Novel Mechanistic Insights and Potential Therapeutic Impact of TRPC6 in Neurovascular Coupling and Ischemic Stroke (original) (raw)
Abstract
Ischemic stroke is one of the most disabling diseases and a leading cause of death globally. Despite advances in medical care, the global burden of stroke continues to grow, as no effective treatments to limit or reverse ischemic injury to the brain are available. However, recent preclinical findings have revealed the potential role of transient receptor potential cation 6 (TRPC6) channels as endogenous protectors of neuronal tissue. Activating TRPC6 in various cerebral ischemia models has been found to prevent neuronal death, whereas blocking TRPC6 enhances sensitivity to ischemia. Evidence has shown that Ca2+ influx through TRPC6 activates the cAMP (adenosine 3’,5’-cyclic monophosphate) response element-binding protein (CREB), an important transcription factor linked to neuronal survival. Additionally, TRPC6 activation may counter excitotoxic damage resulting from glutamate release by attenuating the activity of N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptors of neurons by posttranslational means. Unresolved though, are the roles of TRPC6 channels in non-neuronal cells, such as astrocytes and endothelial cells. Moreover, TRPC6 channels may have detrimental effects on the blood–brain barrier, although their exact role in neurovascular coupling requires further investigation. This review discusses evidence-based cell-specific aspects of TRPC6 in the brain to assess the potential targets for ischemic stroke management.
Keywords: blood–brain barrier, transient receptor potential cation channels, ischemic stroke, neuroprotection, calcium signaling, cAMP response element-binding protein
1. Introduction
In the USA, someone experiences a stroke every 40 s (https://www.cdc.gov/stroke/facts.htm (accessed on 2 January 2021)) or dies of a stroke every 4 min [1]. More than 795,000 people have a stroke every year, with 77% of these being first-time strokes [1]. In 2018, one of every six deaths in America from cardiovascular disease resulted from a stroke, making it the fifth leading cause of death in the USA. Some 87% of all strokes are ischemic strokes, in which blood flow to the brain is blocked, with the remainder classified as hemorrhagic due to rupture of a weakened blood vessel [1]. Moreover, stroke-related costs involving medicines, health care, and lost employment are staggering, totaling almost USD 50 billion between 2014 and 2015 [1].
Stroke is a leading cause of severe long-term disability, reducing mobility in more than half of the survivors 65 years old and over. Stroke is also the second leading cause of death globally [2]. Although the risk of stroke increases with age, it can occur at any age and in 2009, 34% of those hospitalized for stroke were younger than the age of 65 [3]. Despite advances in medical care, the global burden of stroke continues to grow [4]. Current thrombolytic therapy works for treating ischemic stroke, but only in a limited timeframe. No drugs are approved that enhance recovery, and thus, there is a great need to identify viable pharmacological targets. Furthermore, the current COVID-19 pandemic is directly increasing the incidence of ischemic injury and is worsening the incidence and prevalence of stroke in high-risk populations, as a result—in part—of increases in sedentary lifestyles associated with social distancing [5,6].
Stroke has two major types: hemorrhagic and ischemic, with the latter caused by cerebral embolism or thrombosis [7,8]. Despite varied etiologies for ischemia and hemorrhage, oxygen deprivation to neuronal tissue is a common mechanism. With hemorrhagic stroke, which is generally more severe [9], additional damage results from irritation and swelling from pressure build-up in surrounding tissues due to bleeding and blood breakdown products. In ischemic stroke, there is sudden occlusion of cerebral blood vessels, which leads to the interruption of, or reductions in blood supply to the brain tissue, resulting in extensive neuronal death [10]. This process involves a complex cascade of events at both the macro and microscopic levels, involving impaired vascular autoregulation, disruption of the blood–brain barrier (BBB), calcium overload-associated apoptosis, and neuronal death [11,12,13]. A key step is energy depletion from reduced blood flow, leading to Na+/K+ ATPase (sodium pump) failure, which causes cell membrane depolarization and glutamate release. Na+/K+ ATPase failure results in activation of proteases, kinases, and lipases, which contribute to tissue damage and necrosis. There is also a surge in phospholipase A2 activity that results in arachidonic acid (AA) release and enhanced free radical formation and lipid peroxidation [14,15]. Combined with non-neuronal (i.e., glial) cell activation, the neurovascular unit, consisting of astrocytes, endothelial cells and their BBB forming tight junctions, and pericytes, is impaired [16]. BBB disruption is further enhanced by neuronal glutamine release that activates endothelial N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptor-mediated intracellular Ca2+ influx [17,18]. Glutamine is a major contributor to Ca2+ influx in neurons after ischemic stroke, and thus, also to the associated neurotoxicity.
Ischemic events may additionally activate Ca2+ influx via a non-glutamate pathway, including via transient receptor potential cation/canonical (TRPC) channels [19,20]. Increased cytosolic Ca2+ with ischemia can induce apoptosis and neuronal death by several means, including activation of calpains [11,19]. TRPC channels have been linked to vasospasm in hemorrhagic stroke [21]. Paradoxically one family member, TRPC6, has been linked to neuroprotection with ischemic stroke. It is reported that activating TRPC6 in a rat model of cerebral ischemia was shown to prevent neuronal death, whereas blocking TRPC6 enhanced sensitivity to ischemia [22]. One mechanism is that in patients treated for acute ischemic stroke, elevated expression levels in the peripheral blood of miR-488 and miR-135b, which were shown to target the TRPC6 gene, were identified as risk factors or associated with disease severity [23,24]. Here, we assess the evidence for and against the beneficial consequence of TRPC6 activation in ischemic stroke, its cell-specific roles in the brain, what is known about the involvement of TRPC6 in neurovascular coupling, and the potential therapeutic options for targeting TRPC6.
2. TRPC6
TRPC is a subfamily of TRP channels that are expressed in many cell types, including neurons [25,26]. These nonselective, cell membrane cation channels consist of seven members, TRPC 1–7, which depolarize cells via Na+ influx and also allow an influx of extracellular Ca2+, so as to regulate downstream cellular responses. Thus, this facilitates metabolism, membrane depolarization, gene expression, cell proliferation, and apoptosis [27]. Although all members are expressed in the brain and can promote nonselective Ca2+ entry, the spatial and temporal expression patterns of each are unclear. Based on structure–function relationships, the TRPC family is grouped into four subsets: TRPC1, TRPC2, TRPC3/6/7 and TRPC4/5. Besides functioning as homotetramers, combinations of different TRPC subunits can form heterotetrameric complexes, which may regulate responses to neuropeptides and neurotransmitters with different properties than homotetrameric TRPC channels [28]. For instance, TRPC6 has high sequence homology with TRPC3 and TRPC7 subunits, and may form a heterotetramer with TRPC3 [29].
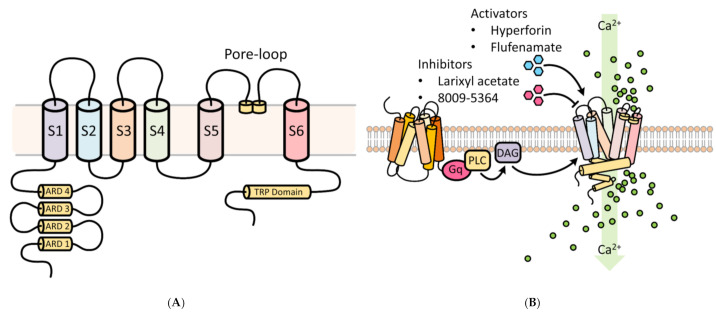
TRPC6 possesses three conserved domains, namely, a pore-loop motif, four NH2 terminal ankyrin repeat domains (ARD), and a COOH-terminal TRP box motif (Figure 1) [30]. The ARD domains are thought to participate in channel heterodimerization and trafficking, whereas the TRP domain may be important for regulating binding with the cytoskeleton and translocation to the cell surface [30]. The pore-loop region is associated with an extracellular selectivity filter and an intracellular gate. Different TRPCs exhibit different Ca2+ and Na+ permeability (P) ratios [31]. The PCa/PNa ratio of TRPC6 is 5, compared to 1.6 for TRPC3 [32,33].
Figure 1.
Functional aspects of transient receptor potential cation 6 (TRPC6) involved in Ca2+ cellular influx. (A) Structural features of the TRPC6 channel. TRPC6 possesses 6 membrane-spanning domains and 3 conserved domains, namely, a pore-loop motif, four NH2 terminal ankyrin repeat domains (ARD), and a COOH-terminal TRP box motif. The ARD domains participate in channel heterodimerization and trafficking, whereas the TRP domain regulates binding with the cytoskeleton and translocation to the cell surface. The pore-loop region (between the S5 and S6) is associated with an extracellular selectivity filter and an intracellular gate and allows for the passage of cations. ARD: ankyrin repeat domain; S1–S6 are the first to sixth transmembrane domains; TRP, transient receptor potential. (B) Regulators of TRPC6 channel activity. Receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) or G protein-coupled receptors (shown) increase TRPC6 activity by stimulating phospholipase C (PLC) to generate diacylglycerol (DAG). Several key experimental activators and inhibitors of TRPC6 are described in Section 6.
TRPC6 activation mediates changes in cytosolic Ca2+, which govern diverse critical cellular functions (Figure 1), such as contraction, apoptosis, neuroprotection, angiogenesis, and cytokine production. TRPC6 and other TRPCs can be activated by phospholipase C (PLC) by numerous stimulations, such as inflammation and ischemia-reperfusion (IR) injury [34]. Through activation of G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) and receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs), PLC can modulate TRPC channel activity by hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate (PIP2) to diacylglycerol (DAG) and inositol trisphosphate (IP3) [35]. DAG activates TRPC3/6/7. IP3 causes Ca2+ release from internal stores, a process that triggers store-operated channel activation and may involve TRPC channels, although exactly how TRPC and store-operated channels interact is unclear [36,37]. Acting in a negative feedback manner, Ca2+ may reduce TRPC channel activity in synergy with protein kinase C (PKC), or via activation of calmodulin [38,39]. Additionally, TRPC3 and possibly TRPC6 may be activated as well in a β-arrestin-1-dependent manner [39,40,41]. These features make TRPC channels potential cellular sensors to respond to environmental changes by regulating intracellular Ca2+.
Structurally, TRPC6 is tethered directly to the cytoskeleton or extracellular matrix [42]. Studies on mouse embryonic fibroblasts and ventricular myocytes have suggested that TRPC6 may mediate the influx of Ca2+ in response to mechanical stress on the cell membrane [43,44]; however, TRPC6, expressed by various mammalian cell lines or in lipid bilayers, does not function as a mechanoreceptor [45,46]. Nonetheless, it may have evolved to discriminate different mechanical stimuli based on its interactions with the cytoskeleton or extracellular components. Therefore, TRPC6 may act as a secondary mechanoreceptor that contributes to the regulation of intracellular Ca2+ or depolarization of the membrane potential through inward Na+ and/or Ca2+ currents.
3. Cell-Specific Roles of TRPC6
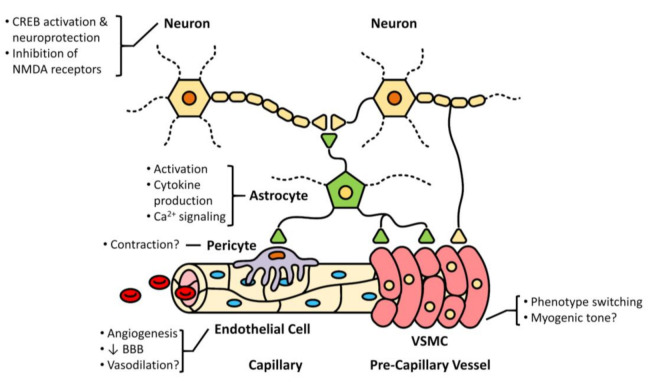
TRPC6 channels are expressed in neurons and other cells of the neurovascular unit (Figure 2). Their cell-specific role and importance to neurovascular coupling, however, requires further investigation.
Figure 2.
TRPC6 and the neurovascular unit regulating homeostatic cerebral blood flow. Depicted are the cellular constituents at the capillary and precapillary levels, as well interactions with neurons and astrocytes. The cell-specific roles of TRPC6 in the context of ischemic stroke, both established and conceptualized, are provided. There is evidence that TRPC6 is expressed in neurons, astrocytes, pericytes, endothelial cells, and vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMC). For more details refer to Section 3.
3.1. Astrocytes
TRPC6 is detected in cultured astrocytes of rats [47,48]. Expression in primary cultures is regulated by glutamate. The NMDA receptor subtypes 2A (NR2A) and 2B (NR2B) are the major components of NR2 subunits of NMDA receptors in the adult brain [49]. NR2A containing NMDA receptors facilitate neuronal death, while blocking NR2B attenuates cell death after ischemic stroke [50,51]. Activation of NR2B-containing NMDA receptors increased TRPC6 degradation, whereas activating NR2A-containing receptors increased expression [48]. TRPC6 is also evident in mouse astrocytes, and the expression increased by treatment with interleukin (IL)-1β [52]. Additionally, it was established that TRPC6 is found in mouse neural stem cells. These undifferentiated precursor cells can differentiate into astrocytes, neurons, oligodendrocytes, and constitutionally express blue/red light-sensitive photoreceptors [53]. This study reported increased proliferation and astrocyte differentiation for mouse neural stem cells, under low power blue light, with TRPC6 being activated by Gq-coupled melanopsin (Opn4). Additionally, TRPC6 expression was detected in astrocytes of the optic nerve head in C57BL/6 mice [54] suggesting potential involvement in glaucoma pathogenesis [55].
Sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) plays a vital role in cell growth, survival, and migration [47,56]. Hisashi et al. demonstrated that S1P increases intracellular Ca2+ concentrations in astrocytes via activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and TRPC6, resulting in the increased expression and release of chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 1 CXCL1 [47]. Beskina et al. demonstrated that TRPC6 is involved in IL-1β-induced Ca2+ signaling in mouse astrocytes. In this study, the expression of TRPC6 was increased in cortical astrocytes of mice treated with IL-1β, while receptor-operated Ca2+ entry was reduced with the knockout (KO) of the Trpc6 gene [52]. The authors suggested that disruption of Ca2+ homeostasis in astrocytes by chronic IL-1β treatment, due to increased TRPC6 activity, might ultimately lead to neurodegenerative diseases.
3.2. Neurons
TRPC6 is expressed in many different brain regions, such as the cortex, hippocampus, cerebellum, basal ganglia, thalamus, hypothalamus, and dorsal root ganglia [57]. Numerous studies have documented that the expression of TRPC6 in primary cultured neurons or neuronal cell lines is protective under various stress conditions [48,58,59,60,61,62].
Ca2+ is a ubiquitous second messenger that affects neuron proliferation and survival in brain development. Ca2+ signals also influence differentiation, dendrite morphology, and axon guidance through actions on cytoskeletal dynamics and cell adhesion [63]. Each neuron expresses a unique set of Ca2+-permeable channels, which allows for the generation of intracellular Ca2+ signals of a particular time course, amplitude, and location [64]. TRPC-meditated Ca2+ influx is involved in nerve-growth-cone guidance, synapse formation, synaptic transmission, neuronal survival, and sensory transduction, downstream of RTKs or GPCRs that are expressed by the neuron [65]. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) is a pro-survival neuronal peptide that is important during brain development. BDNF binds to the receptor tropomyosin receptor kinase B (TrkB), to activate the protein kinase B (Akt) and adenosine 3’,5’-cyclic monophosphate (cAMP) response element-binding protein (CREB) pathways, to promote survival [66]. Downregulation of TRPC6 prevents the protective effect of BDNF on granule cells, leading to apoptosis [67]. Ca2+ influx through TRPC6 activates Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase (CaMK) and MAPK to phosphorylate CREB, an important transcription factor, leading to neuronal survival [63].
3.3. Endothelial Cells
TRPC6 is differentially expressed in endothelial cells from different vascular beds and participates in a diverse range of endothelium-related functions, such as control of vascular tone, regulation of vascular permeability, angiogenesis and remodeling, and apoptosis. In the brain vasculature, TRPC6 is found in mouse microvascular endothelial cells and human cerebral artery endothelial cells [68,69,70].
One of the most crucial functions of the endothelium is maintaining BBB integrity. Several studies have implicated TRPC6 as essential in the regulation of endothelial permeability. Singh et al. reported that Gαq activation of TRPC6 induced Ca2+ entry and activation of Ras homolog family member A (RhoA), which resulted in myosin light chain-dependent endothelial cell shape changes and increased gap formation between endothelial cells [71]. The net effect was the increased permeability of endothelial monolayers. One pathological outcome is lung edema after ischemic-reperfusion injury from TRPC6 recruitment to caveolae of endothelial cells in rats and mice, thereby permitting Ca2+ influx [72,73]. Additionally, Cheng et al. reported that heteromeric TRPC6 is involved in vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-induced Ca2+ influx in human microvascular endothelial cells [74]. This group subsequently demonstrated that VEGF-induced extracellular Ca2+ entry, proliferation, and tube formation are attenuated in human microvascular endothelial cells that overexpress a dominant-negative TRPC6 mutant [75]. Further research is needed to establish what role, if any, TRPC6 plays in endothelial function and BBB integrity in ischemic stroke. Conceivably, activation of TRPC6 in endothelial cells could lead to vasodilation by various means, including the stimulation of nitric oxide synthase 3 (NOS3) [37], but whether this occurs in the cerebral vasculature has not been reported. Excessive cytosolic Ca2+ increases would lead to endothelial cell injury or cell death, leading to loss of gap junctions and increased permeability, thus contributing to cerebral edema and swelling of the brain in ischemic stroke. The increase in cerebrospinal fluid pressure would further restrict blood flow to the penumbra, expanding the infarct in the area at risk.
3.4. Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells (VSMCs)
Activation of TRPC6 in VSMCs of the cerebral vasculature might contribute to the no-reflow phenomena and attenuation of metabolic vasodilation in ischemia. Two recent studies documented that TRPC6 in VSMCs contributes to pressure-induced constriction of cerebral arteries [76,77]. This is an intrinsic characteristic of small arteries and arterioles to constrict in response to increases in intraluminal pressure. Details on exactly how TRPC6 in VSMCs couples to constriction by increasing intracellular Ca2+ are unclear, with some suggestion that it may function, not in the plasma membrane, but rather as a “downstream signal amplifier” mediated via PLC, DAG, cytochrome P450 omega-hydroxylase and 20-Hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid (HETE) [76,78].
4. Neurovascular Coupling in Ischemic Stroke
In ischemic stroke, the dysfunction of the cells in the neurovascular unit and the communication between them characterizes the impaired neurovascular coupling [79,80], which normally acts to compensate for the tissue hypoxia and release of metabolic vasodilators [81,82]. Astrocytes and propagation of hyperpolarization via endothelial cells are a major component of neurovascular coupling, and astrogliosis or reactive astrocytosis is found around cerebral vessels following ischemic stroke [83]. Whether this affects the function of astrocytes to modulate cerebral blood flow via neurovascular coupling is unclear. Ischemic stroke induces cortical spreading depressions (CSDs), which are slowly propagating waves of sustained depolarization of neurons and glial cells. CSDs characterized by injured astrocytes can lead to impaired neurovascular coupling in ischemic stroke [84]. Additionally, in ischemic stroke, astrocytes release 20-HETE to induce vasoconstriction, limiting cerebral blood flow and contributing to the no-reflow phenomena [84,85].
Notably, the vascular response to direct smooth muscle vasodilators is unaffected by ischemic stroke, suggesting that dysfunction in other cell types in cerebral vessels accounts for the impaired neurovascular coupling [86]. However, TRPC6 has been implicated in VSMC phenotype switching under ischemic conditions [87,88]. TRPC6, along with other TRP channels subfamilies, are expressed in pericytes [89]. It is not clear whether capillary contraction in pericytes is directly mediated by TRPC6. However, pericytes regulate capillary diameter to control cerebral blood flow, constrict in response to hypoxia in ischemic stroke and die in rigor. This results in a long-lasting increase in capillary resistance that worsens cerebral ischemic injury after stroke [90]. Loss of pericytes may also exert adverse effects on neurotropic-dependent neuronal survival [84], which could contribute to neurovascular coupling dysfunction. Conversely, cerebral ischemia can induce metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) activation and release in pericytes, which promotes long-term capillary damage and tight-junction breakdown [91]. Taken together, preventing pericyte dysfunction may be a promising therapeutic target for the treatment of ischemic stroke.
Caveolae-mediated transcytosis in endothelial cells, which is suppressed under normal conditions to maintain BBB integrity [92], is activated following ischemic stroke and may contribute to neuroinflammation [84]. On the other hand, the caveolae of arteriolar endothelial cells (aECs) may play an active role in neurovascular coupling and vasodilation by relaying signals from neurons to cerebral smooth muscle cells [93]. Thus, misdirected trafficking of caveolae-dependent endothelial cell communication may underlie the pathology of ischemic stroke. Notably, an intact capillary–arteriole continuum via endothelial cell junctions is a necessary feature of the process, whereby capillary endothelial cells sense increased extracellular K+ from neuronal cell release (due to hypoxia/ischemia) and initiate retrograde hyperpolarization to increase local cerebral blood flow [94]. This process might be impaired by increased Ca2+ entry into endothelial cells via TRPC6 activation.
5. Role of Neuronal TRPC 6 in Ischemic Stroke
TRPC6 is highly expressed in the central nervous system and is important in neuronal development and survival [95]. The overactivation of NMDA receptors occurs after an ischemic stroke due to excessive glutamate-mediated calpain stimulation, which promotes proteolysis of TPRC6 [96]. Degradation of TRPC6 contributes to neuronal death via downregulation of the transcription factor CREB, leading to neuron apoptosis [22,97]. In contrast, inhibition of TRPC6 degradation promotes neuron survival, reduces infarct size, and improves behavioral performance [22]. Furthermore, a TRPC6 activator was found to ameliorate neuronal death in ischemic stroke and this was associated with improved phosphorylated CREB (p-CREB) activity [96]. As noted, the combination treatment of oxiracetam and bone marrow stromal cells increases TRPC6 and p-CREB levels and protects from neuronal death in ischemic stroke [98].
Increased degradation of TRPC6 after ischemic stroke may result in neuronal damage. Activating TRPC6 blocked neuronal death, while inhibiting TRPC6 degradation via a fusion peptide based on the calpain cleavage site (TAT-C6 peptide), reduced infarct size and improved behavioral performance through the CREB signaling pathway [22]. Enhanced TRPC6 expression suppressed NMDA receptor-mediated Ca2+ neurotoxicity, and several molecular probes modulated brain function and promoted neuroprotection and recovery in ischemic stroke by enhancing TRPC6 channel function [20]. Notably, infarct volume in TRPC6 transgenic mice was less than in their wild type littermates, with the transgenic mice exhibiting better behavior performance and lower mortality [20]. It was proposed that TRPC6 might regulate the phosphorylation of NMDA receptors, thereby attenuating their activity.
The immunological pathway is also involved in TRPC6 activity. A study in mice suggests that the deleterious effects of the pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-17A in cerebral IR injury, involves—in part—the degradation of TRPC6 [99]. IL-17A KO or anti-IL-17A monoclonal antibody attenuated activation of calpain 3 days after reperfusion, while recombinant IL-17A increased its activation and IR injury. Brain injury and neurological deficits were primarily abolished by genetic KO of IL-17A, an IL-17A antibody, or a calpain inhibitor. Moreover, the calpain-specific inhibitor increased TRPC6 expression.
On the contrary, TPRC6 expression levels may increase following ischemic stroke, leading to Ca2+ overload that contributes to neuronal death [61]. Indeed, TRPC6 elevation was reported to promote Na+ influx, which induces membrane depolarization and activation of NMDA receptors and Ca2+ influx. In this study, deletion of TPRC6 attenuated Ca2+ overload-induced neurotoxicity in ischemic stroke [61]. Another group also reported that loss of TRPC6, together with TRPC3 and TRPC7, is neuroprotective [100]. KO of TRPC3/6/7 in a mouse cerebral IR model had an anti-apoptotic effect on astrocytes, resulting in reduced infarct volume and neurological deficits [101]. The conflicting results of these studies with a neuroprotective role for TRPC6 may be related to the animal model used, duration of a stroke, and confounding contribution of other TRPC isoforms, as well as potentially to the choice of anesthesia [102]. Initially, TRPC6 may increase Ca2+ in endothelial cells and cause NO generation to compensate for the occlusion and to reduce the size of the area at risk. With prolonged ischemia, the endothelial cells will die, and this compensation will be lost. In neurons, TRPC6 may stimulate protection at first, but may contribute to Ca2+ overload and injury in the long term.
Interestingly, an imbalance in TRPC6 expression (too much or too little) may be associated with neuronal death in ischemic stroke. Alterations in TRPC6 activity following ischemic stroke is likely to alter intracellular Ca2+, that modulates NMDA receptor activity or affects the release of vasoactive mediators, such as nitric oxide (NO) and AA derivatives. Currently unknown, is whether TPRC6 has a role in the abnormalities of neurovascular coupling in ischemic stroke. The activity of neurovascular coupling could be affected under these conditions due to the change in TRPC6 activities. As discussed, activation of TRPC6 in endothelial cells may compromise the integrity of the BBB.
Astrocytes in the ischemic areas are activated after ischemic stroke. These active astrocytes exert both beneficial and harmful effects on neurons in the ischemic area [103]. It is reported that TRPC6 leads to impaired Ca2+ homeostasis and exacerbates mitochondrial dysfunction and endoplasmic reticulum stress so as to promote cellular apoptosis [104], but whether this occurs in activated astrocytes is unclear. There is evidence that astrocytes protect brain tissue after ischemic stroke and reduce the occurrence of disability [22]. They also play an essential role in neural network reconstruction. Studies in mouse models of cerebral ischemia have also shown that astrocytes can transfer into immature neurons after ischemia. Blocking Notch signaling in astrocytes could initiate this process [105]. An earlier study reported that TRPC6 has an essential role in regulating neural stem cell proliferation and differentiation [53]. Unfortunately, whether it is evolved in regulating the transformation of astrocytes into neurons is still unknown.
6. Therapeutic Opportunities
A number of compounds that either activate or inhibit TRPC6 activity have been investigated in biomedical research [106]. Some are discussed here (Figure 1). St John’s wort contains a component, hyperforin, a protonophore, that indirectly activates TRPC6 [107,108] by inhibiting TRPC6 breakdown and attenuates brain damage from transient middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) in rats [96]. Another molecule, the nutritive polyphenol “resveratrol”, when applied for 7 days before MCAO onset, has neuroprotective effects by activating the TRPC6/CREB pathway and decreasing calpain activity [109]. Similarly, neuroprotection in a rat stroke model was observed via TRPC6/CREB using “Neuroprotectin D1” when applied after reperfusion [110]. The predominant constituent of green tea, (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG), introduced immediately after ischemia, demonstrates neuroprotection by decreasing calpain activity and activating TRPC6/CREB via the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MEK)/extracellular pathway [111]. Furthermore, “calycosin”, a major isoflavonoid in Radix Astragali Mongolici, protected against ischemia-induced damage by inhibiting calpain activation and increasing TRPC6 and p-CREB levels [59]. In these studies, the TRPC6-CaMK-CREB pathway is common in mediating the actions of TRPC6 manipulations. Thus, TRPC6/CREB may be crucial in neuronal survival and a potential novel therapeutic target [112,113].
Recent studies have highlighted the benefit of stem cells in stroke recovery [114]. The role of TRPC6 in bone marrow stromal cell (BMSC) transplant was investigated, where the application of BMSCs overexpressing TRPC6 reduced brain injury in a rat IR model [115]. This was associated with synergistic activation and increased levels of TRPC6 in brain tissue, ostensibly due to enhanced production of BDNF, a well-known protective neurotrophic factor. Evidence indicated that decreased neuronal death was due to the TRPC6/CREB pathway and inhibition of calpain activity, a common pathway associated with neuronal survival. A related study with this model demonstrated that BMSCs activate TRPC6 protective p-CREB signaling. Combined therapy of BMSCs with oxiracetam, which inhibited abnormal degradation of TRPC6 by decreasing the activity of calpain, resulted in significantly improved functional restoration and reduced infarct size [98].
The latest research shows potential for new TRPC6 agonists and antagonists in preclinical experiments, specifically related to neuroscience, which may have a useful role in ischemic stroke in the future. Tetrahydrohyperforin (IDN5706), a derivative of hyperforin and TRPC3/6/7 activator, was neuroprotective in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease by negating inhibitory effects of Aβ oligomers in hippocampal tissue [116]. Ladecola et al. showed that IDN5706 might have potential in vascular dementia, where targeting Aβ oligomers may delay cognitive impairment [117].
TRPC6-PAM-C20 is a selective TRPC6 modulator. When tested with another TRPC6 activator OAG (1-oleoyl-1-acetyl-sn-glycerol), there was a synergistic, robust increase in Ca2+ in human platelets [118]. Thus, this agent may have the potential to modulate platelet function before or after ischemic stroke. There is some evidence indicating that TRPC6 plays a critical role in platelet function via receptor-operated calcium (ROC) [119,120] or store-operated calcium (SOC) entry [121]. On the contrary, one report suggests Ca2+ influx via TRPC6 may not have functional relevance in platelet hemostasis [122]. Whether TRPC6 is a potential target for antithrombotic therapy requires further investigation. Another TRPC6 activator, flufenamic acid modulated GABAa receptors, quashing epileptiform activity in the hippocampus [123]. Other TRPC3/6 activators, such as GSK1702934A, transiently increased the perfusion pressure of isolated rat hearts retrogradely perfused via aortic cannulation, an effect blocked by pretreatment with the TRPC3/6 blocker GSK2293017A [124]. OptoBI-1, a derivative of GSK1702934A, is a light-sensitive TRPC3/6/7 agonist that was found to suppress hippocampal action potential firing [125]. Small compound derivatives of piperazine, PPZ1 and PPZ2, are TRPC3/6/7 agonists that can induce BDNF-like neurite growth and neuroprotection in cultured neurons by triggering Ca2+ dependent CREB signaling [126]. Thus, PPZ1 and PPZ2 represent potential agents for post-stroke recovery.
Inhibitors of TRPC6, such as larixyl acetate [127] and GsMTx4 [128], have been shown to have protective actions against traumatic brain injury and myocardial infarction. Synthetic 20-HETE has TRPC6 activation effects, whereas blocking 20-HETE formation with N-hydroxy-N’-(4-n-butyl-2-methylphenyl)formamidine (HET0016) reduced cerebral infarction volume and improved cerebral blood flow in a pediatric-rat pup cardiac asphyxia model [129] and MCAO in adult rats [130]. SAR7334 and the tryptoline derivative 8009-5364 are other highly specific TRPC6 antagonists that diminished acute hypoxia-induced vasoconstriction in the lung [131]. Their activity in the brain is yet to be thoroughly tested but they may be useful during subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH)-related vasoconstriction damage. Similarly, BI 749327, although not investigated in the brain, has a cardio/renal protective effect by reducing fibrosis [132].
So far, preclinical safety tests have not been completed on any of these agents and none have been approved for clinical trials in humans. Thus, their potential clinical efficacy cannot be asserted definitively. However, their potential benefit against damage from cerebral ischemia warrants further investigation.
7. Conclusions and Clinical Perspectives
Stroke care is limited due to the lack of effective primary or good secondary preventative agents that can control the excitotoxic damage that results from ischemic infarction. In addition, there is a definite need for medications that can help in stroke recovery. Various pathways discussed in this review that involve TRPC6 can provide neuroprotection and assist post-stroke recovery. Several small molecules targeting TRPC6 have been shown to demonstrate potential benefits in animal experiments. Many of these molecules have the potential to be translated into human clinical trials. However, there is further need for studies that could help determine the mechanisms underlying these benefits. Additional knowledge on the cell-specific role of TRPC6, utilizing cell-specific KOs of TRPC6, as well as information on the implications of its involvement in neurovascular coupling, is critically needed. Whether targeting TRPC6 alone or as a combination of various TRPC channels will mitigate the harm of stroke and enhance recovery, only time and science will tell.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Mary A. Willis and Parminder Vig for their support and for providing departmental research funds to cover part of the publication fees.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.F., S.S.; writing—original draft preparation, S.S., Y.L., S.W., H.Z., X.F., J.Z., B.Z., Z.W.; writing—review and editing, G.W.B., F.F., R.J.R. and S.S.; visualization, L.F.; funding acquisition, S.S., F.F., R.J.R., Z.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by grants AG050049 (F.F.), AG057842 (F.F.), HL138685 (R.J.R.), DK104184 (R.J.R.), P20GM104357 (F.F., Z.W., R.J.R.) P01 HL51971 (Z.W.), R00DK113280 (Z.W.), from the National Institutes of Health; 20PRE35210043 (S.W.) from the American Heart Association.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Virani S.S., Alonso A., Benjamin E.J., Bittencourt M.S., Callaway C.W., Carson A.P., Chamberlain A.M., Chang A.R., Cheng S., Delling F.N., et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2020 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2020;141:e139–e596. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Lopez A.D., Mathers C.D., Ezzati M., Jamison D.T., Murray C.J. Global and regional burden of disease and risk factors, 2001: Systematic analysis of population health data. Lancet. 2006;367:1747–1757. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(06)68770-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Hall M.J., Levant S., DeFrances C.J. Hospitalization for Stroke in U.S. Hospitals, 1989–2009. Volume 85. US Department of Health and Human Services; Washington, DC, USA: 2012. pp. 1–8. NCHS Data Brief. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Gorelick P.B. The global burden of stroke: Persistent and disabling. Lancet Neurol. 2019;18:417–418. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(19)30030-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Fifi J.T., Mocco J. COVID-19 related stroke in young individuals. Lancet Neurol. 2020;19:713–715. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(20)30272-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Jakobsson J., Malm C., Furberg M., Ekelund U., Svensson M. Physical Activity during the Coronavirus (COVID-19) Pandemic: Prevention of a Decline in Metabolic and Immunological Functions. Front. Sports Act. Living. 2020;2:57. doi: 10.3389/fspor.2020.00057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Grysiewicz R.A., Thomas K., Pandey D.K. Epidemiology of ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke: Incidence, prevalence, mortality, and risk factors. Neurol. Clin. 2008;26:871–895. doi: 10.1016/j.ncl.2008.07.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Kim S.M., Jung J.M., Kim B.J., Lee J.S., Kwon S.U. Cilostazol Mono and Combination Treatments in Ischemic Stroke: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Stroke. 2019;50:3503–3511. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.119.026655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Andersen K.K., Olsen T.S., Dehlendorff C., Kammersgaard L.P. Hemorrhagic and ischemic strokes compared: Stroke severity, mortality, and risk factors. Stroke. 2009;40:2068–2072. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.108.540112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Sekerdag E., Solaroglu I., Gursoy-Ozdemir Y. Cell Death Mechanisms in Stroke and Novel Molecular and Cellular Treatment Options. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2018;16:1396–1415. doi: 10.2174/1570159X16666180302115544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Bano D., Nicotera P. Ca2+ signals and neuronal death in brain ischemia. Stroke. 2007;38(Suppl. 2):674–676. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.0000256294.46009.29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Smith W.S. Pathophysiology of focal cerebral ischemia: A therapeutic perspective. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2004;15:S3–S12. doi: 10.1097/01.RVI.0000108687.75691.0C. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Shekhar S., Liu R., Travis O.K., Roman R.J., Fan F. Cerebral Autoregulation in Hypertension and Ischemic Stroke: A Mini Review. J. Pharm. Sci. Exp. Pharmacol. 2017;2017:21–27. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Durukan A., Tatlisumak T. Acute ischemic stroke: Overview of major experimental rodent models, pathophysiology, and therapy of focal cerebral ischemia. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2007;87:179–197. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2007.04.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Muralikrishna Adibhatla R., Hatcher J.F. Phospholipase A2, reactive oxygen species, and lipid peroxidation in cerebral ischemia. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2006;40:376–387. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2005.08.044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Yang C., Hawkins K.E., Dore S., Candelario-Jalil E. Neuroinflammatory mechanisms of blood-brain barrier damage in ischemic stroke. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2019;316:C135–C153. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00136.2018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Unterberg A.W., Stover J., Kress B., Kiening K.L. Edema and brain trauma. Neuroscience. 2004;129:1021–1029. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2004.06.046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Iadecola C. Regulation of the cerebral microcirculation during neural activity: Is nitric oxide the missing link? Trends Neurosci. 1993;16:206–214. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(93)90156-G. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Huang Q., Wang X., Lin X., Zhang J., You X., Shao A. The Role of Transient Receptor Potential Channels in Blood-Brain Barrier Dysfunction after Ischemic Stroke. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020;131:110647. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Li H., Huang J., Du W., Jia C., Yao H., Wang Y. TRPC6 inhibited NMDA receptor activities and protected neurons from ischemic excitotoxicity. J. Neurochem. 2012;123:1010–1018. doi: 10.1111/jnc.12045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Huang J. TRPC Channels and Stroke. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017;976:61–71. doi: 10.1007/978-94-024-1088-4_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Du W., Huang J., Yao H., Zhou K., Duan B., Wang Y. Inhibition of TRPC6 degradation suppresses ischemic brain damage in rats. J. Clin. Investig. 2010;120:3480–3492. doi: 10.1172/JCI43165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Liang J., Zhang Z. Higher Peripheral Blood MiR-488 Level Predicts Poor Prognosis of Acute Ischemic Stroke. Clin. Lab. 2020;66 doi: 10.7754/Clin.Lab.2020.191230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Yang S., Zhan X., He M., Wang J., Qiu X. miR-135b levels in the peripheral blood serve as a marker associated with acute ischemic stroke. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020;19:3551–3558. doi: 10.3892/etm.2020.8628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Montell C., Birnbaumer L., Flockerzi V., Bindels R.J., Bruford E.A., Caterina M.J., Clapham D.E., Harteneck C., Heller S., Julius D., et al. A unified nomenclature for the superfamily of TRP cation channels. Mol. Cell. 2002;9:229–231. doi: 10.1016/S1097-2765(02)00448-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Dietrich A., Chubanov V., Kalwa H., Rost B.R., Gudermann T. Cation channels of the transient receptor potential superfamily: Their role in physiological and pathophysiological processes of smooth muscle cells. Pharmacol. Ther. 2006;112:744–760. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2006.05.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Gees M., Colsoul B., Nilius B. The role of transient receptor potential cation channels in Ca2+ signaling. Cold Spring Harbor Perspect. Biol. 2010;2:a003962. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a003962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Gualdani R., Gailly P. How TRPC Channels Modulate Hippocampal Function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020;21:3915. doi: 10.3390/ijms21113915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Hirschler-Laszkiewicz I., Tong Q., Conrad K., Zhang W., Flint W.W., Barber A.J., Barber D.L., Cheung J.Y., Miller B.A. TRPC3 activation by erythropoietin is modulated by TRPC6. J. Biol. Chem. 2009;284:4567–4581. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M804734200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Venkatachalam K., Montell C. TRP channels. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2007;76:387–417. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.75.103004.142819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Kamouchi M., Philipp S., Flockerzi V., Wissenbach U., Mamin A., Raeymaekers L., Eggermont J., Droogmans G., Nilius B. Properties of heterologously expressed hTRP3 channels in bovine pulmonary artery endothelial cells. J. Physiol. 1999;518:345–358. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1999.0345p.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Zitt C., Obukhov A.G., Strubing C., Zobel A., Kalkbrenner F., Luckhoff A., Schultz G. Expression of TRPC3 in Chinese hamster ovary cells results in calcium-activated cation currents not related to store depletion. J. Cell Biol. 1997;138:1333–1341. doi: 10.1083/jcb.138.6.1333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Hofmann T., Obukhov A.G., Schaefer M., Harteneck C., Gudermann T., Schultz G. Direct activation of human TRPC6 and TRPC3 channels by diacylglycerol. Nature. 1999;397:259–263. doi: 10.1038/16711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Kelly M.J., Qiu J., Ronnekleiv O.K. TRPCing around the hypothalamus. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2018;51:116–124. doi: 10.1016/j.yfrne.2018.05.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Moran M.M., Xu H., Clapham D.E. TRP ion channels in the nervous system. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2004;14:362–369. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2004.05.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Nilius B., Owsianik G., Voets T., Peters J.A. Transient receptor potential cation channels in disease. Physiol. Rev. 2007;87:165–217. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00021.2006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Thakore P., Earley S. Transient Receptor Potential Channels and Endothelial Cell Calcium Signaling. Compr. Physiol. 2019;9:1249–1277. doi: 10.1002/cphy.c180034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Putney J.W., Tomita T. Phospholipase C signaling and calcium influx. Adv. Biol. Regul. 2012;52:152–164. doi: 10.1016/j.advenzreg.2011.09.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Chen X., Sooch G., Demaree I.S., White F.A., Obukhov A.G. Transient Receptor Potential Canonical (TRPC) Channels: Then and Now. Cells. 2020;9:1983. doi: 10.3390/cells9091983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Chai Z., Chen Y., Wang C. beta-arrestin-1: Bridging GPCRs to active TRP channels. Channels (Austin) 2017;11:357–359. doi: 10.1080/19336950.2017.1324003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Liu C.H., Gong Z., Liang Z.L., Liu Z.X., Yang F., Sun Y.J., Ma M.L., Wang Y.J., Ji C.R., Wang Y.H., et al. Arrestin-biased AT1R agonism induces acute catecholamine secretion through TRPC3 coupling. Nat. Commun. 2017;8:14335. doi: 10.1038/ncomms14335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Patel A., Sharif-Naeini R., Folgering J.R., Bichet D., Duprat F., Honore E. Canonical TRP channels and mechanotransduction: From physiology to disease states. Pflugers Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2010;460:571–581. doi: 10.1007/s00424-010-0847-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Dyachenko V., Husse B., Rueckschloss U., Isenberg G. Mechanical deformation of ventricular myocytes modulates both TRPC6 and Kir2.3 channels. Cell Calcium. 2009;45:38–54. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2008.06.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Lei L., Lu S., Wang Y., Kim T., Mehta D., Wang Y. The role of mechanical tension on lipid raft dependent PDGF-induced TRPC6 activation. Biomaterials. 2014;35:2868–2877. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2013.12.030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Nikolaev Y.A., Cox C.D., Ridone P., Rohde P.R., Cordero-Morales J.F., Vasquez V., Laver D.R., Martinac B. Mammalian TRP ion channels are insensitive to membrane stretch. J. Cell Sci. 2019;132 doi: 10.1242/jcs.238360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Mederos y Schnitzler M., Storch U., Meibers S., Nurwakagari P., Breit A., Essin K., Gollasch M., Gudermann T. Gq-coupled receptors as mechanosensors mediating myogenic vasoconstriction. EMBO J. 2008;27:3092–3103. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2008.233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Shirakawa H., Katsumoto R., Iida S., Miyake T., Higuchi T., Nagashima T., Nagayasu K., Nakagawa T., Kaneko S. Sphingosine-1-phosphate induces Ca2+ signaling and CXCL1 release via TRPC6 channel in astrocytes. Glia. 2017;65:1005–1016. doi: 10.1002/glia.23141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Qu Z., Wang Y., Li X., Wu L., Wang Y. TRPC6 expression in neurons is differentially regulated by NR2A- and NR2B-containing NMDA receptors. J. Neurochem. 2017;143:282–293. doi: 10.1111/jnc.14215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Hardingham G.E., Fukunaga Y., Bading H. Extrasynaptic NMDARs oppose synaptic NMDARs by triggering CREB shut-off and cell death pathways. Nat. Neurosci. 2002;5:405–414. doi: 10.1038/nn835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Chen M., Lu T.J., Chen X.J., Zhou Y., Chen Q., Feng X.Y., Xu L., Duan W.H., Xiong Z.Q. Differential roles of NMDA receptor subtypes in ischemic neuronal cell death and ischemic tolerance. Stroke. 2008;39:3042–3048. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.108.521898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Liu Y., Wong T.P., Aarts M., Rooyakkers A., Liu L., Lai T.W., Wu D.C., Lu J., Tymianski M., Craig A.M., et al. NMDA receptor subunits have differential roles in mediating excitotoxic neuronal death both in vitro and in vivo. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2007;27:2846–2857. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0116-07.2007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Beskina O., Miller A., Mazzocco-Spezzia A., Pulina M.V., Golovina V.A. Mechanisms of interleukin-1beta-induced Ca2+ signals in mouse cortical astrocytes: Roles of store- and receptor-operated Ca2+ entry. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2007;293:C1103–C1111. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00249.2007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Wang M., Xu Z., Liu Q., Sun W., Jiang B., Yang K., Li J., Gong Y., Liu Q., Liu D., et al. Nongenetic optical modulation of neural stem cell proliferation and neuronal/glial differentiation. Biomaterials. 2019;225:119539. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2019.119539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Choi H.J., Sun D., Jakobs T.C. Astrocytes in the optic nerve head express putative mechanosensitive channels. Mol. Vis. 2015;21:749–766. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Fan Q., Huang W.B., Zhang X.L. TRPC6: An underlying target for human glaucoma. Int. J. Ophthalmol. 2012;5:523–526. doi: 10.3980/j.issn.2222-3959.2012.04.23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Belkacemi T., Niermann A., Hofmann L., Wissenbach U., Birnbaumer L., Leidinger P., Backes C., Meese E., Keller A., Bai X., et al. TRPC1- and TRPC3-dependent Ca2+ signaling in mouse cortical astrocytes affects injury-evoked astrogliosis in vivo. Glia. 2017;65:1535–1549. doi: 10.1002/glia.23180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Zeng C., Tian F., Xiao B. TRPC Channels: Prominent Candidates of Underlying Mechanism in Neuropsychiatric Diseases. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016;53:631–647. doi: 10.1007/s12035-014-9004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Zeitler S., Schumacher F., Monti J., Anni D., Guhathakurta D., Kleuser B., Friedland K., Fejtova A., Kornhuber J., Rhein C. Acid Sphingomyelinase Impacts Canonical Transient Receptor Potential Channels 6 (TRPC6) Activity in Primary Neuronal Systems. Cells. 2020;9:2502. doi: 10.3390/cells9112502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Guo C., Ma Y., Ma S., Mu F., Deng J., Duan J., Xiong L., Yin Y., Wang Y., Xi M., et al. The Role of TRPC6 in the Neuroprotection of Calycosin against Cerebral Ischemic Injury. Sci. Rep. 2017;7:3039. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-03404-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Shao Z., Wang L., Liu S., Wang X. Tetramethylpyrazine Protects Neurons from Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation-Induced Death. Med. Sci. Monit. 2017;23:5277–5282. doi: 10.12659/MSM.904554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Chen J., Li Z., Hatcher J.T., Chen Q.H., Chen L., Wurster R.D., Chan S.L., Cheng Z. Deletion of TRPC6 Attenuates NMDA Receptor-Mediated Ca2+ Entry and Ca2+-Induced Neurotoxicity Following Cerebral Ischemia and Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation. Front. Neurosci. 2017;11:138. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2017.00138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.He C., Gao P., Cui Y., Li Q., Li Y., Lu Z., Ma H., Zhao Y., Li L., Sun F., et al. Low-glucose-sensitive TRPC6 dysfunction drives hypoglycemia-induced cognitive impairment in diabetes. Clin. Transl. Med. 2020;10:e205. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Tai Y., Feng S., Du W., Wang Y. Functional roles of TRPC channels in the developing brain. Pflug. Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2009;458:283–289. doi: 10.1007/s00424-008-0618-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Lang S.B., Stein V., Bonhoeffer T., Lohmann C. Endogenous brain-derived neurotrophic factor triggers fast calcium transients at synapses in developing dendrites. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2007;27:1097–1105. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3590-06.2007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Sun Y., Sukumaran P., Bandyopadhyay B.C., Singh B.B. Physiological Function and Characterization of TRPCs in Neurons. Cells. 2014;3:455–475. doi: 10.3390/cells3020455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Dong Y., Pu K., Duan W., Chen H., Chen L., Wang Y. Involvement of Akt/CREB signaling pathways in the protective effect of EPA against interleukin-1beta-induced cytotoxicity and BDNF down-regulation in cultured rat hippocampal neurons. BMC Neurosci. 2018;19:52. doi: 10.1186/s12868-018-0455-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Jia Y., Zhou J., Tai Y., Wang Y. TRPC channels promote cerebellar granule neuron survival. Nat. Neurosci. 2007;10:559–567. doi: 10.1038/nn1870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Brown R.C., Wu L., Hicks K., O’Neil R.G. Regulation of blood-brain barrier permeability by transient receptor potential type C and type v calcium-permeable channels. Microcirculation. 2008;15:359–371. doi: 10.1080/10739680701762656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Yip H., Chan W.Y., Leung P.C., Kwan H.Y., Liu C., Huang Y., Michel V., Yew D.T., Yao X. Expression of TRPC homologs in endothelial cells and smooth muscle layers of human arteries. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2004;122:553–561. doi: 10.1007/s00418-004-0720-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Zuccolo E., Laforenza U., Negri S., Botta L., Berra-Romani R., Faris P., Scarpellino G., Forcaia G., Pellavio G., Sancini G., et al. Muscarinic M5 receptors trigger acetylcholine-induced Ca2+ signals and nitric oxide release in human brain microvascular endothelial cells. J. Cell Physiol. 2019;234:4540–4562. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Singh I., Knezevic N., Ahmmed G.U., Kini V., Malik A.B., Mehta D. Galphaq-TRPC6-mediated Ca2+ entry induces RhoA activation and resultant endothelial cell shape change in response to thrombin. J. Biol. Chem. 2007;282:7833–7843. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M608288200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Samapati R., Yang Y., Yin J., Stoerger C., Arenz C., Dietrich A., Gudermann T., Adam D., Wu S., Freichel M., et al. Lung endothelial Ca2+ and permeability response to platelet-activating factor is mediated by acid sphingomyelinase and transient receptor potential classical 6. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012;185:160–170. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201104-0717OC. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Weissmann N., Sydykov A., Kalwa H., Storch U., Fuchs B., Mederos y Schnitzler M., Brandes R.P., Grimminger F., Meissner M., Freichel M., et al. Activation of TRPC6 channels is essential for lung ischaemia-reperfusion induced oedema in mice. Nat. Commun. 2012;3:649. doi: 10.1038/ncomms1660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Cheng H.W., James A.F., Foster R.R., Hancox J.C., Bates D.O. VEGF activates receptor-operated cation channels in human microvascular endothelial cells. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2006;26:1768–1776. doi: 10.1161/01.ATV.0000231518.86795.0f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Hamdollah Zadeh M.A., Glass C.A., Magnussen A., Hancox J.C., Bates D.O. VEGF-mediated elevated intracellular calcium and angiogenesis in human microvascular endothelial cells in vitro are inhibited by dominant negative TRPC6. Microcirculation. 2008;15:605–614. doi: 10.1080/10739680802220323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Nemeth Z., Hildebrandt E., Ryan M.J., Granger J.P., Drummond H.A. Pressure-induced constriction of the middle cerebral artery is abolished in TrpC6 knockout mice. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2020;319:H42–H50. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00126.2020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Wang Q., Leo M.D., Narayanan D., Kuruvilla K.P., Jaggar J.H. Local coupling of TRPC6 to ANO1/TMEM16A channels in smooth muscle cells amplifies vasoconstriction in cerebral arteries. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2016;310:C1001–C1009. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00092.2016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Inoue R., Jensen L.J., Jian Z., Shi J., Hai L., Lurie A.I., Henriksen F.H., Salomonsson M., Morita H., Kawarabayashi Y., et al. Synergistic activation of vascular TRPC6 channel by receptor and mechanical stimulation via phospholipase C/diacylglycerol and phospholipase A2/omega-hydroxylase/20-HETE pathways. Circ. Res. 2009;104:1399–1409. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.108.193227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Salinet A.S., Silva N.C., Caldas J., de Azevedo D.S., de-Lima-Oliveira M., Nogueira R.C., Conforto A.B., Texeira M.J., Robinson T.G., Panerai R.B., et al. Impaired cerebral autoregulation and neurovascular coupling in middle cerebral artery stroke: Influence of severity? J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 2019;39:2277–2285. doi: 10.1177/0271678X18794835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Lin W.H., Hao Q., Rosengarten B., Leung W.H., Wong K.S. Impaired neurovascular coupling in ischaemic stroke patients with large or small vessel disease. Eur. J. Neurol. 2011;18:731–736. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-1331.2010.03262.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Girouard H., Iadecola C. Neurovascular coupling in the normal brain and in hypertension, stroke, and Alzheimer disease. J. Appl. Physiol. 2006;100:328–335. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00966.2005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Bundo M., Inao S., Nakamura A., Kato T., Ito K., Tadokoro M., Kabeya R., Sugimoto T., Kajita Y., Yoshida J. Changes of Neural Activity Correlate with the Severity of Cortical Ischemia in Patients with Unilateral Major Cerebral Artery Occlusion. Stroke. 2002;33:61–66. doi: 10.1161/hs0102.101816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.McConnell H.L., Li Z., Woltjer R.L., Mishra A. Astrocyte dysfunction and neurovascular impairment in neurological disorders: Correlation or causation? Neurochem. Int. 2019;128:70–84. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2019.04.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Freitas-Andrade M., Raman-Nair J., Lacoste B. Structural and Functional Remodeling of the Brain Vasculature Following Stroke. Front. Physiol. 2020;11:948. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.00948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Attwell D., Buchan A.M., Charpak S., Lauritzen M., Macvicar B.A., Newman E.A. Glial and neuronal control of brain blood flow. Nature. 2010;468:232–243. doi: 10.1038/nature09613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Hu X., De Silva T.M., Chen J., Faraci F.M. Cerebral Vascular Disease and Neurovascular Injury in Ischemic Stroke. Circ. Res. 2017;120:449–471. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.308427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Nishida M., Tanaka T., Mangmool S., Nishiyama K., Nishimura A. Canonical Transient Receptor Potential Channels and Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Plasticity. J. Lipid Atheroscler. 2020;9:124–139. doi: 10.12997/jla.2020.9.1.124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Numaga-Tomita T., Shimauchi T., Oda S., Tanaka T., Nishiyama K., Nishimura A., Birnbaumer L., Mori Y., Nishida M. TRPC6 regulates phenotypic switching of vascular smooth muscle cells through plasma membrane potential-dependent coupling with PTEN. FASEB J. 2019;33:9785–9796. doi: 10.1096/fj.201802811R. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Hariharan A., Weir N., Robertson C., He L., Betsholtz C., Longden T.A. The Ion Channel and GPCR Toolkit of Brain Capillary Pericytes. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2020;14:601324. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2020.601324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Hall C.N., Reynell C., Gesslein B., Hamilton N.B., Mishra A., Sutherland B.A., O’Farrell F.M., Buchan A.M., Lauritzen M., Attwell D. Capillary pericytes regulate cerebral blood flow in health and disease. Nature. 2014;508:55–60. doi: 10.1038/nature13165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Underly R.G., Levy M., Hartmann D.A., Grant R.I., Watson A.N., Shih A.Y. Pericytes as Inducers of Rapid, Matrix Metalloproteinase-9-Dependent Capillary Damage during Ischemia. J. Neurosci. 2017;37:129. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2891-16.2016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Andreone B.J., Chow B.W., Tata A., Lacoste B., Ben-Zvi A., Bullock K., Deik A.A., Ginty D.D., Clish C.B., Gu C. Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability Is Regulated by Lipid Transport-Dependent Suppression of Caveolae-Mediated Transcytosis. Neuron. 2017;94:581–594.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2017.03.043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Chow B.W., Nuñez V., Kaplan L., Granger A.J., Bistrong K., Zucker H.L., Kumar P., Sabatini B.L., Gu C. Caveolae in CNS arterioles mediate neurovascular coupling. Nature. 2020;579:106–110. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2026-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Filosa J.A. Upstream current for a downstream flow. Nat. Neurosci. 2017;20:631–633. doi: 10.1038/nn.4542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Xu P., Xu J., Li Z., Yang Z. Expression of TRPC6 in renal cortex and hippocampus of mouse during postnatal development. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:e38503. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0038503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Lin Y., Zhang J.C., Fu J., Chen F., Wang J., Wu Z.L., Yuan S.Y. Hyperforin attenuates brain damage induced by transient middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) in rats via inhibition of TRPC6 channels degradation. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 2013;33:253–262. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2012.164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Shukla A., Bosenberg M.W., MacPherson M.B., Butnor K.J., Heintz N.H., Pass H.I., Carbone M., Testa J.R., Mossman B.T. Activated cAMP response element binding protein is overexpressed in human mesotheliomas and inhibits apoptosis. Am. J. Pathol. 2009;175:2197–2206. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2009.090400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Wang J., Sun R., Li Z., Pan Y. Combined bone marrow stromal cells and oxiracetam treatments ameliorates acute cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury through TRPC6. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. (Shanghai) 2019;51:767–777. doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmz059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Zhang J., Mao X., Zhou T., Cheng X., Lin Y. IL-17A contributes to brain ischemia reperfusion injury through calpain-TRPC6 pathway in mice. Neuroscience. 2014;274:419–428. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.06.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Zhang E., Liao P. Brain transient receptor potential channels and stroke. J. Neurosci. Res. 2015;93:1165–1183. doi: 10.1002/jnr.23529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Chen X., Lu M., He X., Ma L., Birnbaumer L., Liao Y. TRPC3/6/7 Knockdown Protects the Brain from Cerebral Ischemia Injury via Astrocyte Apoptosis Inhibition and Effects on NF-кB Translocation. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017;54:7555–7566. doi: 10.1007/s12035-016-0227-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Hoffmann U., Sheng H., Ayata C., Warner D.S. Anesthesia in Experimental Stroke Research. Transl. Stroke Res. 2016;7:358–367. doi: 10.1007/s12975-016-0491-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Higashi Y., Aratake T., Shimizu S., Shimizu T., Saito M. [Brain zinc dyshomeostasis and glial cells in ischemic stroke] Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi Folia Pharmacol. Jpn. 2019;154:138–142. doi: 10.1254/fpj.154.138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Wang Z., do Carmo J.M., da Silva A.A., Fu Y., Hall J.E. Mechanisms of Synergistic Interactions of Diabetes and Hypertension in Chronic Kidney Disease: Role of Mitochondrial Dysfunction and ER Stress. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2020;22:15. doi: 10.1007/s11906-020-1016-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Magnusson J.P., Göritz C., Tatarishvili J., Dias D.O., Smith E.M., Lindvall O., Kokaia Z., Frisén J. A latent neurogenic program in astrocytes regulated by Notch signaling in the mouse. Science. 2014;346:237–241. doi: 10.1126/science.346.6206.237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Prikhodko V., Chernyuk D., Sysoev Y., Zernov N., Okovityi S., Popugaeva E. Potential Drug Candidates to Treat TRPC6 Channel Deficiencies in the Pathophysiology of Alzheimer’s Disease and Brain Ischemia. Cells. 2020;9:2531. doi: 10.3390/cells9112351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Leuner K., Kazanski V., Muller M., Essin K., Henke B., Gollasch M., Harteneck C., Muller W.E. Hyperforin--a key constituent of St. John’s wort specifically activates TRPC6 channels. FASEB J. 2007;21:4101–4111. doi: 10.1096/fj.07-8110com. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Sell T.S., Belkacemi T., Flockerzi V., Beck A. Protonophore properties of hyperforin are essential for its pharmacological activity. Sci. Rep. 2014;4:7500. doi: 10.1038/srep07500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Lin Y., Chen F., Zhang J., Wang T., Wei X., Wu J., Feng Y., Dai Z., Wu Q. Neuroprotective effect of resveratrol on ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats through TRPC6/CREB pathways. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2013;50:504–513. doi: 10.1007/s12031-013-9977-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Yao C., Zhang J., Chen F., Lin Y. Neuroprotectin D1 attenuates brain damage induced by transient middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats through TRPC6/CREB pathways. Mol. Med. Rep. 2013;8:543–550. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2013.1543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Yao C., Zhang J., Liu G., Chen F., Lin Y. Neuroprotection by (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate in a rat model of stroke is mediated through inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum stress. Mol. Med. Rep. 2014;9:69–76. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2013.1778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Sossin W.S., Barker P.A. Something old, something new: BDNF-induced neuron survival requires TRPC channel function. Nat. Neurosci. 2007;10:537–538. doi: 10.1038/nn0507-537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Liu L., Gu L., Chen M., Zheng Y., Xiong X., Zhu S. Novel Targets for Stroke Therapy: Special Focus on TRPC Channels and TRPC6. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2020;12:70. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2020.00070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Chrostek M.R., Fellows E.G., Crane A.T., Grande A.W., Low W.C. Efficacy of stem cell-based therapies for stroke. Brain Res. 2019;1722:146362. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2019.146362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Li W., Yang F., Gao J., Tang Y., Wang J., Pan Y. Over-Expression of TRPC6 via CRISPR Based Synergistic Activation Mediator in BMSCs Ameliorates Brain Injury in a Rat Model of Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion. Neuroscience. 2019;415:147–160. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2019.06.041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Montecinos-Oliva C., Schuller A., Parodi J., Melo F., Inestrosa N.C. Effects of tetrahydrohyperforin in mouse hippocampal slices: Neuroprotection, long-term potentiation and TRPC channels. Curr. Med. Chem. 2014;21:3494–3506. doi: 10.2174/0929867321666140716091229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Iadecola C. The pathobiology of vascular dementia. Neuron. 2013;80:844–866. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2013.10.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Hafner S., Urban N., Schaefer M. Discovery and characterization of a positive allosteric modulator of transient receptor potential canonical 6 (TRPC6) channels. Cell Calcium. 2019;78:26–34. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2018.12.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Vemana H.P., Karim Z.A., Conlon C., Khasawneh F.T. A critical role for the transient receptor potential channel type 6 in human platelet activation. PLoS ONE. 2015;10:e0125764. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0125764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Paez Espinosa E.V., Lin O.A., Karim Z.A., Alshbool F.Z., Khasawneh F.T. Mouse transient receptor potential channel type 6 selectively regulates agonist-induced platelet function. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2019;20:100685. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2019.100685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Hassock S.R., Zhu M.X., Trost C., Flockerzi V., Authi K.S. Expression and role of TRPC proteins in human platelets: Evidence that TRPC6 forms the store-independent calcium entry channel. Blood. 2002;100:2801–2811. doi: 10.1182/blood-2002-03-0723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Ramanathan G., Gupta S., Thielmann I., Pleines I., Varga-Szabo D., May F., Mannhalter C., Dietrich A., Nieswandt B., Braun A. Defective diacylglycerol-induced Ca2+ entry but normal agonist-induced activation responses in TRPC6-deficient mouse platelets. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2012;10:419–429. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2011.04596.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Fernandez M., Lao-Peregrin C., Martin E.D. Flufenamic acid suppresses epileptiform activity in hippocampus by reducing excitatory synaptic transmission and neuronal excitability. Epilepsia. 2010;51:384–390. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1167.2009.02279.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Xu X., Lozinskaya I., Costell M., Lin Z., Ball J.A., Bernard R., Behm D.J., Marino J.P., Schnackenberg C.G. Characterization of Small Molecule TRPC3 and TRPC6 agonist and Antagonists. Biophys. J. 2013;104:454a. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2012.11.2513. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Tiapko O., Shrestha N., Lindinger S., Guedes de la Cruz G., Graziani A., Klec C., Butorac C., Graier W.F., Kubista H., Freichel M., et al. Lipid-independent control of endothelial and neuronal TRPC3 channels by light. Chem. Sci. 2019;10:2837–2842. doi: 10.1039/C8SC05536J. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Sawamura S., Hatano M., Takada Y., Hino K., Kawamura T., Tanikawa J., Nakagawa H., Hase H., Nakao A., Hirano M., et al. Screening of Transient Receptor Potential Canonical Channel Activators Identifies Novel Neurotrophic Piperazine Compounds. Mol. Pharmacol. 2016;89:348–363. doi: 10.1124/mol.115.102863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Urban N., Wang L., Kwiek S., Rademann J., Kuebler W.M., Schaefer M. Identification and Validation of Larixyl Acetate as a Potent TRPC6 Inhibitor. Mol. Pharmacol. 2016;89:197–213. doi: 10.1124/mol.115.100792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Ward C.W., Sachs F., Bush E.D., Suchyna T.M. GsMTx4-D provides protection to the D2.mdx mouse. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2018;28:868–877. doi: 10.1016/j.nmd.2018.07.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Shaik J.S., Poloyac S.M., Kochanek P.M., Alexander H., Tudorascu D.L., Clark R.S., Manole M.D. 20-Hydroxyeicosatetraenoic Acid Inhibition by HET0016 Offers Neuroprotection, Decreases Edema, and Increases Cortical Cerebral Blood Flow in a Pediatric Asphyxial Cardiac Arrest Model in Rats. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 2015;35:1757–1763. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2015.117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Poloyac S.M., Zhang Y., Bies R.R., Kochanek P.M., Graham S.H. Protective effect of the 20-HETE inhibitor HET0016 on brain damage after temporary focal ischemia. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 2006;26:1551–1561. doi: 10.1038/sj.jcbfm.9600309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Urban N., Hill K., Wang L., Kuebler W.M., Schaefer M. Novel pharmacological TRPC inhibitors block hypoxia-induced vasoconstriction. Cell Calcium. 2012;51:194–206. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2012.01.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Lin B.L., Matera D., Doerner J.F., Zheng N., Del Camino D., Mishra S., Bian H., Zeveleva S., Zhen X., Blair N.T., et al. In vivo selective inhibition of TRPC6 by antagonist BI 749327 ameliorates fibrosis and dysfunction in cardiac and renal disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2019;116:10156–10161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1815354116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]