Analysis of the Arabidopsis mitochondrial proteome - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2001 Dec;127(4):1711-27.
Affiliations
- PMID: 11743115
- PMCID: PMC133575
Analysis of the Arabidopsis mitochondrial proteome
A H Millar et al. Plant Physiol. 2001 Dec.
Abstract
The complete set of nuclear genes that encode proteins targeted to mitochondria in plants is currently undefined and thus the full range of mitochondrial functions in plants is unknown. Analysis of two-dimensional gel separations of Arabidopsis cell culture mitochondrial protein revealed approximately 100 abundant proteins and 250 low-abundance proteins. Comparison of subfractions of mitochondrial protein on two-dimensional gels provided information on the soluble, membrane, or integral membrane locations of this protein set. A total of 170 protein spots were excised, trypsin-digested, and matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization/time of flight mass spectrometry spectra obtained. Using this dataset, 91 of the proteins were identified by searching translated Arabidopsis genomic databases. Of this set, 81 have defined functions based on sequence comparison. These functions include respiratory electron transport, tricarboxylic acid cycle metabolism, amino acid metabolism, protein import, processing, and assembly, transcription, membrane transport, and antioxidant defense. A total of 10 spectra were matched to Arabidopsis putative open reading frames for which no specific function has been determined. A total of 64 spectra did not match to an identified open reading frame. Analysis of full-length putative protein sequences using bioinformatic tools to predict subcellular targeting (TargetP, Psort, and MitoProt) revealed significant variation in predictions, and also a lack of mitochondrial targeting prediction for several characterized mitochondrial proteins.
Figures
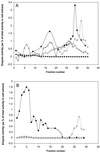
Figure 1
Isolation of Arabidopsis mitochondria by density centrifugation. The organelle pellet from homogenized Arabidopsis cell culture was loaded onto a Percoll step gradient consisting of steps of 40% (fractions 31–35), 23% (fractions 11–30), and 18% Percoll (fractions 1–10; A). After centrifugation, mitochondria were recovered from the 40%:23% interface (fractions 26–35) and were loaded onto a self-forming Percoll gradient containing 28% Percoll (B). One-milliliter fractions were collected from both gradients (from top to bottom) and the activities of cytochrome c oxidase (▪), catalase (○), alkaline pyrophosphatase (▵), and alcohol dehydrogenase (♦) were assayed in each fraction. Values are expressed as a percentage of the total activity in the initial cell extract.
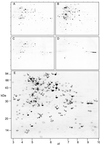
Figure 2
Two-dimensional separations of Arabidopsis mitochondrial proteins (pI 3–10) fractionated on the degree of membrane association. A, Total mitochondrial proteins; B, soluble proteins; C, total membrane proteins; D, integral membrane proteins based on Na2CO3 treatment; and E, predicted localization of 165 protein spots on the basis of distribution in A through D. Circled, black spots are annotated as I, S, or P. Circled, unannotated gray spots could not be assigned as I, S, or P based on their distribution between the gels. Numbers on the x axis are pI and numbers on the y axis are apparent molecular mass (kilodaltons) in E. A through D, Ticks marks show the position of pI 3 to 10 and the six molecular mass markers presented in E.
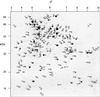
Figure 3
Two-dimensional separation of Arabidopsis total mitochondrial proteins (pI 3–10). A total of 170 protein spots from this map were excised, digested, and analyzed by MALDI-ToF to yield a peptide mass fingerprint for DB searching. Numbers indicate spot number for comparison with text and Table II. Numbers on the x axis are pI and numbers on the y axis are apparent molecular mass (kilodaltons).
Similar articles
- Proteomic approach to identify novel mitochondrial proteins in Arabidopsis.
Kruft V, Eubel H, Jänsch L, Werhahn W, Braun HP. Kruft V, et al. Plant Physiol. 2001 Dec;127(4):1694-710. Plant Physiol. 2001. PMID: 11743114 Free PMC article. - Towards an analysis of the rice mitochondrial proteome.
Heazlewood JL, Howell KA, Whelan J, Millar AH. Heazlewood JL, et al. Plant Physiol. 2003 May;132(1):230-42. doi: 10.1104/pp.102.018986. Plant Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12746528 Free PMC article. - Experimental analysis of the Arabidopsis mitochondrial proteome highlights signaling and regulatory components, provides assessment of targeting prediction programs, and indicates plant-specific mitochondrial proteins.
Heazlewood JL, Tonti-Filippini JS, Gout AM, Day DA, Whelan J, Millar AH. Heazlewood JL, et al. Plant Cell. 2004 Jan;16(1):241-56. doi: 10.1105/tpc.016055. Epub 2003 Dec 11. Plant Cell. 2004. PMID: 14671022 Free PMC article. - The plant mitochondrial proteome.
Millar AH, Heazlewood JL, Kristensen BK, Braun HP, Møller IM. Millar AH, et al. Trends Plant Sci. 2005 Jan;10(1):36-43. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2004.12.002. Trends Plant Sci. 2005. PMID: 15642522 Review. - Prediction of Peroxisomal Matrix Proteins in Plants.
Reumann S, Chowdhary G. Reumann S, et al. Subcell Biochem. 2018;89:125-138. doi: 10.1007/978-981-13-2233-4_5. Subcell Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30378021 Review.
Cited by
- Characterization of the Mitochondrial Proteome in the Ctenophore Mnemiopsis leidyi Using MitoPredictor.
Muthye V, Lavrov DV. Muthye V, et al. Methods Mol Biol. 2024;2757:239-257. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3642-8_10. Methods Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38668970 - Capsicum chinense Jacq.-derived glutaredoxin (CcGRXS12) alters redox status of the cells to confer resistance against pepper mild mottle virus (PMMoV-I).
Kumar RMS, Ramesh SV, Sun Z, Thankappan S, Nulu NPC, Binodh AK, Kalaipandian S, Srinivasan R. Kumar RMS, et al. Plant Cell Rep. 2024 Apr 1;43(4):108. doi: 10.1007/s00299-024-03174-2. Plant Cell Rep. 2024. PMID: 38557872 - Topological data analysis reveals a core gene expression backbone that defines form and function across flowering plants.
Palande S, Kaste JAM, Roberts MD, Segura Abá K, Claucherty C, Dacon J, Doko R, Jayakody TB, Jeffery HR, Kelly N, Manousidaki A, Parks HM, Roggenkamp EM, Schumacher AM, Yang J, Percival S, Pardo J, Husbands AY, Krishnan A, Montgomery BL, Munch E, Thompson AM, Rougon-Cardoso A, Chitwood DH, VanBuren R. Palande S, et al. PLoS Biol. 2023 Dec 5;21(12):e3002397. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3002397. eCollection 2023 Dec. PLoS Biol. 2023. PMID: 38051702 Free PMC article. - In Vivo Epitope Tagging of Plant Mitochondria.
Kuhnert F, Weber APM. Kuhnert F, et al. Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2379:253-264. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1791-5_14. Methods Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 35188666 - Protein Processing in Plant Mitochondria Compared to Yeast and Mammals.
Heidorn-Czarna M, Maziak A, Janska H. Heidorn-Czarna M, et al. Front Plant Sci. 2022 Feb 2;13:824080. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.824080. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35185991 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Chevallet M, Santoni V, Poinas A, Rouquie D, Fuchs A, Kieffe S, Rossignol M, Lunardi J, Garin J, Rabilloud T. New zwitterionic detergents improve the analysis of membrane proteins by two-dimensional electrophoresis. Electrophoresis. 1998;19:1901–1909. - PubMed
- Choi K, Roh K, Kim J, Sim W. Genomic cloning and characterization of mitochondrial elongation factor Tu (EF-Tu) gene (tufM) from maize (Zea mays L.) Gene. 2000;257:233–242. - PubMed
- Claros MG, Vincens P. Computational method to predict mitochondrially imported proteins and their targeting sequences. Eur J Biochem. 1996;241:779–786. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases