Cohort profile: the National Health Insurance Service-National Health Screening Cohort (NHIS-HEALS) in Korea (original) (raw)
Abstract
Purpose
The National Health Insurance Service-Health Screening Cohort (NHIS-HEALS) is a cohort of participants who participated in health screening programmes provided by the NHIS in the Republic of Korea. The NHIS constructed the NHIS-HEALS cohort database in 2015. The purpose of this cohort is to offer relevant and useful data for health researchers, especially in the field of non-communicable diseases and health risk factors, and policy-maker.
Participants
To construct the NHIS-HEALS database, a sample cohort was first selected from the 2002 and 2003 health screening participants, who were aged between 40 and 79 in 2002 and followed up through 2013. This cohort included 514 866 health screening participants who comprised a random selection of 10% of all health screening participants in 2002 and 2003.
Findings to date
The age-standardised prevalence of anaemia, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, obesity, hypercholesterolaemia and abnormal urine protein were 9.8%, 8.2%, 35.6%, 2.7%, 14.2% and 2.0%, respectively. The age-standardised mortality rate for the first 2 years (through 2004) was 442.0 per 100 000 person-years, while the rate for 10 years (through 2012) was 865.9 per 100 000 person-years. The most common cause of death was malignant neoplasm in both sexes (364.1 per 100 000 person-years for men, 128.3 per 100 000 person-years for women).
Future plans
This database can be used to study the risk factors of non-communicable diseases and dental health problems, which are important health issues that have not yet been fully investigated. The cohort will be maintained and continuously updated by the NHIS.
Keywords: Cohort Studies, risk factors, National Health Programs, administrative claims
Strengths and limitations of this study.
- It is a cohort with a large sample size, with a relatively low rate of attrition over more than 10 years.
- It contains the date and cause of death, which were determined using the national database and extensive information on healthcare usage regarding inpatient and outpatient visits to healthcare institutions and medication histories.
- Variables on health behaviours are limited since those data were obtained from self-reporting. In addition, the disease diagnoses in the claim data might not accurately reflect patients’ medical conditions.
Introduction
The National Health Insurance Service-Health Screening Cohort (NHIS-HEALS) is a cohort of participants who participated in health screening programmes provided by the NHIS in the Republic of Korea (hereafter ‘Korea’). The purpose of this cohort is to offer relevant and useful data for a wide range of health researchers.
NHIS-HEALS is based on information obtained through the national health screening programmes of Korea. Since 1995, the NHIS has provided general national health screening programmes, including an oral health screening programme, to improve the health status of Koreans through the prevention and early detection of diseases.1 2 In 2007, a health screening programme for transitional ages, aimed at those aged 40 and 66 years, was also launched.3 NHIS-HEALS incorporates information from these three major health screening programmes for the adult Korean population (see online supplementary figure 1). All insured adults are eligible for a general health screening programme that is biennially conducted (annually for manual workers). The participation rate in the general health screening programme among the eligible population was 74.8% in 2014.4 The general health screening programme can be applied at least once every 2 years for the entire population of Korean adults aged 40 years or older. The healthcare institutions for screening are designated according to the Framework Act on Health Examinations, and must meet the standards of manpower, facilities and equipment.
Supplementary material 1
bmjopen-2017-016640supp001.pdf (191.7KB, pdf)
The NHIS established the National Health Information Database (NHID) in 2011, which incorporates all data from the NHIS and consists of five databases:5 an eligibility database, a national health screening database, a healthcare usage database, a long-term care insurance database and a healthcare provider database. The NHID covers the entire population of Korea (50 million) and thus has proven unwieldy for researchers. The NHIS constructed a representative 2% sample cohort database, the NHIS-National Sample Cohort (NHIS-NSC),6 but the NHIS-NSC did not meet the high demand for research requiring both health screening data and long-term health outcomes. The NHIS therefore constructed the NHIS-HEALS cohort database in 2015 to support a wide range of public research. The NHIS-HEALS has been made publicly available to facilitate wider use of the health screening database, and includes a larger sample of health screening participants than the NHIS-NSC.
Cohort description
The participants of the cohort
The eligibility criteria for the general health screening programme provided by the NHIS varied according to the insurance type of beneficiaries. Employed individuals were eligible at all ages, while the self-employed were eligible if they were the head of household of a family. The dependents of the employed and family members of the self-employed heads of household were eligible only for those aged 40 years or older. Among the beneficiaries of the medical aid programme, which is a tax-based governmental programme for low-income families that covers approximately 3% of all Koreans, heads of household 19–64 years of age and family members 41–64 years of age were eligible for the general health screening programme. Medical aid beneficiaries have been included in the general health screening programme since 2012.
To construct the NHIS-HEALS database, a sample cohort was first selected from the 2002 and 2003 health screening participants, who were aged between 40 and 79 in 2002 and followed up through 2013. This cohort included 514 866 health screening participants who comprised a 10% simple random sample of all health screening participants in 2002 and 2003. Since only a small proportion of people aged less than 40 participated in the health screening programme, and the response rate was very low among people aged 80 years or older, the NHIS-HEALS was limited to adults aged 40 to 79 years. Gender-specific and age-specific distributions of the cohort population, the source population (all health screening participants) and the overall Korean population are presented in online supplementary table 1.7 Under the current National Health Insurance Act, the data can only be used for research purposes without patients’ individual consent. Nevertheless, identification is difficult because the sample was drawn from the entire population and the data use deidentified individual keys that were created for the NHIS-HEALS.
The general characteristics of the cohort population at baseline are presented in table 1. A total of 54.2% of the participants were men. The number of participants aged 40–44 years was highest among all age groups, accounting for a quarter of the sample (25.2%). A total of 55.3% of the participants lived in non-metropolitan areas, which covers some urban areas and all rural areas. The most common insurance type was health insurance for the employed. A total of 0.6% of the participants had any disabilities. The biennial screening participant rates ranged from 65.1% to 70.9% during the 2004–2013 period. Of the sample population, 31.6% participated six times in the health screening programmes during the follow-up period. A total of 42.3% of the men and 96.2% of the women were non-smokers. Nearly half of the men (45.7%) drank alcohol more than once per week, while most of the women (82.5%) rarely drank. Of the men, 49.7% never engaged in exercise at least once per week, compared with 67.0% of the women.
Table 1.
General characteristics of the National Health Insurance Service-Health Screening Cohort subjects at baseline (2002–2003)
| Variables | n | % | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | Men | 279 125 | 54.2 |
| Women | 235 741 | 45.8 | |
| Age | 40–44 | 129 979 | 25.2 |
| Mean: 52.641 | 45–49 | 107 002 | 20.8 |
| SD: 9.635 | 50–54 | 80 080 | 15.6 |
| 55–59 | 64 952 | 12.6 | |
| 60–64 | 59 328 | 11.5 | |
| 65–69 | 41 828 | 8.1 | |
| 70–74 | 21 615 | 4.2 | |
| 75–79 | 10 082 | 2.0 | |
| Region | Seoul metropolitan city | 89 344 | 17.4 |
| Other metropolitan cities | 141 055 | 27.4 | |
| Non-metropolitan area | 284 467 | 55.3 | |
| Insurance type | Self-employed insured | 197 992 | 38.5 |
| Employed insured | 316 359 | 61.4 | |
| Medical aid beneficiary | 515 | 0.0 | |
| Disability | No | 511 964 | 99.4 |
| Yes | 2902 | 0.6 | |
| No of participants (biennial) in 2002–2013 | 2002–2003 | 514 866 | 100.0 |
| 2004–2005 | 334 966 | 65.1 | |
| 2006–2007 | 352 158 | 68.4 | |
| 2008–2009 | 361 043 | 70.1 | |
| 2010–2011 | 364 757 | 70.9 | |
| 2012–2013 | 345 693 | 67.1 | |
| The frequency of biennial screening participation in 2002–2013 | 6 | 162 782 | 31.6 |
| 5 | 129 786 | 25.2 | |
| 4 | 88 755 | 17.2 | |
| 3 | 58 628 | 11.4 | |
| 2 | 42 042 | 8.2 | |
| 1 | 32 873 | 6.4 | |
| Risk factors in 2002–2003 (baseline) | Men/Women | Men %/Women% | |
| Cigarette smoking | Non-smoker | 112 577/218 147 | 42.3/96.2 |
| Ex-smoker | 41 519/2170 | 15.6/1.0 | |
| Current smoker | 112 143/6476 | 42.1/2.9 | |
| Smoking duration | <10 years | 18 724/3108 | 12.2/36.0 |
| 10–29 years | 93 620/3646 | 60.9/42.2 | |
| ≥30 years | 41 318/1892 | 26.9/21.9 | |
| Alcohol drinking | Rarely | 96 441/189 721 | 35.1/82.5 |
| 2–3 times per month | 52 995/24 104 | 19.3/10.5 | |
| More than once per week | 125 688/16 134 | 45.7/7.0 | |
| Exercise | None | 134 524/153 342 | 49.7/67.0 |
| 1–2 times per week | 80 104/37 738 | 29.6/16.5 | |
| More than three times per week | 55 916/37 669 | 20.7/16.5 |
Follow-up interval
The cohort was followed up through 2013 annually for the eligibility information including death information and healthcare usage (all participants), and not annually for the health screening information (only those who meet the eligibility criteria, biennially, for the screening programme and those who participated in the screening programme). Information on death (date and cause of death) from Statistics Korea was individually linked using unique personal identification numbers. By law, all deaths must be reported to Statistics Korea. Personal information regarding insurance contribution (a proxy for income), residential area and disability status was tracked every year from the eligibility database. The eligibility information was collected from the Public Information Sharing System, National Tax Service and Ministry of Health and Welfare of Korea, and managed by the NHIS, which has 178 regional branches and approximately 13 000 employees across Korea. As the NHIS covers the entire population of Korea, the healthcare usage information included all visits (inpatient, outpatient and pharmacy visits) to healthcare facilities that occurred in Korea. Information about the healthcare facilities was also monitored annually. Regarding the health screening follow-ups, 31.6% of the participants were monitored biennially until 2013, and 93.6% of the participants were examined at least once after a baseline screening. The cohort will be maintained and continuously updated by the NHIS.
