Mechanism of exogenous nucleic acids and their precursors improving the repair of intestinal epithelium after gamma-irradiation in mice - PubMed (original) (raw)
Mechanism of exogenous nucleic acids and their precursors improving the repair of intestinal epithelium after gamma-irradiation in mice
Da-Xiang Cui et al. World J Gastroenterol. 2000 Oct.
Abstract
AIM:To clone expressed genes associated with repair of irradiation-damaged mice intestinal gland cells treated by small intestinal RNA, and to explore the molecular mechanism of exogenous nucleic acids improving repair of intestinal crypt.METHODS:The animal mode of test group and control group was established, forty-five mice being irradiated by gamma ray were treated with small intestinal RNA as test group, forty mice being irradiated by gamma ray were treated with physiological saline as control group,five mice without irradiation were used as normal control, their jejunal specimens were collected respectively at 6h, 12h,24h, 4d and 8d after irradiation. Then by using LD-PCR based on subtractive hybridization, these gene fragments differentially expressed between test group and control group were obtained, and then were cloned into T vectors as well as being sequenced. Obtained sequences were screened against. GeneBank, if being new sequences, they were submitted to GeneBank.RESULTS:Ninety clones were associated with repair of irradiation-damaged intestinal gland cells treated by intestinal RNA. These clones from test group of 6h, 12h, 24h, 4d and 8d were respectively 18, 22, 25, 13, 12. By screening against GeneBank, 18 of which were new sequences, the others were dramatically similar to the known sequences, mainly similar to hsp, Nmi,Dutt1, alkaline phosphatase, homeobox, anti-CEA ScFv antibody, arginine/serine kinase and BMP-4,repA. Eighteen gene fragments were new sequences,their accept numbers in GeneBank were respectively AF240164-AF240181.CONCLUSION:Ninety clones were obtained to be associated with repair of irradiation damaged mice intestinal gland cells treated by small intestinal RNA, which may be related to abnormal expression of genes and matched proteins of hsp, Nmi, Dutt1, Na, K-ATPase,alkalineph-osphatase, glkA, single stranded replicative centromeric gene as well as 18 new sequences.
Figures
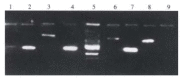
Figure 1
Electrophoresis result of production of LD-PCR. 1: Marker; 2, 6: Positive control; 3, 4, 5, 7, 8: Results of 6 h, 12 h, 24 h, 4 d and 8 d; 9: Negative control
Figure 2
Results of cloning and identification of production of PCR. 1-4, 6-9: Results of part products cut by Bstz1; 5: Marker Ninety of positive clones were obtained from test group, positive clones of 6 h, 12 h, 24 h, 4 d and 8 d in test group were respectively eighteen, twenty-two, twenty-five, thirteen, twelve.
Figure 3
Part results of hybridization with RNA. A: Test group; B: Control group. Dot blots confirmed that these genes were overexpressed in test group, and lower expressed in control group, that is, these genes were associated with repair of intestinal gland cells treated by RNA.
Figure 4
Not available
Similar articles
- Patterns of gene expression along the crypt-villus axis in mouse jejunal epithelium.
Cheng H, Bjerknes M. Cheng H, et al. Anat Rec. 1996 Jan;244(1):78-94. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0185(199601)244:1<78::AID-AR8>3.0.CO;2-B. Anat Rec. 1996. PMID: 8838426 - Differentially expressed proteins of gamma-ray irradiated mouse intestinal epithelial cells by two-dimensional electrophoresis and MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry.
Zhang B, Su YP, Ai GP, Liu XH, Wang FC, Cheng TM. Zhang B, et al. World J Gastroenterol. 2003 Dec;9(12):2726-31. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i12.2726. World J Gastroenterol. 2003. PMID: 14669322 Free PMC article. - [Analysis of differential express gene between keloid and normal skin by suppression subtractive hybridization].
Luo Y, Gao J, Zhao F. Luo Y, et al. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2006 May;20(5):495-8. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2006. PMID: 16752832 Chinese. - Protective effect of total flavonoids of Engelhardia roxburghiana Wall. leaves against radiation-induced intestinal injury in mice and its mechanism.
Wu S, Tian C, Tu Z, Guo J, Xu F, Qin W, Chang H, Wang Z, Hu T, Sun X, Ning H, Li Y, Gou W, Hou W. Wu S, et al. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023 Jul 15;311:116428. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.116428. Epub 2023 Mar 28. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36997130 - [Development of IgHV family specific nucleic acid vaccine against lymphoma by construction of fusion gene of immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region and cytokine].
Liu H, Zhu P, Lin NJ, Zhang Y, Bu DF, Wang YJ, Wang YQ, Yang Y. Liu H, et al. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2004 Jan 2;84(1):48-53. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2004. PMID: 14990159 Chinese.
Cited by
- Relationship between overexpression of NK-1R, NK-2R and intestinal mucosal damage in acute necrotizing pancreatitis.
Shi X, Gao NR, Guo QM, Yang YJ, Huo MD, Hu HL, Friess H. Shi X, et al. World J Gastroenterol. 2003 Jan;9(1):160-4. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i1.160. World J Gastroenterol. 2003. PMID: 12508374 Free PMC article.
References
- Cui DX, Yan XJ, Su CZ. Differentially expressed genes in GC7901 or GES 1 were isolated by optimized differential display RT PCR and their primary clinical significance. Disi Junyi Daxue Xuebao. 1998;19:601–605.
- Potten CS, Hendry JH. Radiation and Gut. London: Elsevier. 1995:1–307.
- Zeng GY, Liu AP, Zhou YK. Effect of exogenous nucleic acids and their precursors on the intestinal crypt survival in mice after abdominal γ - irradiation. China-Janan Medical Conference Beijing. 1992;5:968.
- Zhou YK, Zeng GY, Liu AP. Effect of intraluminal administration of intes-tinal crypt cells on the crypt of lieberkuhn in irradiated mice. Internatinal Confere nce on Biological Effects of Large Dose lonizing and Nonionzing radiation Hangzhou, China, 1988: 125
- Cui DX, Zen GY, Yan XJ, Ren DQ, Wang F, Zhao T, Tian FR, Su CZ. Differentially expressed genes related with injury of human intestinal epithe-lium cell by γ-ray. J Radiat Res Radiat Proces. 2000;18:73–76.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials