this basis, DSS colitis has become a useful model for the study of the innate immune mechanisms involved in the development of intestinal inflammation; indeed, multiple studies have highlighted the critical roles that innate cells such as macrophages and neutrophils play in mucosal inflammation.4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 This has led to the insight that macrophages are important sources of proinflammatory cytokines as well as cytokines that regulate epithelial barrier function and proliferation and that neutrophils are important contributors to tissue damage.
Figure 1.
Mechanism of dextran sulfate sodium (DSS) colitis. DSS colitis is most essentially a colitis due to loss of epithelial barrier function and entry of luminal organisms or their products into the lamina propria. Such entry results in stimulation of innate and adaptive lymphoid elements and secretion of proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines. In addition, it results in the influx of cells with cytotoxic potential such as neutrophils and inflammatory macrophages.
In a related vein, DSS colitis has been used to explore the role of innate immune mechanisms in colitis induction such as those initiated by Toll-like receptors (TLR) and dectin receptors or inflammasome stimulation.6, 7, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16 An important finding here was the discovery that mice with gene deletions affecting TLR signaling such as _Tlr2_−/−, _Tlr4_−/−, and _Myd88_−/− exhibit exacerbation of DSS colitis because the signaling in epithelial cells and macrophages that depends on these innate signaling components promotes epithelial proliferation and epithelial barrier restoration and limits bacterial translocation and inflammation.6, 10, 11 Therefore, the ability of these effectors to promote restoration of epithelial function is even more important to the development of inflammation than their effect on production of effector cytokines. TLR4/MyD88 signaling is also required for neutrophil recruitment to the damaged mucosa, as DSS-treated TLR4/MyD88 knockout mice exhibit a decrease in neutrophil infiltrates due to reduced chemokine expression by macrophages and diminished chemotactic response by neutrophils.6 Furthermore, MyD88 signaling in macrophages has been found to support and promote proliferation and survival of colonic epithelial progenitors thereby facilitating efficient repair responses after DSS injury.7
Because the primary lesion in DSS colitis involves disruption of the epithelium, it lends itself to the study of factors that maintain or reestablish the integrity of the epithelium during or after injury. Many of these studies have centered on the effects of TLR and cytokine stimulation and have shown that factors derived from hematopoietic cells as well as factors derived from the epithelial cells themselves affect integrity. With respect to TLR stimulation, TLR2 ligand administration lessens the severity of DSS colitis whereas TLR2-deficiency enhances severity of DSS colitis. These observations can be explained in part by the effects of TLR2 ligand stimulation of the epithelial cell barrier function or epithelial cell apoptosis and in part by the ability of TLR2 to induce anti-inflammatory interleukin-10 (IL-10) production.11 In addition, activation of epithelial TLR4 can lead to the release of factors that have positive effects on epithelial cell growth and reduce the severity of DSS colitis.17 This model has been used to show that granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and IL-33 released by epithelial cells (and other nonhematopoietic cells) have positive and negative effects on epithelial cell renewal, respectively.18, 19 Yet another focus of studies of epithelial reconstitution in DSS colitis is the role of various intracellular signaling pathways in such reconstitution. An interesting example of the latter type of study is one showing that inhibition of the Wnt pathway by the Wnt antagonist Dkk1 favors epithelial cell renewal during DSS colitis.20
Any discussion of the use of DSS colitis must also mention the series of studies in which this model has been applied to the evaluation of NLRP3 inflammasome responses because this TLR-activated innate immune mechanism results in the secretion of IL-1β and IL-18, two cytokines with potential effects on epithelial cell integrity. However, the outcome of inflammasome responses in DSS colitis has proven to be unexpectedly complex. The reason this might be is that while IL-1β is clearly a key proinflammatory cytokine in DSS colitis,21, 22, 23, 24 the function of IL-18 is somewhat ambiguous. Thus, whereas initial work concluded that IL-18 is required for induction of DSS colitis,21, 25, 26 later work showed that a deficiency in NLRP3 inflammasome activity and production of IL-18 as well as a defect in IL-18 signaling increases susceptibility to DSS colitis.13, 14, 27, 28, 29 In all likelihood, the basis of these findings is that, as noted herein, IL-18 has an important direct or indirect role in epithelial cell restitution and repair after injury.29, 30
The DSS colitis model has also been used extensively to study colon cancer developing in relation to colonic inflammation, such as that occurring in patients with long-standing ulcerative colitis.31, 32, 33 For such study, mice are administered a single dose of azoxymethane, a genotoxic colonic carcinogen that gives rise to colon adenomas or carcinomas but only when such administration is followed by induction of DSS colitis or another type of chronic colitis.34 The mechanism of neoplastic development in this model is not yet completely understood. However, it is likely that a simple initiator-promoter model, with azoxymethane serving as the initiator and the repair after cycles of DSS-induced injury serving as the promoter, is involved. One contributing factor to the development of cancer in this model may be that the neutrophils produce large amounts of IL-1β, which leads to macrophage and dendritic production of IL-6, a cytokine that acts as a tumor promoter.35 IL-18 also comes into the picture here because _IL18_−/− and _Il18r1_−/− mice display increased susceptibility to DSS colitis neoplasia.29 This effect of IL-18 may be channeled through IL-22 and IL-22bp (binding protein), the latter a decoy protein that neutralizes IL-22. This possibility arises from the fact that, on the one hand, the interplay between IL-22 and IL-22bp has been shown to impact epithelial cell growth and repair and thus control tumorigenesis in the colon, and, on the other hand, these factors are regulated by IL-18 and the NLRP3 or NLRP6 inflammasomes.30
Finally, and more recently, DSS colitis has provided a platform for the investigation of the effects of the gut microbiome on colitis development. This is exemplified by studies demonstrating that the NOD2 abnormalities give rise to mice that develop changes in susceptibility to DSS colitis and that the latter is associated with (or perhaps caused by) changes in the gut microbiome.22, 36 In addition, it has been shown that mice deficient in NLRP6, an inflammasome protein produced exclusively in epithelial cells, results in more severe DSS colitis, because NLRP6 inflammasome-induced IL-18 production in the epithelial cell microenvironment controls the growth of Prevotellaceae species within the crypts. Interestingly, such susceptibility to colitis is also manifest in coreared normal mice without NLRP6 abnormalities.15 Similarly, lack of NLRP6 leads to more severe colorectal cancer, a phenotype that is also transmissible through microbiota transfer to wild-type mice.37, 38, 39
Even though DSS colitis is caused primarily by disruption of the epithelium and activation of macrophages and neutrophils the absence of adaptive immunity, it should be noted that T-cell responses can aggravate the inflammatory response when both innate and adaptive immunity are intact. A polarized TH1 response has been observed in acute colitis whereas a mixed TH1/TH2 response was found in a chronic form of DSS colitis, achieved by repeated cycles of DSS administration.8 These T-cell responses result in effector cytokine production that contributes to the high levels of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and IL-6 produced by macrophages in both forms of DSS colitis.
As apparent from this discussion, DSS colitis has been put to good use in the study of many of the attributes of intestinal inflammation. It should not be assumed, however, that this model is an accurate mimic of human IBD, as massive epithelial cell damage and wholesale invasion of the lamina propria by microbes is unlikely to be a primary mechanism of the human disease. This difference between DSS colitis and human IBD is also reflected in the fact that chronic DSS colitis is characterized by a mixed T-cell proinflammatory cytokine response, whereas chronic human IBD is characterized by polarized T-cell responses. Particularly in the study of primary epithelial cell defects as a mechanism of human IBD initiation, DSS colitis must be used with caution as it causes a more widespread and indiscriminate lesion than is likely to occur in human disease.
Trinitrobenzene Sulfonic Acid Colitis
Intrarectal administration of the haptenating agent 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (TNBS) renders colonic proteins immunogenic to the host immune system and thereby initiates an mucosal immune response that drives colitis in susceptible mouse strains.40 Intrarectal TNBS administration to SJL/J or C57BL/10 mice induces a transmural colitis mainly driven by a TH1-mediated immune response and characterized by infiltration of the lamina propria with CD4+ T cells, neutrophils, and macrophages as well as development of severe diarrhea, weight loss, and rectal prolapse.41 As some of these characteristics resemble features of Crohn’s disease, TNBS colitis has been widely used in the study of immunologic aspects relevant to this disease, including cytokine secretion patterns, mechanisms of oral tolerance, and effects of potential immunotherapies.
It is now well established that cytokine responses are key elements that control the inflammatory mechanisms underlying IBD. Indeed, it was noted early on that interferon-γ (IFN-γ) synthesis, in particular, is a characteristic feature of Crohn’s disease that might be responsible for the inflammation observed in this disease.42 Thus, it was highly significant that inflammation in TNBS colitis was associated with elevated levels of IFN-γ and that prevention of IFN-γ production by anti-IL-12p40 treatment completely abrogated both nascent and established disease.41 It was this finding and those derived from subsequent related studies43, 44 that paved the way for the development of a humanized anti-IL-12p40 antibody for treatment of patients with Crohn’s disease that is reported to be highly effective in controlling this disease in phase II and III clinical trials, even in patients who are unresponsive to anti-TNF-α.45, 46
Although IL-12p40-neutralizing antibody was originally intended to block the pathogenic contributions of IL-12, it was later found that the p40 receptor subunit for IL-12 couples with p19 to form the receptor for IL-23, and that the latter is essential to the stability of the TH17 response.47 Several studies were therefore conducted to define the role of IL-23 in experimental colitis and to determine whether IL-12 or IL-23 drives the dominant effector response in these models.48, 49 With respect to TNBS colitis, p19−/− mice, which lack IL-23, were unexpectedly found to develop even more severe colitis than wild-type mice.48 This correlated with the fact that mice with TNBS colitis lacking IL-23 express increased amounts of IL-1248 and that IL-17A production can suppress the induction of T-bet, a major transcriptional regulator of IFN-γ production.50 Thus, in TNBS colitis the TH1 response appears to be the dominant effector response, and the TH17 responses seem to play both effector as well as regulatory roles in the inflammation. As we will discuss, a somewhat different situation may be obtained in other models such as adoptive transfer colitis, where the TH17 responses appear to be dominant although both TH1 and TH17 responses result in cells producing IFN-γ (see the further discussion herein).
In a recent study, TL1a (TNFSF15) was also shown to be involved in the pathogenesis of TNBS colitis, in that treatment of mice with anti-TL1a completely blocked colitis induction.51 Because abrogation of TH1 cytokine responses also blocks colitis induction, this finding implies an underlying relation between TL1a and TH1 responses; however, at the moment, this link is undefined. One possibility based on the fact that TL1a acts as a T-cell costimulation factor is that TL1a costimulation is necessary for the generation of the TH1 response. Another possibility based on TL1a signaling via DR3 (TNFSFR15) and its capacity to induce IL-1β via the NLRP3 inflammasome is that IL-1β production is a necessary antecedent of the TH1 response. Further work will be necessary to decide between these as well as other possibilities.
As alluded to earlier, susceptibility to TNBS colitis and the type of cytokine response that is induced by TNBS administration varies significantly among mouse strains. In BALB/c mice, for instance, TNBS colitis has been associated with TH2-mediated hypertrophy of colonic patches, a phenotype that is accentuated in the absence of IFN-γ.52 A TH2 component was also observed in C57BL/6 mice deficient in IL-12 and IFN-γ.53 Similarly, BALB/c mice are the preferred strain for induction of chronic TNBS colitis, in which repeated administration of low doses of TNBS results in a less intense and more sustained inflammation than obtained in the single, high-dose acute TNBS colitis described in SJL/J mice. This chronic model has shown that cytokine expression patterns are dynamic in that they change as the inflammation evolves. Thus, in this setting inflammation is characterized by sequential responses, with the initial TH1 cell response accompanied by high levels of IL-12 and IFN-γ that is subsequently replaced by a persistent TH17 cell response accompanied by persistent IL-13 and transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) secretion.54 Such evolution may also be characteristic of human IBD, at least in part.
Chronic TNBS colitis in BALB/c mice is also associated with persistent lamina propria fibrosis. This model has therefore been used to study the potential mechanisms underlying the intestinal fibrosis that accompanies human IBD. As shown in the initial report of chronic TNBS colitis, this model is characterized by increased collagen deposition as well as production of factors associated with fibrosis including insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I), tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 (TIMP-1), and TGF-β.55 Subsequent studies explored the mechanism of such fibrosis and provided evidence that TGF-β production induced by IL-13, acting via IL-13Rα2, was an initiator of a fibrotic program that involved early growth response protein 1 (Egr-1), IGF-I, and myofibroblast production of collagen.56 Other studies have provided evidence that fibrosis in this model is induced by substance P acting via the neurokinin-1 receptor57 and can be opposed by the antimicrobial peptide cathelicidin.58 Interestingly, fibrosis in chronic TNBS colitis may also be induced by TL1a, as it has been shown that this factor also induces fibrogenic factors and it is said to have direct collagen-inducing effects on fibroblasts in vitro.59
Despite continued administration of TNBS to BALB/c mice, chronic intestinal inflammation ultimately resolves as does production of proinflammatory IL-17 driving the inflammation. Extensive studies of this resolution of inflammation have determined that persistent IL-13 secretion and accompanying signaling via signal transducer and activator of transcription 6 (STAT6) results in changes in glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK-3β) phosphorylation and that this in turn induces expression of IL-10, a regulatory cytokine. This set of observations suggests that the spontaneous waning of human Crohn’s disease inflammation may also be due to glycogen synthase kinase-3β induction of IL-10.60
Under normal circumstances, when both innate and adaptive immunity are present, T-cell-derived cytokines, particularly IFN-γ, are critical in TNBS colitis as described earlier. Studies in SCID and _Rag1_−/− mice, however, have shown that innate immunity is also involved in the development of TNBS colitis because in response to TNBS these mice develop a colitis that is superficially similar to that observed in their wild-type counterparts.61 In addition, production of enabling cytokines such as IL-12 resulting from stimulation of innate cells by various innate stimuli such as TLR ligands is necessary for the initiation and maintenance of the T-cell responses operative in the inflammation. Indeed, inhibition of innate responses by the NOD2 ligand muramyl dipeptide has been shown to prevent TNBS colitis.62
The TNBS colitis model has also been used to explore mechanisms of mucosal homeostasis and the role of NOD2 in the maintenance of such homeostasis. In part, these studies centered on effects of NOD2 on expansion of regulatory T cell (Treg) in the lamina propria–bearing latency-associated protein (LAP), a molecule that binds to TGF-β. These Treg proliferate in response to the entry of luminal bacteria or their products into the lamina propria and thus quell inflammation.63 Because NOD2 is an intracellular bacterial sensor that recognizes the peptidoglycan constituent muramyl dipeptide,64 it was initially assumed that abnormal Nod2 function would result in uncontrolled invasion of microorganisms into the lamina propria and associated inflammatory responses. On the contrary, NOD2-deficient mice do not develop spontaneous colonic inflammation and are resistant to TNBS colitis. This may reflect increased intestinal permeability to luminal bacteria or their bacterial products and expansion of regulatory LAP+ T cells.65 This interpretation is supported by the observation that adoptive transfer of lamina propria T cells from NOD2-deficient mice to NOD2-deficient recipient mice—but not adoptive transfer of LAP+ T-cell-depleted lamina propria T cells—provided protection from TNBS colitis. Overall, these studies demonstrated that NOD2 deficiency may paradoxically protect an individual from inflammation by maintaining gut homeostasis under conditions in which proinflammatory influences arising form other factors are relatively mild.
It is often forgotten that the TNBS colitis model has contributed to our understanding of the relation of oral tolerance mechanisms and to the concept that intestinal inflammation can result from a loss of immune tolerance. In particular, it was shown early on that oral administration of TNBS-haptenated colonic proteins before intrarectal instillation of TNBS suppressed colitis and that this suppression was dependent on TGF-β-producing regulatory T cells.66 Furthermore, it was shown that the development of such Tregs depended on the production of IL-10, thereby establishing the latter as a key anti-inflammatory cytokine.67 It was also shown that the feeding of TNBS-haptenated colonic proteins “cross-protected” mice from the development of oxazolone colitis (another form of hapten-induced colitis), albeit to a lesser extent than it protected mice from TNBS colitis.68 This protection was associated with cells that exhibited a regulatory phenotype. Overall, these studies were the first to link oral tolerance with the development of antigen independent Tregs that are capable of controlling gut inflammation.
As our discussion of TNBS colitis has indicated, this induced model of colitis, while differing in important ways from human IBD, has served as an important source of information about the cytokines driving human IBD and the way to therapy of the human disease. In addition, it remains a highly useful platform for studying several aspects of human IBD such as the factors guiding its spontaneous resolution and fibrosis.
Oxazolone Colitis
Intrarectal administration of a haptenating agent other than TNBS was initially expected to give rise to a colitis similar to TNBS colitis. It therefore came as a surprise that administration of oxazolone (4-ethoxymethylene-2-phenyl-2-oxazolin-5-one), a haptenating agent that, like TNBS, induces a delayed skin reaction, elicits colonic inflammation that differs markedly from that caused by TNBS and that resembles many features of ulcerative colitis rather than Crohn’s disease.69, 70, 71 In particular, administration of a single dose of oxazolone leads to acute superficial inflammation of the mucosa in the distal colon. This is characterized by infiltration of lymphocytes and neutrophils, lamina propria edema, and ulcerations.69 A similar but longer-lasting colitis can be achieved by subcutaneous sensitization with oxazolone before a single-dose intrarectal challenge.70 As in the case of TNBS colitis, oxazolone colitis is most easily elicited in SJL/J or C57BL/10 mice whereas C57BL/6 mice are more resistant to this colitis. Chronic colitis can also be induced in BALB/c mice by weekly administration of low oxazolone doses.
The cellular and cytokine responses underlying oxazolone colitis differ markedly from those in TNBS colitis. Oxazolone colitis is characterized by robust IL-13 production originating from lamina propria CD4+ natural killer T (NKT) cells rather than by conventional CD4+ T cells producing IFN-γ (Figure 2). Importantly, both IL-13 and NKT cells are involved in oxazolone colitis, as IL-13 blockade by an IL-13Rα2-Fc fusion protein prevented colitis, and oxazolone failed to induce colitis in NKT cell-deficient mice.70 These observations may be explained by data showing that NKT cells are cytotoxic to epithelial cells bearing NKT cell targets and this cytotoxicity can be augmented by IL-13.72 In contrast, IL-13 reduced epithelial barrier function by increasing epithelial cell apoptosis as well as tight junction permeability via claudin-2 and tricellulin.73, 74, 75, 76, 77 This detrimental effect of IL-13 on epithelial barrier function is abetted by IL-9, another TH2-like cytokine shown to be produced during oxazolone colitis.78
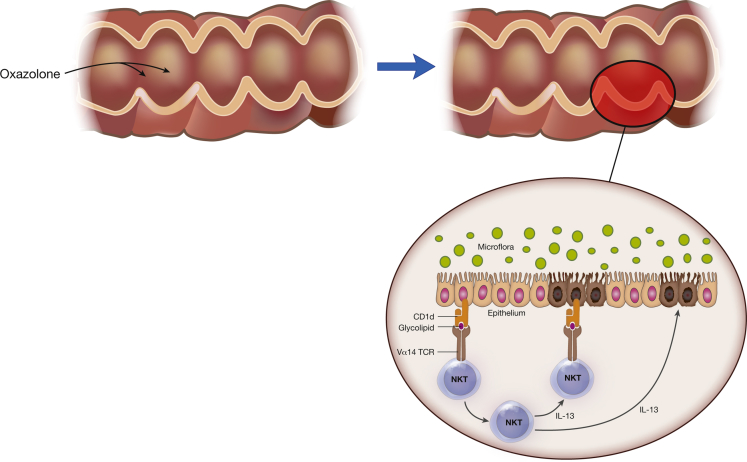
Figure 2.
Mechanism of oxazolone colitis. Oxazolone colitis is driven by natural killer T (NKT) cells that originate in the cytokine milieu of epithelial cells subjected to damage by oxazolone as well as hematopoietic cells in the lamina propria. As shown in the figure, the NKT cells are activated by glycolipids presented to them in the context of CD1 and then mediate toxicity via their direct cytotoxic activity directed at target epithelial cells bearing glycolipid antigen. Alternatively, the NKT cells mediate tissue damage via their production of interleukin-13, a cytokine that has been shown to affect tight junction proteins and to thereby affect epithelial barrier function.
The origin of the IL-13 response in oxazolone colitis is as yet poorly understood although there is some evidence that it is induced by IL-33 originating from damaged epithelial cells.79 IL-25 produced by epithelial cells may also contribute.79 Alternatively, IL-9 may be produced as a result of T-cell stimulation by IL-13 and TGF-β, both of which are abundant in oxazolone colitis.
The importance and value of the oxazolone colitis model is that it resembles human ulcerative colitis not only with respect to morphology but also with respect to immunopathogenesis. Ulcerative colitis is characterized by increased production of IL-13 and IL-9 and has a lamina propria infiltrate containing NKT cells capable of producing IL-13.72, 78 One important difference between oxazolone colitis and ulcerative colitis, however, is that in the latter inflammation the NKT cells are so-called type II NKT cells, which do not have the invariant T-cell receptors characteristic of the more familiar type I NKT cells. It has been shown that the type II NKT cells in ulcerative colitis recognize and respond to sulfatide glycolipids.80 This suggests that ulcerative colitis may be driven by the epithelial-cell release of a sulfatide glycolipid that induces NKT cells and IL-13.
Adoptive Transfer Colitis
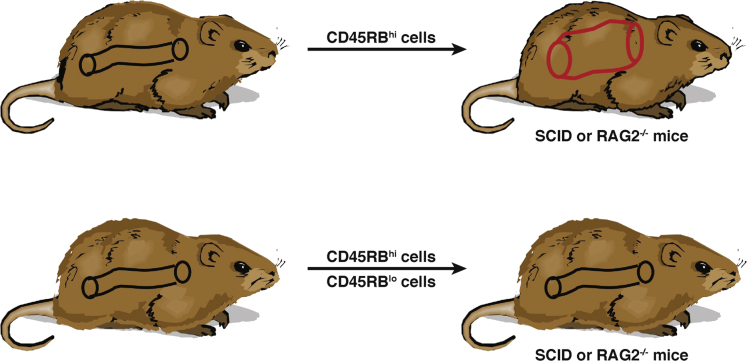
A major step forward in the development of murine models of intestinal inflammation came with the discovery that adoptive transfer of naïve CD4+ T cells (CD4+CD45RBhigh T cells) from donor mice into syngeneic immunodeficient (lymphopenic) SCID or _Rag1_−/− recipient mice causes a wasting disease and a primarily colonic inflammation that develops 5 to 10 weeks after treatment. In contrast, transfer of mature CD4+CD45RBlow T cells or cotransfer of both naïve and mature T cells into the recipient mice did not cause colitis81, 82, 83, 84 (Figure 3). This initially curious and unexplained finding was then shown to be due to the fact that the mature T-cell population contains Treg cells that expand and suppress inflammation whereas the naïve T-cell population lacks such cells. These Treg cells were first characterized as CD4+CD25+ T cells in studies showing that transfer of CD4+CD45RBlow T cells depleted of CD4+CD25+ cells into recipient mice induced disease.83 More recently, however, similar studies have shown that the regulatory cells are the now familiar forkhead box P3+ (Foxp3+) Treg cells. Given the crucial role of Treg cells in this model of colitis and the importance of understanding the mechanisms that control intestinal immune homeostasis, the cell transfer model has positioned itself as one of the most widely used models of experimental colitis.
Figure 3.
The cell transfer colitis model. Cell transfer colitis is initiated in lymphopenic (SCID or Rag−/−) mice that are the recipients of naïve CD45RBhigh T cells, a cell population that cannot be induced to generate regulatory T cells in a timely fashion to prevent the expansion of effector T cells that mediate inflammation. However, if the naïve T cells are transferred in the company of mature CD45RBlow T cells that already contain regulatory T cells, the latter prevent the development of inflammation. This model thus provides a way of isolating the function of effector cells and regulatory cells.
It is now widely accepted that Foxp3+ Treg cells exert their suppressive function and antagonize effector T cells in the gut through multiple mechanisms, including the production of the cytokines IL-10, TGF-β, and IL-35.85, 86 Early studies highlighted an immunoregulatory role of IL-10 by showing that administration of anti-IL-10 receptor antibodies or transfer of CD4+ T cells deficient in IL-10 to _Rag1_−/− hosts resulted in severe colitis.87, 88 Later studies probing the mechanism of IL-10 regulatory activity in the transfer colitis model showed that Foxp3+ cells deficient in the IL-10 receptor subunit β (IL-10Rβ) failed to protect recipient mice from colitis and lost their ability to express Foxp3, suggesting that IL-10R signaling in regulatory cells is important for the maintenance of their function.89
The role of IL-10 in regulatory T-cell function does not exclude a role for TGF-β. The latter was demonstrated by studies showing that protection from colitis by Treg cells did not occur when TGF-β-deficient CD4+CD25+ T cells were cotransferred into recipient mice and by the observation that systemic administration of anti-TGF-β antibody blocked the ability of CD4+CD25+ T cells to attenuate colitis.90, 91 In addition, TGF-β expressed on the surface of CD4+CD25+ T cells in association with LAP mediated CD4+CD25+ T-cell suppression in vitro and CD4+LAP+, but not CD4+LAP−, T cells protected recipient mice from colitis.92 Finally, and perhaps most importantly, naïve T cells made unresponsive to TGF-β via expression of a dominant negative TGF-β receptor type II could not be suppressed by Treg cells.93
Although extensively studied, the precise nature of the inflammatory response that regulatory cells suppress in the transfer colitis model has, at least until recently, been challenging to define. The area of controversy concerned the relative importance of the contributions of the TH1 and TH17 effector T-cell responses to the colonic inflammation. The earliest studies considered transfer colitis to be a TH1-mediated model, as it resulted in the development of a large population of T cells producing IFN-γ and TNF-α in the lamina propria of recipient mice.82 In addition, anti-IFN-γ treatment of the transferred mice ameliorated colitis,82 and transfer of naïve T cells lacking T-bet, which are unable to produce IFN-γ, failed to induce colitis.94
The discovery of the fact that T cells can differentiate into TH17 cells under the influence of IL-23 raised the possibility that IL-17 (IL-17A and IL-17F) and other cytokines also associated with the TH17 differentiation pathway such as IL-23, IL-21, and IL-22 might be the main players driving inflammation in transfer colitis rather than IFN-γ. Evidence supporting this possibility quickly became available and included studies showing that (1) _Rag1_−/− recipient mice also deficient in IL-23p19 did not develop colitis upon transfer of naïve T cells;49 (2) colitis was not induced by transfer of naïve T cells lacking the IL-23 receptor;95 (3) transfer of IL-17A-producing (previously polarized TH17) antigen-specific T cells into SCID mice caused severe colitis that could be prevented by an anti-IL-23p19 antibody;96 and (4) naïve T cells deficient in RORγt, the master regulator of TH17 cells, failed to induce colitis in lymphopenic hosts whereas systemic administration of recombinant IL-17A restored susceptibility to colitis.97 These rather convincing studies establishing the TH17 response as the major effector pathway in transfer colitis ran up against the fact that the number of T cells producing IFN-γ is far greater than those producing IL-17 in the lamina propria of mice with transfer colitis.98, 99 Thus, in spite of strong evidence to the contrary, the TH1 response still appeared to be the main effector T-cell response underlying this model of colitis. A similar argument can be made in Crohn’s disease.100
Recent studies have resolved this apparent contradiction by showing that TH17 responses that generate IL-17-producing TH17 cells are inherently plastic and can also give rise to TH1 cells producing IFN-γ. This was initially evident in studies demonstrating the accumulation of an IL-17+IFN-γ+ T-cell subpopulation in transfer colitis.95, 101 More importantly, IL-17F reporter mice were used to show that, in the absence of TGF-β, IL-23 and IL-12 convert TH17 cells into “TH1-like” IFN-γ-producing cells, and that transfer of previously polarized IL-17F+ TH17 cells to _Rag1_−/− mice resulted in the development of colitis accompanied by the progressive disappearance of IL-17+ cells and the appearance of IFN-γ+ cells in the inflamed mucosa.102 Finally, linear transformation from TH17 to apparent TH1 cells via intermediate TH17/TH1 cells was observed in studies using RORγt reporter mice in which the initial population of transferred cells could be unequivocally identified as TH17 cells.101 Overall, then, current data support the view that transfer colitis is in fact largely mediated by TH1 cells producing IFN-γ, but the latter have an atypical origin in that for the most part they originate indirectly from a TH17 differentiation pathway depending initially on IL-23 rather than directly from a TH1 differentiation pathway depending only on IL-12.
As already discussed in relation to TNBS colitis, IL-17 production in transfer colitis can paradoxically suppress inflammation by blocking the development of TH1 cells producing IFN-γ, which has for greater proinflammatory potential. Consistent with this, transfer of naïve T cells from IL-17A KO mice to Rag1 −/− mice induces a more aggressive wasting disease with earlier onset and higher levels of IFN-γ relative to disease following transfer of wild-type naïve T cells.50 These findings were explained by showing that TH1 cells express IL-17 receptors, and that IL-17A signaling through those receptors decreases TH1 differentiation by inhibiting production of T-bet, a key transcriptional regulator of IFN-γ production. Interestingly, this interference between potentially colitogenic TH1 and TH17 cells may be bidirectional. Studies using parabiotic mice in whom TH1 and TH17 colitis was induced separately, before surgery and effector cells mixing, showed that colitogenic responses mediated by TH1 cells or TH17 cells are in competition and down-modulate one other.98
The TH17 T-cell differentiation pathway—or, more specifically, a major component of this pathway, IL-23—has also be shown to negatively influence regulatory T-cell responses. In initial studies supporting this idea, it was demonstrated that IL-23p19-deficient mice exhibit an increased number of Treg cells in the colon;103 in addition, transfer of naïve T cells to _Rag1_−/− mice deficient in IL-23p19, which might be expected to not induce colitis because of lack of IL-17, does in fact induce colitis in situations where recipient mice could not mount a regulatory T-cell response due to lack of IL-10, TGF-β, or CD4+Foxp3+ T cells.103 Finally, and most convincingly, the numbers of Foxp3+ Treg cells in the colon of _Rag1_−/− recipient mice reconstituted with IL-23 receptor-deficient T cells are increased.95 Taken together, these findings demonstrate rather unequivocally that IL-23 production favors the development of inflammation by mediating TH17 effector cell responses and by inhibiting Foxp3+ regulatory T-cell differentiation.
Recent studies have provided data supporting the idea that the described negative effect of IL-23 on regulatory T-cell development is not unopposed. In particular, IL-33, a cytokine constitutively expressed by epithelial cells in response to tissue damage, enhances regulatory T-cell stability and function in transfer colitis.104 Moreover, Treg cells that lack the IL-33 receptor (ST2) lost their Foxp3 expression over time and were unable to protect mice from adoptive transfer colitis.104 Consistent with previous observations establishing an important role for the transcription factor GATA-3 in regulatory T-cell function,105, 106 it was shown that ST2-expression in Tregs was largely dependent on GATA-3.104 Overall, then, Treg activity in transfer colitis is under the yin of IL-23 and the yang of IL-33, which operate in opposing fashions to regulate inflammation. A similar regime may govern Crohn’s disease because IL-33 has also been found in inflamed tissues of IBD patients.107, 108, 109, 110, 111
Whereas the main effect of IL-23 in relation to the induction of TH17 T-cell differentiation is to stabilize and ensure the survival of IL-17 cells initially induced by TGF-β and IL-6 or IL-1β,112, 113, 114 this cytokine may also have other effects that influence inflammation in transfer colitis. Along these lines, there is some evidence that IL-23 induces IL-17-producing cells with more proinflammatory potential (such as TH17 cells) that do not coproduce IL-10.114, 115, 116 In addition, there is emerging evidence that transfer colitis, presumably as a result of IL-23 production, is accompanied by increased granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor117 and IL-5 production (personal communication from F. Powrie), both cytokines that can profoundly affect the nature of the inflammatory infiltrate in transfer colitis.
Finally, it is important to mention that although it is primarily linked to TH17 T-cell development, IL-23 induces innate lymphoid cells, a recently discovered population shown to express IL-17, IL-22, and IFN-γ and to mediate intestinal inflammation in models of innate colitis, particularly when they produce IFN-γ.118 There is also some evidence that small numbers of these cells accumulate in the inflamed mucosa of Crohn’s disease patients, and it has been postulated that these cells play a role in the initiation of Crohn’s disease.119
As in most other colitis models,120, 121, 122, 123 adoptive transfer colitis does not develop in germ-free mice.124 This important fact suggests that, as in DSS colitis, transfer colitis is marked by a change in epithelial barrier function and that it is the entry of either commensal bacteria or bacterial components into the lamina propria that then drives the inflammation. However, there is no evidence that a particular subset of bacterial organisms serve as colitogenic organisms in transfer colitis (or indeed in human IBD); instead, it is likely that a large and diverse subset of organisms with particular ability to penetrate an impaired epithelial layer act together to induce inflammation.125 It should also be noted that commensal bacteria are thought to contribute to intestinal immune homeostasis and confer protection from the development of inflammation. This is nicely demonstrated by the fact that transfer colitis conducted in immunodeficient mice colonized with Helicobacter hepaticus results in a severe colitis that is abrogated by co-colonization with Bacteroides fragilis.126 The observed protective activity of B. fragilis requires the molecule polysaccharide A (PSA); co-colonization with a mutant B. fragilis lacking PSA failed to ameliorate colitis whereas oral administration of PSA reduced the disease. Colonization of mice with B. fragilis was later shown to facilitate Treg differentiation and IL-10 production.127 Other commensal bacteria from clusters IV and XIVa of the Clostridium genus have also been shown to induce accumulation of Treg in the colon and confer resistance to colitis in mice.128 There is some evidence that this occurs via bacterial secretion of short-chain fatty acids that induce epigenetic changes favoring Foxp3+ T-cell development.129
This overview of the cell transfer model reminds us of the extraordinary contributions of this model to the study of intestinal inflammation. In particular, it has been used with great effect to define the role of regulatory cells in such inflammation and to thus establish the fact that mucosal homeostasis depends on a balance between mucosal proinflammatory effector function and anti-inflammatory regulatory function. This said, it cannot be assumed that a model that depends on cell expansion in a lymphopenic host mimics human IBD. Further, it is yet to be proven that a qualitative or quantitative defect in regulatory cell development is present in IBD patients and is a contributor to disease pathogenesis.130
Interleukin-10 Knockout Mice
One of the earliest models of intestinal inflammation was that identified in mice with IL-10 deficiency.131 This model continues to have great value given the important anti-inflammatory function of this cytokine, already discussed in relation to other experimental models of colitis. In addition, it is now known that genetic polymorphisms at the IL-10 locus confer increased risk of both ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease132, 133 and, perhaps more importantly a familial form of early onset Crohn’s disease has been identified that is due to homozygous mutations in subunits of the IL-10 receptor: IL10RA and IL10RB.134
Mice with targeted deletion of IL-10 (_Il10_−/−) develop spontaneous inflammation of the colon characterized by the presence of an inflammatory infiltrate made up of lymphocytes, macrophages, and neutrophils.131 The inflammation is initially driven by a proinflammatory TH1 T-cell response and as such is ameliorated by systemic administration of anti-IL-12p40, and to a lesser extent anti-IFN-γ.135 However, for as yet unexplained reasons, the production of IL-12 and IFN-γ decreases over time and is to some extent superseded by progressive increases in the production of the TH2 cytokines IL-4 and IL-13.136 _Blimp1_−/− and _Il10rb_−/− mice, which also have a defect in IL-10 production or responsiveness, recapitulate the phenotype of _Il10_−/− mice and thus support the presumption that lack of IL-10 production is directly responsible for the intestinal inflammation in such mice.137, 138 In addition, deletion of IL-10 in all T cells or specifically in Foxp3+ Treg cells also results in spontaneous colitis, indicating that IL-10 derived from these cells is important to the maintenance of gut homeostasis.139, 140
Stimulation of the mucosal immune system by commensal microflora is critical for the development of colitis in IL-10-deficient mice, as the latter do not develop colitis in a germ-free environment but do develop colitis several weeks after transfer from a germ-free environment to a pathogen-free environment. Such stimulation is most likely dependent on the sensing of commensal microbes by Toll-like receptors, as MyD88 deficiency in colonic mononuclear phagocytes completely prevents colitis.121, 141, 142 It should be noted, however, that onset of inflammation in IL-10-deficient mice can be initiated by administration of piroxicam, an nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug that induces oxidative stress.143 The mechanism of this effect is unknown, but it could be associated with activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome, which is sensitive to such stress.
A related observation is that mice lacking both IL-10 and PTEN (phosphatase and tensin homolog on chromosome 10), a phosphatase that regulates cell proliferation and receptivity to TLR stimulation, develop colitis more rapidly and with greater severity than _IL-10_−/− mice and also form colonic tumors.144 This greater susceptibility to colitis is reversed in mice lacking the ability to respond to TLR4 stimulation, indicating that the lack of PTEN is operating, at least in part, by increasing responsiveness to TLR stimulation. An interesting additional observation is that PTEN/IL-10 deficient mice have a fecal microbiome that contains increased amounts of Bacteroides organisms. suggesting that the lack of PTEN may also influence disease pathogeneses via effects on the microbiome.
The finding that TLR ligand stimulation is critical for induction of colitis in IL-10-deficient mice suggests that macrophage dysfunction associated with the absence of IL-10 is a major cause of inflammation in such mice. This possibility is supported by a recent study showing that failure of intestinal resident macrophages to respond to IL-10 (because of lack of IL-10 receptor expression) led to the development of a proinflammatory macrophage migratory profile essential for the development of spontaneous colitis.145 In addition, a related report showed that IL-10 sensing by anti-inflammatory macrophages was important for their ability to establish mucosal homeostasis.146 Finally, monocyte-derived macrophages from early onset Crohn’s disease patients harboring loss of function mutations in IL10RA and IL10RB also exhibit impaired differentiation and function.146 However, these studies should not be interpreted to indicate that macrophage dysfunction is the only abnormality accounting for inflammation in IL-10 deficiency, as Treg cells also depend on IL-10 and thus Treg cell dysfunction likely plays an important role.
Conclusions
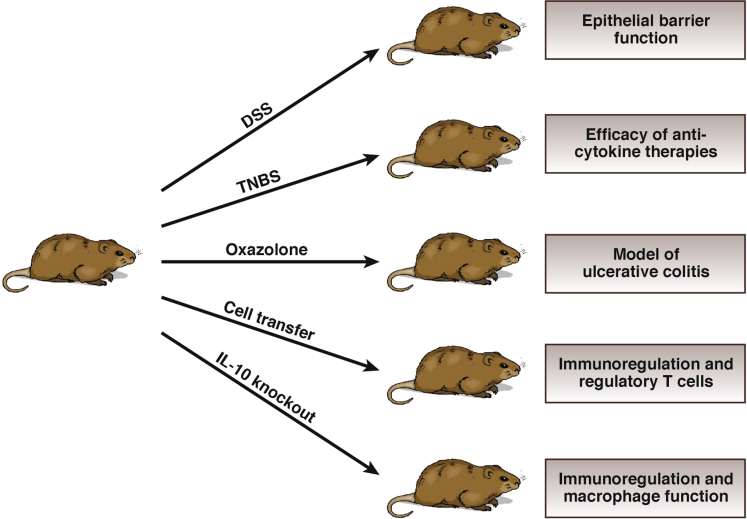
The five models of intestinal inflammation we have discussed (Figure 4) provide a survey of the extensive and sometimes complex mechanisms operative in the genesis of intestinal inflammation and pathogenesis of IBD. Table 1 briefly describes a number of additional models; at our present level of understanding, these models usually focus on particular rather than general abnormalities and mechanisms of gut inflammation. Finally, it is worth noting that even though the study of models of inflammation is no longer in its infancy, an enormous body of knowledge has yet to be harvested from the application of this biologic methodology.
Figure 4.
The five experimental models of inflammation discussed in the text are grouped here in relation to their varying inducing conditions. To the right of the individual mouse models are the major mucosal immune functions/therapies/diseases that are best addressed using these respective models.
Footnotes
Conflicts of interest The authors disclose no conflicts.
Funding This work was supported in part by the Intramural Research Program of the National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases.
References
- 1.Hermiston M.L., Gordon J.I. Inflammatory bowel disease and adenomas in mice expressing a dominant negative N-cadherin. Science. 1995;270:1203–1207. doi: 10.1126/science.270.5239.1203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Okayasu I., Hatakeyama S., Yamada M. A novel method in the induction of reliable experimental acute and chronic ulcerative colitis in mice. Gastroenterology. 1990;98:694–702. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(90)90290-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Cooper H.S., Murthy S.N., Shah R.S., Sedergran D.J. Clinicopathologic study of dextran sulfate sodium experimental murine colitis. Lab Invest. 1993;69:238–249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Dieleman L.A., Ridwan B.U., Tennyson G.S. Dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis occurs in severe combined immunodeficient mice. Gastroenterology. 1994;107:1643–1652. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(94)90803-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Krieglstein C.F., Cerwinka W.H., Sprague A.G. Collagen-binding integrin α1β1 regulates intestinal inflammation in experimental colitis. J Clin Invest. 2002;110:1773–1782. doi: 10.1172/JCI200215256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Fukata M., Michelsen K.S., Eri R. Toll-like receptor-4 is required for intestinal response to epithelial injury and limiting bacterial translocation in a murine model of acute colitis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2005;288:G1055–G1065. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00328.2004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Pull S.L., Doherty J.M., Mills J.C. Activated macrophages are an adaptive element of the colonic epithelial progenitor niche necessary for regenerative responses to injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005;102:99–104. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0405979102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Dieleman L.A., Palmen M.J., Akol H. Chronic experimental colitis induced by dextran sulphate sodium (DSS) is characterized by TH1 and Th2 cytokines. Clin Exp Immunol. 1998;114:385–391. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.1998.00728.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Chami B., Yeung A.W., van Vreden C. The role of CXCR3 in DSS-induced colitis. PLoS One. 2014;9:e101622. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0101622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Rakoff-Nahoum S., Paglino J., Eslami-Varzaneh F. Recognition of commensal microflora by toll-like receptors is required for intestinal homeostasis. Cell. 2004;118:229–241. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2004.07.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Cario E., Gerken G., Podolsky D.K. Toll-like receptor 2 controls mucosal inflammation by regulating epithelial barrier function. Gastroenterology. 2007;132:1359–1374. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2007.02.056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Iliev I.D., Funari V.A., Taylor K.D. Interactions between commensal fungi and the C-type lectin receptor Dectin-1 influence colitis. Science. 2012;336:1314–1317. doi: 10.1126/science.1221789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Dupaul-Chicoine J., Yeretssian G., Doiron K. Control of intestinal homeostasis, colitis, and colitis-associated colorectal cancer by the inflammatory caspases. Immunity. 2010;32:367–378. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2010.02.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Zaki M.H., Boyd K.L., Vogel P. The NLRP3 inflammasome protects against loss of epithelial integrity and mortality during experimental colitis. Immunity. 2010;32:379–391. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2010.03.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Elinav E., Strowig T., Kau A.L. NLRP6 inflammasome regulates colonic microbial ecology and risk for colitis. Cell. 2011;145:745–757. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.04.022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Sokol H., Conway K.L., Zhang M. Card9 mediates intestinal epithelial cell restitution, T-helper 17 responses, and control of bacterial infection in mice. Gastroenterology. 2013;145:591–601.e3. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2013.05.047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Hsu D., Fukata M., Hernandez Y.G. Toll-like receptor 4 differentially regulates epidermal growth factor-related growth factors in response to intestinal mucosal injury. Lab Invest. 2010;90:1295–1305. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2010.100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Egea L., McAllister C.S., Lakhdari O. GM-CSF produced by nonhematopoietic cells is required for early epithelial cell proliferation and repair of injured colonic mucosa. J Immunol. 2013;190:1702–1713. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1202368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Sedhom M.A., Pichery M., Murdoch J.R. Neutralisation of the interleukin-33/ST2 pathway ameliorates experimental colitis through enhancement of mucosal healing in mice. Gut. 2013;62:1714–1723. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2011-301785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Koch S., Nava P., Addis C. The Wnt antagonist Dkk1 regulates intestinal epithelial homeostasis and wound repair. Gastroenterology. 2011;141:259–268.e1–8. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2011.03.043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Siegmund B., Lehr H.A., Fantuzzi G., Dinarello C.A. IL-1 beta-converting enzyme (caspase-1) in intestinal inflammation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2001;98:13249–13254. doi: 10.1073/pnas.231473998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Maeda S., Hsu L.C., Liu H. Nod2 mutation in Crohn’s disease potentiates NF-κB activity and IL-1β processing. Science. 2005;307:734–738. doi: 10.1126/science.1103685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Saitoh T., Fujita N., Jang M.H. Loss of the autophagy protein Atg16L1 enhances endotoxin-induced IL-1β production. Nature. 2008;456:264–268. doi: 10.1038/nature07383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Bersudsky M., Luski L., Fishman D. Non-redundant properties of IL-1α and IL-1β during acute colon inflammation in mice. Gut. 2014;63:598–609. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2012-303329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Siegmund B., Fantuzzi G., Rieder F. Neutralization of interleukin-18 reduces severity in murine colitis and intestinal IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha production. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2001;281:R1264–R1273. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.2001.281.4.R1264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Sivakumar P.V., Westrich G.M., Kanaly S. Interleukin 18 is a primary mediator of the inflammation associated with dextran sulphate sodium induced colitis: blocking interleukin 18 attenuates intestinal damage. Gut. 2002;50:812–820. doi: 10.1136/gut.50.6.812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Takagi H., Kanai T., Okazawa A. Contrasting action of IL-12 and IL-18 in the development of dextran sodium sulphate colitis in mice. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2003;38:837–844. doi: 10.1080/00365520310004047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Reuter B.K., Pizarro T.T. Commentary: the role of the IL-18 system and other members of the IL-1R/TLR superfamily in innate mucosal immunity and the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease: friend or foe? Eur J Immunol. 2004;34:2347–2355. doi: 10.1002/eji.200425351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Salcedo R., Worschech A., Cardone M. MyD88-mediated signaling prevents development of adenocarcinomas of the colon: role of interleukin 18. J Exp Med. 2010;207:1625–1636. doi: 10.1084/jem.20100199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Huber S., Gagliani N., Zenewicz L.A. IL-22BP is regulated by the inflammasome and modulates tumorigenesis in the intestine. Nature. 2012;491:259–263. doi: 10.1038/nature11535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Rutter M., Saunders B., Wilkinson K. Severity of inflammation is a risk factor for colorectal neoplasia in ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology. 2004;126:451–459. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2003.11.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Jess T., Loftus E.V., Jr, Velayos F.S. Risk of intestinal cancer in inflammatory bowel disease: a population-based study from olmsted county, Minnesota. Gastroenterology. 2006;130:1039–1046. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2005.12.037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Gupta R.B., Harpaz N., Itzkowitz S. Histologic inflammation is a risk factor for progression to colorectal neoplasia in ulcerative colitis: a cohort study. Gastroenterology. 2007;133:1099–1105. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2007.08.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Tanaka T., Kohno H., Suzuki R. A novel inflammation-related mouse colon carcinogenesis model induced by azoxymethane and dextran sodium sulfate. Cancer Sci. 2003;94:965–973. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2003.tb01386.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Wang Y., Wang K., Han G.C. Neutrophil infiltration favors colitis-associated tumorigenesis by activating the interleukin-1 (IL-1)/IL-6 axis. Mucosal Immunol. 2014;7:1106–1115. doi: 10.1038/mi.2013.126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Natividad J.M., Petit V., Huang X. Commensal and probiotic bacteria influence intestinal barrier function and susceptibility to colitis in Nod1−/−; Nod2−/− mice. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2012;18:1434–1446. doi: 10.1002/ibd.22848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Chen G.Y., Liu M., Wang F. A functional role for Nlrp6 in intestinal inflammation and tumorigenesis. J Immunol. 2011;186:7187–7194. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1100412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Normand S., Delanoye-Crespin A., Bressenot A. Nod-like receptor pyrin domain-containing protein 6 (NLRP6) controls epithelial self-renewal and colorectal carcinogenesis upon injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2011;108:9601–9606. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1100981108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Hu B., Elinav E., Huber S. Microbiota-induced activation of epithelial IL-6 signaling links inflammasome-driven inflammation with transmissible cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013;110:9862–9867. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1307575110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Neurath M., Fuss I., Strober W. TNBS-colitis. Int Rev Immunol. 2000;19:51–62. doi: 10.3109/08830180009048389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Neurath M.F., Fuss I., Kelsall B.L. Antibodies to interleukin 12 abrogate established experimental colitis in mice. J Exp Med. 1995;182:1281–1290. doi: 10.1084/jem.182.5.1281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Strober W., Fuss I.J. Proinflammatory cytokines in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel diseases. Gastroenterology. 2011;140:1756–1767. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2011.02.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Davidson N.J., Hudak S.A., Lesley R.E. IL-12, but not IFN-gamma, plays a major role in sustaining the chronic phase of colitis in IL-10-deficient mice. J Immunol. 1998;161:3143–3149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Simpson S.J., Shah S., Comiskey M. T cell-mediated pathology in two models of experimental colitis depends predominantly on the interleukin 12/Signal transducer and activator of transcription (Stat)-4 pathway, but is not conditional on interferon gamma expression by T cells. J Exp Med. 1998;187:1225–1234. doi: 10.1084/jem.187.8.1225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Mannon P.J., Fuss I.J., Mayer L., Anti ILCsDSG Anti-interleukin-12 antibody for active Crohn’s disease. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:2069–2079. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa033402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Sandborn W.J., Feagan B.G., Fedorak R.N. Ustekinumab Crohn’s Disease Study G. A randomized trial of ustekinumab, a human interleukin-12/23 monoclonal antibody, in patients with moderate-to-severe Crohn’s disease. Gastroenterology. 2008;135:1130–1141. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.07.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Oppmann B., Lesley R., Blom B. Novel p19 protein engages IL-12p40 to form a cytokine, IL-23, with biological activities similar as well as distinct from IL-12. Immunity. 2000;13:715–725. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(00)00070-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Becker C., Dornhoff H., Neufert C. Cutting edge: IL-23 cross-regulates IL-12 production in T cell-dependent experimental colitis. J Immunol. 2006;177:2760–2764. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.177.5.2760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Hue S., Ahern P., Buonocore S. Interleukin-23 drives innate and T cell-mediated intestinal inflammation. J Exp Med. 2006;203:2473–2483. doi: 10.1084/jem.20061099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.O’Connor W., Jr, Kamanaka M., Booth C.J. A protective function for interleukin 17A in T cell-mediated intestinal inflammation. Nat Immunol. 2009;10:603–609. doi: 10.1038/ni.1736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Meylan F., Song Y.J., Fuss I. The TNF-family cytokine TL1A drives IL-13-dependent small intestinal inflammation. Mucosal Immunol. 2011;4:172–185. doi: 10.1038/mi.2010.67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Dohi T., Fujihashi K., Rennert P.D. Hapten-induced colitis is associated with colonic patch hypertrophy and T helper cell 2-type responses. J Exp Med. 1999;189:1169–1180. doi: 10.1084/jem.189.8.1169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Dohi T., Fujihashi K., Kiyono H. Mice deficient in Th1- and Th2-type cytokines develop distinct forms of hapten-induced colitis. Gastroenterology. 2000;119:724–733. doi: 10.1053/gast.2000.16500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Fichtner-Feigl S., Fuss I.J., Preiss J.C. Treatment of murine Th1- and Th2-mediated inflammatory bowel disease with NF-kappa B decoy oligonucleotides. J Clin Invest. 2005;115:3057–3071. doi: 10.1172/JCI24792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Lawrance I.C., Wu F., Leite A.Z. A murine model of chronic inflammation-induced intestinal fibrosis down-regulated by antisense NF-kappa B. Gastroenterology. 2003;125:1750–1761. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2003.08.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Fichtner-Feigl S., Young C.A., Kitani A. IL-13 signaling via IL-13R alpha2 induces major downstream fibrogenic factors mediating fibrosis in chronic TNBS colitis. Gastroenterology. 2008;135:2003–2013.e1–7. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.08.055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Koon H.W., Shih D., Karagiannides I. Substance P modulates colitis-associated fibrosis. Am J Pathol. 2010;177:2300–2309. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2010.100314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Yoo J.H., Ho S., Tran D.H.-Y. Antifibrogenic effects of the antimicrobial peptide cathelicidin in murine colitis-associated fibrosis. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015;1:55–74.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2014.08.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Shih D.Q., Zheng L., Zhang X. Inhibition of a novel fibrogenic factor Tl1a reverses established colonic fibrosis. Mucosal Immunol. 2014;7:1492–1503. doi: 10.1038/mi.2014.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Fichtner-Feigl S., Kesselring R., Martin M. IL-13 orchestrates resolution of chronic intestinal inflammation via phosphorylation of glycogen synthase kinase-3β. J Immunol. 2014;192:3969–3980. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1301072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Fiorucci S., Mencarelli A., Palazzetti B. Importance of innate immunity and collagen binding integrin alpha1beta1 in TNBS-induced colitis. Immunity. 2002;17:769–780. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(02)00476-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Watanabe T., Asano N., Meng G. NOD2 downregulates colonic inflammation by IRF4-mediated inhibition of K63-linked polyubiquitination of RICK and TRAF6. Mucosal Immunol. 2014;7:1312–1325. doi: 10.1038/mi.2014.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Boirivant M., Amendola A., Butera A. A transient breach in the epithelial barrier leads to regulatory T-cell generation and resistance to experimental colitis. Gastroenterology. 2008;135:1612–1623.e5. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.07.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Girardin S.E., Boneca I.G., Viala J. Nod2 is a general sensor of peptidoglycan through muramyl dipeptide (MDP) detection. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:8869–8872. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C200651200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Amendola A., Butera A., Sanchez M. Nod2 deficiency is associated with an increased mucosal immunoregulatory response to commensal microorganisms. Mucosal Immunol. 2014;7:391–404. doi: 10.1038/mi.2013.58. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Neurath M.F., Fuss I., Kelsall B.L. Experimental granulomatous colitis in mice is abrogated by induction of TGF-beta-mediated oral tolerance. J Exp Med. 1996;183:2605–2616. doi: 10.1084/jem.183.6.2605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Fuss I.J., Boirivant M., Lacy B., Strober W. The interrelated roles of TGF-beta and IL-10 in the regulation of experimental colitis. J Immunol. 2002;168:900–908. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.168.2.900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Boirivant M., Strober W., Fuss I.J. Regulatory cells induced by feeding TNP-haptenated colonic protein cross-protect mice from colitis induced by an unrelated hapten. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2005;11:48–55. doi: 10.1097/00054725-200501000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Boirivant M., Fuss I.J., Chu A., Strober W. Oxazolone colitis: a murine model of T helper cell type 2 colitis treatable with antibodies to interleukin 4. J Exp Med. 1998;188:1929–1939. doi: 10.1084/jem.188.10.1929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Heller F., Fuss I.J., Nieuwenhuis E.E. Oxazolone colitis, a Th2 colitis model resembling ulcerative colitis, is mediated by IL-13-producing NK-T cells. Immunity. 2002;17:629–638. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(02)00453-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Olszak T., An D., Zeissig S. Microbial exposure during early life has persistent effects on natural killer T cell function. Science. 2012;336:489–493. doi: 10.1126/science.1219328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Fuss I.J., Heller F., Boirivant M. Nonclassical CD1d-restricted NK T cells that produce IL-13 characterize an atypical Th2 response in ulcerative colitis. J Clin Invest. 2004;113:1490–1497. doi: 10.1172/JCI19836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Heller F., Florian P., Bojarski C. Interleukin-13 is the key effector Th2 cytokine in ulcerative colitis that affects epithelial tight junctions, apoptosis, and cell restitution. Gastroenterology. 2005;129:550–564. doi: 10.1016/j.gastro.2005.05.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Dohi T., Borodovsky A., Wu P. TWEAK/Fn14 pathway: a nonredundant role in intestinal damage in mice through a TWEAK/intestinal epithelial cell axis. Gastroenterology. 2009;136:912–923. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.11.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Kawashima R., Kawamura Y.I., Oshio T. Interleukin-13 damages intestinal mucosa via TWEAK and Fn14 in mice-a pathway associated with ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology. 2011;141:2119–2129.e8. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2011.08.040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Krug S.M., Bojarski C., Dames P. Impaired epithelial barrier for macromolecules in ulcerative colitis is caused by downregulation of the tricellular tight junction protein tricellulin, mediated by the interleukin-13 receptor α2-activated pathway. [Abstract 410.] Gasteroenterology. 2014;146(Suppl 1):S88. [Google Scholar]
- 77.Weber C.R., Raleigh D.R., Su L. Epithelial myosin light chain kinase activation induces mucosal interleukin-13 expression to alter tight junction ion selectivity. J Biol Chem. 2010;285:12037–12046. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.064808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Gerlach K., Hwang Y., Nikolaev A. TH9 cells that express the transcription factor PU.1 drive T cell-mediated colitis via IL-9 receptor signaling in intestinal epithelial cells. Nat Immunol. 2014;15:676–686. doi: 10.1038/ni.2920. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Camelo A., Barlow J.L., Drynan L.F. Blocking IL-25 signalling protects against gut inflammation in a type-2 model of colitis by suppressing nuocyte and NKT derived IL-13. J Gastroenterol. 2012;47:1198–1211. doi: 10.1007/s00535-012-0591-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Fuss I.J., Joshi B., Yang Z. IL-13Rα2-bearing, type II NKT cells reactive to sulfatide self-antigen populate the mucosa of ulcerative colitis. Gut. 2014;63:1728–1736. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2013-305671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Powrie F., Leach M.W., Mauze S. Phenotypically distinct subsets of CD4+ T cells induce or protect from chronic intestinal inflammation in C. B-17 scid mice. Int Immunol. 1993;5:1461–1471. doi: 10.1093/intimm/5.11.1461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Powrie F., Leach M.W., Mauze S. Inhibition of Th1 responses prevents inflammatory bowel disease in scid mice reconstituted with CD45RBhi CD4+ T cells. Immunity. 1994;1:553–562. doi: 10.1016/1074-7613(94)90045-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Read S., Malmstrom V., Powrie F. Cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 plays an essential role in the function of CD25+CD4+ regulatory cells that control intestinal inflammation. J Exp Med. 2000;192:295–302. doi: 10.1084/jem.192.2.295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Leach M.W., Bean A.G., Mauze S. Inflammatory bowel disease in C.B-17 scid mice reconstituted with the CD45RBhigh subset of CD4+ T cells. Am J Pathol. 1996;148:1503–1515. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Vignali D.A., Collison L.W., Workman C.J. How regulatory T cells work. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008;8:523–532. doi: 10.1038/nri2343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Shevach E.M. Mechanisms of foxp3+ T regulatory cell-mediated suppression. Immunity. 2009;30:636–645. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2009.04.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Asseman C., Mauze S., Leach M.W. An essential role for interleukin 10 in the function of regulatory T cells that inhibit intestinal inflammation. J Exp Med. 1999;190:995–1004. doi: 10.1084/jem.190.7.995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Davidson N.J., Leach M.W., Fort M.M. T helper cell 1-type CD4+ T cells, but not B cells, mediate colitis in interleukin 10-deficient mice. J Exp Med. 1996;184:241–251. doi: 10.1084/jem.184.1.241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Murai M., Turovskaya O., Kim G. Interleukin 10 acts on regulatory T cells to maintain expression of the transcription factor Foxp3 and suppressive function in mice with colitis. Nat Immunol. 2009;10:1178–1184. doi: 10.1038/ni.1791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Powrie F., Carlino J., Leach M.W. A critical role for transforming growth factor-beta but not interleukin 4 in the suppression of T helper type 1-mediated colitis by CD45RBlow CD4+ T cells. J Exp Med. 1996;183:2669–2674. doi: 10.1084/jem.183.6.2669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Nakamura K., Kitani A., Strober W. Cell contact-dependent immunosuppression by CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells is mediated by cell surface-bound transforming growth factor beta. J Exp Med. 2001;194:629–644. doi: 10.1084/jem.194.5.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Nakamura K., Kitani A., Fuss I. TGF-beta 1 plays an important role in the mechanism of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cell activity in both humans and mice. J Immunol. 2004;172:834–842. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.172.2.834. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Fahlen L., Read S., Gorelik L. T cells that cannot respond to TGF-beta escape control by CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells. J Exp Med. 2005;201:737–746. doi: 10.1084/jem.20040685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Neurath M.F., Weigmann B., Finotto S. The transcription factor T-bet regulates mucosal T cell activation in experimental colitis and Crohn’s disease. J Exp Med. 2002;195:1129–1143. doi: 10.1084/jem.20011956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Ahern P.P., Schiering C., Buonocore S. Interleukin-23 drives intestinal inflammation through direct activity on T cells. Immunity. 2010;33:279–288. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2010.08.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Elson C.O., Cong Y., Weaver C.T. Monoclonal anti-interleukin 23 reverses active colitis in a T cell-mediated model in mice. Gastroenterology. 2007;132:2359–2370. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2007.03.104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Leppkes M., Becker C., Ivanov I.I. RORγ-expressing Th17 cells induce murine chronic intestinal inflammation via redundant effects of IL-17A and IL-17F. Gastroenterology. 2009;136:257–267. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.10.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Mikami Y., Kanai T., Sujino T. Competition between colitogenic Th1 and Th17 cells contributes to the amelioration of colitis. Eur J Immunol. 2010;40:2409–2422. doi: 10.1002/eji.201040379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Griseri T., Asquith M., Thompson C., Powrie F. OX40 is required for regulatory T cell-mediated control of colitis. J Exp Med. 2010;207:699–709. doi: 10.1084/jem.20091618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Sakuraba A., Sato T., Kamada N. Th1/Th17 immune response is induced by mesenteric lymph node dendritic cells in Crohn’s disease. Gastroenterology. 2009;137:1736–1745. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2009.07.049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Sujino T., Kanai T., Ono Y. Regulatory T cells suppress development of colitis, blocking differentiation of T-helper 17 into alternative T-helper 1 cells. Gastroenterology. 2011;141:1014–1023. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2011.05.052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Lee Y.K., Turner H., Maynard C.L. Late developmental plasticity in the T helper 17 lineage. Immunity. 2009;30:92–107. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2008.11.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Izcue A., Hue S., Buonocore S. Interleukin-23 restrains regulatory T cell activity to drive T cell-dependent colitis. Immunity. 2008;28:559–570. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2008.02.019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Schiering C., Krausgruber T., Chomka A. The alarmin IL-33 promotes regulatory T-cell function in the intestine. Nature. 2014;513:564–568. doi: 10.1038/nature13577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Wang Y., Su M.A., Wan Y.Y. An essential role of the transcription factor GATA-3 for the function of regulatory T cells. Immunity. 2011;35:337–348. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2011.08.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Wohlfert E.A., Grainger J.R., Bouladoux N. GATA3 controls Foxp3(+) regulatory T cell fate during inflammation in mice. J Clin Invest. 2011;121:4503–4515. doi: 10.1172/JCI57456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Beltran C.J., Nunez L.E., Diaz-Jimenez D. Characterization of the novel ST2/IL-33 system in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2010;16:1097–1107. doi: 10.1002/ibd.21175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Kobori A., Yagi Y., Imaeda H. Interleukin-33 expression is specifically enhanced in inflamed mucosa of ulcerative colitis. J Gastroenterol. 2010;45:999–1007. doi: 10.1007/s00535-010-0245-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Palmer G., Gabay C. Interleukin-33 biology with potential insights into human diseases. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2011;7:321–329. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2011.53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Pastorelli L., Garg R.R., Hoang S.B. Epithelial-derived IL-33 and its receptor ST2 are dysregulated in ulcerative colitis and in experimental Th1/Th2 driven enteritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107:8017–8022. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0912678107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Seidelin J.B., Bjerrum J.T., Coskun M. IL-33 is upregulated in colonocytes of ulcerative colitis. Immunol Lett. 2010;128:80–85. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2009.11.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Veldhoen M., Hocking R.J., Atkins C.J. TGFβ in the context of an inflammatory cytokine milieu supports de novo differentiation of IL-17-producing T cells. Immunity. 2006;24:179–189. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2006.01.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Zhou L., Ivanov I.I., Spolski R. IL-6 programs TH-17 cell differentiation by promoting sequential engagement of the IL-21 and IL-23 pathways. Nat Immunol. 2007;8:967–974. doi: 10.1038/ni1488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Ghoreschi K., Laurence A., Yang X.P. Generation of pathogenic TH17 cells in the absence of TGF-beta signalling. Nature. 2010;467:967–971. doi: 10.1038/nature09447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.McGeachy M.J., Bak-Jensen K.S., Chen Y. TGF-beta and IL-6 drive the production of IL-17 and IL-10 by T cells and restrain TH-17 cell-mediated pathology. Nat Immunol. 2007;8:1390–1397. doi: 10.1038/ni1539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Lee Y., Awasthi A., Yosef N. Induction and molecular signature of pathogenic TH17 cells. Nat Immunol. 2012;13:991–999. doi: 10.1038/ni.2416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Griseri T., McKenzie B.S., Schiering C., Powrie F. Dysregulated hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell activity promotes interleukin-23-driven chronic intestinal inflammation. Immunity. 2012;37:1116–1129. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2012.08.025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Buonocore S., Ahern P.P., Uhlig H.H. Innate lymphoid cells drive interleukin-23-dependent innate intestinal pathology. Nature. 2010;464:1371–1375. doi: 10.1038/nature08949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Geremia A., Arancibia-Carcamo C.V., Fleming M.P. IL-23-responsive innate lymphoid cells are increased in inflammatory bowel disease. J Exp Med. 2011;208:1127–1133. doi: 10.1084/jem.20101712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Dianda L., Hanby A.M., Wright N.A. T cell receptor-alpha beta-deficient mice fail to develop colitis in the absence of a microbial environment. Am J Pathol. 1997;150:91–97. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Sellon R.K., Tonkonogy S., Schultz M. Resident enteric bacteria are necessary for development of spontaneous colitis and immune system activation in interleukin-10-deficient mice. Infect Immun. 1998;66:5224–5231. doi: 10.1128/iai.66.11.5224-5231.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Garrett W.S., Lord G.M., Punit S. Communicable ulcerative colitis induced by T-bet deficiency in the innate immune system. Cell. 2007;131:33–45. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.08.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Schultz M., Tonkonogy S.L., Sellon R.K. IL-2-deficient mice raised under germfree conditions develop delayed mild focal intestinal inflammation. Am J Physiol. 1999;276:G1461–G1472. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1999.276.6.G1461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Aranda R., Sydora B.C., McAllister P.L. Analysis of intestinal lymphocytes in mouse colitis mediated by transfer of CD4+, CD45RBhigh T cells to SCID recipients. J Immunol. 1997;158:3464–3473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Palm N.W., de Zoete M.R., Cullen T.W. Immunoglobulin A coating identifies colitogenic bacteria in inflammatory bowel disease. Cell. 2014;158:1000–1010. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.08.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Mazmanian S.K., Round J.L., Kasper D.L. A microbial symbiosis factor prevents intestinal inflammatory disease. Nature. 2008;453:620–625. doi: 10.1038/nature07008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Round J.L., Mazmanian S.K. Inducible Foxp3+ regulatory T-cell development by a commensal bacterium of the intestinal microbiota. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107:12204–12209. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0909122107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Atarashi K., Tanoue T., Shima T. Induction of colonic regulatory T cells by indigenous Clostridium species. Science. 2011;331:337–341. doi: 10.1126/science.1198469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Arpaia N., Campbell C., Fan X. Metabolites produced by commensal bacteria promote peripheral regulatory T-cell generation. Nature. 2013;504:451–455. doi: 10.1038/nature12726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Lord J.D., Valliant-Saunders K., Hahn H. Paradoxically increased FOXP3+ T cells in IBD do not preferentially express the isoform of FOXP3 lacking exon 2. Dig Dis Sci. 2012;57:2846–2855. doi: 10.1007/s10620-012-2292-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Kuhn R., Lohler J., Rennick D. Interleukin-10-deficient mice develop chronic enterocolitis. Cell. 1993;75:263–274. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)80068-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Franke A., Balschun T., Karlsen T.H. Sequence variants in IL10, ARPC2 and multiple other loci contribute to ulcerative colitis susceptibility. Nat Genet. 2008;40:1319–1323. doi: 10.1038/ng.221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Franke A., McGovern D.P., Barrett J.C. Genome-wide meta-analysis increases to 71 the number of confirmed Crohn’s disease susceptibility loci. Nat Genet. 2010;42:1118–1125. doi: 10.1038/ng.717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Glocker E.O., Kotlarz D., Boztug K. Inflammatory bowel disease and mutations affecting the interleukin-10 receptor. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:2033–2045. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0907206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Berg D.J., Davidson N., Kuhn R. Enterocolitis and colon cancer in interleukin-10-deficient mice are associated with aberrant cytokine production and CD4+ TH1-like responses. J Clin Invest. 1996;98:1010–1020. doi: 10.1172/JCI118861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Spencer D.M., Veldman G.M., Banerjee S. Distinct inflammatory mechanisms mediate early versus late colitis in mice. Gastroenterology. 2002;122:94–105. doi: 10.1053/gast.2002.30308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Spencer S.D., Di Marco F., Hooley J. The orphan receptor CRF2–4 is an essential subunit of the interleukin 10 receptor. J Exp Med. 1998;187:571–578. doi: 10.1084/jem.187.4.571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Martins G.A., Cimmino L., Shapiro-Shelef M. Transcriptional repressor Blimp-1 regulates T cell homeostasis and function. Nat Immunol. 2006;7:457–465. doi: 10.1038/ni1320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Roers A., Siewe L., Strittmatter E. T cell-specific inactivation of the interleukin 10 gene in mice results in enhanced T cell responses but normal innate responses to lipopolysaccharide or skin irritation. J Exp Med. 2004;200:1289–1297. doi: 10.1084/jem.20041789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Rubtsov Y.P., Rasmussen J.P., Chi E.Y. Regulatory T cell-derived interleukin-10 limits inflammation at environmental interfaces. Immunity. 2008;28:546–558. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2008.02.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Rakoff-Nahoum S., Hao L., Medzhitov R. Role of toll-like receptors in spontaneous commensal-dependent colitis. Immunity. 2006;25:319–329. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2006.06.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Hoshi N., Schenten D., Nish S.A., Walther Z. MyD88 signalling in colonic mononuclear phagocytes drives colitis in IL-10-deficient mice. Nat Commun. 2012;3:1120. doi: 10.1038/ncomms2113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Narushima S., Spitz D.R., Oberley L.W. Evidence for oxidative stress in NSAID-induced colitis in IL10−/− mice. Free Radic Biol Med. 2003;34:1153–1166. doi: 10.1016/s0891-5849(03)00065-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Im E., Jung J., Pothoulakis C., Rhee S.H. Disruption of Pten speeds onset and increases severity of spontaneous colitis in Il10−/− mice. Gastroenterology. 2014;147:667–679.e10. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2014.05.034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Zigmond E., Bernshtein B., Friedlander G. Macrophage-restricted interleukin-10 receptor deficiency, but not IL-10 deficiency, causes severe spontaneous colitis. Immunity. 2014;40:720–733. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2014.03.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Shouval D.S., Biswas A., Goettel J.A. Interleukin-10 receptor signaling in innate immune cells regulates mucosal immune tolerance and anti-inflammatory macrophage function. Immunity. 2014;40:706–719. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2014.03.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Velcich A., Yang W., Heyer J. Colorectal cancer in mice genetically deficient in the mucin Muc2. Science. 2002;295:1726–1729. doi: 10.1126/science.1069094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Van der Sluis M., De Koning B.A. Muc2-deficient mice spontaneously develop colitis, indicating that MUC2 is critical for colonic protection. Gastroenterology. 2006;131:117–129. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2006.04.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.An G., Wei B., Xia B. Increased susceptibility to colitis and colorectal tumors in mice lacking core 3-derived O-glycans. J Exp Med. 2007;204:1417–1429. doi: 10.1084/jem.20061929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Fu J., Wei B., Wen T. Loss of intestinal core 1-derived O-glycans causes spontaneous colitis in mice. J Clin Invest. 2011;121:1657–1666. doi: 10.1172/JCI45538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Panwala C.M., Jones J.C., Viney J.L. A novel model of inflammatory bowel disease: mice deficient for the multiple drug resistance gene, mdr1a, spontaneously develop colitis. J Immunol. 1998;161:5733–5744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Resta-Lenert S., Smitham J., Barrett K.E. Epithelial dysfunction associated with the development of colitis in conventionally housed mdr1a−/− mice. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2005;289:G153–G162. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00395.2004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Collett A., Tanianis-Hughes J., Carlson G.L. Comparison of P-glycoprotein-mediated drug-digoxin interactions in Caco-2 with human and rodent intestine: relevance to in vivo prediction. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2005;26:386–393. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2005.07.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Powell N., Walker A.W., Stolarczyk E. The transcription factor T-bet regulates intestinal inflammation mediated by interleukin-7 receptor+ innate lymphoid cells. Immunity. 2012;37:674–684. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2012.09.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.Nenci A., Becker C., Wullaert A. Epithelial NEMO links innate immunity to chronic intestinal inflammation. Nature. 2007;446:557–561. doi: 10.1038/nature05698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Zaph C., Troy A.E., Taylor B.C. Epithelial-cell-intrinsic IKK-beta expression regulates intestinal immune homeostasis. Nature. 2007;446:552–556. doi: 10.1038/nature05590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Matsumoto S., Okabe Y., Setoyama H. Inflammatory bowel disease-like enteritis and caecitis in a senescence accelerated mouse P1/Yit strain. Gut. 1998;43:71–78. doi: 10.1136/gut.43.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158.Kaser A., Lee A.H., Franke A. XBP1 links ER stress to intestinal inflammation and confers genetic risk for human inflammatory bowel disease. Cell. 2008;134:743–756. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.07.021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159.Adolph T.E., Tomczak M.F., Niederreiter L. Paneth cells as a site of origin for intestinal inflammation. Nature. 2013;503:272–276. doi: 10.1038/nature12599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160.Takeda K., Clausen B.E., Kaisho T. Enhanced Th1 activity and development of chronic enterocolitis in mice devoid of Stat3 in macrophages and neutrophils. Immunity. 1999;10:39–49. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(00)80005-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161.Kobayashi M., Kweon M.N., Kuwata H. Toll-like receptor-dependent production of IL-12p40 causes chronic enterocolitis in myeloid cell-specific Stat3-deficient mice. J Clin Invest. 2003;111:1297–1308. doi: 10.1172/JCI17085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 162.Pickert G., Neufert C., Leppkes M. STAT3 links IL-22 signaling in intestinal epithelial cells to mucosal wound healing. J Exp Med. 2009;206:1465–1472. doi: 10.1084/jem.20082683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 163.Watanabe M., Ueno Y., Yajima T. Interleukin 7 transgenic mice develop chronic colitis with decreased interleukin 7 protein accumulation in the colonic mucosa. J Exp Med. 1998;187:389–402. doi: 10.1084/jem.187.3.389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 164.Totsuka T., Kanai T., Nemoto Y. IL-7 Is essential for the development and the persistence of chronic colitis. J Immunol. 2007;178:4737–4748. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.178.8.4737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 165.Nemoto Y., Kanai T., Makita S. Bone marrow retaining colitogenic CD4+ T cells may be a pathogenic reservoir for chronic colitis. Gastroenterology. 2007;132:176–189. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2006.10.035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 166.Nemoto Y., Kanai T., Kameyama K. Long-lived colitogenic CD4+ memory T cells residing outside the intestine participate in the perpetuation of chronic colitis. J Immunol. 2009;183:5059–5068. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0803684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 167.Nemoto Y., Kanai T., Shinohara T. Luminal CD4+ T cells penetrate gut epithelial monolayers and egress from lamina propria to blood circulation. Gastroenterology. 2011;141:2130–2139.e11. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2011.08.035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 168.Nemoto Y., Kanai T., Takahara M. Bone marrow-mesenchymal stem cells are a major source of interleukin-7 and sustain colitis by forming the niche for colitogenic CD4 memory T cells. Gut. 2013;62:1142–1152. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2012-302029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]