The key variables
The key variables of the NHIS-HEALS, which were mainly constructed from the variables of the NHID, are presented in table 2 and online supplementary table 2. The eligibility database included information about income-based insurance contributions (a proxy for income), demographic variables, and date and cause of death. Variables for specific health problems and risk factors from questionnaires (cigarette smoking status/dose/duration, frequency per week and amount per day of alcohol drinking—regardless of the type of alcohol, type and days per week of physical activity, medical history and family history) and bioclinical laboratory results (blood pressure, fasting glucose, lipid profile, haemoglobin, urine stick test, creatinine, liver enzyme, body mass index and waist circumference) were included in the health screening database. Some variables changed during the follow-up period. The healthcare usage database was based on data collected during the process of claiming healthcare services and included information on records of inpatient and outpatient usage (diagnosis, length of stay, treatment costs and services received) and prescription records (drug code, days prescribed and daily dosage). The healthcare provider database included information on types of healthcare institutions, healthcare human resources and equipment.
Table 2.
Major variables in the National Health Insurance Service-National Health Screening Cohort database
| Domain | Variables | Year | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | |||
| Target health problems | Hypertension | Systolic blood pressure | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Diastolic blood pressure | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||
| Diabetes mellitus | Fasting blood glucose | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |
| Dyslipidaemia | Total cholesterol | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |
| Triglyceride | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||||||
| HDL (high densitiy lipoprotein) cholesterol | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||||||
| LDL (low density lipoprotein) cholesterol | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||||||
| Anaemia | Haemoglobin | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |
| Kidney/urinary disease | Urine glucose | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||||||
| Urine blood | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||||
| Urine pH | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||||
| Urine protein | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||
| Chronic kidney disease | Creatinine | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||||||||
| Liver disease | AST (aspartate transaminase)[SGOT (serum glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase)] | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |
| ALT (alanine transaminase)[SGPT (serum glutamic-pyruvic transaminase)} | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||
| r-GTP (gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase) | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||
| Frailty/lower leg weakness | Neurological examination for lower leg for subjects at age 40 or 66 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||||||
| Osteoporosis | Bone density for subjects at age 40 or 66 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||||||
| Periodontal diseases | Dental examination | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |
| Cognitive impairment, depression | Mental health screening | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||||||
| Common and uncommon diseases | Disease diagnosis per ICD-10 codes; Operation and procedure history, Medication history (generic name code, dose, duration of prescription, and material codes) | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |
| All-cause and cause- specific deaths | Vital statistics including dates and causes of deaths | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |
| Risk factors | Cigarette smoking | Cigarette smoking status | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Daily smoking dose | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||||
| Past daily smoking dose | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||||||
| Current daily smoking dose | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||||||
| Smoking duration | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||||
| Smoking duration (ex-smoker) | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||||||
| Smoking duration (current smoker) | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||||||
| Alcohol | Drinking frequency | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||||||
| Days of drinking per week | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||||||
| Amount of drinking per count | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||||
| Amount of drinking per day | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||||||
| Obesity | Body mass index | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |
| Waist circumference | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||||||||
| Physical activity | Days of activity per week | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||||||
| Days of vigorous activity per week | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||||||
| Days of moderate activity per week | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||||||
| Days of mild activity per week | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||||||
| Dental caries, etc | Dental examination | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |
| Medical history and family history | Medical history | Hypertension, diabetes mellitus, dyslipidaemia, pulmonary tuberculosis, stroke, ischaemic heart disease, etc | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Family history | Hypertension, diabetes mellitus, stroke, ischaemic heart disease etc | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |
| Healthcare usage | Date of visit, types of medical institutions (clinics/hospitals/tertiary hospitals/public health centres), types of visit (inpatient/outpatient/emergency/intensive care), length of stay, medical cost (insurer/patient) | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |
| Healthcare provider | Location, type of hospitals, no of beds, medical equipment, human resources, specialties of physicians | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |
| Socioeconomic and demographic factors | Age, sex, age, residential area, insurance type (the employee insured, the self-employed insured, dependents, medical aid), monthly insurance contributions (a proxy for income), types and grades of disabilities | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
Findings to date
As the NHIS-HEALS was launched in December 2015, no noteworthy studies have yet been published. However, several studies using the health screening and healthcare usage database of the NHID have been published. Studies have examined the associations of body mass index with cancer risk8 and mortality,9 glucose levels with cancer risk10 and hospitalisation,11 smoking with cancer12 13 and diabetes mellitus,14 physical activities with body mass index15 and cholesterol levels with cancer risk.16 These research results have had positive impacts on health promotion by raising awareness of various public health issues, with an example being the lawsuit against the tobacco industry by the NHIS.17 The NHIS-HEALS will provide additional strong evidence regarding the issues that were assessed in previous studies using the NHID by including the cause of death, unlike the NHID.
We herein present the basic statistics of NHIS-HEALS for future data users. We calculated the prevalence rates of various conditions, the incidence density of those conditions, healthcare usage rates and mortality. The rates were age-standardised using the census population of Statistics Korea in 2005 and the world standard population.18 The rates that were standardised using the world standard are presented below.
Prevalence rates for specific health problems identified from the health screening database at baseline (2002–2003) are presented in table 3. The age-standardised prevalence of anaemia in the NHIS-HEALS was 9.8%, with a higher rate in women (15.5%) than men (5.9%) (p<0.001). The age-standardised prevalence of diabetes mellitus was 8.4%, while the age-standardised prevalence of hypertension in the NHIS-HEALS was 36.1%. The prevalence of diabetes and hypertension was higher in men than women (p<0.001). The age-standardised prevalence of obesity (body mass index of 30 kg/m2 or greater) in NHIS-HEALS was 2.7%, while the prevalence of overweight (body mass index of 25 kg/m2 or greater, but less than 30 kg/m2) was 31.0%. The age-standardised prevalence of hypercholesterolaemia in the NHIS-HEALS was 14.3%; the rate was higher in women (16.0%) than men (12.4%) (p<0.001). The age-standardised prevalence of abnormal urine protein tests was 2.0%, and the rate was the same (2.0%) in both sexes. When we compared these results with those of the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey for participants aged 40 or over,19 generally similar levels of prevalence of anaemia, diabetes, hypertension, obesity and hypercholesterolaemia were found.
Table 3.
Crude and age-standardised (with the 2005 Korean census and world standard populations as references) prevalence rates (%) for specific health problems in the health screening database of the National Health Insurance Service-National Health Screening Cohort database at baseline, 2002–2003
| All | Men | Women | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cohort n | Crude rates | Age-standardised rates | Cohort n | Crude rates | Age-standardised rates | Cohort n | Crude rates | Age-standardised rates | ||||
| Census | WHO | Census | WHO | Census | WHO | |||||||
| Anaemia* | 514 256 | 9.2 | 9.8 | 9.8 | 278 866 | 4.4 | 5.6 | 5.9 | 235 390 | 15.6 | 15.9 | 15.5 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 514 190 | 7.9 | 8.2 | 8.4 | 278 826 | 9.0 | 9.4 | 9.6 | 235 364 | 6.2 | 6.4 | 6.6 |
| Prediabetes† | 23.9 | 23.8 | 23.9 | 26.0 | 25.9 | 25.9 | 20.8 | 20.7 | 20.9 | |||
| Hypertension | 514 581 | 34.4 | 35.6 | 36.1 | 278 989 | 38.0 | 39.1 | 39.4 | 235 592 | 29.8 | 30.3 | 31.0 |
| High-normal‡ | 17.0 | 16.9 | 16.8 | 17.8 | 17.8 | 17.8 | 15.7 | 15.5 | 15.6 | |||
| Abnormal liver function test§ | 514 286 | 6.2 | 5.8 | 5.8 | 278 866 | 5.7 | 5.3 | 5.1 | 235 420 | 6.5 | 6.3 | 6.4 |
| Obesity | 514 350 | 2.9 | 2.7 | 2.7 | 278 901 | 2.1 | 1.9 | 1.9 | 235 449 | 3.7 | 3.6 | 3.6 |
| Overweight¶ | 32.1 | 31.2 | 31.0 | 33.1 | 31.4 | 31.0 | 30.6 | 29.8 | 30.1 | |||
| Hypercholesterolaemia** | 513 887 | 14.3 | 14.2 | 14.3 | 278 681 | 13.0 | 12.5 | 12.4 | 235 206 | 15.8 | 15.6 | 16.0 |
| Abnormal urine blood†† | 513 046 | 5.9 | 6.0 | 6.1 | 278 228 | 3.2 | 3.4 | 3.4 | 234 818 | 9.3 | 9.3 | 9.4 |
| Abnormal urine protein‡‡ | 513 095 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 278 252 | 1.9 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 234 843 | 1.9 | 2.0 | 2.0 |
The incidence density for specific health problems based on information from the health screening database in 2005–2013 is presented in table 4. To identify incident cases, we excluded patients who were previously diagnosed in the first 3 years (2002–2004) of the study period, because the data did not include the baseline information (participants’ screening and healthcare usage records before 2002). With reference to previous studies,20–22 the exclusion period was set as the first 2 years, starting in 2002 (2002–2003) or 2003 (2003–2004). The incidence density was highest for hypertension (4.7%), followed by anaemia (2.9%), hypercholesterolaemia (2.6%), abnormal urine blood (2.3%) and diabetes mellitus (1.7%).
Table 4.
Crude and age-standardised (with the 2005 Korean census and world standard populations as references) incidence density (per 100 person-years) for specific health problems in the health screening database of the National Health Insurance Service-National Health Screening Cohort database, 2005–2013
| All | Men | Women | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cohort n | Crude rates | Age-standardised rates | Cohort n | Crude rates | Age-standardised rates | Cohort n | Crude rates | Age-standardised rates | ||||
| Census | WHO | Census | WHO | Census | WHO | |||||||
| Incidence density (2005–2013) | ||||||||||||
| Anaemia* | 450 207 | 2.6 | 2.9 | 2.9 | 259 787 | 1.9 | 2.3 | 2.4 | 190 420 | 3.7 | 3.8 | 3.8 |
| Diabetes mellitus† | 461 760 | 1.7 | 1.7 | 1.7 | 243 937 | 2.1 | 2.1 | 2.1 | 217 823 | 1.2 | 1.3 | 1.3 |
| Hypertension‡ | 299 857 | 4.1 | 4.6 | 4.7 | 146 050 | 4.4 | 4.8 | 4.9 | 153 807 | 3.8 | 4.4 | 4.5 |
| Abnormal liver function test§ | 471 917 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 1.3 | 255 924 | 1.1 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 215 993 | 1.8 | 1.8 | 1.8 |
| Obesity¶ | 496 720 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 270 970 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 225 750 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 |
| Hypercholesterolaemia ** | 420 838 | 2.7 | 2.6 | 2.6 | 230 116 | 2.0 | 1.9 | 1.9 | 190 722 | 3.4 | 3.4 | 3.4 |
| Abnormal urine blood †† | 471 226 | 2.4 | 2.3 | 2.3 | 264 380 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 206 846 | 3.7 | 3.6 | 3.6 |
| Abnormal urine protein‡‡ | 499 428 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 269 992 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 229 436 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.7 |
The healthcare usage rates of 10 major diseases at baseline based on the healthcare usage database are presented in online supplementary table 3. The rates were highest for acute upper respiratory infections and influenza (46.5%), followed by dyspepsia and other diseases of the stomach and duodenum (29.7%) and other diseases of the eye and adnexa (22.3%).
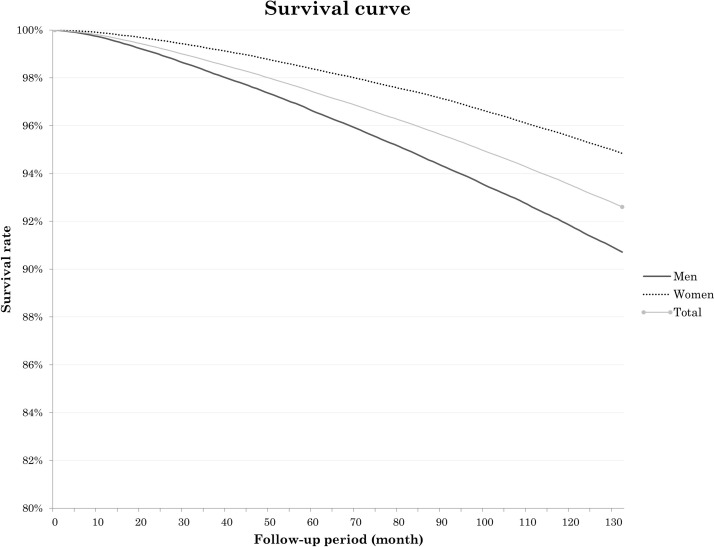
The mortality rates of the cohort population are presented in table 5, and survival curve of participants is presented in figure 1. We calculated mortality rates using the entire sample data of NHIS-HEALS from 2003 to 2013. The age-standardised (defined with reference to the Korean census population) mortality rate for the first 2 years (through 2004) was 463.6 per 100 000 person-years, while the rate for 5 years (through 2007) was 678.3 per 100 000 person-years and the rate for 10 years (through 2012) was 910.2 per 100 000 person-years. In men, the mortality rate was higher than in women (2-year mortality rates of 680.4 per 100 000 person-years for men and 250.8 per 100 000 person-years for women) (p<0.001).
Table 5.
Number of all-cause deaths through 2012 (10 years after baseline) and crude and age-standardised (with the 2005 Korean census and world standard populations as references) mortality rates (per 100 000 person-years) in the National Health Insurance Service-National Health Screening Cohort database
| All-cause | No of cohort population* | All | Men | Women | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No of deaths | Crude rate | Age-standardised mortality rates | No of deaths | Crude rate | Age-standardised mortality rates | No of deaths | Crude rate | Age-standardised mortality rates | |||||
| Census | WHO | Census | WHO | Census | WHO | ||||||||
| Mortality rates (2003–2012)† | |||||||||||||
| 2 year (2004) | 512 802 | 3705 | 360.2 | 442.0 | 463.6 | 2748 | 493.1 | 648.9 | 680.4 | 957 | 203.1 | 238.3 | 250.8 |
| 5 year (2007) | 503 007 | 13 097 | 513.0 | 646.0 | 678.3 | 9 336 | 676.5 | 917.8 | 963.0 | 3761 | 320.6 | 383.9 | 404.8 |
| 10 year (2012) | 483 421 | 33 058 | 657.9 | 865.9 | 910.2 | 22 684 | 839.0 | 1199.9 | 1260.5 | 10 374 | 447.0 | 556.2 | 586.4 |
Figure 1.
Survival curve of participants by sex in the National Health Insurance Service-National Health Screening Cohort database.
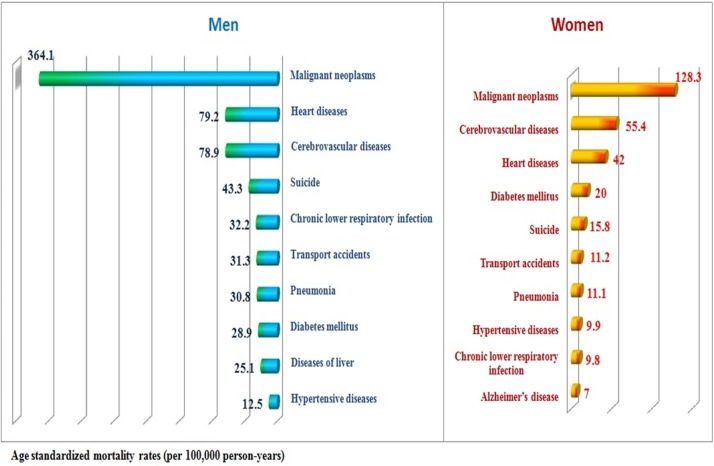
The major causes of death by sex during the follow-up period (2003–2013) are presented in table 6 and figure 2. Causes of death were classified using the list of 56 causes of death of Statistics Korea, which was derived from the list of 80 causes of death for the tabulation of mortality statistics recommended by WHO. The most common cause of death was malignant neoplasm in both sexes (406.6 per 100 000 person-years for men, 140.5 per 100 000 person-years for women). Heart disease was the second most common cause in men (91.0 per 100 000 person-years) and the third most common cause in women (50.8 per 100 000 person-years). Cerebrovascular diseases were the third most common cause in men (89.0 per 100 000 person-years) and the second most common cause in women (64.5 per 100 000 person-years). Suicide was the fourth most common cause overall (31.6 per 100 000 person-years), the fourth most common cause in men (45.6 per 100 000 person-years) and the fifth most common cause in women (16.9 per 100 000 person-years).
Table 6.
Cause-specific death rates for leading causes of death (2003–2013) and age-standardised (with the 2005 Korean census and world standard populations as references) mortality rates (per 100 000 person-years) in the National Health Insurance Service-National Health Screening Cohort database
| Rank | All | Men | Women | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cause of death | Crude rates | Age-standardised rates | Cause of death | Crude rates | Age-standardised rates | Cause of death | Crude rates | Age-standardised rates | ||||
| Census | WHO | Census | WHO | Census | WHO | |||||||
| 1 | Malignant neoplasms | 269.5 | 239.5 | 264.4 | Malignant neoplasms | 365.8 | 364.1 | 406.6 | Malignant neoplasms | 157.6 | 128.3 | 140.5 |
| 2 | Cerebrovascular diseases | 68.8 | 66.9 | 76.5 | Heart diseases | 71.7 | 79.2 | 91.0 | Cerebrovascular diseases | 63.5 | 55.4 | 64.5 |
| 3 | Heart diseases | 59.7 | 60.8 | 70.8 | Cerebrovascular diseases | 73.3 | 78.9 | 89.0 | Heart diseases | 45.7 | 42.0 | 50.8 |
| 4 | Suicide | 32.1 | 30.0 | 31.6 | Suicide | 44.3 | 43.3 | 45.6 | Diabetes mellitus | 22.8 | 20.0 | 23.5 |
| 5 | Diabetes mellitus | 25.6 | 24.5 | 28.1 | Chronic lower respiratory infections | 26.8 | 32.2 | 38.1 | Suicide | 18.0 | 15.8 | 16.9 |
| 6 | Transport accidents | 23.8 | 21.6 | 22.6 | Transport accidents | 33.2 | 31.3 | 32.6 | Transport accidents | 12.8 | 11.2 | 12.0 |
| 7 | Chronic lower respiratory infections | 19.0 | 19.8 | 23.7 | Pneumonia | 19.7 | 30.8 | 39.7 | Pneumonia | 9.8 | 11.1 | 14.5 |
| 8 | Pneumonia | 15.1 | 19.5 | 25.1 | Diabetes mellitus | 28.1 | 28.9 | 32.3 | Hypertensive diseases | 11.2 | 9.9 | 11.8 |
| 9 | Diseases of liver | 18.0 | 15.6 | 16.3 | Diseases of liver | 28.2 | 25.1 | 26.0 | Chronic lower respiratory infections | 10.0 | 9.8 | 12.3 |
| 10 | Hypertensive diseases | 10.0 | 11.0 | 13.5 | Hypertensive diseases | 8.9 | 12.5 | 15.8 | Alzheimer’s disease | 4.6 | 7.0 | 9.9 |
Figure 2.
The major 10 causes of death by sex in the cohort sample of the National Health Insurance Service-National Health Screening Cohort database.
Strengths and limitations
The NHIS-HEALS has several strengths. First, it is a cohort with a large sample size (n=514 866), with a relatively low rate of attrition over more than 10 years of follow-up due to the nature of the national administration data. Second, a questionnaire survey, physical examination, dental health screening and clinical laboratory tests were performed for all cohort members. This database can be used to study the risk factors of non-communicable diseases and dental health problems, which are an important health issue that has not yet been fully investigated. Third, the NHIS-HEALS contains the date and cause of death, which were determined using the national database for cause of death produced by Statistics Korea, which allows investigations such as burden-of-disease studies. Statistics Korea annually reports cause of death statistics, and a previous study reported the accuracy of the cause of death to be 92%.23 Fourth, the NHIS-HEALS contains extensive information on healthcare usage regarding inpatient and outpatient visits to healthcare institutions and medication histories.
The NHIS-HEALS also has weaknesses. The study subjects are slightly younger than the general population of Korea. Variables on health behaviours are limited since those data were obtained from self-reporting in nationwide health screenings. In addition, the disease diagnosis variables in the healthcare claim data might not accurately reflect patients’ medical conditions, but only healthcare usage sensitive to the Korean fee-for-service payment and reimbursement system.
Footnotes
Contributors: SCS, SKP, YHK, HCK, SAS, S-LJ contributed to the conception of this article. YYK, JHP, C-HD, J-SS were involved in manuscript writing and revision. Y-YK, JHP, H-JK, E-JL, SH were involved in data analysis and interpretation. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding: This work was supported by National Health Insurance Service (NHIS) in Korea.
Competing interests: None declared.
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Data sharing statement: The data can be accessed on the National Health Insurance Data Sharing Service homepage of the NHIS (http://nhiss.nhis.or.kr). Applications to use the NHIS-HEALS data will be reviewed by the inquiry committee of research support and, once approved, raw data will be provided to the applicant with a fee. Although, the data are coded in English and numbers, not in Korean (Hangul), use of individual data is allowed only for Korean researchers at the moment, but it would be possible for researchers outside the country to gain access to the data by conducting a joint study with Korean researchers.
References
- 1.National Health Insurance Service (NHIS), Korea. National Health Insurance System of Korea, 2015. http://www.nhis.or.kr/static/html/wbd/g/a/wbdga0704.html (accessed date 13 July 2016).
