KEGG: kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes - PubMed (original) (raw)
KEGG: kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes
M Kanehisa et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000.
Abstract
KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) is a knowledge base for systematic analysis of gene functions, linking genomic information with higher order functional information. The genomic information is stored in the GENES database, which is a collection of gene catalogs for all the completely sequenced genomes and some partial genomes with up-to-date annotation of gene functions. The higher order functional information is stored in the PATHWAY database, which contains graphical representations of cellular processes, such as metabolism, membrane transport, signal transduction and cell cycle. The PATHWAY database is supplemented by a set of ortholog group tables for the information about conserved subpathways (pathway motifs), which are often encoded by positionally coupled genes on the chromosome and which are especially useful in predicting gene functions. A third database in KEGG is LIGAND for the information about chemical compounds, enzyme molecules and enzymatic reactions. KEGG provides Java graphics tools for browsing genome maps, comparing two genome maps and manipulating expression maps, as well as computational tools for sequence comparison, graph comparison and path computation. The KEGG databases are daily updated and made freely available (http://www. genome.ad.jp/kegg/).
Figures
Figure 1
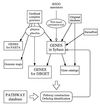
Procedures used to organize and annotate the GENES database.
Figure 2
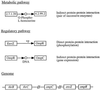
The generalized protein–protein interaction includes an indirect protein–protein interaction by two successive enzymes, a direct protein–protein interaction, and another indirect protein–protein interaction by gene expression. The nodes of the generalized protein–protein interaction network are gene products, which can be directly correlated with genes in the genome.
Similar articles
- KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes.
Ogata H, Goto S, Sato K, Fujibuchi W, Bono H, Kanehisa M. Ogata H, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999 Jan 1;27(1):29-34. doi: 10.1093/nar/27.1.29. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999. PMID: 9847135 Free PMC article. - The KEGG databases at GenomeNet.
Kanehisa M, Goto S, Kawashima S, Nakaya A. Kanehisa M, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002 Jan 1;30(1):42-6. doi: 10.1093/nar/30.1.42. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002. PMID: 11752249 Free PMC article. - KEGG for integration and interpretation of large-scale molecular data sets.
Kanehisa M, Goto S, Sato Y, Furumichi M, Tanabe M. Kanehisa M, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Jan;40(Database issue):D109-14. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr988. Epub 2011 Nov 10. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22080510 Free PMC article. - The KEGG database.
Kanehisa M. Kanehisa M. Novartis Found Symp. 2002;247:91-101; discussion 101-3, 119-28, 244-52. Novartis Found Symp. 2002. PMID: 12539951 Review. - KEGG as a glycome informatics resource.
Hashimoto K, Goto S, Kawano S, Aoki-Kinoshita KF, Ueda N, Hamajima M, Kawasaki T, Kanehisa M. Hashimoto K, et al. Glycobiology. 2006 May;16(5):63R-70R. doi: 10.1093/glycob/cwj010. Epub 2005 Jul 13. Glycobiology. 2006. PMID: 16014746 Review.
Cited by
- Identifying critical modules and biomarkers of intervertebral disc degeneration by using weighted gene co-expression network.
Zhou D, Liu T, Mei Y, Lv J, Cheng K, Cai W, Gao S, Guo D, Xie X, Liu Z. Zhou D, et al. JOR Spine. 2024 Oct 18;7(4):e70004. doi: 10.1002/jsp2.70004. eCollection 2024 Dec. JOR Spine. 2024. PMID: 39430414 Free PMC article. - Salivary Transcriptome and Mitochondrial Analysis of Autism Spectrum Disorder Children Compared to Healthy Controls.
Cannon M, Toma R, Ganeshan S, de Jesus Alvarez Varela E, Vuyisich M, Banavar G. Cannon M, et al. NeuroSci. 2024 Aug 6;5(3):276-290. doi: 10.3390/neurosci5030022. eCollection 2024 Sep. NeuroSci. 2024. PMID: 39483288 Free PMC article. - Mechanism of CXCL8 regulation of methionine metabolism to promote angiogenesis in gliomas.
Chang J, Pan Y, Jiang F, Xu W, Wang Y, Wang L, Hu B. Chang J, et al. Discov Oncol. 2024 Nov 2;15(1):614. doi: 10.1007/s12672-024-01467-2. Discov Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39488622 Free PMC article. - Gene Expression Profiling Regulated by lncRNA H19 Using Bioinformatic Analyses in Glioma Cell Lines.
Chae Y, Roh J, Im M, Jang W, Kim B, Kang J, Youn B, Kim W. Chae Y, et al. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2024 Nov-Dec;21(6):608-621. doi: 10.21873/cgp.20477. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2024. PMID: 39467632 Free PMC article. - Early inflammation as a footprint of increased mortality risk in infants living with HIV from three African countries.
Morrocchi E, Pascucci GR, Cotugno N, Pighi C, Dominguez-Rodriguez S, Petrara MR, Tagarro A, Kuhn L, Cotton MF, Otwombe K, Lain MG, Vaz P, Barnabas SL, Spyer MJ, Lopez E, Fernández-Luis S, Nhampossa T, Maiga AI, Dolo O, De Rossi A, Rojo P, Giaquinto C, Lichterfeld M, Violari A, Smit T, Behuhuma O, Klein N, De Armas L, Pahwa S, Rossi P, Palma P; EPIICAL consortium. Morrocchi E, et al. Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 28;14(1):25792. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-74066-4. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39468166 Free PMC article.
References
- Kanehisa M. (1999) Post-Genome Informatics. Oxford University Press, Oxford, UK.
- Kanehisa M. (1997) Trends Genet., 13, 375–376. - PubMed
- Kanehisa M. (1997) Trends Biochem. Sci., 22, 442–444. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases