Phylogenetic network for European mtDNA - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2001 Jun;68(6):1475-84.
doi: 10.1086/320591. Epub 2001 May 10.
Affiliations
- PMID: 11349229
- PMCID: PMC1226134
- DOI: 10.1086/320591
Phylogenetic network for European mtDNA
S Finnilä et al. Am J Hum Genet. 2001 Jun.
Abstract
The sequence in the first hypervariable segment (HVS-I) of the control region has been used as a source of evolutionary information in most phylogenetic analyses of mtDNA. Population genetic inference would benefit from a better understanding of the variation in the mtDNA coding region, but, thus far, complete mtDNA sequences have been rare. We determined the nucleotide sequence in the coding region of mtDNA from 121 Finns, by conformation-sensitive gel electrophoresis and subsequent sequencing and by direct sequencing of the D loop. Furthermore, 71 sequences from our previous reports were included, so that the samples represented all the mtDNA haplogroups present in the Finnish population. We found a total of 297 variable sites in the coding region, which allowed the compilation of unambiguous phylogenetic networks. The D loop harbored 104 variable sites, and, in most cases, these could be localized within the coding-region networks, without discrepancies. Interestingly, many homoplasies were detected in the coding region. Nucleotide variation in the rRNA and tRNA genes was 6%, and that in the third nucleotide positions of structural genes amounted to 22% of that in the HVS-I. The complete networks enabled the relationships between the mtDNA haplogroups to be analyzed. Phylogenetic networks based on the entire coding-region sequence in mtDNA provide a rich source for further population genetic studies, and complete sequences make it easier to differentiate between disease-causing mutations and rare polymorphisms.
Figures
Figure 1
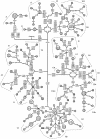
Phylogenetic network based on variation in the coding sequence in mtDNA from 192 Finnish subjects. The outgroup is mtDNA from an African individual (Ingman et al. ; GenBank accession number AF346980). Numbers inside the nodes denote samples. Unless marked otherwise, the polymorphic variants, shown on the lines connecting the nodes, are transitions. Superscripts indicate transversions or inserted nucleotides. Position 10398 was down-weighted in the analysis, but otherwise the weights of the nucleotide positions were equal. A reticulation due to variation at position 15884 within haplogroup W was resolved by assuming a back mutation in samples 72 and 73. The following substitutions were common to all samples: 3423G→T, 4985G→A, 9559G→C, 11335T→C, 13702G→C, 14199G→T, 14272G→C, 14365G→C, 14368G→C, and 3106delC. i = insertion; d 9bp = 9-bp deletion in the CO II-tRNALys intergenic region; @ = back mutation; h = heteroplasmic mutation.
Figure 2
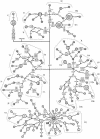
Phylogenetic network of mtDNA, based on variation in the D-loop sequence. The outgroup is mtDNA from an African individual (Ingman et al. ; GenBank accession number AF346980). Fast-evolving sites 303, 311, and 16519 were not included in the network. i = insertion; d = deletion; @ = back mutation. The superscripts indicate transversions or inserted or deleted nucleotides. For further information, see the legend to figure 1.
Comment in
- The mitochondrial gene tree comes of age.
Richards M, Macaulay V. Richards M, et al. Am J Hum Genet. 2001 Jun;68(6):1315-20. doi: 10.1086/320615. Epub 2001 May 10. Am J Hum Genet. 2001. PMID: 11349234 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
- Phylogenetic network of the mtDNA haplogroup U in Northern Finland based on sequence analysis of the complete coding region by conformation-sensitive gel electrophoresis.
Finnilä S, Hassinen IE, Ala-Kokko L, Majamaa K. Finnilä S, et al. Am J Hum Genet. 2000 Mar;66(3):1017-26. doi: 10.1086/302802. Am J Hum Genet. 2000. PMID: 10712215 Free PMC article. - Phylogenetic network and physicochemical properties of nonsynonymous mutations in the protein-coding genes of human mitochondrial DNA.
Moilanen JS, Majamaa K. Moilanen JS, et al. Mol Biol Evol. 2003 Aug;20(8):1195-210. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msg121. Epub 2003 May 30. Mol Biol Evol. 2003. PMID: 12777521 - Reduced-median-network analysis of complete mitochondrial DNA coding-region sequences for the major African, Asian, and European haplogroups.