- 2.Cho B, Lee CM. Current situation of national health screening systems in Korea. J Korean Med Assoc 2010;53:363–70. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Kim HS, Shin DW, Lee WC, et al. . National screening program for transitional ages in Korea: a new screening for strengthening primary prevention and follow-up care. J Korean Med Sci 2012;27:S70–5. 10.3346/jkms.2012.27.S.S70 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.National Health Insurance Service (NHIS). National Health Screening Statistical Yearbook. Seoul: National Health Insurance Service. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Cheol Seong S, Kim YY, Khang YH, et al. . Data Resource Profile: The National Health Information Database of the National Health Insurance Service in South Korea. Int J Epidemiol 2016. dyw253 10.1093/ije/dyw253 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Lee J, Lee JS, Park SH, et al. . Cohort Profile: The National Health Insurance Service-National Sample Cohort (NHIS-NSC), South Korea. Int J Epidemiol 2017;46:dyv319 10.1093/ije/dyv319 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Statistics Korea. http://kosis.kr/eng/statisticsList/statisticsList_01List.jsp?vwcd=MT_ETITLE&parentId=B#SubCont (accessed date 24 July 2016).
- 8.Jee SH, Yun JE, Park EJ, et al. . Body mass index and cancer risk in Korean men and women. Int J Cancer 2008;123:1892–6. 10.1002/ijc.23719 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Kim NH, Lee J, Kim TJ, et al. . Body mass index and mortality in the general population and in subjects with chronic disease in Korea: A nationwide cohort study (2002-2010). PLoS One 2015;10:e0139924 10.1371/journal.pone.0139924 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Jee SH, Ohrr H, Sull JW, et al. . Fasting serum glucose level and cancer risk in Korean men and women. JAMA 2005;293:194–202. 10.1001/jama.293.2.194 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Ki M, Baek S, Yun YD, et al. . Age-related differences in diabetes care outcomes in Korea: a retrospective cohort study. BMC Geriatr 2014;14:111 10.1186/1471-2318-14-111 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Yun YD, Back JH, Ghang H, et al. . Hazard ratio of smoking on lung cancer in Korea according to histological type and gender. Lung 2016;194:281–9. 10.1007/s00408-015-9836-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Jee SH, Samet JM, Ohrr H, et al. . Smoking and cancer risk in Korean men and women. Cancer Causes Control 2004;15:341–8. 10.1023/B:CACO.0000027481.48153.97 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Hur NW, Kim HC, Nam CM, et al. . Smoking cessation and risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus: Korea Medical Insurance Corporation Study. Eur J Cardiovasc Prev Rehabil 2007;14:244–9. 10.1097/01.hjr.0000239474.41379.79 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Lee DC, Park I, Jun TW, et al. . Physical activity and body mass index and their associations with the development of type 2 diabetes in Korean men. Am J Epidemiol 2012;176:43–51. 10.1093/aje/kwr471 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Kitahara CM, Berrington de González A, Freedman ND, et al. . Total cholesterol and cancer risk in a large prospective study in Korea. J Clin Oncol 2011;29:1592–8. 10.1200/JCO.2010.31.5200 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Nam HW. Health insurer to sue tobacco firms. The Korea Times. [newspaper on the internet] 2014. http://www.koreatimes.co.kr/www/news/nation/2016/05/116_150460.html (accessed date 24 July 2016). [Google Scholar]
- 18.Ahmad OB, Boschi-Pinto C, Lopez AD, et al. ; Age standardization of rates: a new WHO standard. vol, 9 Geneva: World Health Organization, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Ministry of Health and Welfare of Korea. Korea Institute for Health and Social Affairs (KIHASA). 2001 National Health and Nutrition Survey - Health Examination -. Seoul: Ministry of Health and Welfare of Korea, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Porepa L, Ray JG, Sanchez-Romeu P, et al. . Newly diagnosed diabetes mellitus as a risk factor for serious liver disease. CMAJ 2010;182:E526–E531. 10.1503/cmaj.092144 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Mazzaglia G, Ambrosioni E, Alacqua M, et al. . Adherence to antihypertensive medications and cardiovascular morbidity among newly diagnosed hypertensive patients. Circulation 2009;120:1598–605. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.108.830299 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Vamos EP, Harris M, Millett C, et al. . Association of systolic and diastolic blood pressure and all cause mortality in people with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes: retrospective cohort study. BMJ 2012;345:e5567 10.1136/bmj.e5567 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Won TY, Kang BS, Th I, et al. . The study of accuracy of death statistics. J Korean Soc Emerg Med 2007;18:256–62. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary material 1
bmjopen-2017-016640supp001.pdf (191.7KB, pdf)