Endothelin and the Renal Vasculature (original) (raw)
. Author manuscript; available in PMC: 2017 Jan 9.
Abstract
Endothelin is one of the most potent renal vasoconstrictors. Endothelin plays an essential role in the regulation of renal blood flow, glomerular filtration, sodium and water transport, and acid-base balance. ET-1, ET-2 and ET-3 are the three distinct endothelin isoforms comprising the endothelin family. ET-1 is the major physiologically relevant peptide and exerts its biological activity through two G-protein coupled receptors, ETA and ETB. Both ETA and ETB are expressed by the renal vasculature. While ETA are mainly expressed by vascular smooth muscle cells, ETB are expressed by both renal endothelial and vascular smooth muscle cells. Activation of the endothelin system, or over-expression of downstream endothelin signaling pathways, has been implicated in several pathophysiological conditions including hypertension, acute kidney injury, diabetic nephropathy and immune nephritis. In the current review, we will focus on the effects of endothelin on the renal microvasculature, and update recent findings on endothelin in the regulation of renal hemodynamics.
Keywords: Kidney, afferent arteriole, efferent arteriole, autoregulation, glomerular filtration
Introduction
The release of a potent vasoconstrictor substance by endothelium was initially identified in the media of cultured bovine aortic endothelial cells.1 This vasoconstrictor substance was ultimately isolated, sequenced, and cloned in 1988.2 Endothelin (ET) is a 21-amino acid polypeptide derived from endothelial cells and many other cell types, and is recognized as the most potent endogenous vasoconstrictor yet described. ET is generated from prepro-ET, a large precursor peptide that is cleaved via specific proteolytic processing to produce a 39-amino acid precursor, big-ET.3 Big-ET is further catabolized to the active form of ET by ET-converting enzymes expressed in endothelial cells and vascular smooth muscle cells.4, 5 Generally, big-ET itself does not bind to ET receptors, therefore it has no known influence on vascular reactivity.6 ET exists in three isoforms, ET-1, ET-2 and ET-3.7 These isoforms encoded by different genes and possess different biological activities despite significant structural similarities.7 ET-1 is the most potent vasoconstrictor substance among these three peptides and the only ET peptide reportedly found to be expressed in endothelial cells,8 where it acts in a paracrine or autocrine manner on adjacent endothelial or vascular smooth muscle cells.
Abundant evidence shows that ET is not only produced from endothelium but is also synthesized and released from non-vascular cell types such as renal epithelial and mesangial cells.9-12 All three isoforms of ET (ET-1, ET-2 and ET-3) are detected in many tissues and organs, including brain, lung, kidney and heart.11, 13 ET production by the kidney is much higher than any other organ.12 Using radioimmunoassay, Kitamura et al,14 showed that the lung and renal inner medulla from rats or pigs contained much higher levels of ET compared to other organs. The ET-1 content reached 8.7 pg/mg wet tissue in the inner medulla of rat kidney while less than 1 pg/mg wet tissue was detected in other tissues including the renal cortex and outer medulla.14 The high ET-1 expression levels in the renal inner medulla suggest a potentially important role for ET-1 in regulating sodium and water balance under physiological conditions and perhaps in regulating medullary blood flow. There is also evidence suggesting that ET-1 is generated from glomerular endothelial cells as well as the renal microvasculature because big-ET and the mature ET-1 peptide co-localize to these areas.15 Additionally, prepro-ET and ET-1 co-localize to smooth muscle cells of rat aorta,16 however, it remains unclear whether ET-1 is produced by renal microvascular smooth muscle cells.
Locally generated ET-1 is primarily released from the basolateral side of endothelial cells.17 Therefore, in normal healthy persons, the plasma ET-1 concentration is typically very low and averages between 0.5 and 5 pM.10, 18 In diabetic and hypertensive patients, plasma ET-1 concentrations can be increased several fold compared to normal healthy individuals.19
The physiological or pathophysiological effects of ET are mediated through activation of two ET receptors, ETA and ETB, which belong to the heterotrimeric guanine nucleotide protein-coupled receptor family. ETA and ETB are ubiquitously expressed in human and animal tissues.10, 12 In the vasculature, ETA predominate and appear to be exclusively expressed by vascular smooth muscle cells. Activation of ETA leads to a robust vasoconstrictor response.10, 12 In contrast, ETB are expressed in both endothelial cells and vascular smooth muscle cells. Activation of ETB on renal endothelial cells activates NOS3 to stimulate nitric oxide release and prostacyclin synthase to stimulate release of prostacyclin (PGI2) and perhaps other vasodilators.20, 21 Activation of ETB expressed in vascular smooth muscle cells leads to vasoconstriction via an as yet unknown intracellular signaling pathway.10, 12
Additionally, in vivo and in vitro studies indicate that ETB act as “ET-1 clearance receptors”.22-25 ETB sequester ET-1 and reduce circulating ET-1 concentrations23, 24, whereas ETB antagonists or genetic mutation of ETB elevates plasma ET-1 concentrations.26 For example, plasma ET-1 concentration is increased in endothelial cell specific ETB knockout mice despite unchanged preproET-1 mRNA levels.25 Interestingly, although the plasma ET-1 concentration was elevated in endothelial cell specific ETB knockout mice, arterial pressures remained unchanged even during high-salt intake.24 Global ETB deficient rats, on the other hand, develop hypertension with high salt intake.27 The mechanism(s) underlying the blood pressure effect of selective versus global deletion/mutation of ETB remain(s) to be determined but may reflect differential roles of endothelial ETB compared to ETB expressed in other tissues such as vascular smooth muscle cells or renal tubular epithelial cells.
Studies using receptor competition-binding assays show that the three best-characterized endogenous ET peptides exhibit different binding affinities for ETA and ETB. ETA exhibit a higher binding affinity for ET-1 and ET-2 and a substantially weaker affinity for ET-3, but all three ET peptides show similar binding affinities for ETB.9 These disparate binding characteristics for the different ET peptides have been exploited in early pharmacological studies to map ET receptor distribution in a variety of tissues.28
ET Receptor Expression in Kidneys
Although both ETA and/or ETB are ubiquitously expressed in the kidney, the distribution and density of each receptor varies across different regions of the kidney as well as across different species.10, 12, 28 For example, Gellai et al,29 reported that the relative expression of ETA and ETB in the rat kidney was equal in cortex while expression of ETB was much higher in medulla (70:30). This observation was confirmed by others showing greater ETB expression in the renal medulla and particularly in the inner medulla.22, 30
In a recent study, Kelland et al, using in situ hybridization, observed a high density of ETB binding sites in mouse renal inner medulla, while ETA expression was relatively low in kidney.25 The receptor binding ratio of ETA to ETB expression averaged 22:78 in the canine renal cortex compared to approximately 40:60 in the medulla.31 Using positron emission tomography to quantify receptor density in vivo, Johnstrom et al,22 found that medullary ETB expression is double that in the cortex of rabbit kidney. Similar to animal studies, ETB abundance is found to exceed ETA abundance in human kidneys. The ratio of ETA to ETB averaged approximately 30:70 in the human renal cortex and renal medulla,32 however, the density of ETB expression is greater in the medulla than in the cortex (33 verses 9 amol/mm2).22
Renal Vascular ETA and ETB Receptor Expression
There are abundant ETA and ETB throughout the renal vasculature.33-37 Radioligand binding studies show that the proportion of ETA and ETB in membranes of preglomerular vessels averages 40:60 in rabbits34 and approximately 50:50 in rats.35 Studies using ligand binding and autoradiography by Kuc and Davenport36 suggest that the human kidney contains 70% ETB. The ratio of ETA to ETB is approximately 90:10 in the renal artery and about 92:8 in the renal vein, suggesting an important role for ETA in regulating renal vascular reactivity.33 Similar to human kidney, ETA are the predominant receptors present in rat renal vascular smooth muscle. ETB however, are detected largely in endothelial cells of renal vessels and glomeruli.37 Variations in the distribution of ETA and ETB along the renal vasculature could result in disparate effects of ET-1 on renal hemodynamics. Accordingly, it is important to know how ETA and ETB differentially influence renal vascular reactivity to ET-1 and how this influences renal hemodynamics and renal function.
Effect of ET in Renal Hemodynamics
Stabilizing renal hemodynamics is critical for maintenance of body fluid homeostasis and the control of blood pressure. The renal microcirculation is uniquely controlled by the balance of preglomerular and postglomerular microvascular resistance. Although autoregulation of renal blood flow and glomerular filtration rate are tightly regulated by the combination of myogenic reactivity and tubuloglomerular feedback, alterations in afferent and efferent arteriole resistance by vasoactive agents would be reflected in changes in renal blood flow or/and glomerular filtration rate. The resistance of afferent and efferent arterioles is influenced by a host of intra- and extra-renal factors and mechanisms including sympathetic nerve activity, angiotensin II, prostaglandins, nitric oxide, ATP, adenosine as well as ET.38
Since the discovery of ET-1, numerous studies have demonstrated ET control of organ perfusion under physiological and pathophysiological conditions.11, 12 The kidney is more sensitive to exogenous ET-1 as compared to all other organs.39 ET-1 causes a marked and prolonged renal vasoconstriction manifested by profound reductions in renal blood flow and glomerular filtration rate.31, 40-45 ET-1 vasoconstricts both afferent and efferent arterioles, however which segment exhibits the greatest sensitivity to ET-1 remains controversial.
An early study was conducted in anesthetized Munich-Wistar rats to evaluate the effect of exogenous ET-1 on renal hemodynamics.46 Intravenous infusion of ET-1 evoked biphasic responses on arterial pressure but monophasic responses on renal blood flow. Mean arterial pressure initially fell followed by a sustained pressor response. At a low dose of ET-1, glomerular filtration rate was unaffected but renal blood flow decreased significantly, leading to a marked increase in filtration fraction. This observation suggests that ET-1 acts on both pre- and post-glomerular microvascular segments. This was confirmed using micropuncture where ET-1 infusion increased glomerular capillary hydrostatic pressure and decreased renal plasma flow despite the absence of changes in single nephron glomerular filtration rate.46 These data suggest that ET-1 exerts a proportionately greater effect on efferent arteriolar reactivity over that of afferent arterioles. In contrast, a study using the in situ split hydronephrotic kidney preparation showed that ET-1 is a more potent vasoconstrictor of afferent arterioles than efferent arterioles.47 Similar observations were reported in canine kidneys where intrarenal arterial infusion of exogenous ET-1 reduced renal blood flow and glomerular filtration rate without altering systemic blood pressure.31 The reduction of renal blood flow and glomerular filtration rate was abolished by administration of the selective ETA antagonist, BQ123. Infusion of the ETB agonist, sarafotoxin 6c, had little effect on renal blood flow or glomerular filtration rate but did induce a marked increase in urine flow and sodium excretion. Together, these observations suggest that ETA play a predominant role in controlling renal microvascular reactivity while ETB contribute more prominently to renal handling of sodium and water reabsorption.
ET-1 is also a powerful vasoconstrictor in rabbit kidneys.40 Infusion of ET-1 decreased total renal blood flow and cortical blood flow while medullary blood flow increased40 ET-1-induced reduction of cortical perfusion was attenuated by ETA blockade but enhanced by ETB blockade.40 Taken together, these studies indicate that ETA are the predominant ET receptor mediating ET-1-induced renal vasoconstriction in dogs and rabbits while ETB exert a vasodilatory influence on renal medullary vasculature.
In contrast to dogs and rabbits, studies in anesthetized rats indicate that both ETA and ETB contribute to ET-1 mediated renal vasoconstriction, but ETB may play a more prominent role in vivo.41-45 Intravenous infusion of ET-1 usually decreases renal blood flow and glomerular filtration rate in anesthetized rats. Interestingly, infusion of ET-1 is accompanied by a transient reduction in blood pressure followed by a sustained pressor response. ETA antagonists abrogated the pressor effects of ET-1 but had little effect on the renal hemodynamic response.41, 45 These results suggest that circulating ET-1 and locally generated intrarenal ET-1 are regulated by different mechanisms. Additionally, several studies found that ET-1, the ETB ligand (ET-3) or an ETB agonist (sarafotoxin 6c) elicited similar reductions in renal blood flow.42, 44, 45 The reduction of renal blood flow induced by ET-1 was partially blocked by ETA antagonists but completely eliminated by combined ET blockade.44, 45 A/B Furthermore, prevention of ETB activation with BQ-788 augmented the ET-1 induced reduction of renal blood flow,44 suggesting that ET-1 elicits both vasoconstrictor and vasodilator effects. Augmentation of the ET-1-induced reduction of renal blood flow by BQ-788 could reflect ETB-dependent release of vasodilators or reduced ET-1 clearance due to ETB blockade. Collectively, these findings indicate that both ETA and ETB contribute to the renal microvascular response to ET-1 and that ETB may play a more prominent role in rats through both vasoconstrictor or vasodilator influences on renal microvascular reactivity.
As mentioned earlier, the distribution and density of ETA and ETB expression in kidney varies between different species. Accordingly, differences in receptor distribution could lead to unique responses of afferent and efferent arterioles to ET-1, and may have a distinct impact on glomerular capillary pressure and hence glomerular hemodynamics. Conflicting outcomes probably also reflect species-specific variations as well as differing experimental conditions.
Effect of ET on Renal Microvascular Reactivity
In vivo whole kidney studies suggest that ET-1 regulates renal vascular function. The distribution of ETA and ETB along the different renal vascular segments blurs data interpretation on which receptor is responsible for the renal hemodynamic responses to ET-1 at the whole kidney level. Several in vitro models have provided insights into the segment specific effects of ET-1 along the renal microvasculature.46, 48-50 In vitro studies have utilized partially resected kidneys, hydronephrotic models and isolation of renal microvascular segments to directly assess the effects of ET on afferent and efferent arteriolar diameters.47, 51, 52
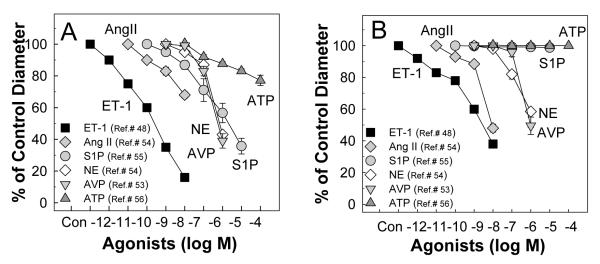
The in vitro blood perfused juxtamedullary nephron preparation is used to directly assess renal microvascular reactivity in a setting where renal tubular and vascular interactions are preserved.38 As illustrated in Figure 1, all three of ET peptides (ET-1, ET-2, ET-3) evoke concentration dependent vasoconstriction of afferent (Figure 1A) and efferent (Figure 1B) arterioles.48 ET-1 produced a significant decrease in afferent and efferent arteriole diameter at concentrations of 10−12 M and 10−11 M, respectively, and was more potent than ET-2 or ET-3. Afferent arteriolar responses to higher concentrations of ET-1 were more profound than efferent arteriolar responses, with a decline in afferent arteriolar diameter of 83% compared to 67% for efferent arteriole diameter at a concentration of 10−8 M (Fig. 1A and 1B). ET-3 was essentially ineffective at lower peptide concentrations but then showed similar efficacy to ET-1, yielding greater vasoconstriction for afferent than efferent arterioles. Interestingly, ET-2 did not show any segment specific differences between afferent or efferent arterioles. Compared to other renal vasoconstrictors (Figure 2) such as angiotensin II,53, 54 arginine vasopressin,53 norepinephrine,54 sphingosine-1-phosphate,55 and ATP,56 ET-1 is the most potent vasoconstrictor of both afferent (Figure 2A) and efferent (Figure 2B) arterioles.
Figure 1.
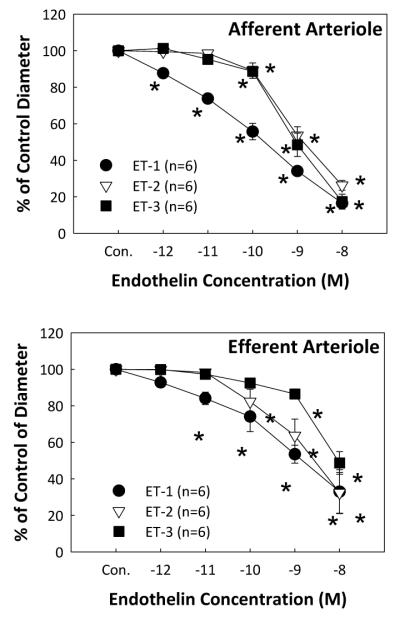
Renal microvascular responses to endothelins
Kidneys were superfused with increasing concentrations of ET-1, ET-2 or ET-3 from 10−12 to 10−8 M (5 minutes at each concentration) using the in vitro blood-perfused juxtamedullary nephron preparation while perfusion pressure was maintained at 100 mmHg. Afferent arteriolar responses (A) and efferent arteriolar responses (B) were measured at 12-second intervals and calculated from the average of all measurements obtained during the final 2 minutes of each 5-minute period. Data are expressed as the percent of control diameter. Values are mean ± SEM. *P<0.05 vs. control diameter in same group. Figure is modified from.48
Figure 2.
Comparison of effect of ET-1 with other common vasoconstrictors on afferent and efferent arteriolar reactivity in the rat juxtamedullary nephron preparation
A: the vasoconstriction of afferent arterioles to ET-148 (square symbols) is greater than the vasoconstriction induced by other GPCR agonists, angiotensin II (Ang II),53, 54 arginine vasopressin (AVP),53 norepinephrine (NE),54 sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P),55 and ATP.56 B: the vasoconstriction of efferent arterioles to ET-148 (square symbols) is also greater than the vasoconstriction evoked by Ang II,53 AVP,53 and NE54 while efferent arterioles did not show any detectable responses to S1P55 and ATP.56 All of the studies were conducted using the rat juxtamedullary nephron preparation.
The concentration-response relationship of afferent arterioles for ET-1 was shifted to the right by ETA or ETB blockers.48 When ETA and ETB blockers were employed in combination, the ET-1-mediated vasoconstriction of afferent arterioles was completely abolished. This complete abolition indicates that both ETA and ETB exert vasoconstrictor influences on rat juxtamedullary afferent arterioles.48 Notably, either ETA or ETB antagonism blocked the afferent arteriole vasoconstriction to low concentrations of ET-1. Whether this signals an unexplained ETA/ETB interaction (also suggested by Fellner and Arendshorst57) or some unique difference in the renal vascular ET receptors themselves remains to be understood.
ETA blockade has a different effect on the efferent arteriole response to ET-1. Instead of vasoconstriction, low concentrations of ET-1 vasodilated efferent arterioles during ETA blockade, whereas the response reverted to vasoconstriction when the ET concentrations reached 10−9 M.48 This observation suggests a dual effect of ETB in regulating efferent arteriole resistance. The dual effect of ETB was supported by studies using the selective ETB agonist, sarafotoxin 6c, which yielded efferent arteriolar vasodilation under control conditions, but vasoconstriction during ETB blockade.48 Together, these observations suggest ETB play a dual role in the efferent arteriole response to ET. How this impacts ET-mediated regulation of renal hemodynamics remains unclear.
The in vitro hydronephrotic kidney provides clear visibility of the complete renal vascular tree but lacks renal tubular structures.58 Studies using the in vitro hydronephrotic rat kidney reveal ET-1 to be a potent vasoconstrictor of afferent arterioles while having only a slight vasoconstrictor effect on efferent arterioles.47, 52 In contrast, early studies using isolated, perfused rabbit microvessels showed that afferent arterioles were more sensitive to ET-1 stimulation than efferent arterioles.51 They also showed that ET-1 caused long lasting vasoconstriction of afferent and efferent arterioles. While the concentration-response relationship may vary between experimental settings, it is clear that ET-1 is an important modulator of renal microvascular function and thus glomerular hemodynamics.
Genetic approaches have provided useful insights into ET control of the renal microvasculature. Schildroth et al50 used isolated, perfused afferent and efferent arterioles from ETB deficient mice and their wild type controls to show that ET-1 induces a greater vasoconstriction of afferent arterioles than efferent arterioles. The study also showed that the vasoconstriction caused by ET-1 in the afferent arterioles is due primarily to ETA, while ET-1-mediated vasoconstriction of the efferent arteriole requires both ETA and ETB; the efferent arteriole response is influenced by ETB-mediated release of nitric oxide.50
Role of ET in Medullary Microcirculation
The medullary microcirculation is supplied by blood from the vasa recta which are important regulators of medullary blood flow, pressure natriuresis/diuresis and arterial pressure.59 ETA and ETB have been detected in rat vasa recta. ETA are located on pericytes located along the vasa recta, while ETB are expressed on endothelial cells in the vasa recta.36, 37 The pioneering study by Pallone et al,59 using isolated perfused rat descending vasa recta, revealed that ET peptides (ET-1, ET-2 and ET-3) caused potent vasoconstriction of descending vasa recta.60 The rank order potency of the ET peptides is ET-1>ET-2>ET-3. Compared to the effect of ET-1 on afferent or efferent arteriolar responses, isolated perfused descending vasa recta appear to be more sensitive to ET-1.48-50 ET-1 mediated vasoconstriction of descending vasa recta was first apparent at 10−16 M and the descending vasa recta lumen was almost completely collapsed at 10−10 M ET-1. ET-1 mediated vasoconstriction of descending vasa recta was attenuated by specific ETA antagonists (BQ-123 or BQ-610) or a combination of ETA and ETB antagonists (BQ-123 and BQ-788) but the vasoconstriction was unaffected by an ETB antagonism (BQ-788) alone, suggesting selective involvement of ETA in the ET-1-induced vasoconstriction. In contrast, ET-3 mediated vasoconstriction of descending vasa recta was blocked by an ETB antagonist.60 Thus, both ETA and ETB are expressed in descending vasa recta and contribute to the vasoconstrictor response of descending vasa recta. The effect of ET-1 on vasa recta was recently confirmed by an in vitro model system using a live kidney slice to assess pericyte reactivity. Crawford et al61 reported that infusion of ET-1 (10−8 M) decreased descending vasa recta diameter particularly at sites where pericytes were visible. This observation suggests that ET regulates the contractile state of the vasa recta pericytes. In addition, the intense vasoconstriction exhibited by descending vasa recta in response to ET-1 suggests that ET-1 might play an important role in the development of renal injury in conditions where the renal ET system is upregulated, such as ischemia-reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury.
Endogenous ET-1 in Regulating Renal Microvascular Function
There is compelling evidence that ET regulates renal vascular resistance, but how does ET affect basal renal microvascular function? Several studies have looked at the impact of genetic alterations of ET-1 or ET receptors on renal microvascular function.50, 62 Kisanuki et al,62 demonstrated that endothelial cell-specific ET-1 knockout mice exhibit a mean arterial pressure that is 10-12 mmHg lower compared to controls. Schildroth et al.50 used isolated perfused afferent and efferent arterioles from ETB receptor deficient mice and saw no difference in resting diameter in either the afferent or the efferent arterioles compared to controls. Other studies have used a pharmacological approach to investigate the role of ETA and ETB on basal renal microvascular resistance.20, 21, 41, 43, 63 Multiple studies have shown that renal blood flow and glomerular filtration rate are unaltered by ETA blockade in conscious rats, implying that ETA do not contribute significantly to basal renal microvascular resistance and renal blood flow.21, 41, 63 Qui et al,63 showed that combined ETA and ETB blockade reduced glomerular capillary pressure by increasing preglomerular resistance without having a significant effect on calculated postglomerular resistance. Selective ETB blockade reduced renal blood flow without altering systemic arterial blood pressure.21 The decline in renal blood flow observed during ETB blockade was prevented when the animals were pretreated with L-NAME and ibuprofen.21 Collectively, these data imply that endogenous ET-1 influences basal renal microvascular resistance through activation of ETB and ensuing release of nitric oxide and/or prostacyclin. This may indicate that ETB activation confers a tonic vasodilatory influence on the renal microcirculation under normal physiological conditions.
Salt intake regulates ETB in the renal microcirculation. Inscho et al,48 showed that ET-1 or sarafotoxin 6c constricted afferent arterioles from rats fed a normal salt diet, whereas this response was attenuated in rats fed a high salt diet.49 Rats fed high salt had increased expression of ETB in preglomerular microvessels.49 Therefore, a high salt diet increases ETB expression, which favors an increase in renal blood flow and glomerular filtration rate to facilitate excretion of the excess dietary salt load. The link between an increased dietary salt load and the ET receptor system requires further investigation.
Contribution of ET to Renal Autoregulation
Renal vascular reactivity is closely integrated with tubular function via the intrinsic renal autoregulatory mechanism. This integrated system is designed to provide the kidney with a stable work environment in which to process the massive filtered load of plasma and maintain body fluid homeostasis and blood pressure control. Renal autoregulation is accomplished by the combined influences of the myogenic mechanism and the tubuloglomerular feedback response. The myogenic mechanism is an intrinsic property of preglomerular microvessels by which afferent arterioles rapidly constrict in response to increases in transmural pressure. Tubuloglomerular feedback is the fine adjustment linking glomerular hemodynamics and tubular reabsorption. Given the important role of ET-1 and ETB signaling in regulating sodium and water transport and renal microvascular reactivity, it is reasonable to speculate that ET is involved in the renal autoregulatory process. The role of ET in renal autoregulation however, is still uncertain. An early study in dogs found that renal blood flow and glomerular filtration rate remained fairly stable during ETA blockade, although there was a pronounced decrease in renal vascular resistance,64 suggesting that ET-1 regulates basal preglomerular vascular resistance but is not directly involved in renal autoregulation. This is supported by a micropuncture study in rats where the stop-flow pressure response to loop perfusion, an index of the tubuloglomerular feedback response, was unaffected by a pressor dose of ET-1 despite a dramatic reduction in renal blood flow and glomerular filtration rate.65 In contrast, exposure of macula densa cells to ET-1 abruptly increased single nephron glomerular filtration rate without changes in systemic or renal hemodynamics,66 suggesting that ET-1 may influence tubuloglomerular feedback responses. In addition, application of the non-selective ETA/B receptor antagonist, bosentan, or the ETB blocker, BQ-788, diminished L-NAME-augmentation of autoregulation,67 consistent with in vivo findings where myogenic reactivity was significantly impaired by pretreatment with BQ-788.68 These results suggest that ET-1 may be involved in resetting renal autoregulation by release of nitric oxide via ETB receptor activation. However, neither ETA nor ETB antagonists alone or in combination affected the impaired myogenic autoregulatory component in chronic Ang II-infused rats fed a high NaCl diet.69 The disparity noted above may reflect differences in the experimental conditions or the methods used to deliver the drugs.
Intracellular Signaling Pathways in ET-induced Renal Responses
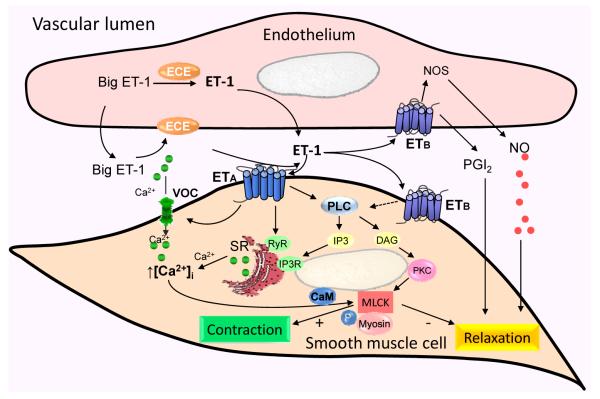
ET receptor activation has been linked to several intracellular signaling pathways, including cytosolic Ca2+, phospholipase-C, phospholipase-D, protein kinase-C, mitogen activated protein kinases, and tyrosine kinase.10, 12 ETA activate phospholipase-C, generating diacylglycerol and inositol triphosphate, which in turn stimulates Ca2+ release from intracellular stores leading to vasoconstriction.10, 12 (Figure 3) In contrast, activation of ETB in endothelial cells stimulates nitric oxide synthase and prostacyclin synthase to release the vasodilators, nitric oxide and/or prostacyclin, respectively.20, 21 Downstream signaling of ETB activation in renal microvascular smooth muscle cells remains incompletely understood.
Figure 3.
Possible intracellular signaling pathways for ET in the renal microvasculature
ET-1 is produced from big ET-1 catabolized by the ET-converting enzyme (ECE) expressed in endothelial cells. The majority of ET-1 is released towards the basolateral side of the endothelium. ET-1 acts in a paracrine/autocrine manner to influence endothelial or vascular smooth muscle cell function via activation of ETA and ETB receptors. Activation of ETA receptors in vascular smooth muscle cells increases cytosolic calcium concentration ([Ca2+]i) by activating voltage-gated calcium channels (VOC), mobilization of Ca2+ from the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) by activating phospholipase-C (PLC), diacylglycerol (DAG) and inositol triphosphate (IP3) as well as cyclic adenine diphosphate ribose (cADPR) cyclase/ ryanodine receptor (RyR) pathways. Activation of endothelial ETB receptors releases nitric oxide (NO) and prostaglandins (PGs) leading to vasodilation. Activation of ETB receptors in vascular smooth muscle cells mediates vasoconstriction through undefined intracellular mechanisms (dashed arrow). PKC, protein kinase-C; CaM, calmodulin; MLCK, myosin light chain kinase; MLCK; +, stimulate; -, inhibit.
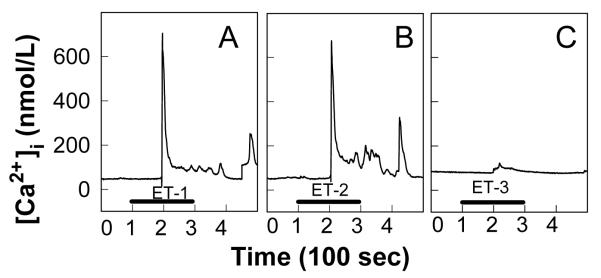
Voltage-dependent, L-type Ca2+ channels (L-VDCC) are an important signaling pathway in regulating basal renal microvascular resistance and in affecting preglomerular microvascular responses to vasoactive stimuli. The role of L-VDCC signaling in ET-1 mediated vasoconstriction is controversial. Pharmacological blockade of L-VDCC eliminated ET-1-induced renal vasoconstriction in some studies47, 51, 70-72 while others showed little effect on ET-mediated renal vasoconstriction or ET-induced increases in cytosolic Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i).73, 74 Application of ET-1 or ET-2 to freshly isolated preglomerular microvascular smooth muscle cells elicited a biphasic increase in [Ca2+]i, with a rapid initial increase followed by a smaller, but sustained, plateau as shown in Figures 4A and 4B, respectively.75 The plateau was abolished by superfusion with nominally Ca2_+-free medium while the magnitude of the initial peak was unchanged, suggesting that the initial peak of [Ca2+]i is stimulated by Ca2+_ release from intracellular stores and the sustained plateau of [Ca2+]i is generated by Ca2+ influx. In contrast, activation of ETB receptors by ET-3 (Figure 4C) or sarafotoxin 6c evoked very small and monophasic increases in [Ca2+]i.74, 75 Furthermore, blockade of L-VDCC with diltilazem had no effect on ET-1-induced increases in [Ca2+]i. This is consistent with in vivo and in vitro findings showing that the reduction of renal blood flow or decrease in afferent arteriolar diameter induced by ET-1 or sarafotoxin 6c was only slightly attenuated by LVDCC blockers.74 These data suggest that L-VDCC do not play a major role in ET-1 and ETB -mediated afferent arteriolar vasoconstriction in rats. This seems to contradict studies in hydronephrotic rat kidney where the ET-1-induced afferent arteriolar vasoconstriction was completely blocked by nifedipine, indicating a prominent role for LVDCC in ET-1-mediated afferent arteriolar responses.47
Figure 4.
Effect of ETs on cytosolic Ca2+ concentration in single rat preglomerular microvascular smooth muscle cells
Typical cytosolic Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i) recordings obtained from single smooth muscle cells isolated from rat preglomerular microvessels in response to 100 nmol/L ET-1, ET-2, and ET-3 are depicted in panels A, B, and C, respectively. The black bar indicates the period of ET peptide administration. The time between two major ticks in X axis represents 100 second intervals. Figure is modified from.75
Recently, a series studies by Arendshorst’s group suggest that cyclic adenine diphosphate ribose (cADPR) cyclase/ryanodine receptor-mediated Ca2+ signaling pathways play an important role in ET-1-mediated vasoconstriction in afferent arterioles.76 Application of ET-1 to vascular smooth muscle cells from rat preglomerular microvessels increased [Ca2+]i which was attenuated by nicotinamide, a ribosyl cyclase inhibitor,57 however, treatment with cADPR cyclase inhibitors did not alter the sarafotoxin 6c-induced increase in [Ca2+]i.57 The increased [Ca2+]i induced by ET-1 was also attenuated by application of tempol or apocynin,57 indicating that the cADPR-induced preglomerular response to ET-1 involves the superoxide-NADPH oxidase pathway. This group also found that nicotinamide or the ryanodine receptor blocker, ruthenium red, reduced the ET-1 mediated decline in renal blood flow by roughly 50% when ET-1 was administered alone or in combination with BQ-123 or BQ-788 in anesthetized Sprague-Dawley rats.77 These data implicate cADPR as an important signaling mechanism for the renal microvascular effects of ET. This conclusion is supported by studies conducted using mice lacking the major mammalian ADPR cyclase (CD38-/-).77 Mice deficient in the ADPR cyclase exhibited renal blood flow responses to ET-1 that were nearly 50% smaller than their WT controls. These results suggest that cADPR and ryanodine receptor signaling play a role in the renal microvascular response to ET-1 involving both ETA and ETB.
Substantial evidence also suggests that activation of ETA and ETB receptors in the renal microvasculature is coupled with a variety of second messenger pathways such as cytochrome _P_-450 metabolites,78 RhoA/Rho-kinase pathway,79 reactive oxygen species,80 and nitric oxide.81 Interested readers are referred to several excellent and more comprehensive reviews on these topics.12, 82
ET and Kidney Diseases
Several studies support a role for ET in the development of hypertension, ischemia-reperfusion induced acute kidney injury and other kidney diseases. The renal vascular ET system is upregulated under several pathophysiological conditions as evidenced by elevated renal vascular and tissue ET content and/or increased ET receptor expression.83-89 ET receptor antagonists targeting ETA hold promise for treating hypertension and hypertension-associated renal injury.90
Alteration of ET and ET Receptor Expression in Hypertensive Kidney Disease
Abundant studies suggest an important role of the ET system in hypertension-associated kidney disease.19, 83-86 Plasma ET-1 concentrations are increased 3-4 fold in patients with diabetes or hypertension compared to healthy human subjects.19 ET-1 levels are significantly increased in plasma and in kidney tissue in salt sensitive hypertensive animal models such as DOCA-salt rats, Dahl salt-sensitive rats and in Ang II-infused hypertensive rats.83-86 For example, vascular and renal ET-1 protein content was increased in Dahl salt-sensitive hypertensive rats.86 Rats treated with an ETA antagonist not only showed a reduction of tissue ET-1 levels but also exhibited improved endothelial function, suggesting that ETA-dependent increases in renal ET-1 contribute to renal vascular injury in Dahl-salt sensitive hypertensive rats.86 Together, these studies suggest an important role of ET-1 in mediating endothelial injury and development of hypertensive renal injury.
Alteration of ET and ET Receptor Expression in Ischemia-reperfusion Kidney Injury
As a potent renal vasoconstrictor, ET-1 is postulated to contribute to the pathogenesis of ischemia-reperfusion induced acute kidney injury.87-89, 91, 92 ET-1 is increased in peritubular capillaries in the cortex of ischemic rat kidneys.87 Plasma ET-1 concentration and renal ET-1 levels are elevated in ischemia-reperfusion induced acute kidney injury rats.88, 89 ETA and ETB mRNA is increased in renal vascular beds in ischemia-reperfusion induced acute kidney injury rats.89 Furthermore, treatment with anti-ET-1 antibodies, ETA antagonists, or deletion of vascular endothelial ET-1 expression protects the kidney against ischemia-reperfusion induced acute kidney injury.91, 92 Taken together, these studies suggest an important role for ET-1 in the development of ischemia-reperfusion induced acute kidney injury, however, more work needs to be done on the role of ET in changes in renal microvascular function in the setting of renal ischemia-reperfusion injury.
In summary, ET is the most potent renal vasoconstrictor known and the kidney is a major producer of ET. Studies have identified several mechanisms by which ET contributes to the regulation of kidney function in general, and renal vascular function in particular. Variations in ETA and ETB distribution and density along the renal vasculature could result in a complex microvascular response to ET-1. The renal ET system may have an impact on glomerular capillary pressure and hence glomerular hemodynamics. Better understanding of how ETA and ETB differentially influence renal vascular reactivity to ET-1 will be important in clarifying the role of ET in regulating renal hemodynamics and renal function. Insights gained will help frame clinical trials in an effort to develop better therapeutic strategies for the prevention or treatment of hypertension or ischemia associated kidney disease.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge grant support from National Institutes of Health (DK-44628, HL-098135, HL-095499) for EW Inscho and the American Heart Association (10SDG3770010) for Z Guan and pre-doctoral fellowship (14PRE20460061) for JP VanBeusecum.
Footnotes
Publisher's Disclaimer: This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final citable form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
Financial disclosure and conflict of interest statements: none.
References
- 1.Hickey KA, Rubanyi G, Paul RJ, Highsmith RF. Characterization of a coronary vasoconstrictor produced by cultured endothelial cells. Am J Physiol. 1985;248(5 Pt 1):C550–6. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1985.248.5.C550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Yanagisawa M, Kurihara H, Kimura S, Tomobe Y, Kobayashi M, Mitsui Y, Yazaki Y, Goto K, Masaki T. A novel potent vasoconstrictor peptide produced by vascular endothelial cells. Nature. 1988;332(6163):411–5. doi: 10.1038/332411a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Itoh Y, Yanagisawa M, Ohkubo S, Kimura C, Kosaka T, Inoue A, Ishida N, Mitsui Y, Onda H, Fujino M, et al. Cloning and sequence analysis of cDNA encoding the precursor of a human endothelium-derived vasoconstrictor peptide, endothelin: identity of human and porcine endothelin. FEBS Lett. 1988;231(2):440–4. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80867-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Russell FD, Davenport AP. Secretory pathways in endothelin synthesis. Br J Pharmacol. 1999;126(2):391–8. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0702315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Johnstrom P, Fryer TD, Richards HK, Maguire JJ, Clark JC, Pickard JD, Davenport AP. Positron emission tomography of [18F]-big endothelin-1 reveals renal excretion but tissue-specific conversion to [18F]-endothelin-1 in lung and liver. Br J Pharmacol. 2010;159(4):812–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.00641.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Kimura S, Kasuya Y, Sawamura T, Shinimi O, Sugita Y, Yanagisawa M, Goto K, Masaki T. Conversion of big endothelin-1 to 21-residue endothelin-1 is essential for expression of full vasoconstrictor activity: structure-activity relationships of big endothelin-1. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1989;13(Suppl 5):S5–7. doi: 10.1097/00005344-198900135-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Inoue A, Yanagisawa M, Kimura S, Kasuya Y, Miyauchi T, Goto K, Masaki T. The human endothelin family: three structurally and pharmacologically distinct isopeptides predicted by three separate genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989;86(8):2863–7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Sakurai T, Yanagisawa M, Masaki T. Molecular characterization of endothelin receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1992;13(3):103–8. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(92)90038-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Sakurai T, Yanagisawa M, Takuwa Y, Miyazaki H, Kimura S, Goto K, Masaki T. Cloning of a cDNA encoding a non-isopeptide-selective subtype of the endothelin receptor. Nature. 1990;348(6303):732–5. doi: 10.1038/348732a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Simonson MS. Endothelins: multifunctional renal peptides. Physiol Rev. 1993;73(2):375–411. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1993.73.2.375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Barton M, Yanagisawa M. Endothelin: 20 years from discovery to therapy. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2008;86(8):485–98. doi: 10.1139/Y08-059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Kohan DE, Inscho EW, Wesson D, Pollock DM. Physiology of endothelin and the kidney. Comprehensive Physiology. 2011;1(2):883–919. doi: 10.1002/cphy.c100039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kedzierski RM, Yanagisawa M. Endothelin system: the double-edged sword in health and disease. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2001;41:851–76. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.41.1.851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kitamura K, Tanaka T, Kato J, Eto T, Tanaka K. Regional distribution of immunoreactive endothelin in porcine tissue: abundance in inner medulla of kidney. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989;161(1):348–52. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91603-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Karet FE, Davenport AP. Localization of endothelin peptides in human kidney. Kidney Int. 1996;49(2):382–7. doi: 10.1038/ki.1996.56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hahn AW, Resink TJ, Scott-Burden T, Powell J, Dohi Y, Buhler FR. Stimulation of endothelin mRNA and secretion in rat vascular smooth muscle cells: a novel autocrine function. Cell Regul. 1990;1(9):649–59. doi: 10.1091/mbc.1.9.649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Wagner OF, Christ G, Wojta J, Vierhapper H, Parzer S, Nowotny PJ, Schneider B, Waldhausl W, Binder BR. Polar secretion of endothelin-1 by cultured endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1992;267(23):16066–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Treiber FA, Jackson RW, Davis H, Pollock JS, Kapuku G, Mensah GA, Pollock DM. Racial differences in endothelin-1 at rest and in response to acute stress in adolescent males. Hypertension. 2000;35(3):722–5. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.35.3.722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Schneider JG, Tilly N, Hierl T, Sommer U, Hamann A, Dugi K, Leidig-Bruckner G, Kasperk C. Elevated plasma endothelin-1 levels in diabetes mellitus. Am J Hypertens. 2002;15(11):967–72. doi: 10.1016/s0895-7061(02)03060-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Takayanagi R, Kitazumi K, Takasaki C, Ohnaka K, Aimoto S, Tasaka K, Ohashi M, Nawata H. Presence of non-selective type of endothelin receptor on vascular endothelium and its linkage to vasodilation. FEBS Lett. 1991;282(1):103–6. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80454-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Matsuura T, Miura K, Ebara T, Yukimura T, Yamanaka S, Kim S, Iwao H. Renal vascular effects of the selective endothelin receptor antagonists in anaesthetized rats. Br J Pharmacol. 1997;122(1):81–6. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0701349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Johnstrom P, Rudd JH, Richards HK, Fryer TD, Clark JC, Weissberg PL, Pickard JD, Davenport AP. Imaging endothelin ETB receptors using [18F]-BQ3020: in vitro characterization and positron emission tomography (microPET) Exp Biol Med. 2006;231(6):736–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Fukuroda T, Fujikawa T, Ozaki S, Ishikawa K, Yano M, Nishikibe M. Clearance of circulating endothelin-1 by ETB receptors in rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994;199(3):1461–5. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.1395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Bagnall AJ, Kelland NF, Gulliver-Sloan F, Davenport AP, Gray GA, Yanagisawa M, Webb DJ, Kotelevtsev YV. Deletion of endothelial cell endothelin B receptors does not affect blood pressure or sensitivity to salt. Hypertension. 2006;48(2):286–93. doi: 10.1161/01.HYP.0000229907.58470.4c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Kelland NF, Kuc RE, McLean DL, Azfer A, Bagnall AJ, Gray GA, Gulliver-Sloan FH, Maguire JJ, Davenport AP, Kotelevtsev YV, Webb DJ. Endothelial cell-specific ETB receptor knockout: autoradiographic and histological characterisation and crucial role in the clearance of endothelin-1. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2010;88(6):644–51. doi: 10.1139/Y10-041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Berthiaume N, Yanagisawa M, Labonte J, D’Orleans-Juste P. Heterozygous knock-Out of ET(B) receptors induces BQ-123-sensitive hypertension in the mouse. Hypertension. 2000;36(6):1002–7. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.36.6.1002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Taylor TA, Gariepy CE, Pollock DM, Pollock JS. Gender differences in ET and NOS systems in ETB receptor-deficient rats: effect of a high salt diet. Hypertension. 2003;41(3 Pt 2):657–62. doi: 10.1161/01.HYP.0000048193.85814.78. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Davenport AP, Maguire JJ. Pharmacology of renal endothelin receptors. Contrib Nephrol. 2011;172:1–17. doi: 10.1159/000328678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Gellai M, DeWolf R, Pullen M, Nambi P. Distribution and functional role of renal ET receptor subtypes in normotensive and hypertensive rats. Kidney Int. 1994;46(5):1287–94. doi: 10.1038/ki.1994.396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Waeber C, Hoyer D, Palacios JM. Similar distribution of [125I]sarafotoxin-6b and [125I]endothelin-1, -2, -3 binding sites in the human kidney. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990;176(2):233–6. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)90534-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Brooks DP, DePalma PD, Pullen M, Nambi P. Characterization of canine renal endothelin receptor subtypes and their function. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1994;268(3):1091–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Nambi P, Pullen M, Wu HL, Aiyar N, Ohlstein EH, Edwards RM. Identification of endothelin receptor subtypes in human renal cortex and medulla using subtype-selective ligands. Endocrinology. 1992;131(3):1081–6. doi: 10.1210/endo.131.3.1324149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Davenport AP, Kuc RE, Maguire JJ, Harland SP. ETA receptors predominate in the human vasculature and mediate constriction. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1995;26(Suppl 3):S265–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Edwards RM, Trizna W. Characterization of 125I-endothelin-1 binding to rat and rabbit renal microvasculature. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1995;274(3):1084–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.De Leon H, Garcia R. Characterization of endothelin receptor subtypes in isolated rat renal preglomerular microvessels. Regul Pept. 1995;60(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(95)00112-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Kuc R, Davenport AP. Comparison of endothelin-A and endothelin-B receptor distribution visualized by radioligand binding versus immunocytochemical localization using subtype selective antisera. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2004;44(Suppl 1):S224–6. doi: 10.1097/01.fjc.0000166260.35099.d5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Wendel M, Knels L, Kummer W, Koch T. Distribution of endothelin receptor subtypes ETA and ETB in the rat kidney. J Histochem Cytochem. 2006;54(11):1193–203. doi: 10.1369/jhc.5A6888.2006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Navar LG, Inscho EW, Majid SA, Imig JD, Harrison-Bernard LM, Mitchell KD. Paracrine regulation of the renal microcirculation. Physiol Rev. 1996;76(2):425–536. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1996.76.2.425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Clozel M, Clozel JP. Effects of endothelin on regional blood flows in squirrel monkeys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989;250(3):1125–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Evans RG, Madden AC, Oliver JJ, Lewis TV. Effects of ETA- and ETB-receptor antagonists on regional kidney blood flow, and responses to intravenous endothelin-1, in anaesthetized rabbits. J Hypertens. 2001;19(10):1789–99. doi: 10.1097/00004872-200110000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Pollock DM, Opgenorth TJ. Evidence for endothelin-induced renal vasoconstriction independent of ETA receptor activation. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 1993;264(1 Pt 2):R222–6. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1993.264.1.R222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Cristol JP, Warner TD, Thiemermann C, Vane JR. Mediation via different receptors of the vasoconstrictor effects of endothelins and sarafotoxins in the systemic circulation and renal vasculature of the anaesthetized rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1993;108(3):776–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb12877.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Gellai M, Fletcher T, Pullen M, Nambi P. Evidence for the existence of endothelin-B receptor subtypes and their physiological roles in the rat. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 1996;271(1 Pt 2):R254–61. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1996.271.1.R254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Just A, Olson AJ, Arendshorst WJ. Dual constrictor and dilator actions of ETB receptors in the rat renal microcirculation: interactions with ETA receptors. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2004;286(4):F660–8. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00368.2003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Wellings RP, Corder R, Warner TD, Cristol JP, Thiemermann C, Vane JR. Evidence from receptor antagonists of an important role for ETB receptor-mediated vasoconstrictor effects of endothelin-1 in the rat kidney. Br J Pharmacol. 1994;111(2):515–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb14767.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.King AJ, Brenner BM, Anderson S. Endothelin: a potent renal and systemic vasoconstrictor peptide. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 1989;256(6 Pt 2):F1051–8. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.256.6.F1051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Loutzenhiser R, Epstein M, Hayashi K, Horton C. Direct visualization of effects of endothelin on the renal microvasculature. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 1990;258(1 Pt 2):F61–8. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.258.1.F61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Inscho EW, Imig JD, Cook AK, Pollock DM. ETA and ETB receptors differentially modulate afferent and efferent arteriolar responses to endothelin. Br J Pharmacol. 2005;146(7):1019–26. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Schneider MP, Inscho EW, Pollock DM. Attenuated vasoconstrictor responses to endothelin in afferent arterioles during a high-salt diet. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2007;292(4):F1208–14. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00280.2006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Schildroth J, Rettig-Zimmermann J, Kalk P, Steege A, Fahling M, Sendeski M, Paliege A, Lai EY, Bachmann S, Persson PB, Hocher B, Patzak A. Endothelin type A and B receptors in the control of afferent and efferent arterioles in mice. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2011;26(3):779–89. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfq534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Edwards RM, Trizna W, Ohlstein EH. Renal microvascular effects of endothelin. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 1990;259(2 Pt 2):F217–21. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.259.2.F217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Takenaka T, Forster H, Epstein M. Protein kinase C and calcium channel activation as determinants of renal vasoconstriction by angiotensin II and endothelin. Circ Res. 1993;73(4):743–50. doi: 10.1161/01.res.73.4.743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Ikenaga H, Fallet RW, Carmines PK. Basal nitric oxide production curtails arteriolar vasoconstrictor responses to ANG II in rat kidney. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 1996;271(2 Pt 2):F365–73. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1996.271.2.F365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Inscho EW, Imig JD, Cook AK. Afferent and efferent arteriolar vasoconstriction to angiotensin II and norepinephrine involves release of Ca2+ from intracellular stores. Hypertension. 1997;29(1 Pt 2):222–7. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.29.1.222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Guan Z, Singletary TS, Cook AK, Hobbs JL, Pollock JS, Inscho EW. Sphingosine-1-phosphate evokes unique segment specific vasoconstriction of the renal microvasculature. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology. 2014 doi: 10.1681/ASN.2013060656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Guan Z, Giddens MI, Osmond DA, Cook AK, Hobbs JL, Zhang S, Yamamoto T, Pollock JS, Pollock DM, Inscho EW. Immunosuppression preserves renal autoregulatory function and microvascular P2X1 receptor reactivity in ANG II-hypertensive rats. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2013;15(304(6)):F801–7. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00286.2012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Fellner SK, Arendshorst W. Endothelin-A and -B receptors, superoxide, and Ca2+ signaling in afferent arterioles. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2007;292(1):F175–84. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00050.2006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Nobiling R, Buhrle CP, Hackenthal E, Helmchen U, Steinhausen M, Whalley A, Taugner R. Ultrastructure, renin status, contractile and electrophysiological properties of the afferent glomerular arteriole in the rat hydronephrotic kidney. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1986;410(1):31–42. doi: 10.1007/BF00710903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Pallone TL, Zhang Z, Rhinehart K. Physiology of the renal medullary microcirculation. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2003;284(2):F253–66. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00304.2002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Silldorff EP, Yang S, Pallone TL. Prostaglandin E2 abrogates endothelin-induced vasoconstriction in renal outer medullary descending vasa recta of the rat. J Clin Invest. 1995;95(6):2734–40. doi: 10.1172/JCI117976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Crawford C, Kennedy-Lydon T, Sprott C, Desai T, Sawbridge L, Munday J, Unwin RJ, Wildman SS, Peppiatt-Wildman CM. An intact kidney slice model to investigate vasa recta properties and function in situ. Nephron Physiol. 2012;120(3):17–31. doi: 10.1159/000339110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Kisanuki YY, Emoto N, Ohuchi T, Widyantoro B, Yagi K, Nakayama K, Kedzierski RM, Hammer RE, Yanagisawa H, Williams SC, Richardson JA, Suzuki T, Yanagisawa M. Low blood pressure in endothelial cell-specific endothelin 1 knockout mice. Hypertension. 2010;56(1):121–8. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.109.138701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Qiu C, Samsell L, Baylis C. Actions of endogenous endothelin on glomerular hemodynamics in the rat. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 1995;269(2 Pt 2):R469–73. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1995.269.2.R469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Berthold H, Munter K, Just A, Kirchheim HR, Ehmke H. Contribution of endothelin to renal vascular tone and autoregulation in the conscious dog. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 1999;276(3 Pt 2):F417–24. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1999.276.3.F417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Takabatake T, Ise T, Ohta K, Kobayashi K. Effects of endothelin on renal hemodynamics and tubuloglomerular feedback. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 1992;263(1 Pt 2):F103–8. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1992.263.1.F103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Romano G, Giagu P, Favret G, Bartoli E. Effect of endothelin 1 on proximal reabsorption and tubuloglomerular feedback. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2000;23(6):360–5. doi: 10.1159/000025984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Kramp R, Fourmanoir P, Caron N. Endothelin resets renal blood flow autoregulatory efficiency during acute blockade of NO in the rat. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2001;281(6):F1132–40. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.0078.2001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Shi Y, Lau C, Cupples WA. Interactive modulation of renal myogenic autoregulation by nitric oxide and endothelin acting through ETB receptors. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2007;292(1):R354–61. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00440.2006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Saeed A, Dibona GF, Guron G. Effects of endothelin receptor antagonists on renal hemodynamics in angiotensin II-infused rats on high NaCl intake. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2012;36(1):258–67. doi: 10.1159/000343415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Madeddu P, Yang XP, Anania V, Troffa C, Pazzola A, Soro A, Manunta P, Tonolo G, Demontis MP, Varoni MV. Efficacy of nifedipine to prevent systemic and renal vasoconstrictor effects of endothelin. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 1990;259(2 Pt 2):F304–11. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.259.2.F304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Yukimura T, Miura K, Yamashita Y, Shimmen T, Okumura M, Yamanaka S, Saito M, Yamamoto K. Effects of the calcium channel antagonist nicardipine on renal action of endothelin in dogs. Contrib Nephrol. 1991;90:105–10. doi: 10.1159/000420131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Takahashi K, Katoh T, Fukunaga M, Badr KF. Studies on the glomerular microcirculatory actions of manidipine and its modulation of the systemic and renal effects of endothelin. Am Heart J. 1993;125(2 Pt 2):609–19. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(93)90211-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Fretschner M, Endlich K, Gulbins E, Lang RE, Schlottmann K, Steinhausen M. Effects of endothelin on the renal microcirculation of the split hydronephrotic rat kidney. Ren Physiol Biochem. 1991;14(3):112–27. doi: 10.1159/000173394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Pollock DM, Jenkins JM, Cook AK, Imig JD, Inscho EW. L-type calcium channels in the renal microcirculatory response to endothelin. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2005;288(4):F771–7. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00315.2004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Schroeder AC, Imig JD, LeBlanc EA, Pham BT, Pollock DM, Inscho EW. Endothelin-mediated calcium signaling in preglomerular smooth muscle cells. Hypertension. 2000;35(1 Pt 2):280–6. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.35.1.280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Arendshorst WJ, Thai TL. Regulation of the renal microcirculation by ryanodine receptors and calcium-induced calcium release. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2009;18(1):40–9. doi: 10.1097/MNH.0b013e32831cf5bd. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Thai TL, Arendshorst WJ. ADP-ribosyl cyclase and ryanodine receptors mediate endothelin ETA and ETB receptor-induced renal vasoconstriction in vivo. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2008;295(2):F360–8. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00512.2007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Imig JD, Pham BT, LeBlanc EA, Reddy KM, Falck JR, Inscho EW. Cytochrome P450 and cyclooxygenase metabolites contribute to the endothelin-1 afferent arteriolar vasoconstrictor and calcium responses. Hypertension. 2000;35(1 Pt 2):307–12. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.35.1.307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Cavarape A, Endlich N, Assaloni R, Bartoli E, Steinhausen M, Parekh N, Endlich K. Rho-kinase inhibition blunts renal vasoconstriction induced by distinct signaling pathways in vivo. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2003;14(1):37–45. doi: 10.1097/01.asn.0000039568.93355.85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Just A, Whitten CL, Arendshorst WJ. Reactive oxygen species participate in acute renal vasoconstrictor responses induced by ETA and ETB receptors. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2008;294(4):F719–28. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00506.2007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Just A, Olson AJ, Falck JR, Arendshorst WJ. NO and NO-independent mechanisms mediate ETB receptor buffering of ET-1-induced renal vasoconstriction in the rat. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2005;288(5):R1168–77. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00550.2004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Bouallegue A, Daou GB, Srivastava AK. Endothelin-1-induced signaling pathways in vascular smooth muscle cells. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2007;5(1):45–52. doi: 10.2174/157016107779317161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Kassab S, Miller MT, Novak J, Reckelhoff J, Clower B, Granger JP. Endothelin-A receptor antagonism attenuates the hypertension and renal injury in Dahl salt-sensitive rats. Hypertension. 1998;31(1 Pt 2):397–402. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.31.1.397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Lariviere R, Thibault G, Schiffrin EL. Increased endothelin-1 content in blood vessels of deoxycorticosterone acetate-salt hypertensive but not in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Hypertension. 1993;21(3):294–300. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.21.3.294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Matsumura Y, Kuro T, Kobayashi Y, Konishi F, Takaoka M, Wessale JL, Opgenorth TJ, Gariepy CE, Yanagisawa M. Exaggerated vascular and renal pathology in endothelin-B receptor-deficient rats with deoxycorticosterone acetate-salt hypertension. Circulation. 2000;102(22):2765–73. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.102.22.2765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Barton M, Vos I, Shaw S, Boer P, D’Uscio LV, Grone HJ, Rabelink TJ, Lattmann T, Moreau P, Luscher TF. Dysfunctional renal nitric oxide synthase as a determinant of salt-sensitive hypertension: mechanisms of renal artery endothelial dysfunction and role of endothelin for vascular hypertrophy and Glomerulosclerosis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2000;11(5):835–45. doi: 10.1681/ASN.V115835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Wilhelm SM, Simonson MS, Robinson AV, Stowe NT, Schulak JA. Endothelin up-regulation and localization following renal ischemia and reperfusion. Kidney Int. 1999;55(3):1011–8. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1755.1999.0550031011.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Shibouta Y, Suzuki N, Shino A, Matsumoto H, Terashita Z, Kondo K, Nishikawa K. Pathophysiological role of endothelin in acute renal failure. Life Sci. 1990;46(22):1611–8. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(90)90392-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Ruschitzka F, Shaw S, Gygi D, Noll G, Barton M, Luscher TF. Endothelial dysfunction in acute renal failure: role of circulating and tissue endothelin-1. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1999;10(5):953–62. doi: 10.1681/ASN.V105953. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Rautureau Y, Schiffrin EL. Endothelin in hypertension: an update. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2012;21(2):128–36. doi: 10.1097/MNH.0b013e32834f0092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Chan L, Chittinandana A, Shapiro JI, Shanley PF, Schrier RW. Effect of an endothelin-receptor antagonist on ischemic acute renal failure. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 1994;266(1 Pt 2):F135–8. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1994.266.1.F135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Gellai M, Jugus M, Fletcher T, DeWolf R, Nambi P. Reversal of postischemic acute renal failure with a selective endothelin A receptor antagonist in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1994;93(2):900–6. doi: 10.1172/JCI117046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]