Herrnstadt C, Elson JL, Fahy E, Preston G, Turnbull DM, Anderson C, Ghosh SS, Olefsky JM, Beal MF, Davis RE, Howell N. Herrnstadt C, et al. Am J Hum Genet. 2002 May;70(5):1152-71. doi: 10.1086/339933. Epub 2002 Apr 5. Am J Hum Genet. 2002. PMID: 11938495 Free PMC article. - The complete mitochondrial genome of the Caulerpa lentillifera (Ulvophyceae, Chlorophyta): Sequence, genome content, organization structure and phylogenetic consideration.
Zheng F, Liu H, Jiang M, Xu Z, Wang Z, Wang C, Du F, Shen Z, Wang B. Zheng F, et al. Gene. 2018 Oct 5;673:225-238. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2018.06.050. Epub 2018 Jun 19. Gene. 2018. PMID: 29933020 - The complete mitochondrial DNA sequence of the basal hexapod Tetrodontophora bielanensis: evidence for heteroplasmy and tRNA translocations.
Nardi F, Carapelli A, Fanciulli PP, Dallai R, Frati F. Nardi F, et al. Mol Biol Evol. 2001 Jul;18(7):1293-304. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a003914. Mol Biol Evol. 2001. PMID: 11420368
Cited by
- Neurological manifestations in adult patients with the m.3243A>G variant in mitochondrial DNA.
Majamaa K, Kärppä M, Moilanen JS. Majamaa K, et al. BMJ Neurol Open. 2024 Sep 24;6(2):e000825. doi: 10.1136/bmjno-2024-000825. eCollection 2024. BMJ Neurol Open. 2024. PMID: 39324021 Free PMC article. - Pan-Evo: The Evolution of Information and Biology's Part in This.
Sherwin WB. Sherwin WB. Biology (Basel). 2024 Jul 8;13(7):507. doi: 10.3390/biology13070507. Biology (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39056700 Free PMC article. Review. - HaploCart: Human mtDNA haplogroup classification using a pangenomic reference graph.
Rubin JD, Vogel NA, Gopalakrishnan S, Sackett PW, Renaud G. Rubin JD, et al. PLoS Comput Biol. 2023 Jun 7;19(6):e1011148. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1011148. eCollection 2023 Jun. PLoS Comput Biol. 2023. PMID: 37285390 Free PMC article. - Variation in the Substitution Rates among the Human Mitochondrial Haplogroup U Sublineages.
Översti S, Palo JU. Översti S, et al. Genome Biol Evol. 2022 Jul 2;14(7):evac097. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evac097. Genome Biol Evol. 2022. PMID: 35731946 Free PMC article. - Discordance in maternal and paternal genetic markers in lesser long-nosed bat Leptonycteris yerbabuenae, a migratory bat: recent expansion to the North and male phylopatry.
Trejo-Salazar RE, Castellanos-Morales G, Hernández-Rosales D, Gámez N, Gasca-Pineda J, Morales Garza MR, Medellin R, Eguiarte LE. Trejo-Salazar RE, et al. PeerJ. 2021 Sep 29;9:e12168. doi: 10.7717/peerj.12168. eCollection 2021. PeerJ. 2021. PMID: 34703665 Free PMC article.
References
Electronic-Database Information
- Life Sciences and Engineering Technology Solutions, http://www.fluxus-engineering.com
- GenBank Overview, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Genbank/GenbankOverview.html (for outgroup mtDNA from an African individual [accession number AF346980])
References
- Anderson S, Bankier AT, Barrell BG, deBruijn MHL, Coulson AR, Drouin J, Eperon IC, Nierlich DP, Roe BA, Sanger F, Schreier PH, Smith AJH, Staden R, Young IG (1981) Sequence and organization of the human mitochondrial genome. Nature 290:457–465 - PubMed
- Andrews RM, Kubacka I, Chinnery PF, Lightowlers RN, Turnbull DM, Howell N (1999) Reanalysis and revision of the Cambridge reference sequence for human mitochondrial DNA. Nat Genet 23:147 - PubMed
- Awadalla P, Eyre-Walker A, Smith JM (1999) Linkage disequilibrium and recombination in hominid mitochondrial DNA. Science 286:2524–2525 - PubMed
- Cavalli-Sforza LL, Menozzi P, Piazza A (1994) The history and geography of human genes. Princeton University Press, Princeton, NJ
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources