Self-Association of CIITA and Its Transactivation Potential (original) (raw)
Abstract
The major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II transactivator (CIITA) regulates the expression of genes involved in the immune response, including MHC class II genes and the interleukin-4 gene. Interactions between CIITA and sequence-specific, DNA-binding proteins are required for CIITA to function as an activator of MHC class II genes. CIITA also interacts with the coactivators CBP (also called p300), and this interaction leads to synergistic activation of MHC class II promoters. Here, we report that CIITA forms complexes with itself and that a central region, including the GTP-binding domain is sufficient for self-association. Additionally, this central region interacts with the C-terminal leucine-rich repeat as well as the N-terminal acidic domain. LXXLL motifs residing in the GTP-binding domain are essential for self-association. Finally, distinct differences exist among various CIITA mutant proteins with regard to activation function, subcellular localization, and association with wild-type protein and dominant-negative potential.
Major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II molecules present exogenously derived antigenic peptides to CD4+ T cells. The recognition of alien peptide by these T cells allows a host to immunologically respond to foreign pathogens. MHC class II molecules are constitutively expressed on B cells and dendritic cells and inducible upon other cells, such as macrophages, all of which are capable of the uptake and processing of foreign invaders. In the absence of MHC class II molecules, individuals are unable to mount a T-cell-mediated immune response and overwhelming infection ensues. A group of immunodeficient patients which lack MHC class II molecules have been identified, and this disease has been coined bare lymphocyte syndrome (BLS) (8, 15). One class of these BLS patients (group A) lack MHC class II molecules on their cellular surfaces due to a defect in the MHC class II transactivator, CIITA (38).
The regulation of MHC class II gene expression is primarily at the transcriptional level. The promoters of MHC class II genes contain at least four conserved sequences: the S, X, X2, and Y boxes (reviewed in reference 28). These _cis_-acting elements are occupied by sequence-specific transcription factors; the heterotrimeric NF-Y complex binds to the Y box (25), the multimeric RFX proteins bind to the S and X boxes (10, 21), and the cyclic AMP response element binding protein (CREB) binds to the X2 box (31). Protein-protein interactions stabilize the binding of these proteins to MHC class II promoter DNA as illustrated by interactions between the RFX complex and NF-Y (33, 40, 41). and the enhancement of RFX complex binding facilitated by CREB (27, 41). However, the binding of all of these transcription factors to their respective _cis_-acting elements is insufficient to lead to MHC class II promoter activity. CIITA is required for both the constitutive and the gamma interferon-inducible expression of MHC class II genes (4, 38, 39). CIITA does not bind directly to DNA. The exact mechanism of CIITA action is not known, but it is thought that the interaction of CIITA with sequence-specific DNA binding proteins, as well as the basal transcriptional machinery, is required for its function (see below). Therefore, it is not surprising that CIITA can act as an activator and a repressor depending on the target promoter (14, 36).
CIITA contains four domains—acidic (A), proline-serine-threonine-rich (PST), GTP-binding domain (GBD), and leucine-rich repeat (LRR)—all of which are required to activate the MHC class II promoter. The acidic transcriptional activation domain interacts with TAFII32 (12). Recruitment of the coactivator protein CBP (also known as p300) by the acidic domain has also been reported and shown to lead to synergistic activation of MHC class II promoters and the repression of the interleukin-4 (IL-4) promoter (13, 23, 36). The PST domain is essential for CIITA function but the role of this domain remains unknown (6). The binding of GTP to the GBD is required for efficient translocation of CIITA from the cytoplasm to the nucleus (17). The GBD of CIITA contains three consensus motifs for GTP binding: a P-loop–Walker A motif (421GKAGQGKS428), a magnesium coordination site (462DAYG465), and a motif likely to confer GTP-binding specificity (559SKAD562). Mutation in any of these sites significantly reduces transactivation activity (6). The GBD also contains two LXXLL motifs (466LQDLL470 and 526LRGLL530). These motifs serve as protein-protein interaction domains exemplified by their role in the interaction between ligand-bound nuclear hormone receptors and their coactivators (18, 32). To date, no specific interaction between these LXXLL motifs and other proteins have been identified; however, they are essential for CIITA function (3). Recent work has established that there are multiple interactions CIITA forms with the DNA-binding proteins that bind the MHC class II promoter, including RFX5 and RFXANK, NF-YB and NF-YC, and CREB (9, 16, 43). Except for RFXANK and NF-YC, which bind the amino-terminal region of CIITA, the GBD of CIITA serves as the likely domain for these interactions. Along with these properties, the GBD interacts with the amino terminus of the coactivator p300 (36). The fourth domain of CIITA contains at least four LRRs. The CIITA LRR falls into the ribonuclease inhibitor-like subfamily of LRR-containing proteins characterized by a XXXLXXLXLXXN/CXLXXXGOXXLXXOLXX (L, leucine; X, any amino acid; O, nonpolar residue; “G”, indicates more than 30% identity) repeat (22). One role of LRR domains is to mediate protein-protein interactions (30, 34). CIITA proteins with LRR truncations and LRR mutations cannot activate the MHC class II promoter, suggesting that all four repeats are required for transactivation potential (5, 16).
NOD1, an Apaf-1-like molecule which plays an important role in cell death, shares a similar domain organization with CIITA: an effector domain, a nucleotide-binding domain, and an LRR domain (19). Importantly, NOD1 self-association is critical for its function (19, 20). Based on these observations, we sought to determine if CIITA could form complexes with itself and if self-association was required for CIITA to activate MHC class II promoters. We document that CIITA interacts with itself through LXXLL motifs found in a 162-amino-acid region which includes the GTP-binding domain. In addition to associating with itself, this domain also interacts with the amino and carboxyl portions of the protein. Multiple mutants of CIITA were analyzed and differed in their ability to activate MHC class II promoters, interact with wild-type CIITA, and act as dominant-negative proteins.
MATERIALS & METHODS
Cell culture and transfections.
The human kidney cell line 293T was maintained in Clicks medium with 10% fetal bovine serum, 100 U of penicillin per ml, 100 μg of streptomycin per ml, 2 mM l-glutamine, and 10−5 M β-mercaptoethanol. Cells were grown at 37°C with 5% CO2. Transfection of 293T cells for functional assays and biochemical interactions was performed using the calcium phosphate method. For reporter gene assays, 105 cells were plated in 12-well plates and transfected with 0.1 μg of reporter construct, 0.1 μg of CIITA plasmid, and 0.1 μg of β-galactosidase expression vector per well. Samples were run in duplicate for each experiment. For biochemical assays, 106 cells were plated in 10-cm plates and transfected with 8 μg of each CIITA plasmid, unless otherwise indicated in the text. Raji and RJ2.2.5 cells were maintained in RPMI containing the same supplements as for the 293T cells. To generate stable transfectants of RJ2.2.5 cells, 5 × 106 RJ2.2.5 cells were mixed with 25 μg of DNA in 500 μl of medium, followed by electroporation (250 V, 960 μF). Cells were then selected under 1 mg of G418 per ml.
Plasmid constructs.
The Eα-luciferase containing 2 kb of Eα promoter (_Bgl_I-_Bal_I) and the cytomegalovirus promoter-driven β-galactosidase (14), hemagglutinin (HA)-tagged wild-type CIITA (11), FLAG-tagged wild-type CIITA, and FLAG-CIITA(1–1130, K427E) (5, 6) have been previously described. All constructs were made using the expression vector pCDNA3 containing an HA or FLAG epitope at the N terminus. PCR-mediated mutagenesis was used to generate internal deletion and amino acid substitution mutants. The primers used to generate mutants are shown below, followed by their usage. The number indicates the starting position of the primer that corresponds to the published human CIITA cDNA sequence (38), and the “5-” or “3-” indicates the direction of priming: 5-116 with _Eco_RI and the FLAG tag, CTGGAATTCATGGACTACAAAGACGATGACGATAAACGTTGCCTGGCTCCA; 5-308 with _Eco_RI and FLAG tag, CTGGAATTCATGGACTACAAAGACGATGACGATAAATACTCAGAACCCGACACA; 5-377 with _Eco_RI and FLAG tag, CTGGAATTCA TGGACTACAAAGACGATGACGATAAAGATGAAGAGACCAGGGAG; 5-584 with _Cla_I, CCATCGATCACTGGAAGCCAGCTGAG; 5-584 with _Eco_RI and FLAG tag, CTGGAATTCATGGACTACAAAGACGATGACGATAAAATGCACTGGAAGCCAGCTGAG; 5-1334 with _Xba_I, TGCTCTAGACACCGGCGGCCGCGTGAGACACGAGTG; 5-1335 with LXXLL substitution, CACCGGCGGCCGCGTGAGACACGAGTGATTGCTGTGCTG; 5-1499 with LL-to-AA substitution, GCCTATGGCCTGCAGGATGCGGCCTTCTCCCTGGGCCCACAG; 5-1502 with LXXLL substitution, CGTCCGGGGGATGCCTATGGCGCGGCGGCTGCGGCCTTCTTCCTGGGCCCACAGCCA; 5-1682 with LXXLL substitution, TGCTCCGCCGCGGCTGCGGCGGCCGGCCTTTTCCAGAAGAAG; 3-307 with _Cla_I, CCATCGATGAGCTCAATCTCTTCTTCTCC; 3-376 with _Cla_I, CCATCGATACCTTCCATGTCACACAACAG; 3-466 with _Cla_I, CCATCGATGTCCTTGCTCAGGCCCTC; 3-1099, ATGCTCGAGTCAGGAGACCTCTCCAGCTGCCGG; 3–1101, TTGGAGACCTCTCCAGCTGCC; 3–1528 with LXXLL substitution, GGAGAAGGCCGCAGCCGCCGCGCCATAGGCATCCCCCGGACG; 3–1528 with LL-to-AA substitution, GGAGAAGGCCGCATCCTGCAGGCCATAGGCATCCCCCGGACG; 3-1708 with LXXLL substitution, GCCGGCCGCCGCAGCCGCGGCGGAGCAGGGCTCCGCCGGTGC; 3-1890, TCTTGGTGCTCTGTCATCCCT; 5-584 with an _Eco_RI site and the FLAG tag, CTGGAATTCATGGACTACAAAGACGATGACG ATAAAATGCACTGGAAGCCAGCTGAG; and 3-1099 with _Xho_I, ATGCTCGAGTCAGGAGACCTCTCCAGCTGCCGG.
CIITA(158–1130) was generated by PCR using 5-584 and 3-1101, followed by digestion with _Eco_RI and _Sph_I (positions 584 to 1015). The _Eco_RI-_Sph_I fragment was ligated with the rest of the 3 fragment of the wild type and resulted in the deletion of amino acids 1 to 157. The other deletion mutants of the acidic domain were generated by PCR using appropriate sets of primers followed by digestion with _Eco_RI and _Cla_I to produce the 5′ end of the acidic domain. The primers used for acidic deletions were 5-116 and 3-307 for CIITA(1–64:158–1130), 5-308 and 3-376 for CIITA(64–87:158–1130), 5-377 and 3-466 for CIITA(88–117:158–1130), and 5-377 and 3-1101, for CIITA(88–1130). Fragment 584-1015 was produced by PCR using 5-584 and 3-1101, followed by digestion with _Cla_I and _Sph_I (positions 584 to 1015). The rest of the 3′ end of the gene, _Sph_I (1015 to end of CIITA gene), was derived from the wild type. The final acidic deletion mutants were made by ligating three fragments. CIITA(408–857) was constructed by digesting the PCR product generated using the 5-1334 and 3-1890 primers with _Xba_I and _Nco_I (positions 1334 to 1824). This _Xba_I-_Nco_I fragment was fused with a fragment from _Nco_I to _Xba_I of CIITA(1–873) (see below). CIITA(408–570) was derived from CIITA(408–857) by digesting with _Xba_I and _Nco_I (nucleotides 1334 to 1824). The LXXLL mutation was generated by overlapping PCR. In order to introduce the substitution in the first motif, two primary PCR reactions were performed using two sets of primers: one set with 5-1335 and 3-1528 with the LXXLL substitution and the second set with 5-1502 with the LXXLL substitution and 3-1890. The secondary PCR was carried out using the primary PCR product as a template and 5-1335 and 3-1890 as primers. The PCR product was digested with _Not_I and _Apa_I and replaced the wild-type _Not_I-_Apa_I fragment. The second motif was mutated using the same strategy except that 5-1335 and 3-1708 with the LXXLL substitution, 5-1682 with the LXXLL substitution, and 3-1890 were used as primers. The PCR product was digested with _Apa_I and _Nco_I. The double LXXLL mutant was generated by ligating two restriction fragments, _Not_I-_Apa_I and _Apa_I-_Nco_I, containing LxxLL substitutions. LL-to-AA substitution was made by overlapping PCR with 5-1499 and 3-1528 containing proper mutations. The PCR product was digested with _Not_I and _Nco_I and replaced the wild-type _Not_I-_Nco_I fragment. CIITA(408–570)-LXXLL(466, 526) was constructed by using the _Not_I-_Nco_I fragment of the LXXLL double mutant. CIITA(1–873) was generated by introducing a stop codon at the nucleotide position 2702. An _Xba_I site was added after the stop codon to facilitate the cloning. CIITA(980–1130) was generated by using a fragment from _Bam_HI (position 3048) to the 3′ end of the cDNA. The A/PST region, CIITA(1–331), was generated using the _Eco_RI-_Hin_dIII (position 1 to 1103) fragment of the wild-type CIITA containing the FLAG epitope and cloned into pCDNA3. The PST expression vector, CIITA(157–329) was made by PCR using 5-584 containing an _Eco_RI site and the FLAG tag and 3-1099 with _Xho_I. The PCR product was digested with _Eco_RI and _Xho_I and cloned into pCDNA3. The integrity of the mutants was confirmed by sequencing.
Flow cytometry.
Cells were washed and resuspended in cold 1× phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) supplemented with 1% fetal bovine serum. Staining was performed in the same buffer, and samples were analyzed on a FACScan (Becton Dickinson). W6/32 and L243 were used for MHC class I and class II analyses, respectively.
Luciferase assays.
At 2 days posttransfection, cells were harvested, washed with 1× PBS, and lysed in 1× Reporter lysis buffer (Promega, Madison, Wis.). One-half of the lysate was used for the luciferase assay, and one-third of the lysate was used for the β-galactosidase assay as previously described (14). β-Galactosidase readings were used to normalize the relative luciferase activity of each sample for all transfections.
Immunoprecipitation and Western blotting.
At 2 days posttransfection, the cells were harvested and washed with 1× PBS. Whole-cell lysates were made by resuspending the cell pellet in 100 μl of ice-cold lysis buffer (1% Triton X-100, 25 mM Tris [pH 7.4], 150 mM NaCl, 1 mM EDTA, 1 mM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride, 10 μg of leupeptin per ml, 10 μg of aprotonin per ml) for 1 h on ice. Cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions were prepared as described previously (7). For whole-cell and subcellular fractionation, 8 μg of each lysate was saved for analysis of protein expression (designated lysate or “L” in text), and the remainder was normalized to equal levels and resuspended in 500 μl of ice-cold lysis buffer and precleared with protein A-Sepharose (Pharmacia, Piscataway, N.J.). Then 2 μg of anti-HA antibody (Santa Cruz Biotech, Santa Cruz, Calif.) was added to the precleared lysates and incubated for 1 h on ice. A total of 25 μl of protein A-Sepharose (50% slurry) was added per immunoprecipitation reaction and rotated at 4°C for 3 to 8 h. Reactions were next spun at 660 × g for 5 min to pellet the Sepharose beads and then washed with cell lysis buffer. This process was repeated twice more, and then the pellet was resuspended in sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) loading buffer. Proteins were resolved on SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) gels and transferred to polyvinylidene difluoride (Millipore, Bedford, Mass; NEN, Boston, Mass.) using a semidry gel electrophoresis apparatus (Bio-Rad, Hercules, Calif.). Membranes were blocked in 1× Tris-buffered saline (pH 7.4) containing 0.05% Tween 20 (TBS-T), 1% bovine serum albumin, and 4% dry milk overnight at 4°C and probed with anti-FLAG (M2; Sigma, St. Louis, Mo.), anti-HA (Santa Cruz Biotech), anti-GRP78 (N-20; Santa Cruz Biotech), or anti-p300 (N-15; Santa Cruz Biotech) antibodies in blocking solution for at least 1 h at room temperature. Membranes were washed three times in TBS-T for 15 min each and then probed with horseradish peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibodies (Jackson Immunoresearch Laboratories, West Grove, Pa.) in blocking solution for 1 h at room temperature. Membranes were washed five times in TBS-T for 15 min each time and then analyzed by using chemiluminescence (NEN). Blots were stripped in stripping solution (62.5 mM Tris, pH 6.7; 2% SDS; 100 mM β-mercaptoethanol) and placed at 50°C for 30 min, washed in TBS-T for 1 h, and then blocked and probed as previously described.
In vitro transcription and translation and in vitro binding assays.
We performed 100-μl in vitro transcription and translation reactions according to the manufacturer's suggested protocol (Promega). For the in vitro binding assays, the products of the in vitro transcription and translation reactions, or equal amounts of cell lysates, in microgram quantities as determined by protein assay (Bio-Rad), made from different plates of 293T cells were mixed together on ice in a total volume of 600 μl of cell lysis buffer containing 150 mM NaCl for 2.5 h, with inversion of the tubes every 30 min. Immunoprecipitation reactions were performed as described above. One-twentieth of each lysate or in vitro reaction was saved for analysis of input protein.
RESULTS
Cellular, but not in vitro transcribed and translated, CIITA forms complexes with itself.
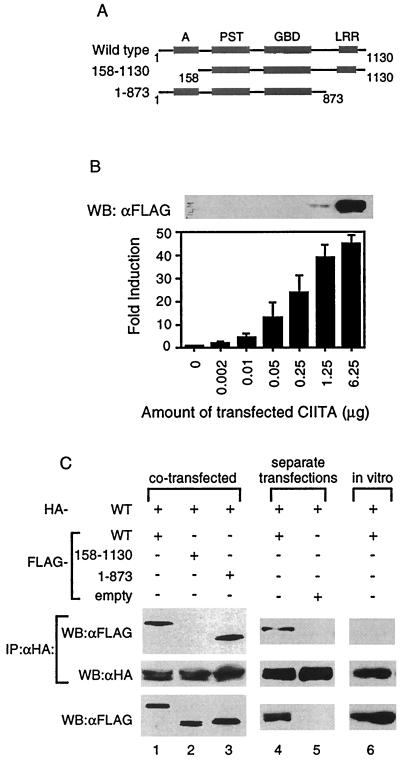
The purpose of our study was to determine whether CIITA associates with itself, which may affect its ability to transactivate the MHC class II gene. Therefore, it is important to assess the amount of CIITA protein which can be detected using our detection systems. To do this, a constant amount of MHC class II promoter-driven luciferase was transfected into 106 293T cells with an increasing amount of FLAG-tagged wild-type CIITA expression plasmid (Fig. 1A). The levels of CIITA protein and induction of MHC class II promoter activity were measured by Western blot and luciferase activity, respectively. We were unable to detect CIITA protein if less that 1.25 μg of CIITA plasmid was transfected (Fig. 1B, top panel). Loading twice the amount of cell lysate (16 versus 8 μg) and a longer exposure did not produce detectable levels of CIITA below this point (data not shown). However, these undetectable levels of CIITA protein were sufficient to activate the MHC class II promoter, indicating that CIITA is a potent transcription factor (Fig. 1B). Based on these data, and in order to visualize CIITA interactions, 8 μg of CIITA expression vector was used for transfection throughout our study, unless otherwise noted. This level most probably lead to an overexpression of CIITA protein. However, the inability to perform experiments with multitagged CIITA protein from endogenous levels of CIITA, in addition to the vast number of interactions that CIITA has with other proteins while residing in cells (see Discussion), led us to use a transfection system to visualize CIITA self-interactions.
FIG. 1.
CIITA forms complexes with itself in cells. (A) Schematic diagram of the wild-type and mutant forms of CIITA used for interaction studies. Domains of CIITA are as depicted: acidic, A; proline-, serine-, and threonine-rich, PST; GTP-binding domain, GBD; and LRRs. The number indicates the amino acid number of the CIITA (38). (B) Undetectable levels of CIITA proteins by Western blot can activate the MHC class II gene. One million 293T cells were plated in 10-cm plates and the next day were transfected with the indicated amount of FLAG-CIITA expression plasmid, 2 μg of MHC class II promoter-driven luciferase, and 2 μg of β-galactosidase expression vector. The total amount of plasmid for each transfection was kept constant by the addition of the empty pCDNA3 vector. Two days later, whole-cell lysates were made for luciferase assays and Western blot. A total of 8 μg of the cell lysate was used for the Western blot. The fold induction was calculated by setting the luciferase value obtained without the CIITA expression plasmid transfected equal to 1. Samples were normalized for transfection efficiency using β-galactosidase values. Western blot is representative of two separate experiments, and the error bars represent the standard error of the mean of three separate experiments performed in duplicate. (C) CIITA self-associates. The top two panels represent Western blot analysis of anti-HA immunoprecipitation reactions performed on 293T cells that were cotransfected (lanes 1 to 3) or were transfected separately and then mixed in vitro (lanes 4 and 5) with the forms of CIITA as indicated. The in vitro column (lane 6) is from an immunoprecipitation reaction of in vitro-transcribed and -translated HA- and FLAG-tagged CIITA (see Materials and Methods). The membrane was probed with anti-FLAG antibodies, stripped, and reprobed with anti-HA antibodies. The bottom panel represents 1/20 of the cell lysates (lanes 1 to 5) or in vitro transcription and translation reactions (lane 6) used in the binding assays and immunoprecipitation reactions. Each part of panel C is representative of at least three separate experiments.
In order to determine if CIITA interacts with itself, HA-tagged wild-type CIITA (HA-WT) was cotransfected with the various FLAG-tagged CIITA constructs shown in Fig. 1A into 293T cells. Anti-HA immunoprecipitation reactions were performed to pull out the HA-WT and associated proteins. The product of the immunoprecipitation reaction was immunoblotted and probed for FLAG-tagged CIITA. HA-WT formed complexes with wild-type CIITA, as well as with a mutant lacking the LRR domain, CIITA(1–873) (Fig. 1C, lanes 1 and 3). However, it did not interact with CIITA protein lacking the acidic domain, CIITA(158–1130) although CIITA(158–1130) protein was expressed at a level comparable to that of other proteins tested (Fig. 1C, lane 2).
We then asked if CIITA proteins could self-associate if each tagged version came from a different source instead of being cotransfected into the same cells. The inability to obtain recombinant CIITA protein led us to use two different methods to answer this question. First, HA- and FLAG-tagged wild-type CIITA DNA were each individually transfected into separate plates of 293T cells. Two days later, lysates from each plate were made, mixed, and incubated on ice, and then anti-HA immunoprecipitation reactions performed. Wild-type CIITA retained the ability to associate with itself under these conditions (Fig. 1C, lane 4). Second, we produced HA- and FLAG-tagged wild-type CIITA proteins using in vitro transcription and translation reactions. The products of these reactions were mixed and incubated on ice, followed by immunoblotting. Unlike CIITA proteins which were made in cells, the CIITA proteins made in vitro failed to self-associate (Fig. 1C, lane 6) while retaining the ability to associate with the coactivator CBP (13, 23; data not shown). The addition of 293T cell extract did not restore the interaction (data not shown), suggesting that cellular modification of CIITA may be required for self-association.
Analysis of acidic domain mutants.
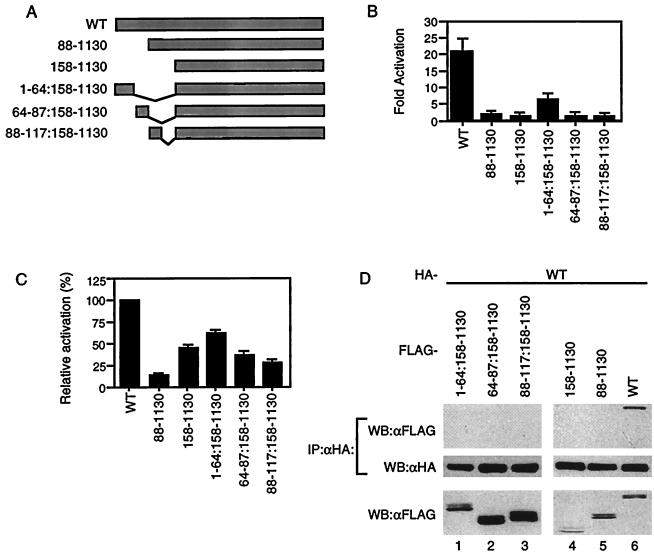
The data that wild-type CIITA did not interact with the mutant lacking the acidic domain led us to further investigate the importance of this domain. CIITA expression constructs which contain deletions of different regions of the acidic domain were made and tested for their ability to transactivate the MHC class II promoter (Fig. 2A). All mutants were incapable of activation except mutant CIITA(1–64:158–1130), which could transactivate but only at 25% of the level of wild-type protein (Fig. 2B). A CIITA mutant lacking the entire acidic domain has been previously shown to be a potent dominant-negative protein (42). We therefore tested the dominant-negative activity of each mutant by cotransfecting the mutants with the MHC class II promoter-driven reporter in the presence of wild-type CIITA. Various levels of dominant-negative function were observed (Fig. 2C, lanes 2 to 6). CIITA(1–64:158–1130), the only mutant to have some activation function, had the least ability to repress wild-type protein, while CIITA(88–1130) could block most of the wild-type CIITA function. Finally, these mutants were tested for their ability to interact with wild-type protein. None of the mutants showed detectable levels of association (Fig. 2D). This indicates that the entire acidic domain is required for self-association which, in turn, seems to be necessary to activate the MHC class II promoter. CIITA(1–64:158–1130) may undergo self-association, but the degree of association may be too low to be detected.
FIG. 2.
An intact acidic domain is indispensable for CIITA self-association. (A) Diagram of mutants used. (B) Wild-type and mutant CIITA were tested for their ability to activate MHC class II promoters in 293T cells. The fold activation was calculated as in Fig. 1B. (C) Mutants were tested for dominant-negative activity. 293T cells were cotransfected with 100 ng of wild-type CIITA expression plasmid (lane 1) or 100 ng of wild-type CIITA plus 100 ng of mutant DNA expression plasmid (lanes 2 to 6), along with the MHC class II promoter-driven luciferase. DNA levels in all transfections were kept constant by the addition of empty pCDNA3 vector DNA. The luciferase activity of cells transfected with the wild type in the absence of the mutants was set at 100%. (D) Wild-type CIITA does not interact with any of the acidic domain mutants. HA-tagged wild-type and FLAG-tagged CIITA mutant constructs were expressed in 293T cells. Anti-HA immunoprecipitation reactions were performed on whole-cell lysates, run on SDS–6% PAGE gels, transferred to membranes, and probed for FLAG-tagged protein. The membrane was then stripped and reprobed with anti-HA antibodies. The bottom panel represents 1/20 of the cell lysate. Each part of the figure is representative of three independent experiments.
A 162-amino-acid region containing the GTP-binding domain is sufficient for self-association.
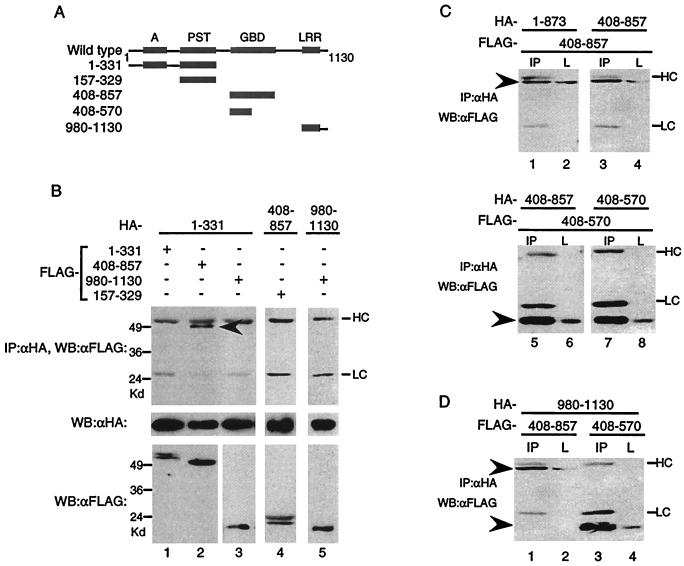
Since the mutant lacking the acidic domain did not self-associate, we next tested whether the acidic domain by itself could self-associate. When amino acids 1 to 331 containing the A/PST region (HA-1–331) was coexpressed with the FLAG-tagged version of itself, it did not self associate (Fig. 3B, lane 1). However, it did associate with CIITA(408–857) containing the GBD (Fig. 3B, lane 2). The PST domain by itself, CIITA(157–329), did not associate with CIITA(408–857) (Fig. 3B, lane 4). This suggests that the acidic domain, in the context of CIITA(1–331), is the region which is binding to CIITA(408–857). Finally, the LRR, CIITA(980–1130), did not interact with CIITA(1–331) or associate with itself (Fig. 3B, lanes 3 and 5). Together, neither the N-terminal nor the C-terminal domains of CIITA associate with each other or with themselves.
FIG. 3.
CIITA(408–570) is sufficient for self-association. (A) Diagram depicting CIITA mutants used to study interactions. (B) The acidic domain interacts with CIITA(408–857). HA-tagged CIITA(1–331), CIITA(408–857), or CIITA(980–1103) was cotransfected with the FLAG-tagged constructs shown. Anti-HA immunoprecipitation reactions were loaded on SDS–9% PAGE gels and probed with anti-FLAG antibodies (top panel). The blot was stripped and reprobed with anti-HA antibodies (middle panel). One-twentieth of each lysate was analyzed for expression of the FLAG-tagged proteins (bottom panel). HC and LC denote the antibody heavy chain and light chain, and the arrowheads indicate the CIITA mutant proteins for this and subsequent parts of the figure. CIITA(408–570) interacts with itself (C) and the LRR (D). Transfections were done as in previous figures, and 1/20 of the cell lysate (L) or the immunoprecipitation reaction using anti-HA antibodies (IP) was subjected to SDS–10 to 12% to PAGE, followed by Western blot analysis with anti-FLAG antibodies. Each part of the figure is representative of at least three separate experiments.
In addition to an overall conservation in domain organization, the nucleotide-binding domains of CIITA and NOD1 share high levels of homology. Furthermore, the nucleotide-binding domain of Nod1 is sufficient for self-association (19). Therefore, we examined whether CIITA can self-associate through regions including the GBD. CIITA(408– 857) was able to associate with CIITA(1–873), as well as with itself (Fig. 3C, lanes 1 to 4). To further delineate the region that is responsible for self-association, we generated a truncated version of CIITA(408–857). CIITA(408–570) interacted with CIITA(408–857), and it was sufficient to interact with itself (Fig. 3C, lanes 5 to 8). Both CIITA(408–857) and CIITA(408–570) also interacted with the C-terminal LRR (Fig. 3D, lanes 1 to 4). Therefore, CIITA(408–857) interacts with multiple domains of CIITA.
LXXLL motifs, but not GTP binding, are necessary for self-association.
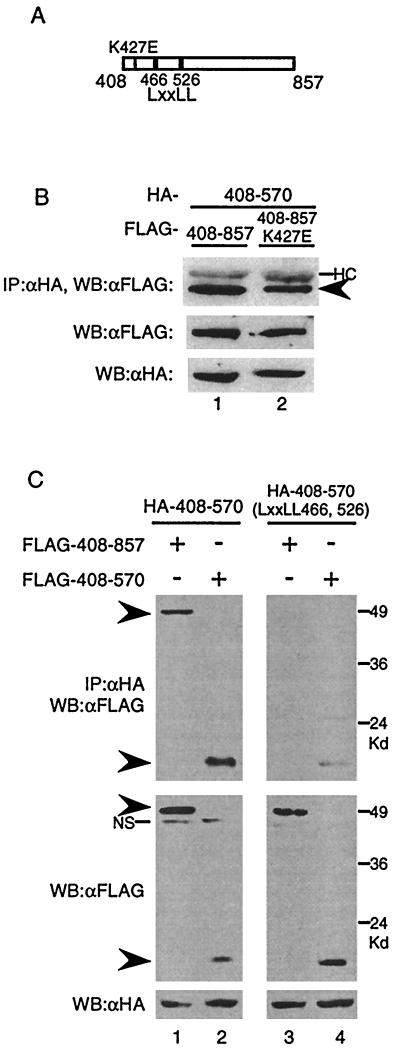
Since CIITA(408–857) could form complexes with itself, we sought to further characterize this domain. CIITA(408–857) harbors GTP-binding motifs which, when mutated in the context of full-length CIITA, inhibits GTP binding and nuclear translocation (17). Therefore, we asked if GTP binding plays a role in mediating self-association. To test this, we created a construct that expresses CIITA(408–857) with a substitution in the P-loop region necessary for GTP binding: CIITA(408–857)K427E (Fig. 4A, thin line). When FLAG-CIITA(408–857) or FLAG-CIITA(408–857)K427E were tested for association with HA-CIITA(408–570), both showed interaction (Fig. 4B). This implies that GTP binding is not a prerequisite for self-association of this region.
FIG. 4.
(A) Diagram of CIITA(408–857). The thin line indicates the K427E mutant in the P-loop region of the GTP-binding motif, and the thick lines represent the LXXLL motifs. (B) GTP binding is not necessary for CIITA(408–857)-CIITA(408–570) interactions. HA- CIITA(408–570) expression plasmid was cotransfected with either FLAG-CIITA(408–857) or FLAG-CIITA(408–857) DNA with the K427E mutation. An anti-HA immunoprecipitation reaction was run on an SDS–9% PAGE gel and probed with anti-FLAG antibodies. One-twentieth of the cell lysate was run on an SDS–9% PAGE gel, transferred to a membrane, and probed with anti-FLAG or anti-HA antibodies to measure the protein input levels. (C) LXXLL motifs are essential for association of CIITA(408–857) with CIITA(408–570). Cotransfections into 293T cells were performed with the indicated plasmids. Immunoprecipitations and Western blotting were done as in panel B. Arrowheads indicate the mutant proteins. NS, nonspecific bands. Each part of the figure is representative of at least three separate experiments.
In addition to the consensus motifs necessary for GTP binding, CIITA(408–570) contains two LXXLL (L, leucine; X, any amino acid) motifs residing at amino acids 466 and 526 that are conserved in both mice and humans. A previous study documented that the LXXLL motifs are required for CIITA to activate the MHC class II promoter (3). To test the role the LXXLL motifs may play in self-association, we replaced all 10 amino acids of both LXXLL motifs with alanine in the context of CIITA(408–570), resulting in CIITA(408–570)-LXXLL(466, 526) (Fig. 4A, thick lines). When the CIITA(408–570)-LXXLL(466, 526) mutant was tested, it was not able to associate with CIITA(408–857) (Fig. 4C, lane 3) and it displayed a severely compromised ability to interact with CIITA(408–570) compared to that of the wild type (Fig. 4C, compare lanes 2 and 4). Hence, LXXLL motifs appear to be crucial for the association of CIITA(408–570) with CIITA(408–857) and CIITA(408–570).
LXXLL motifs in the context of full-length CIITA are critical for transactivation potential, subcellular localization, and self-association.
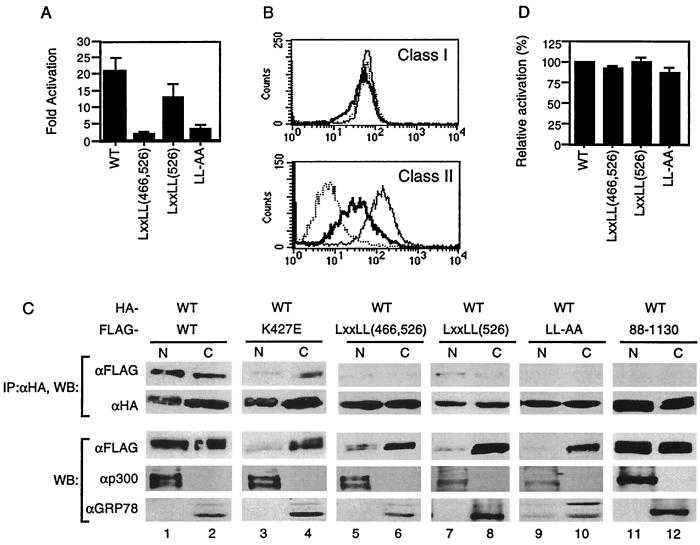
Our data suggest that the intact LXXLL motifs are important for self-association. However, this was demonstrated by using a smaller domain and not the entire protein. To determine whether the same motifs are also important for self-association in the context of the full-length protein, we generated a full-length CIITA containing substitutions at both LXXLL motifs, LXXLL(466, 526). We also replaced five amino acids of each LXXLL motif individually with alanine, generating LXXLL(466) and LXXLL(526). In addition, two leucine residues, amino acids 469 and 470, were substituted with alanine (LL-AA). We first tested if the LXXLL mutants could activate the MHC class II promoter. None of the LXXLL substitutions were able to transactivate the MHC class II promoter except LXXLL(526) which showed partial activity (Figure 5A).
FIG. 5.
The LXXLL motifs are crucial for transactivation function and self-association. (A) 293T cells were cotransfected with the MHC class II promoter-driven luciferase and the indicated plasmid. The fold activation was calculated as in Fig. 1B. (B) Intact LXXLL motifs are required for transactivation function. RJ2.2.5 cells were stably transfected with wild-type and the LXXLL(526) mutant DNA. Stable transfectants were then stained with the antibody recognizing MHC class I (top panel) or MHC class II (bottom panel) and analyzed by flow cytometry. Dotted line, RJ2.2.5 cells; thick line, RJ2.2.5 cells transfected with LXXLL(526); thin line, RJ2.2.5 cells transfected with wild-type CIITA. (C) 293T cells were transfected with the indicated plasmids, and nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions were prepared. Equal amounts (micrograms) of lysates from each fraction were used for immunoprecipitation with anti-HA, followed by Western blotting with anti-HA or anti-FLAG antibodies. Anti-p300 and anti-GRP78 antibodies were used to assess the degree of contamination during cell fractionation. N and C, nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions, respectively. Each part of the figure is representative of three independent experiments. (D) LXXLL motifs do not behave as dominant-negative proteins. Transfections were performed as in Fig. 2C using wild-type CIITA, the LXXLL mutants, and the MHC class II promoter-driven luciferase constructs. The relative activation was calculated using the luciferase values of the wild type in the absence of the mutant as 100%.
We next asked whether the LXXLL mutants behave the same with regard to endogenous MHC class II genes. To do this, each LXXLL mutant was stably transfected into RJ2.2.5 B cells which do not express MHC class II due to a defect in the CIITA gene (1, 38). Stable transfectants were selected and tested for MHC expression by flow cytometric analysis. Consistent with the transient-transfection data, LXXLL(526) could not completely restore endogenous MHC class II expression in RJ2.2.5 cells (Fig. 5B). LXXLL(466) and LXXLL(466, 526) did not lead to MHC class II expression in these cells (data not shown). Together, these data suggest that the first LXXLL motif is critical for CIITA function.
We then tested if the loss of transactivation function could be attributed to the inability of CIITA to self-associate. Wild-type CIITA and each mutant DNA were cotransfected into 293T cells followed by immunoblotting. In addition, nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions were prepared for immunoprecipitation to determine the location of self-association. The nuclear protein p300 or the cytoplasmic protein GRP78 served as a reference for the purity of each subcellular fraction. Wild-type CIITA was present in the nucleus as well as in the cytoplasm, and self-association occurred in both compartments (Fig. 5C, lanes 1 and 2). The GTP-binding mutant, K427E, in the context of full-length CIITA had a severely compromised ability to translocate to the nucleus, in agreement with previously published data (17). However, this mutant retained the ability to associate with wild-type CIITA (Fig. 5C, lanes 3 and 4), a result consistent with the data that GTP binding seems to be less critical for CIITA self-association (Fig. 4B). In contrast, the LXXLL mutants, which also exhibited poor translocation to the nucleus (Figure 5C, lanes 5-10), did not show detectable association with wild-type CIITA, except for LXXLL(526), with reproducibly limited association (Fig. 5C, lanes 7 and 8). Therefore, together with the data from Fig. 4C, we conclude that the LXXLL motifs are crucial for self-association.
CIITA proteins which do not bind GTP due to mutations in the magnesium coordination sequence of the GTP-binding motif possess transdominant repression capabilities (6). We therefore asked if the LXXLL mutant proteins had similar properties. None of the LXXLL mutants behaved as dominant-negative proteins (Fig. 5D). This might be due to the lack of interaction of the LXXLL mutants with wild-type CIITA or to their inability to translocate to the nucleus. In contrast, the acidic domain mutant, CIITA(88–1130), which could not activate the MHC class II gene, was very much like wild-type protein in its nuclear and cytoplasmic localization, while displaying no ability to associate with wild-type CIITA (Fig. 5C, lanes 11 and 12).
DISCUSSION
CIITA is known to exert its transactivation function by interacting with other proteins that bind the MHC class II promoter (11–13, 23, 29, 35, 40, 43). Here, we observe that self-association of CIITA appears to be important for CIITA function, which may serve as an additional regulatory event for MHC class II gene transcription. Many DNA-binding proteins and coactivators interact with overlapping regions of CIITA, predominantly through the acidic domain and the GBD (9, 16, 43). How can CIITA form contacts with all of these proteins simultaneously? One solution may be that only a subset of DNA-binding proteins directly contact CIITA, while the rest are associated with CIITA through another protein(s) which is already bound to CIITA. Another possibility is that the formation of a CIITA complex might work to expose binding surfaces on CIITA, making its conformation competent to bind multiple DNA-binding proteins simultaneously. The role that the MHC class II promoter plays in orchestrating these events deserves further analysis.
We identified the central region of CIITA, amino acids 408 to 570 containing the GTP-binding and LXXLL motifs, as playing an important role in CIITA self-association. This region interacts with itself, the amino-terminal domain of CIITA (A/PST), and the carboxyl-terminal LRR (Fig. 3). Therefore, the central region containing the GBD is a focal point for interactions with multiple domains, which is in agreement with recently published work (26). We demonstrated that the acidic domain plays a critical role for self-association since mutants lacking the acidic domain cannot self-associate. However, the A/PST domain by itself could not self-associate. This indicates that the interaction of the acidic domain with CIITA(408–857) may be essential for the proper folding of CIITA proteins necessary for CIITA complex formation. On the other hand, the LRR is dispensable for self-association but required for CIITA transactivation potential (Fig. 1C and reference 16, respectively).
Interestingly, the coactivators CBP interact with CIITA through the acidic domain (13, 23), as well as through CIITA(408–857) (36). Hence, these interactions may facilitate CIITA self-association by providing this proper folding, which brings the acidic domain and the GBD together. It is tempting to speculate that acetylation of CIITA by CBP may be required for this process, but this remains to be proven.
Although the CIITA(408–570) region was sufficient for self-association, whether or not CIITA complex formation results from this region interacting with itself or with other regions in the context of full-length protein remains to be determined. Since we could not detect the self-association of the acidic domain with itself or the LRR with itself, there are several possible interactions which may account for the observed self-association of full-length CIITA. These include interactions between either the acidic domain, the LRR, or the GBD region from one CIITA molecule interacting with the GBD region of another CIITA molecule. It has recently been shown that amino acids 700 to 1130, including the LRR, are capable of self-association (26). In contrast, we could not detect self-association of the LRR domain encompassing amino acids 980 to 1130 (Fig. 3B). This implies, therefore, that residues residing between amino acids 700 and 980 might be capable of self-association. Indeed, we have recently observed self-association of a fragment of CIITA within this region, CIITA(864–979) (T. J. Sisk and C.-H. Chang, unpublished data). Hence, the self-association of 1–335:700–1130 observed by Linhoff et al. may be mediated by this LRR proximal region not by the LRR. Further studies are required to determine the stoichiometry and the orientation of CIITA interaction in relation to DNA-binding proteins.
The analysis of CIITA proteins with mutated acidic domains reveals a relationship between the ability of CIITA self-association and transactivation potential. In particular, CIITA(88–1130) was highly similar to wild-type CIITA in expression level and nuclear and cytoplasmic localization (Fig. 5C). CIITA(88–1130) also retained the ability to interact with CBP, albeit at a lower level than that of the wild type (Sisk and Chang, unpublished). However, the same mutant failed to transactivate the MHC class II promoter and to self-associate (Fig. 2). Therefore, the lack of self-association may be at least partly responsible for the loss of transactivation function of CIITA(88–1130). CIITA mutants which possess these traits may preclude the formation of a functional enhanceosome complex required for gene activation (29) which forms on an intact MHC class II promoter.
LXXLL motifs are shown to play a critical role for transcriptional regulation by facilitating protein-protein interactions (18, 32). Therefore, the same motif in CIITA may mediate a similar interaction of CIITA with itself. Alternatively, the LXXLL motifs may be recognized by an unidentified element(s) necessary for complex formation since in vitro-transcribed and -translated CIITA protein failed to associate with itself. The same element may be required for CIITA nuclear localization in that it might be possible that CIITA interacts with a nuclear membrane protein(s) through LXXLL motifs, which then leads to translocation. Since the LXXLL motif is involved in both self-association and nuclear trafficking, the two events seem related. However, it is not yet clear where in the cellular compartments CIITA association occurs since our data only allow a glimpse of the steady-state level of self-associated CIITA and do not necessarily indicate the site of association. The relationship between the dynamics of CIITA self-association and the nuclear trafficking requires further study.
Since CIITA shares strikingly similar domain organization with NOD1 and Apaf-1, it is noteworthy to mention that self-association of NOD1 and Apaf-1 is required for their function (2a, 19). Apaf-1 and NOD1 are proteins which regulate the activation of enzymes involved in cell death by forming self-complexes, which leads to the activation of downstream molecules in the cell death pathway (2, 19). For Apaf-1, the recognition of a binding partner which binds the carboxyl-terminal regulatory domain is thought to induce the self-association of these proteins (24, 44). Thus, CIITA may undergo a similar conformational change to interact with itself and subsequently with other proteins on the MHC class II promoter. It is not yet clear what might regulate the initial unfolding of CIITA.
CIITA is a potent transcription factor since undetectable levels of CIITA by Western blot were sufficient to activate the MHC class II gene (Fig. 1B). Therefore, it is possible that a cell does not require a high level of self-associated CIITA. Indeed, a recent study reported that approximately 1% of total CIITA was associated with the MHC class II promoter in B cells, but this study did not address whether CIITA presents as a self-associated complex (29). Hence, it would be difficult to observe endogenous CIITA as a complex in B cells. In fact, less than 1% of CIITA in B cells was detectable as a high-molecular-weight complex revealed by gels run under semidenatured conditions (Sisk and Chang, unpublished). However, because CIITA interacts with multiple proteins, it is not possible to conclude whether CIITA seen as a high-molecular-weight complex was composed solely of CIITA or other proteins. We therefore were forced to use the overexpression transfection system to study these interactions. The interactions observed appeared to be specific since there were multiple mutants which failed to associate with the wild-type protein even when overexpressed. Further studies are warranted to determine the degree of self-association of endogenous levels of CIITA.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank Naohiro Inohara and Gabriel Nunez for stimulating discussions of published and unpublished data and Jenny Ting for CIITA expression plasmids. We also express our immense appreciation to Wes Dunnick and Ormond MacDougald and to Tania Gourley for critical review of the manuscript.
This work was supported in part by National Institutes of Health grant AI41510 to C.-H. Chang and Immunology Training Grant T32-AI07413 to T. J. Sisk.
REFERENCES
- 1.Accolla R. Human B cell variants immunoselected against a single Ia antigen subset have lost expression of several Ia antigen subsets. J Exp Med. 1983;157:1053–1058. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.3.1053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Benedict M A, Hu Y, Inohara N, Nunez G. Expression and functional analysis of Apaf-1 isoforms. Extra Wd-40 repeat is required for cytochrome c binding and regulated activation of procaspase-9. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:8461–8468. doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.12.8461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2a.Bertin J, Nir W-J, Fischer C M, Tayber O V, Errada P R, Grant J R, Keilty J J, Grosselin M L, Robison K E, Wong G H W, Glucksmann M A, DiStefano P S. Human CARDY protein is a novel CED-4/Adaf-1 cell death family member that activates NF-κB. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:12955–12958. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.19.12955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Brown J A, Rogers E M, Boss J M. The MHC class II transactivator (CIITA) requires conserved leucine charged domains for interactions with the conserved W box promoter element. Nucleic Acids Res. 1998;26:4128–4136. doi: 10.1093/nar/26.18.4128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Chang C-H, Fontes J, Peterlin M, Flavell R A. Class II, transactivator (CIITA) is sufficient for the inducible expression of major histocompatibility complex class II genes. J Exp Med. 1994;180:1367–1374. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.4.1367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Chin K C, Li G, Ting J P. Activation and transdominant suppression of MHC class II and HLA-DMB promoters by a series of C-terminal class II transactivator deletion mutants. J Immunol. 1997;159:2789–2794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Chin K-C, Li G G-X, Ting J P-Y. Importance of acidic, proline/serine/threonine-rich, and GTP-binding regions in the major histocompatibility complex class II transactivator: generation of transdominant-negative mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1997;94:2501–2506. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.6.2501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Cressman D E, Chin K C, Taxman D J, Ting J P. A defect in the nuclear translocation of CIITA causes a form of type II bare lymphocyte syndrome. Immunity. 1999;10:163–171. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(00)80017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.dePreval C, Lisowska-Grospierre B, Loche M, Griscelli C, Mach B. A trans-acting class II regulatory gene unlinked to the MHC controls expression of HLA class II genes. Nature. 1985;318:291–293. doi: 10.1038/318291a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.DeSandro A M, Nagarajan U M, Boss J M. Associations and interactions between bare lymphocyte syndrome factors. Mol Cell Biol. 2000;20:6587–6599. doi: 10.1128/mcb.20.17.6587-6599.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Durand B, Kobr M, Reith W, Mach B. Functional complementation of major histocompatibility complex class II regulatory mutants by the purified X-box-binding protein RFX. Mol Cell Biol. 1994;14:6839–6847. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.10.6839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Fontes J D, Jabrane-Ferrat N, Toth C R, Peterlin B M. Binding and cooperative interactions between two B-cell-specific transcriptional coactivators. J Exp Med. 1996;183:2517–2521. doi: 10.1084/jem.183.6.2517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Fontes J D, Jiang B, Peterlin B M. The class II trans-activator CIITA interacts with the TBP-associated factor TAFII32. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997;25:2522–2528. doi: 10.1093/nar/25.12.2522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Fontes J D, Kanazawa S, Jean D, Peterlin B M. Interactions between the class II transactivator and CREB binding protein increase transcription of major histocompatibility complex class II genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1999;19:941–947. doi: 10.1128/mcb.19.1.941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Gourley T, Roys S, Lukacs N W, Kunkel S L, Flavell R A, Chang C H. A novel role for the major histocompatibility complex class II transactivator CIITA in the repression of IL-4 production. Immunity. 1999;10:377–386. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(00)80037-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Griscelli C, Lisowska-Grospierre B, Mach B. Combined immunodeficiency with defective expression in MHC class II genes. Immunodeficiency Rev. 1989;1:135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hake S B, Masternak K, Kammerbauer C, Janzen C, Reith W, Steimle V. CIITA leucine-rich repeats control nuclear localization, in vivo recruitment to the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II enhanceosome, and MHC class II gene transactivation. Mol Cell Biol. 2000;20:7716–7725. doi: 10.1128/mcb.20.20.7716-7725.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Harton J A, Cressman D E, Chin K C, Der C J, Ting J P. GTP binding by class II transactivator: role in nuclear import. Science. 1999;285:1402–1405. doi: 10.1126/science.285.5432.1402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Heery D M, Zacharewski T, Pierrat B, Gronemeyer H, Chambon P, Losson R. Efficient transactivation by retinoic acid receptors in yeast requires retinoid X receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1993;90:4281–4285. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.9.4281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Inohara N, Koseki T, del Peso L, Hu Y, Yee C, Chen S, Carrio R, Merino J, Liu D, Ni J, Nunez G. Nod1, an Apaf-1-like activator of caspase-9 and nuclear factor-kappaB. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:14560–14567. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.21.14560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Inohara N, Koseki T, Lin J, del Peso L, Lucas P C, Chen F F, Ogura Y, Nunez G. An induced proximity model for NF-kappa B activation in the Nod1/RICK and RIP signaling pathways. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:27823–27831. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M003415200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Jabrane-Ferrat N, Peterlin B M. Ets-1 activates the DRA promoter in B cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1994;14:7314–7321. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.11.7314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Kajava A V. Structural diversity of leucine-rich repeat proteins. J Mol Biol. 1998;277:519–527. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1998.1643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Kretsovali A, Agalioti T, Spilianakis C, Tzortzakaki E, Merika M, Papamatheakis J. Involvement of CREB binding protein in expression of major histocompatibility complex class II genes via interaction with the class II transactivator. Mol Cell Biol. 1998;18:6777–6783. doi: 10.1128/mcb.18.11.6777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Li P, Nijhawan D, Budihardjo I, Srinivasula S M, Ahmad M, Alnemri E S, Wang X. Cytochrome c and dATP-dependent formation of Apaf-1/caspase-9 complex initiates an apoptotic protease cascade. Cell. 1997;91:479–489. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80434-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Linhoff M W, Wright K L, Ting J P. CCAAT-binding factor NF-Y and RFX are required for in vivo assembly of a nucleoprotein complex that spans 250 base pairs: the invariant chain promoter as a model. Mol Cell Biol. 1997;17:4589–4596. doi: 10.1128/mcb.17.8.4589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Linhoff M W, Harton J A, Cressman D E, Martin B K, Ting J P. Two distinct domains within CIITA mediate self-association: involvement of the GTP-binding and leucine-rich repeat domains. Mol Cell Biol. 2001;21:3001–3011. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.9.3001-3011.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Louis-Plence P, Moreno C S, Boss J M. Formation of a regulatory factor X/X2 box-binding protein/nuclear factor-Y multiprotein complex on the conserved regulatory regions of HLA class II genes. J Immunol. 1997;159:3899–3909. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Mach B, Steimle V, Martinez-Soria E, Reith W. Regulation of MHC class II genes: lessons from a disease. Annu Rev Immunol. 1996;14:301–331. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.14.1.301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Masternak K, Muhlethaler-Mottet A, Villard J, Zufferey M, Steimle V, Reith W. CIITA is a transcriptional coactivator that is recruited to MHC class II promoters by multiple synergistic interactions with an enhanceosome complex. Genes Dev. 2000;14:1156–1166. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Mitts M R, Grant D B, Heideman W. Adenylate cyclase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae is a peripheral membrane protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1990;10:3873–3883. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.3873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Moreno C S, Beresford G W, Louis-Plence P, Morris A C, Boss J M. CREB regulates MHC class II expression in a CIITA-dependent manner. Immunity. 1999;10:143–151. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(00)80015-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Nolte R T, Wisely G B, Westin S, Cobb J E, Lambert M H, Kurokawa R, Rosenfeld M G, Willson T M, Glass C K, Milburn M V. Ligand binding and co-activator assembly of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma. Nature. 1998;395:137–143. doi: 10.1038/25931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Reith W, Siegrist C-A, Durand B, Barras E, Mach B. Function of major histocompatibility complex class II promoters requires cooperative binding between factors RFX and NF-Y. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1994;91:554–558. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.2.554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Schneider R, Schneider-Scherzer E, Thurnher M, Auer B, Schweiger M. The primary structure of human ribonuclease/angiogenin inhibitor (RAI) discloses a novel highly diversified protein superfamily with a common repetitive module. EMBO J. 1988;7:4151–4156. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03310.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Scholl T, Mahanta S K, Strominger J L. Specific complex formation between the type II bare lymphocyte syndrome-associated transactivators CIITA and RFX5. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1997;94:6330–6334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.12.6330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Sisk T J, Gourley T, Roys S, Chang C H. MHC class II transactivator inhibits IL-4 gene transcription by competing with NF-AT to bind the coactivator CREB binding protein (CBP)/p300. J Immunol. 2000;165:2511–2517. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.165.5.2511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Spilianakis C, Papamatheakis J, Kretsovali A. Acetylation by PCAF enhances CIITA nuclear accumulation and transactivation of major hisocompatibility complex class II genes. Mol Cell Biol. 2000;20:8489–8498. doi: 10.1128/mcb.20.22.8489-8498.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Steimle V, Otten L A, Zufferey M, Mach B. Complementation cloning of an MHC class II transactivator mutated in hereditary MHC class II deficiency (or bare lymphocyte syndrome) Cell. 1993;75:135–146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Steimle V, Siegrist C-A, Mottet A, Lisowska-Grospierre B, Mach B. Regulation of MHC class II expression by interferon-γ-mediated by the transactivator gene CIITA. Science. 1994;265:106–109. doi: 10.1126/science.8016643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Villard J, Peretti M, Masternak K, Barras E, Caretti G, Mantovani R, Reith W. A functionally essential domain of RFX5 mediates activation of major histocompatibility complex class II promoters by promoting cooperative binding between RFX and NF-Y. Mol Cell Biol. 2000;20:3364–3376. doi: 10.1128/mcb.20.10.3364-3376.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Wright K L, Vilen B J, Itoh-Lindstrom Y, Moore T L, Li G, Criscitiello M, Cogswell P, Clarke J B, Ting J P. CCAAT box binding protein NF-Y facilitates in vivo recruitment of upstream DNA binding transcription factors. EMBO J. 1994;13:4042–4053. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06721.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Zhou H, Su H S, Zhang X, Douhan III J, Glimcher L H. CIITA-dependent and-independent class II MHC expression revealed by a dominant negative mutant. J Immunol. 1997;158:4741–4749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Zhu X S, Linhoff M W, Li G, Chin K C, Maity S N, Ting J P. Transcriptional scaffold: CIITA interacts with NF-Y, RFX, and CREB to cause stereospecific regulation of the class II major histocompatibility complex promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 2000;20:6051–6061. doi: 10.1128/mcb.20.16.6051-6061.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Zou H, Henzel W J, Liu X, Lutschg A, Wang X. Apaf-1, a human protein homologous to C. elegans CED-4, participates in cytochrome c-dependent activation of caspase-3. Cell. 1997;90:405–413. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80501-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]