GABAC Receptor Sensitivity Is Modulated by Interaction with MAP1B (original) (raw)
Abstract
GABAC receptors contain ρ subunits and mediate feedback inhibition from retinal amacrine cells to bipolar cells. We previously identified the cytoskeletal protein MAP1B as a ρ1 subunit anchoring protein. Here, we analyze the structural basis and functional significance of the MAP1B-ρ1 interaction. Twelve amino acids at the C terminus of the large intracellular loop of ρ1 (and also ρ2) are sufficient for interaction with MAP1B. Disruption of the MAP1B-ρ interaction in bipolar cells in retinal slices decreased the EC50 of their GABAC receptors, doubling the receptors' current at low GABA concentrations without affecting their maximum current at high concentrations. Thus, anchoring to the cytoskeleton lowers the sensitivity of GABAC receptors and provides a likely site for functional modulation of GABACreceptor-mediated inhibition.
Keywords: GABA, ρ subunit, MAP1B, EC50, retina, bipolar, uptake
Ionotropic γ-aminobutyric acid receptors are divided into two classes, GABAA and GABAC, both of which gate chloride channels but have different properties and expression patterns (Rabow et al., 1995;Lukasiewicz, 1996). GABAC receptors are present mainly in the retina, with lower levels in the brain and spinal cord (Cutting et al., 1991; Feigenspan et al., 1993; Qian and Dowling, 1993;Enz et al., 1995; Ogurusu et al., 1995). They are enriched on retinal bipolar cell axon terminals where they receive GABAergic input from amacrine cells (Tachibana and Kaneko, 1987; Feigenspan et al., 1993). GABAC receptor activation inhibits release of glutamate from bipolar cells onto retinal ganglion and amacrine cells and tunes the dynamic range, temporal resolution, and spatial contrast of retinal responses to visual stimuli (Pan and Lipton, 1995; Dong and Werblin, 1998; Euler and Masland, 2000; Shields et al., 2000).
GABAA receptors are hetero-oligomers, formed from α1–6, β1–3, γ1–3, δ, ε, π, and θ subunits (Rabow et al., 1995; Bonnert et al., 1999), whereas GABACreceptors contain distinct ρ subunits that, when expressed in_Xenopus_ oocytes, exhibit properties similar to those of retinal GABAC receptors (Shimada et al., 1992;Feigenspan et al., 1993; Wang et al., 1994). Three ρ subunits have been cloned that can form functional homo-oligomeric receptors (Cutting et al., 1991; Wang et al., 1994; Shingai et al., 1996) but may also form hetero-oligomers with each other or with some GABAA receptor subunits (Zhang et al., 1995;Hackam et al., 1997; Qian and Ripps, 1999). Clustering of ρ subunits occurs at synapses on bipolar axon terminals (Enz et al., 1996; Koulen et al., 1998). We previously reported an interaction between ρ1 and the microtubule-associated protein MAP1B (heavy chain) as a likely mechanism for anchoring GABAC receptors to the cytoskeleton to maintain this clustered distribution (Hanley et al., 1999).
In addition to interacting with MAP1B, ρ1 subunits can bind to a glycine transporter splice variant, GLYT-1E/F (Hanley et al., 2000). These interactions suggest similarities to the organization at the postsynaptic density of excitatory synapses, where an array of multimolecular interactions is involved in the anchoring and signaling of AMPA, NMDA, and metabotropic receptors (Ziff, 1997; Kim and Huganir, 1999). For NMDA receptors, interaction with the cytoskeletal protein α-actinin-2 tethers the receptor and also modulates its inactivation (Wyszynski et al., 1997; Zhang et al., 1998; Krupp et al., 1999). It is unknown whether proteins anchoring inhibitory receptors also modulate channel properties.
Here, we identify the binding site for MAP1B on ρ1 as a 12 amino acid motif, RI(D/N)THAIDKYSR, at the C-terminal end of the intracellular loop between transmembrane regions three and four. Dialysis of retinal bipolar cells with peptides containing this motif, to competitively disrupt the binding of MAP1B to ρ1, decreases the EC50 of GABAC receptors, doubling the amount of current that they produce at low GABA concentrations. These data show, for the first time for an inhibitory synapse, that binding of receptors to the cytoskeleton controls the functional properties of the receptors.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Antibodies. MAP1B was detected using Anti-MAP1B, clone AA6 (Sigma, St. Louis, MO). ρ1mycwas detected using supernatant from 9E10 hybridoma cells.
Glutathione S_-transferase fusion protein production._ Glutathione _S_-transferase-MAP1B is a fusion of GST with amino acids 460–585 of MAP1B [similar to the fusion with residues 460–565 used by Hanley et al. (1999)]. GST-GLYT-1E/F contains the C-terminal 58 amino acids of GLYT-1E/F [GST-clone 6 ofHanley et al. (2000)]. GST-ρ1 contains the intracellular part of human ρ1 between transmembrane domains 3 and 4 (amino acids 355–454), and GST-ρ2, α1, β3, and γ2 were equivalent constructs. GST fusions of ρ1 truncation mutants were constructed by PCR cloning of cDNA fragments into pGEX-4T3, using primers as follows:_ρ_1355–444, 5′ sense primer: CGTGGATCCGAGTATGCGGCCGTCAAC; 3′ antisense primer: GTGGAATTCTCAGTCGATTCTCATGCT;_ρ_1355–449, 5′ sense primer: CGTGGATCCGAGTATGCGGCCGTCAAC; 3′ antisense primer: GTAGAATTCTCAATCAATGGCGTGGGT; _ρ_2, 5′ sense primer: GTGGGATCCGAGTATGCGGCTGTCAAC; 3′ antisense primer: TATGAATTCTCACCTAGAGTATTTGTC. Subsequent synthesis and purification of GST fusions was performed as described by Smith and Johnson (1988).
COS cell transfections. COS cells were cultured at 37°C, 5% CO2, in DMEM (Life Technologies, Gaithersburg, MD) containing 10% fetal calf serum (Life Technologies), 2 mml-glutamine (Life Technologies), penicillin, and streptomycin. Cells were grown to 50–70% confluency, and transfected by electroporation. Ten milligram cytomegalovirus (CMV) promoter-driven expression constructs were used per transfection.
Affinity purification (pull-down assay). This was performed from retinal extract or from transfected COS cells as described previously (Hanley et al., 1999, 2000). Briefly, retinae or transfected COS cells were lysed in 1% Triton X-100 lysis buffer, and insoluble material was removed by centrifugation. Lysates were incubated with GST fusion proteins bound to glutathione-agarose beads at 4°C with rotation for 2 hr. Beads were then washed three times with lysis buffer and resuspended in SDS-PAGE sample buffer, and bound proteins were detected by Western blotting.
Site-directed mutagenesis. Mutations were made in a CMV promoter-driven ρ1myc construct (full-length ρ with the myc tag EQKLISEEDL between amino acids 4 and 5 of the mature peptide) by the Transformer Site-Directed Mutagenesis Kit (Clontech, Cambridge, UK), using the following mutagenic primers: VSM→KKT: AGCAGCTATAAGAAGACTAGAATCGATACC; RID→FNS: GTGAGCATGTTTAACTCGACCCACGCCATT; THA→VSK: ATGAGAATCGATGTATCAAAAATTGATAAATAC; KY→RL: CACGCCATTGATCGTCTATCCAGGATC.
Peptide competition assays. Peptides were synthesized by Altabioscience and stored at −20°C in DMSO at 40 mg/ml. Pull-down assays were performed as above in a volume of 1 ml, followed by washing beads once in lysis buffer. Beads were resuspended in 400 ml lysis buffer, and peptide was added to varying final concentrations. After rotation at 4°C for 15 min, the beads were washed an additional three times in lysis buffer and then resuspended in SDS-PAGE sample buffer, and bound proteins were analyzed by Western blotting. The normal peptide used containing the (rat) binding site amino acids had the sequence X-RINTHAIDKYSR (where X was the antennapedia sequence RQIKIWFQNRRMKWKK, biotinylated at the N terminus; X promotes peptide entry into cells, but this property was not used in the experiments reported here). The peptide with the scrambled version of the binding site had the sequence X-HRTSKINIYRDA. The N-terminally truncated peptide used, THAIDKYSR, did not have the antennapedia sequence added.
Isolated bipolar cells. Approximately one-quarter of an isolated retina from an adult [postnatal day 35 (P35)] rat was incubated at 34°C for 20 min in 2 ml of solution containing (in mm): NaCl 101, KCl 3.7, NaHCO3 25, NaH2PO4 10, Na-pyruvate 1, glucose 15, dl-cysteine 10, plus papain (Sigma P3125, 15 μl/2 ml), then washed four times in extracellular solution and triturated through a Pasteur pipette, before plating into the recording chamber.
Retinal slices. Retinal slices from adult (P35) rats were prepared as described by Werblin (1978) for salamander retina. Briefly, retinal pieces ∼2 mm square were laid on Millipore filter paper, ganglion cell side down; the sclera was gently removed, and the tissue was covered with normal external solution (lacking CoCl2). The retina was then cut into 200-μm-thick slices, each still attached to a strip of Millipore, with a hand-operated razor blade. The slices were rotated through 90°, and the attached Millipore was embedded in lines of Vaseline to hold the slice so that all cell types were visible for patch-clamping using an upright, fixed-stage microscope. ON-bipolar cells were identified, both before whole-cell clamping and after filling with Lucifer yellow from the patch pipette, by the location of their soma in the inner nuclear layer close to the outer plexiform layer, with dendrites ascending to the outer plexiform layer and an axon descending to terminate in the inner part of the inner plexiform layer. Most were probably rod bipolars, or the morphologically similar type 8 and 9 cone ON bipolars in the classification of Euler and Wässle (1998). Experiments were at room temperature (21–25°C).
Electrodes. Electrodes had a resistance of 5–10 MΩ in external solution. The series resistance in whole-cell mode was ∼25 MΩ, giving series resistance voltage errors <3 mV for currents <0.1 nA.
Solutions for electrophysiology. Extracellular solution contained (in mm): NaCl 130, KCl 2.5, MgCl2 2, HEPES 10, glucose 10, CaCl2 2, bicuculline 0.3 (to block GABAA receptors), pH set to 7.4 with NaOH, bubbled with O2. For experiments on slices, CaCl2 was replaced by CoCl2(4 mm) to block synaptic transmission (Euler et al., 1996). Intracellular solution contained (in mm): KCl 135, CaCl2 0.5, Na2EGTA 5, HEPES 10, MgCl2 2, MgATP 2, pH set to 7.2 with KOH, and Lucifer yellow (di-potassium salt) 0.2%. In addition, the solution contained 100 μm of either a peptide including the binding site for MAP1B on ρ1, X-RINTHAIDKYSR, or a peptide containing a scrambled version of the binding site X-HRTSKINIYRDA (see above). In some experiments, the peptidase inhibitors bestatin (10 μm), leupeptin (100 μm), and pepstatin (1 μm) were included to prevent peptide breakdown, with no significant effect on the results.
_Peptide diffusion time to bipolar cell axon terminal.The diffusion constant of the peptides was estimated as_D = 1.07 × 10−10m2/sec by scaling the value for somatostatin (Holladay and Puett, 1976) in proportion to the square root of the ratio of its molecular weight (1638) to that of the peptides used here (3945). For an axon of length L = 50 μm, the diffusion time from the soma to the axon terminal is ∼_L_2/2_D_= 12 sec. Thus, once inside the cell soma, the peptides used should equilibrate through the cell relatively quickly. The time constant for the peptide to equilibrate between the patch pipette and the cell volume is given by τ =_VR_s/(_D_ρ) (Marie and Attwell, 1999), where the cell volume V is ∼850 μm3 (for a 10-μm-diameter soma, 100 μm total length of axon plus dendrites of diameter 2 μm, and a synaptic terminal of diameter 3 μm), the series resistance_R_s is 25 MΩ, and the resistivity of the pipette solution ρ is 0.8 Ωm. With these numbers, τ = 248 sec.
Effect of uptake on GABAC receptor EC50changes. To quantify how uptake reduces the GABA concentration outside bipolar cells in retinal slices, [GABA]o, below the concentration applied in the bulk solution, [GABA]B, we treat a simplified model of the slice in which the bulk solution is separated from the extracellular space by a diffusion barrier of permeability_P_. GABA enters the extracellular space at a rate:
| P([GABA])B−[GABA]0), | Equation 1 |
|---|
and at equilibrium this must equal the rate of uptake into cells:
| U[GABA]0/([GABA]0+KU), | Equation 2 |
|---|
where U and _K_U are the maximum rate and Michaelis-Menten constant of uptake. From Equations 1 and 2:
| [GABA]B=[GABA]0+(U/P)/{1+(KU/[GABA]0)}. | Equation 3 |
|---|
Thus, when the bulk solution [GABA]B is at a value that makes [GABA]o equal the EC50, so a half-maximal current is generated:
| [GABA]B=EC50+(U/P)/{1+(KU/EC50)}. | Equation 4 |
|---|
Because [GABA]o = EC50 = 11 μm (measured in isolated cells in cobalt/zero Ca2+ solution; see Results), when the applied [GABA]B = 40.4 μm (mean EC50 measured for the GABA concentration applied to slices; see Results), and_K_U ∼30 μmfor GAT-1 and GAT-3 in rat (Borden et al., 1994), Equation 4 gives_U_/P = 109.6 μm.
For a 32% reduction (from 40.4 μm) of the [GABA]B generating a half-maximal current, as seen experimentally with the peptide disrupting the MAP1B-ρ interaction (see Results), solving Equation 4 gives an EC50 value of 6.9 μm, i.e., reduced from 11 μm by 37%. Thus, fractional changes in the bulk solution EC50 underestimate fractional changes of the real EC50 by a factor of 32/37 = 0.86, i.e., a 14% underestimate. The presence of uptake therefore has no effect on the conclusion (see Results) that disrupting the ρ-MAP1B interaction approximately doubles the current at low GABA concentrations.
Data analysis
The Hill equation (Eq. 5) was fitted to dose–response data using SigmaPlot. Data are presented as mean ± SEM.
RESULTS
MAP1B binds at the C-terminal end of the ρ1 subunit intracellular domain
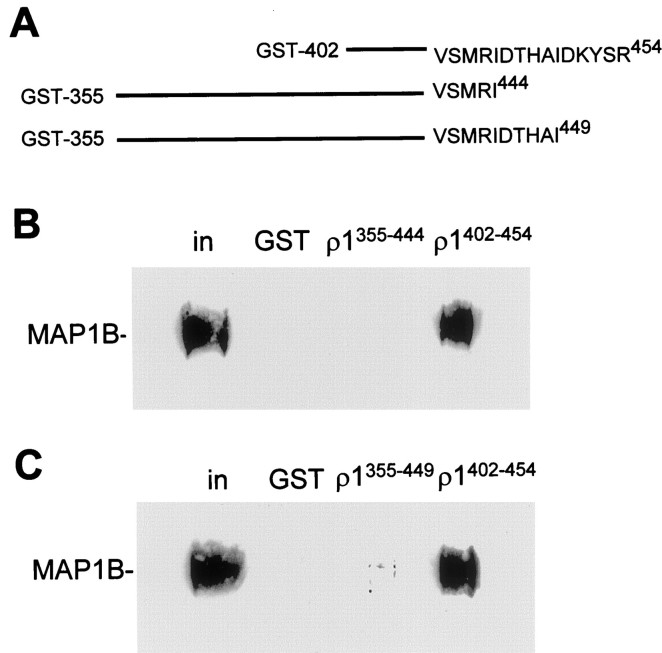
We have previously demonstrated that MAP1B binds to the C-terminal quarter of the TM3–TM4 loop of the human ρ1 subunit, between amino acid residues S434 and R454 (Hanley et al., 1999). To analyze the binding site further, we constructed two C-terminal truncations of the GST fusion protein with the full-length TM3–TM4 loop (GST-ρ1); we have shown previously that the GST fusion with the full loop binds MAP1B (Hanley et al., 1999, their Fig. 2e). These polypeptides, which start at E355 and terminate at I449 or I444, were tested for interaction with MAP1B from retinal extract in pull-down assays. The 10 amino acid truncation (E355-I444) showed no MAP1B binding (Fig.1B), indicating that crucial residues for the interaction are located within the region D445-R454. The five amino acid truncation (E355-I449) showed an extremely low level of MAP1B binding, but it was still higher than the GST control (Fig. 1C). Taken together, these data indicate that the residues required for strong binding to MAP1B are present within the final five amino acids (D450KYSR454) of the intracellular loop and that there are also contributing residues among amino acids D445THAI449.
Fig. 1.
MAP1B binds to the extreme C terminus of the ρ1 TM3–TM4 intracellular loop. Immobilized GST fusion proteins corresponding to C-terminal truncations of the ρ1 intracellular loop were incubated with retinal extract in pull-down assays. MAP1B binding was determined by Western blotting. A, Sequences of the GST fusions with the C-terminal half of ρ1 intracellular loop (ρ1402–454), with a 10 amino acid truncation (355–454) and a five amino acid truncation (355–449).B, Binding of MAP1B to the 10 amino acid truncation fusion protein, compared with binding to the C-terminal half of the intracellular loop ρ1402–454. Other_lanes_ show lack of binding to GST and the input to the assay. in represents the MAP1B present in 1% of the input. C, Same as B but for the five amino acid truncated fusion protein.
Identification of residues required for MAP1B binding on the ρ1 subunit
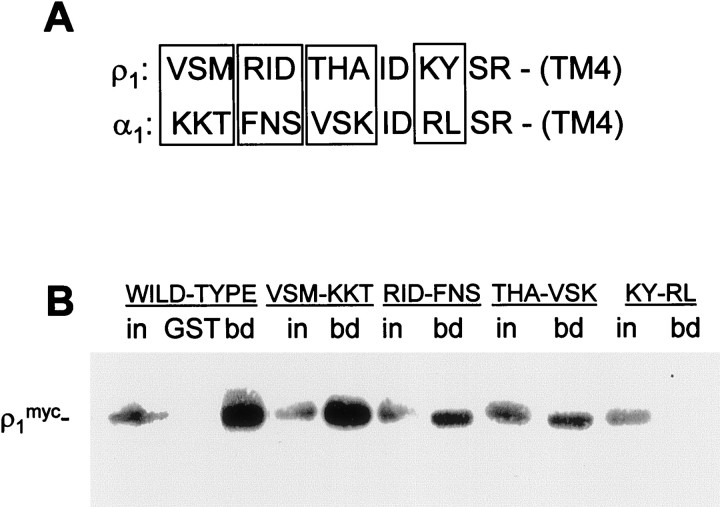
To investigate the importance of specific amino acids in ρ1 for interaction with MAP1B, we performed site-directed mutagenesis of a mammalian expression construct encoding full-length human_myc_-tagged ρ1. COS cells transfected with these constructs were lysed, and binding to GST-MAP1B [containing amino acids 460–585 of MAP1B (Hanley et al., 1999)] was analyzed in pull-down assays. Figure 1 demonstrates that residues at the extreme C terminus of the intracellular ρ1 loop are crucial for the interaction, so we mutated residues in this region adjacent to TM4. We have previously demonstrated that the α1, β3, and γ2 subunits of GABAA receptors do not interact with MAP1B in pull-down assays (Hanley et al., 1999), so we chose to mutate residues in ρ1 to those in α1. Mutations were performed in groups of three residues as shown in Figure2A. Of the six most C-terminal residues of this region, IDKYSR, four are identical in α1 (and also homologous to a range of other ionotropic GABA receptor subunits), so only two of these six amino acids were mutated (KY→RL).
Fig. 2.
Identification of amino acid residues in the ρ1 intracellular loop important for MAP1B binding. Immobilized GST fusion protein corresponding to the ρ1-binding region of MAP1B was incubated with extracts of COS cells transfected with mutants of full-length ρ1myc in pull-down assays. Groups of residues in ρ1 were mutated to the equivalent sequence of the α1 subunit of GABAA receptors. A, Alignment of extreme C-terminal regions of intracellular TM3–TM4 loop of ρ1 and α1 subunits. Amino acid substitutions are shown in boxes; identical amino acids were not mutated. B, Binding of ρ1myc mutants to GST-MAP1B as determined by Western blotting. For each construct, in represents the ρ1myc present in 5% of the input, and_bd_ represents protein bound to GST-MAP1B;GST shows lack of binding of ρ1mycto GST alone.
The most N-terminal mutation, VSM→KKT, did not affect binding of ρ1myc to GST-MAP1B, indicating that these residues are outside the critical binding site. The RID→FNS and THA→VSK mutants both display a reduced interaction with GST-MAP1B, indicating that these residues are important contributors to the interaction. The most C-terminal mutation, KY→RL, abolished binding to undetectable levels. Thus, of the five most C-terminal amino acids shown in Figure 1 to be important for binding to MAP1B, the lysine–tyrosine motif makes a crucial contribution.
Although, theoretically, the mutations and truncations described above could be preventing the binding of MAP1B to ρ1 by altering the conformation of a binding site in a distant part of the ρ1 protein, the results of the experiments described in the next section make this extremely unlikely: a peptide mimicking the C-terminal part of the ρ1 intracellular loop competes with ρ1 for binding to MAP1B.
Block of MAP1B binding to ρ1 by competition with a binding site peptide
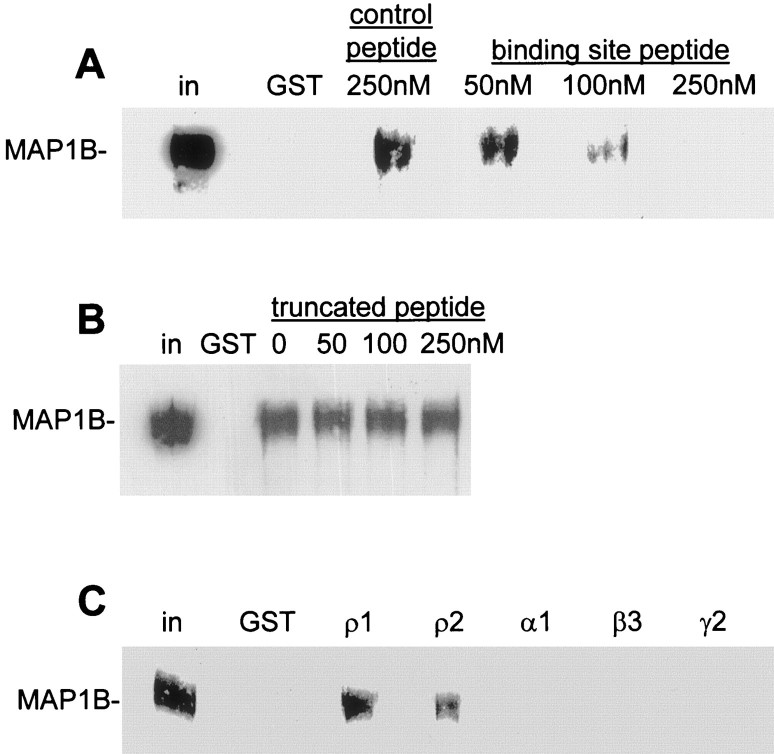
The data above suggest that MAP1B binds to the region RI(D/N)THAIDKYSR in ρ1 (where D/N denotes the human/rat sequence). To further confirm that this sequence represents the binding site, we synthesized a peptide containing this sequence (see Materials and Methods; rat version, as it would be used for biochemical and electrophysiological experiments on rat tissue, as described below). To investigate whether this peptide is sufficient to bind to MAP1B, we performed pull-down assays from rat retinal extract using GST-ρ1. If the peptide is capable of binding to MAP1B, then it will compete with GST-ρ1 for the binding site on MAP1B and result in a reduced level of MAP1B binding to GST-ρ1 beads. The peptide was added to the assay at varying concentrations, and the levels of MAP1B were analyzed by Western blotting (Fig. 3A). Peptide at 50 nm had little effect on the amount of MAP1B bound, but 100 nm significantly reduced the binding, and at 250 nm no binding was detected to GST-ρ1. This competitive inhibition of binding of the human ρ1 sequence to MAP1B using a peptide with the rat ρ1 sequence shows that the one amino acid difference in these sequences (D/N) does not prevent binding. A peptide containing a scrambled version of the binding site, HRTSKINIYRDA, was used as a control (see Materials and Methods); this did not compete for MAP1B binding, even at the highest concentration (250 nm). We also synthesized an N-terminally truncated peptide corresponding to the sequence THAIDKYSR and tested this in a similar pull-down assay (Fig. 3B). This peptide was insufficient to compete for MAP1B binding, demonstrating that, in addition to the KY pair identified above, one or more of the amino acid residues RIN are required for the interaction with MAP1B (interaction of ρ2 with MAP1B, described below, suggests that it is the N and not the RI that is important).
Fig. 3.
Competitive inhibition of MAP1B binding to ρ by peptides. The peptide containing the motif RINTHAIDKYSR (A) but not that containing THAIDKYSR (B) competes for MAP1B binding in retinal pull-down assays. A, Immobilized GST-ρ1 was incubated first with retinal extract, followed by 50–250 nm MAP1B binding site peptide or 250 nm scrambled control peptide. MAP1B bound to beads after this treatment was determined by Western blotting. B, Same as in A, but with truncated binding-site peptide. C, Pull-down assay from retinal lysate using immobilized GST alone or GST fusions of ρ1, ρ2, α1, β3, and γ2 subunit intracellular loops. For all panels, lane labeled GST shows no binding of MAP1B to GST alone, and in represents MAP1B present in 1% of input.
We previously reported that MAP1B does not interact with the α1, β3, or γ2 subunits of GABAA receptors, nor does it interact with the ρ2 subunit of GABACreceptors in the yeast two-hybrid system (Hanley et al., 1999). The sequence of ρ2 at the extreme C terminus of the TM3–TM4 loop is FQNTHAIDKYSR, which is identical to ρ1 with the exception of FQ. To test the possibility that ρ2 can interact with MAP1B, we constructed a GST fusion protein with the TM3–TM4 loop of ρ2 and analyzed binding to MAP1B from retinal extract using a pull-down assay (Fig.3C). MAP1B bound to GST-ρ2 at similar levels to ρ1 in this assay. This apparent discrepancy with the previous negative result for ρ2 in yeast (Hanley et al., 1999) is likely to reflect limitations of the yeast two-hybrid system, because the pull-down assay is performed under more native conditions. Confirming earlier pull-down and immunoprecipitation data (Hanley et al., 1999), in which ρ2 was not tested, MAP1B did not interact with α1, β3, and γ2 (Fig.3C).
The glycine transporter GLYT-1E/F and MAP1B bind to different regions of ρ1
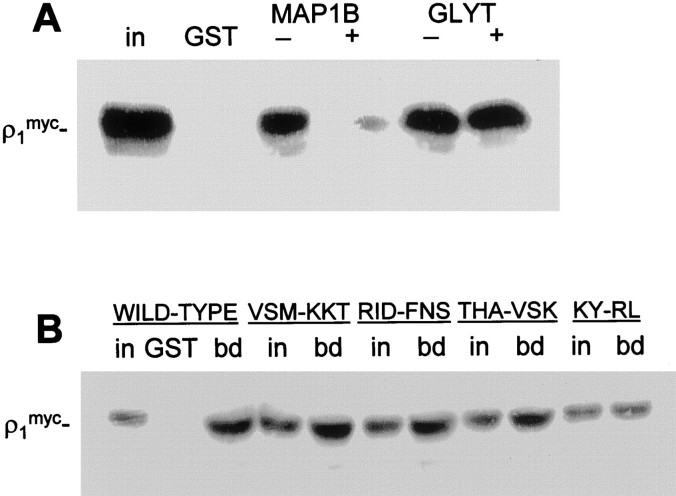
To investigate whether GLYT-1E/F binds to the same region of ρ1 as MAP1B or has a different binding site, we performed assays pulling down myc-tagged ρ1 from COS cells using GST-MAP1B and GST-GLYT-1E/F [containing the 58 most C-terminal amino acids of the bovine transporter (Hanley et al., 2000)]. In each case, the reactions were treated with 250 nm of the peptide corresponding to the MAP1B binding site, or of the scrambled control peptide, and the binding of ρ1 to GST-MAP1B and GST-GLYT-1E/F was determined by Western blotting (Fig.4A). The binding site peptide competed for binding to GST-MAP1B, confirming that this ρ1 sequence is the site of interaction with MAP1B. However, the peptide did not compete for binding to GST-GLYT-1E/F, indicating that the transporter binds to a different region of ρ1. To confirm this result, the MAP1B binding site mutants of ρ1myc were tested for binding to GST-GLYT-1E/F in pull-down assays from transfected COS cell lysate (Fig. 4B). All four mutants show a similar level of binding compared with input, indicating that they bind equally well to GST-GLYT-1E/F and implying that the GLYT-1E/F binding site differs from that for MAP1B.
Fig. 4.
GLYT-1E/F and MAP1B interact with different regions of the ρ1 intracellular loop. A, Immobilized GST-GLYT-1E/F or GST-MAP1B were incubated first with extract of COS cells transfected with ρ1myc, followed by 250 nm of the MAP1B binding site peptide (+) containing RINTHAIDKYSR, or of the peptide containing a scrambled version (−) of the binding site. ρ1myc bound to beads after this treatment was determined by Western blotting. GST shows lack of binding of ρ1myc to GST alone, and_in_ represents the ρ1myc present in 5% of the input. B, Immobilized GST-GLYT-1E/F was incubated with extracts of COS cells transfected with mutants of ρ1myc subunit in pull-down assays. Groups of residues in ρ1 were mutated to the equivalent sequence of α1 subunit of GABAA receptors (Fig. 2). For each construct,in represents the ρ1myc present in 5% of the input, and bd represents protein bound to GST-MAP1B; GST shows lack of binding of ρ1myc to GST alone.
Disrupting the ρ–MAP1B interaction decreases the EC50 of GABAC receptors
To determine whether the interaction of ρ subunits with MAP1B affects the function of GABAC receptors, we whole-cell-clamped rat retinal bipolar cells. Included in the pipette solution, and thus dialyzed into the cells, were peptides (100 μm) including the sequence of the MAP1B-binding domain on ρ1 or a scrambled version of it (see Materials and Methods). The aim, as in the experiments of Figures 3A and4A, was for the binding site peptide to compete with endogenous ρ1 for binding to MAP1B and thus displace MAP1B from ρ1, allowing the effect of MAP1B binding on GABACreceptor-generated currents to be investigated. This strategy has been used successfully previously to disrupt interactions of endogenous proteins with AMPA receptors and glutamate transporters (Nishimune et al., 1998; Marie and Attwell, 1999). Experiments were performed at −60 mV, with the Nernst potential for Cl−near 0 mV, so GABA-evoked currents are inward.
Applying GABA either to isolated bipolar cells or to bipolar cells in retinal slices (see Materials and Methods), in the presence of bicuculline (300 μm) to block GABAAreceptors, generated a current that was blocked by the GABAC receptor blocker (1,2,5,6-tetrahydropyridine-4-yl)methylphosphinic acid (TPMPA) (Fig.5A). Block by TPMPA was only slowly reversible. The response to 30 μm GABA was reduced by 97 ± 2% (n = 4 cells in slices) by 200 μm TPMPA, whereas 2 mm TPMPA reduced the current generated by 300 μm GABA by 93 ± 3% (n = 2).
Fig. 5.
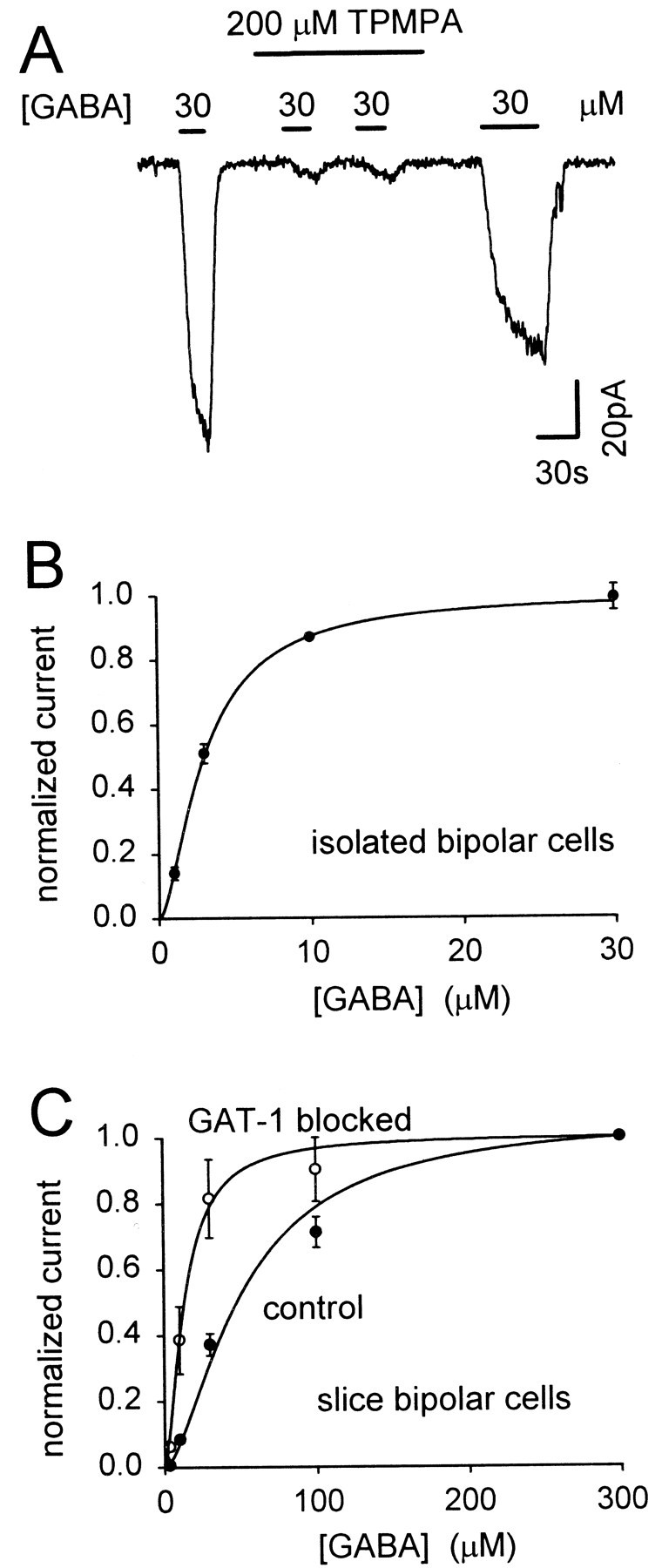
GABAC receptor-evoked currents in retinal bipolar cells with no peptide included in the pipette solution.A, Membrane current of a cell in a slice, clamped to −60 mV, during repeated application of 30 μm GABA in the presence of 300 μm bicuculline to block GABAAreceptors. The GABAC receptor blocker TPMPA (200 μm) greatly reduces the response to GABA. This block was only slowly removed on washing out TPMPA. B, Dose–response curve for the application of GABA to isolated bipolar cells in the presence of 300 μm bicuculline (normalized to the response to 10 μm GABA in each cell and then rescaled to a saturating response of 1). Curve is a Hill equation (Eq.5) with n = 1.6 and a mean EC50 of 3 μm. Data from seven cells. C, Dose–response curves for five bipolar cells in slices, in the presence of 300 μm bicuculline and 4 mmCo2+/0 mm Ca2+, initially in normal conditions (control) and then in the presence of 100 μm SKF89976A (GAT-1 blocked). Hill equations through the data have n = 1.6 and an EC50 of 51 μm in control conditions (mean value was 51.0 ± 3.7 μm) and 13.4 μm with GAT-1 blocked (mean value was 13.4 ± 2.2 μm).
In isolated bipolar cells, GABAC receptors showed an EC50 for GABA of 3.0 ± 0.2 μm (n = 7) (Fig.5B), similar to the 4.2 μm obtained by Feigenspan and Bormann (1994a). However, as found previously (Karschin and Wässle, 1990), whole-cell-clamped isolated cells stayed healthy for only a few minutes, which is not long enough to dialyze into the cell the peptide disrupting the MAP1B-ρ1 interaction. We therefore studied the effect of disrupting this interaction in bipolar cells in retinal slices, which could be clamped for up to 30 min with no deterioration in health. Slice bipolars were also preferred because the cytoskeleton with which the GABAC receptors interact is likely to be less disrupted than in the isolated cells that have been enzyme-treated and triturated. Cobalt chloride (4 mm) was included in the extracellular solution, and calcium was omitted, to block synaptic transmission and ensure that the GABA-evoked currents seen were generated by the recorded cell (Euler et al., 1996).
In bipolar cells in situ in slices, the EC50 for GABA applied in the superfusate was larger than in isolated cells. Dose–response curves for the GABA-evoked current, I, could be fitted approximately by the Hill equation:
| I=Imax[GABA]N/([GABA]N+EC50N), | Equation 5 |
|---|
where _I_max is the maximum current at saturating [GABA], the Hill coefficient, N, was 1.6, and the EC50 varied between cells (range 26–80 μm) with a mean value of 40.4 ± 1.9 μm in 14 cells. Blocking the mainly neuronal GABA transporter GAT-1 with SKF89976A (100 μm) (Borden et al., 1994) decreased the EC50 by fourfold (Fig.5C), making it much closer to the value in isolated cells, showing that the presence of GABA uptake (Johnson et al., 1996), which lowers the GABA concentration around the cells within the slice, is partly responsible for the higher EC50 in slices. The residual difference in EC50, between slice bipolar cells with GAT-1 blocked and isolated bipolar cells, may reflect the use of solution containing cobalt and zero calcium to block synaptic transmission in the slice (Euler et al., 1996): in five isolated bipolar cells this solution increased the EC50 to 11 ± 2 μm [data not shown; cf. Kaneda et al. (1997)]. Mathematical analysis (see Materials and Methods) shows that, although uptake increases the EC50 measured in the slice, the fractional change of EC50 induced by disrupting the MAP1B-ρ1 interaction is similar to that which would be measured if uptake were absent (the fractional change is underestimated by 14%).
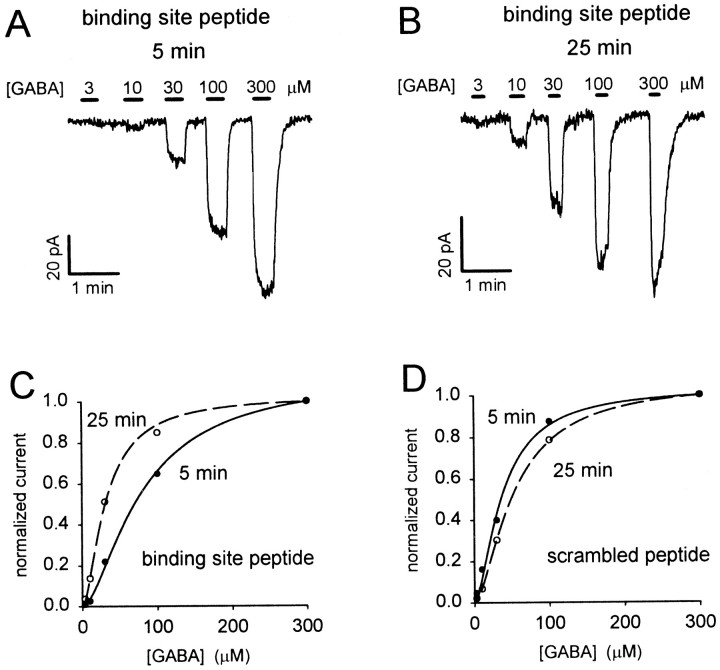
When the peptide mimicking the MAP1B binding site was introduced into slice bipolar cells, the GABA responses changed with time after starting whole-cell clamping, with low GABA doses producing an increased current at later times but the response to high doses changing little (Fig.6A,B). This corresponds to a decrease of EC50 of the dose–response curve (Fig. 6C). By contrast, including the scrambled peptide in the pipette resulted in either no time-dependent change of the GABA responses or a reduction of the fractional response to low [GABA] (Fig. 6D).
Fig. 6.
Effect of dialysis with MAP1B binding site peptide on the GABA dose–response curve in retinal bipolar cells.A, Specimen current responses to different GABA concentrations (in the presence of bicuculline) 5 min after going to whole-cell mode, with the binding site peptide in the pipette.B, Dose–response curve in the same cell as_A_, 25 min after starting whole-cell clamping. Responses in A and B have been scaled to be the same for 300 μm GABA, to compensate for a slight decline with time (Fig. 7A), and to facilitate comparison of the dose dependence of the responses. The relative responses to low doses of GABA are much larger in B than in A.C, Dose–response data from A and_B_, normalized to the current produced by 300 μm GABA, fitted with the Hill equation (Eq. 5) with a Hill coefficient of 1.6. At 5 min the EC50 is 79 μm; at 25 min it is 31 μm.d, Specimen dose–response data as in C, but from a cell clamped with the scrambled peptide in the pipette. Fitting the Hill equation (with a Hill coefficient of 1.6) gives an EC50 of 37 μm at 5 min and 53 μm at 25 min after starting whole-cell clamping.
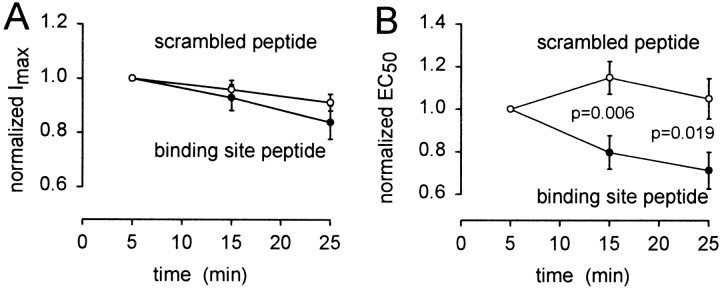
To quantify the change of GABAC receptor properties, we fitted Equation 5 to dose–response data obtained at different times after starting whole-cell clamping, to derive the EC50 and _I_maxfor the receptors. The maximum current showed no significant difference in behavior when the active or scrambled peptides were introduced (Fig.7A). Both showed a slow decrease with time that may reflect an alteration of internal milieu by the non-peptide components of the pipette solution (cf. Feigenspan and Bormann, 1994b). To quantify the change of receptor sensitivity, for each cell we normalized the EC50 values by the EC50 measured at the start of whole-cell recording. This procedure was adopted to remove variability in the initial value of the EC50 (see above) and thus allow us to monitor solely the time-dependent change of EC50 produced by the peptide. Figure7B shows that the binding site peptide led to a decrease of EC50, whereas the scrambled peptide produced no significant change. The data for the two peptides differ significantly after 15 and 25 min recording. Furthermore, this difference is underestimated by our data, because the “initial” value of EC50 by which the subsequent data were normalized was measured 5 min after starting whole-cell clamping, by which time the binding site peptide may already have had some effect. The time constant for filling of the cell by the dialyzed peptides is estimated to be ∼4 min (see Materials and Methods), so the time course of the changes seen with the binding site peptide in Figure 7B may reflect both this filling time and the time needed for competitive displacement of endogenous ρ1 from MAP1B by the peptide.
Fig. 7.
Time-dependent changes in the properties of GABAC receptors induced by competitive removal of MAP1B binding. Maximum current (A) and EC50(B) derived from fitting the Hill equation (Eq.5) to dose–response data measured at different times after starting whole-cell clamping with pipette solution containing the MAP1B binding site peptide (●) or a scrambled version of it (○). Data from each cell were normalized to their values measured 5 min after starting whole-cell clamping, before averaging for these graphs. Data in_A_ are not significantly different for the two peptides. The p values in B are from two-tailed_t_ tests. Eight to thirteen cells contribute to each data point.
The mean data in Figure 7B show that the binding site peptide reduces the EC50 at 25 min after starting whole-cell clamping to 68% of its value with the scrambled peptide, implying a 1.9-fold increase of the current evoked by low doses of GABA (e.g., see specimen data in Fig. 6C). Thus, in the absence of the dialyzing peptide, the interaction with MAP1B roughly halves the size of the current that low doses of GABA generate.
Glycine does not alter GABAC responses
Although the cellular location of GLYT-1E/F transporters is not known, their interaction in vitro with ρ1 suggests that, if these transporters are present in bipolar cells, the rate of glycine uptake could alter GABAC receptor properties (or vice versa). However, we found that applying 300 μm glycine (in the presence of 10 μm strychnine to block glycine receptors) had no effect on the GABAC response of retinal bipolar cells to 30 μm GABA (subsaturating so that we might observe changes in either EC50 or maximum current; five cells; data not shown). No glycine uptake current was detectable in the bipolar cells, so we could not test the effect of GABAC receptor activation on glycine uptake.
DISCUSSION
Our analysis of the binding site for MAP1B on the ρ1 subunits of GABAC receptors suggests that MAP1B binds to the sequence RI(D/N)THAIDKYSR, where D/N denotes the human/rat sequence. Of these residues, the section KY is crucial, because mutating it prevents binding (Fig. 2B) but is not sufficient, because the truncated peptide THAIDKYSR does not prevent binding (Fig.3B) and because mutating THA or RID to the homologous residues in α1 subunits also reduces binding, suggesting that these residues also contribute to binding. Binding occurs whether the residue present at the D/N position is either D or N, because the rat sequence peptide (N) competes well with human ρ1 (D) for binding to MAP1B (Fig. 3A). This may be allowed because although D is charged whereas N is polar, they both have small side chains. The more C-terminal residues ID and SR may contribute to binding but are present in α and β subunits of GABAA receptors, which do not bind MAP1B. The binding site may not extend N-terminally beyond R443 (in the human sequence) because ρ1myc binds efficiently to GST-MAP1B even when V440SM442are mutated to KKT.
The motif RI(D/N)THAIDKYSR in its entirety is not found in any other proteins in the database, but the ρ2 subunit has an equivalent 12 amino acid motif of FQNTHAIDKYSR, which also binds MAP1B in pull-down assays (Fig. 3C). The first two amino acids of these sequences differ, suggesting a minimal binding motif of NTHAIDKYSR. The ρ3 subunit, which was not analyzed, contains the sequence LENNHVIDTYSR. The major GABAA receptor subunits do not show high homology with ρ in this region, the most similar being the β subunits (e.g., β3: LTDVNAIDRWSR). The absence of MAP1B binding to GABAA receptors, which has been demonstrated by pull-down assay and immunoprecipitation from retina (Hanley et al., 1999), is consistent with these differing sequences. GABAA receptors may be anchored to the cytoskeleton through the tubulin binding proteins gephyrin and GABARAP (Essrich et al., 1998; Wang et al., 1999), although direct binding of gephyrin to GABAA receptor subunits has not been shown. The existence of the different tethering molecules for GABAA and GABAC receptors may help to explain their specific location at different synapses and their lack of colocalization in bipolar cells (Koulen et al., 1998). Interestingly, GABARAP shows 31% identity to light-chain-3 of MAP1A and MAP1B, and it binds to γ2 subunits in a C-terminal region of their TM3–TM4 loop at an equivalent position to the MAP1B binding site on ρ1/ρ2.
Dialyzing retinal bipolar cells with a peptide mimicking the MAP1B binding motif, which we have shown to competitively disrupt MAP1B-ρ1 binding (Fig. 3A), led to a 32% decrease in the EC50 of the cells' GABACreceptors, which is sufficient to approximately double the GABA-evoked current at low GABA concentrations (Fig. 6C). At the same time, there was no change of the maximum GABA-evoked current, suggesting that binding of MAP1B to ρ does not alter the number of receptors in the membrane (in contrast to the effect of binding of NSF to AMPA receptors) (Nishimune et al., 1998; Luscher et al., 1999). It is likely that the binding of MAP1B to ρ alters the energetics of the conformation changes that occur when the receptor binds GABA and opens its channel, and in this way MAP1B alters the EC50. A similar phenomenon has been observed for glutamate transporters (Marie and Attwell, 1999). Because MAP1B aggregates ρ1 subunits (Hanley et al., 1999), it is possible that, in addition to changing the EC50, disruption of the MAP1B-ρ interaction may allow GABAC receptors to disperse to a more extrasynaptic location; however, it is likely that the change in EC50 occurs as soon as the ρ subunits detach from MAP1B.
In the retina, the feedback inhibition of bipolar cells by amacrine cells, mediated largely by GABAC receptors, increases the dynamic range of the ganglion cells and produces temporal and spatial shaping of the visual signal, making signals more transient and enhancing edge detection (Dong and Werblin, 1998; Jacobs and Werblin, 1998; Euler and Masland, 2000; Roska et al., 2000; Shields et al., 2000). GABAC receptors produce long duration IPSCs in bipolar cells when amacrine cells release GABA (Lukasiewicz and Shields, 1998; Shields et al., 2000). Lowering the EC50 of GABAC receptors is expected to increase the duration of the synaptic current in the following circumstances. First, if after the peak of the IPSC the extracellular GABA concentration falls slowly compared with the receptor and channel gating kinetics, then if the EC50 is lower the GABA concentration will have to fall to a lower level before the receptors can deactivate, which will take longer. Alternatively, if the GABA concentration falls to zero rapidly (compared with the GABA unbinding/channel gating kinetics), then a lower EC50 is predicted to prolong the IPSC decay provided that the effect of MAP1B on the EC50 is mediated by an alteration of the rate constant for GABA unbinding or for channel opening or closing [but there will be no effect on the IPSC decay if the EC50 is lowered by increasing the GABA binding rate (cf. Jones et al., 1998]. To illustrate this quantitatively, we performed calculations based on the GABACreceptor kinetic scheme of Chang and Weiss (1999) with channel opening occurring when three GABA molecules are bound. Individual rate constants were altered to decrease the EC50 by 32%, as we found [in the Chang and Weiss (1999) model, we used an absolute change from 0.83 μm, when interacting with MAP1B, to 0.56 μm (their standard parameters) in the absence of MAP1B]. Producing this EC50 change by decreasing the GABA unbinding rate, decreasing the channel closing rate, or increasing the channel opening rate led to the IPSC decay time constant being increased by 40, 114, or 89%, respectively.
A prolongation of the IPSC will increase the spatiotemporal filtering mediated by this feedback synapse. In addition, doubling the GABAC receptor-mediated current at the low GABA concentrations likely to be continually present in the retina, where most synapses mediate graded potentials and are tonically active, would produce an extra tonic inhibition of glutamate release from bipolar cell synaptic terminals and thus decrease ganglion cell firing. For such an alteration of information processing to occur, for example during light adaptation, the interaction between MAP1B and ρ subunits would have to be modulated. This could potentially occur by phosphorylation of either of the serine residues in the ρ1 sequence, which are within or flank the MAP1B binding site defined above (S441 and S453 in the human sequence; S441 is a consensus site for PKC phosphorylation).
The MAP1B binding site peptide does not compete for binding of ρ1 to the C-terminal tail of the glycine transporter GLYT-1E/F, and none of the MAP1B binding site mutations in ρ1myc affected binding to GST-GLYT-1E/F (Fig. 4), indicating that the transporter binds to a region on ρ1 distinct from the MAP1B binding site. This suggests that MAP1B and GLYT-1E/F may be able to interact with ρ1 simultaneously, perhaps allowing ρ1 and GLYT-1E/F to be anchored to the cytoskeleton as a complex. The location of GLYT-1E/F in the retina has not yet been determined: previous studies of glycine transporter location have used antibodies raised against transporter C and N termini, which are not present in GLYT-1E/F. Because some bipolar cells accumulate glycine, but not via GLYT-1A or -B (Pow and Hendrickson, 1999), it is possible that GLYT-1E/F is colocalized in bipolar cell synaptic terminals with ρ1 subunits. Application of glycine had no effect on GABAC receptor-mediated currents, implying that if GLYT-1E/F transporters are present, their linkage to ρ1 subunits does not result in transporter activity modulating GABAC receptor properties [it also shows that the potentiation of homomeric ρ1 receptor activity by glycine seen in oocyte expression experiments (Calvo and Miledi, 1995) does not occur for bipolar cell GABAC receptors]. We have been unable to test whether activation of GABACreceptors modulates glycine uptake into bipolar cells, because the glycine uptake present in these cells is too small to generate a detectable current.
In summary, by identifying a motif for MAP1B binding to ρ subunits, we have shown for the first time that inhibitory GABAC receptors have their EC50 modulated by attachment to the cytoskeleton and that they can potentially interact simultaneously with MAP1B and with a glycine transporter. This suggests that the postsynaptic density at inhibitory synapses is likely to comprise as complicated a web of interacting receptors and signaling proteins as occurs at excitatory synapses (Ziff, 1997; Kim and Huganir, 1999).
Footnotes
This work was supported by the Wellcome Trust and the Medical Research Council.
J.G.H and D.B. contributed equally to this work.
Correspondence should be addressed to S. J. Moss, Medical Research Council–Laboratory for Molecular Cell Biology and Department of Pharmacology, University College London, Gower Street, London, WC1E 6BT, UK. E-mail: Steve.Moss@ucl.ac.uk.
REFERENCES
- 1.Bonnert TP, McKernan RM, Farrar S, Le Bourdelles B, Heavens RP, Smith DW, Hewson L, Rigby MR, Sirinathsinghji DJS, Brown N, Wafford KA, Whiting PJ. θ, a novel γ-aminobutyric acid type A receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1999;96:9891–9896. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.17.9891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Borden LA, Dhar TGM, Smith KE, Weinshank RL, Branchek TA, Gluchowski C. Tiagabine, SK&F 89976-A, CI-966 and NNC-711 are selective for the cloned GABA transporter GAT-1. Eur J Pharmacol. 1994;269:219–224. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(94)90089-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Calvo DJ, Miledi R. Activation of GABAρ1 receptors by glycine and β-alanine. NeuroReport. 1995;6:1118–1120. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199505300-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Chang Y, Weiss DS. Channel opening locks agonist onto the GABAC receptor. Nat Neurosci. 1999;2:219–225. doi: 10.1038/6313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Cutting GR, Lu L, O'Hara BF, Kasch LM, Montrose-Rafizadeh C, Donovan DM, Shimada S, Antonarakis SE, Guggino WB, Uhl GR, Kazazian HH., Jr Cloning of the γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) ρ1 cDNA: a GABA receptor subunit highly expressed in the retina. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1991;88:2673–2677. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.7.2673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Dong CJ, Werblin FS. Temporal contrast enhancement via GABAC feedback at bipolar terminals in the tiger salamander retina. J Neurophysiol. 1998;79:2171–2180. doi: 10.1152/jn.1998.79.4.2171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Enz R, Brandstaetter JH, Hartveit E, Wässle H, Bormann J. Expression of GABA receptor ρ1 and ρ2 subunits in the retina and brain of the rat. Eur J Neurosci. 1995;7:1495–1501. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1995.tb01144.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Enz R, Brandstaetter JH, Wässle H, Bormann J. Immunocytochemical localisation of the GABAC receptor ρ subunits in the mammalian retina. J Neurosci. 1996;16:4479–4490. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.16-14-04479.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Essrich C, Lorez M, Benson JA, Fritschy J-M, Luescher B. Postsynaptic clustering of major GABAA receptor subtypes requires the γ2 subunit and gephyrin. Nat Neurosci. 1998;1:563–571. doi: 10.1038/2798. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Euler T, Masland RH. Light-evoked responses of bipolar cells in a mammalian retina. J Neurophysiol. 2000;83:1817–1829. doi: 10.1152/jn.2000.83.4.1817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Euler T, Schneider H, Wässle H. Glutamate responses of bipolar cells in a slice preparation of the rat retina. J Neurosci. 1996;16:2934–2944. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.16-09-02934.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Euler T, Wässle H. Different contributions of GABAA and GABAC receptors to rod and cone bipolar cells in a rat retinal slice preparation. J Neurophysiol. 1998;79:1384–1395. doi: 10.1152/jn.1998.79.3.1384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Feigenspan A, Bormann J. Differential pharmacology of GABAA and GABAC receptors on rat retinal bipolar cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 1994a;288:97–104. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(94)90014-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Feigenspan A, Bormann J. Modulation of GABAC receptors in retinal bipolar cells by protein kinase C. J Physiol (Lond) 1994b;481:325–330. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Feigenspan A, Wässle H, Bormann J. Pharmacology of GABA receptor Cl− channels in rat retinal bipolar cells. Nature. 1993;361:159–161. doi: 10.1038/361159a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hackam AS, Wang T-L, Guggino WB, Cutting GR. The N-terminal domain of human GABA receptor ρ1 subunits contains signals for homooligomeric and heterooligomeric interaction. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:13750–13757. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.21.13750. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Hanley JG, Koulen P, Bedford FK, Gordon-Weeks PR, Moss SJ. The protein MAP1B links GABAC receptors to the cytoskeleton at retinal synapses. Nature. 1999;397:66–69. doi: 10.1038/16258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Hanley JG, Jones EMC, Moss SJ. GABAC receptors interact with a novel splice variant of the glycine transporter, GLYT-1. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:840–846. doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.2.840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Holladay LA, Puett D. Somatostatin conformation: evidence for a stable intramolecular structure from circular dichroism, diffusion, and sedimentation equilibrium. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1976;73:1199–1202. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Jacobs AL, Werblin FS. Spatiotemporal patterns at the retinal output. J Neurophysiol. 1998;80:447–451. doi: 10.1152/jn.1998.80.1.447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Johnson J, Chen TK, Rickman DW, Evans C, Brecha NC. Multiple γ-aminobutyric acid plasma membrane transporters (GAT-1, GAT-2, GAT-3) in the rat retina. J Comp Neurol. 1996;375:212–224. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9861(19961111)375:2<212::AID-CNE3>3.0.CO;2-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Jones MV, Sahara Y, Dzubay JA, Westbrook GL. Defining affinity with the GABAA receptor. J Neurosci. 1998;18:8590–8604. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-21-08590.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Kaneda M, Mochizuki M, Aoki K, Kaneko A. Modulation of GABAC responses by Ca2+ and other divalent cations in horizontal cells of the catfish retina. J Gen Physiol. 1997;110:741–747. doi: 10.1085/jgp.110.6.741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Karschin A, Wässle H. Voltage- and transmitter-gated currents in isolated rod bipolar cells of rat retina. J Neurophysiol. 1990;63:860–876. doi: 10.1152/jn.1990.63.4.860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Kim JH, Huganir RL. Organisation and regulation of proteins at synapses. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1999;11:248–254. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(99)80033-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Koulen P, Brandstätter JH, Enz R, Bormann J, Wässle H. Synaptic clustering of GABAC receptor ρ subunits in the rat retina. Eur J Neurosci. 1998;10:115–127. doi: 10.1046/j.1460-9568.1998.00005.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Krupp JJ, Vissel B, Thomas CG, Heinemann SF, Westbrook GL. Interactions of calmodulin and α-actinin with the NR1 subunit modulate Ca2+-dependent inactivation of NMDA receptors. J Neurosci. 1999;19:1165–1178. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-04-01165.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Lukasiewicz PD. GABAC receptors in the vertebrate retina. Mol Neurobiol. 1996;12:181–194. doi: 10.1007/BF02755587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Lukasiewicz PD, Shields CR. Different combinations of GABAA and GABAC receptors confer different temporal properties to retinal synaptic responses. J Neurophysiol. 1998;79:3157–3167. doi: 10.1152/jn.1998.79.6.3157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Luscher C, Xia H, Beattie EC, Carroll RC, von Zastrow M, Malenka RC, Nicoll RA. Role of AMPA receptor cycling in synaptic transmission and plasticity. Neuron. 1999;24:649–658. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)81119-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Marie H, Attwell D. C terminal interactions modulate the affinity of GLAST glutamate transporters in salamander retinal glial cells. J Physiol (Lond) 1999;520:393–397. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1999.00393.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Nishimune A, Isaac JT, Molnar E, Noel J, Nash SR, Tagaya M, Collingridge GL, Nakanishi S, Henley JM. NSF binding to GluR2 regulates synaptic transmission. Neuron. 1998;21:87–97. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80517-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Ogurusu T, Taira H, Shingai R. Identification of GABAA receptor subunits in rat retina: cloning of the rat GABAA receptor ρ2 cDNA. J Neurochem. 1995;65:964–968. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1995.65030964.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Pan Z-H, Lipton SA. Multiple GABA receptor subtypes mediate inhibition of calcium influx at rat retinal bipolar cell terminals. J Neurosci. 1995;15:2668–2679. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.15-04-02668.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Pow D, Hendrickson AE. Distribution of the glycine transporter glyt-1 in mammalian and non-mammalian retina. Vis Neurosci. 1999;16:231–239. doi: 10.1017/s0952523899162047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Qian H, Dowling JE. Novel GABA responses from rod-driven retinal horizontal cells. Nature. 1993;361:162–164. doi: 10.1038/361162a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Qian H, Ripps H. Response kinetics and pharmacological properties of heteromeric receptors formed by coassembly of GABA rho- and gamma2-subunits. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1999;266:2419–2425. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1999.0941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Rabow LE, Russek SJ, Farb DH. From ion currents to genomic analysis: recent advances in GABAA receptor research. Synapse. 1995;21:189–274. doi: 10.1002/syn.890210302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Roska B, Nemeth E, Orzo L, Werblin FS. Three levels of lateral inhibition: a space–time study of the retina of the tiger salamander. J Neurosci. 2000;20:1941–1951. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-05-01941.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Shields CR, Tran MN, Wong ROL, Lukasiewicz PD. Distinct ionotropic GABA receptors mediate presynaptic and postsynaptic inhibition in retinal bipolar cells. J Neurosci. 2000;20:2673–2682. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-07-02673.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Shimada S, Cutting G, Uhl GR. γ-aminobutyric acid A or C receptor? γ-aminobutyric acid ρ1 receptor RNA induces bicuculline-, barbiturate- and benzodiazepine-insensitive γ-aminobutyric acid responses in Xenopus oocytes. Mol Pharmacol. 1992;41:683–687. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Shingai R, Yanagi K, Fukushima T, Sakata K, Ogurusu T. Functional expression of GABA ρ3 receptors in Xenopus oocytes. Neurosci Res. 1996;26:387–390. doi: 10.1016/s0168-0102(96)01114-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Smith DB, Johnson KS. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988;67:31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Tachibana M, Kaneko A. γ-Aminobutyric acid exerts a local inhibitory action on the axon terminal of bipolar cells: evidence for negative feedback from amacrine cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1987;84:3501–3505. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Wang H, Bedford FK, Brandon NJ, Moss SJ, Olsen RW. GABAA receptor-associated protein links GABAA receptors to the cytoskeleton. Nature. 1999;397:69–72. doi: 10.1038/16264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Wang T-L, Guggino WB, Cutting GR. A novel γ-aminobutyric acid receptor subunit (ρ2) cloned from human retina forms bicuculline-insensitive homooligomeric receptors in Xenopus oocytes. J Neurosci. 1994;14:6524–6531. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-11-06524.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Werblin FS. Transmission along and between rods in the tiger salamander retina. J Physiol (Lond) 1978;280:449–470. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Wyszynski M, Lin J, Rao A, Nigh E, Beggs AH, Craig AM, Sheng M. Competitive binding of α-actinin and calmodulin to the NMDA receptor. Nature. 1997;385:439–442. doi: 10.1038/385439a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Zhang D, Pan Z-H, Zhang X, Brideau AD, Lipton SA. Cloning of a γ-aminobutyric acid type C receptor subunit in rat retina with a methionine residue critical for picrotoxinin channel block. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1995;92:11756–11760. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.25.11756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Zhang D, Ehlers MD, Bernhardt JP, Su CT, Huganir RL. Calmodulin mediates calcium-dependent inactivation of N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors. Neuron. 1998;21:443–453. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80553-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Ziff EB. Enlightening the postsynaptic density. Neuron. 1997;19:1163–1174. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80409-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]