Nucleotide and amino acid complexity of hepatitis C virus quasispecies in serum and liver - PubMed (original) (raw)
Comparative Study
Nucleotide and amino acid complexity of hepatitis C virus quasispecies in serum and liver
B Cabot et al. J Virol. 2000 Jan.
Abstract
The quasispecies nature of the hepatitis C virus (HCV) is thought to play a central role in maintaining and modulating viral replication. Several studies have tried to unravel, through the parameters that characterize HCV circulating quasispecies, prognostic markers of the disease. In a previous work we demonstrated that the parameters of circulating viral quasispecies do not always reflect those of the intrahepatic virus. Here, we have analyzed paired serum and liver quasispecies from 39 genotype 1b-infected patients with different degrees of liver damage, ranging from minimal changes to cirrhosis. Viral level was quantified by real-time reverse transcription-PCR, and viral heterogeneity was characterized through the cloning and sequencing of 540 HCV variants of a genomic fragment encompassing the E2-NS2 junction. Although in 95% of patients, serum and liver consensus HCV amino acid sequences were identical, quasispecies complexity varied considerably between the viruses isolated from each compartment. Patients with HCV quasispecies in serum more complex (26%) than, less complex (28%) than, or similarly complex (41%) to those in liver were found. Among the last, a significant correlation between fibrosis and all the parameters that measure the viral amino acid complexity was found. Correlation between fibrosis and serum viral load was found as well (R = 0.7). With regard to the origin of the differences in quasispecies complexity between serum and liver populations, sequence analysis argued against extrahepatic replication as a quantitatively important contributing factor and supported the idea of a differential effect or different selective forces on the virus depending on whether it is circulating in serum or replicating in the liver.
Figures
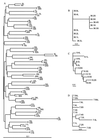
FIG. 1
HCV phylogenetic reconstructions of evolutionary relationships among viruses from patients. The phylogenetic analysis shown consists of unrooted neighbor-joining trees. (A) Serum and liver nucleotide consensus sequences of HCV from each patient. (B and C) Serum and liver HCV nucleotide sequences from the two patients with manifest tissue segregation. (D) Representative tree for the 37 patients without tissue segregation.
Similar articles
- Differences in hepatitis C virus quasispecies composition between liver, peripheral blood mononuclear cells and plasma.
Maggi F, Fornai C, Vatteroni ML, Giorgi M, Morrica A, Pistello M, Cammarota G, Marchi S, Ciccorossi P, Bionda A, Bendinelli M. Maggi F, et al. J Gen Virol. 1997 Jul;78 ( Pt 7):1521-5. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-78-7-1521. J Gen Virol. 1997. PMID: 9225024 - Dynamic behavior of hepatitis C virus quasispecies in patients undergoing orthotopic liver transplantation.
Martell M, Esteban JI, Quer J, Vargas V, Esteban R, Guardia J, Gómez J. Martell M, et al. J Virol. 1994 May;68(5):3425-36. doi: 10.1128/JVI.68.5.3425-3436.1994. J Virol. 1994. PMID: 8151804 Free PMC article. - Distinct composition of viral quasispecies between ascites and serum samples from patients with late stage chronic hepatitis C.
Yeh CT, Chu CM, Liaw YF. Yeh CT, et al. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1996 Oct 14;227(2):524-9. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1996.1540. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1996. PMID: 8878547 - Hepatitis C viral quasispecies.
Gómez J, Martell M, Quer J, Cabot B, Esteban JI. Gómez J, et al. J Viral Hepat. 1999 Jan;6(1):3-16. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2893.1999.t01-1-6120131.x. J Viral Hepat. 1999. PMID: 10847126 Review. - The molecular biology of hepatitis C virus. Genotypes and quasispecies.
Forns X, Bukh J. Forns X, et al. Clin Liver Dis. 1999 Nov;3(4):693-716, vii. doi: 10.1016/s1089-3261(05)70234-8. Clin Liver Dis. 1999. PMID: 11291246 Review.
Cited by
- Intra-host analysis of hepaciviral glycoprotein evolution reveals signatures associated with viral persistence and clearance.
Gömer A, Brown RJP, Pfaender S, Deterding K, Reuter G, Orton R, Seitz S, Bock CT, Cavalleri JMV, Pietschmann T, Wedemeyer H, Steinmann E, Todt D. Gömer A, et al. Virus Evol. 2022 Feb 2;8(1):veac007. doi: 10.1093/ve/veac007. eCollection 2022. Virus Evol. 2022. PMID: 35242360 Free PMC article. - The honeybee (Apis mellifera) developmental state shapes the genetic composition of the deformed wing virus-A quasispecies during serial transmission.
Yañez O, Chávez-Galarza J, Tellgren-Roth C, Pinto MA, Neumann P, de Miranda JR. Yañez O, et al. Sci Rep. 2020 Apr 6;10(1):5956. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-62673-w. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32249797 Free PMC article. - Hepatitis C Virus Genetic Variability, Human Immune Response, and Genome Polymorphisms: Which Is the Interplay?
Lapa D, Garbuglia AR, Capobianchi MR, Del Porto P. Lapa D, et al. Cells. 2019 Apr 3;8(4):305. doi: 10.3390/cells8040305. Cells. 2019. PMID: 30987134 Free PMC article. Review. - Prevalence and Factors Related to Natural Resistance-Associated Substitutions to Direct-Acting Antivirals in Patients with Genotype 1 Hepatitis C Virus Infection.
Esposito I, Marciano S, Haddad L, Galdame O, Franco A, Gadano A, Flichman D, Trinks J. Esposito I, et al. Viruses. 2018 Dec 21;11(1):3. doi: 10.3390/v11010003. Viruses. 2018. PMID: 30577623 Free PMC article. - Small cities face greater impact from automation.
Frank MR, Sun L, Cebrian M, Youn H, Rahwan I. Frank MR, et al. J R Soc Interface. 2018 Feb;15(139):20170946. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2017.0946. J R Soc Interface. 2018. PMID: 29436514 Free PMC article.
References
- Alter H J, Sanchez-Pescador R, Urdea M S, Wilber J C, Lagier R J, Di Bisceglie A M, Shih J W, Neuwald P D. Evaluation of branched DNA signal amplification for the detection of hepatitis C virus RNA. J Viral Hepat. 1995;2:121–132. - PubMed
- Berger S L, Chirgwin J M. Isolation of RNA. Methods Enzymol. 1989;180:3–13. - PubMed
- Brechot C. Hepatitis C virus: molecular biology and genetic variability. Dig Dis Sci. 1996;41:6s–21s. - PubMed
- Bukh J, Miller R H, Purcell R H. Genetic heterogeneity of hepatitis C virus: quasispecies and genotypes. Semin Liver Dis. 1995;15:41–63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases